When you publish your virtual machine (VM) image to Azure Marketplace, the Azure team validates it to ensure that it's bootable, secure, and compatible with Azure. If your VM image fails any of the high-quality tests, it won't be published. You'll receive an error message that describes the issue.
This article explains common error messages during VM image publishing, along with related solutions.
Note
If you have questions about this article or suggestions for improvement, contact Partner Center support.
VM extension failure
Check to see whether your image supports VM extensions.
To enable VM extensions:
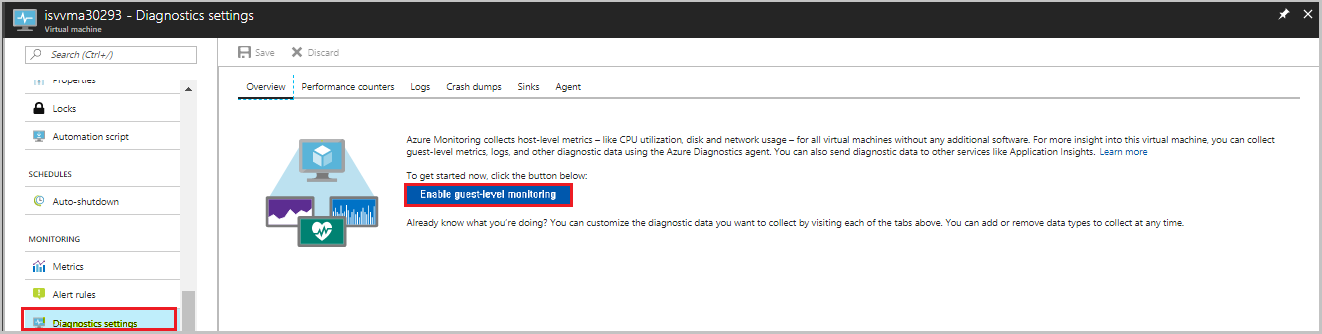
Select your Linux VM.
Go to Diagnostics settings.
Enable base matrices by updating the Storage account.
Select Save.
To verify that the VM extensions are properly activated:
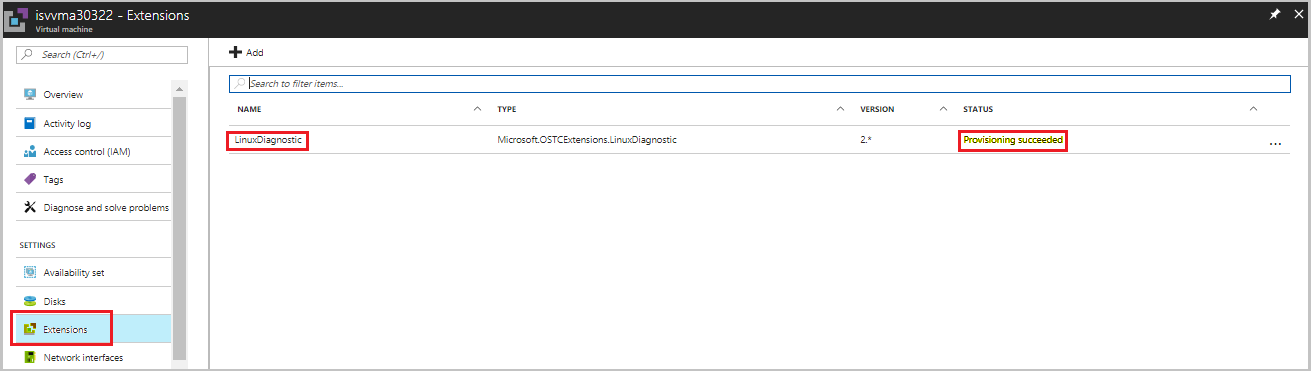
In the VM, select the VM extensions tab, and then verify the status of the Linux Diagnostics Extension.
Check the provisioning status.
- If the status is Provisioning Succeeded, the extensions test case passed.
- If the status is Provisioning Failed, the extensions test case failed, and you need to set the Hardened flag.
If the VM extension fails, see Use Linux Diagnostic Extension to monitor metrics and logs to enable it. If you don't want the VM extension to be enabled, contact the Support team, and ask them to disable it.
VM provisioning issue
Check to ensure that you've followed the VM provisioning process rigorously before you submit your offer. To view the JSON format for provisioning the VM, see Test a virtual machine image.
Provisioning issues can include the following failure scenarios:
| Scenario | Error | Reason | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Invalid virtual hard disk (VHD) | If the specified cookie value in the VHD footer is incorrect, the VHD is considered invalid. | Re-create the image and submit the request. |
| 2 | Invalid blob type | VM provisioning failed because the used blob is a block type instead of a page type. | Re-create the image as page type and submit the request. |
| 3 | Provisioning timeout or not properly generalized | There's an issue with VM generalization. | Re-create the image with generalization and submit the request. |
Note
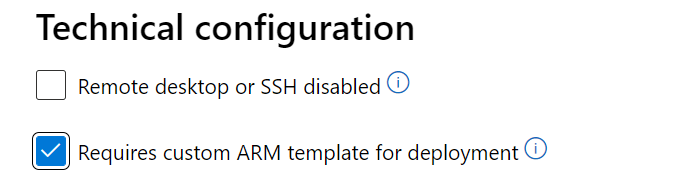
If provision fails as VM image requires a custom ARM template to deploy, enable the checkbox 'Requires custom ARM template for deployment' in 'Technical configuration' page of Partner Center. This helps Certification team take the proper action for this request without failing it for provisioning issue.
VHD specifications
Conectix cookie and other VHD specifications
The 'conectix' string is part of the VHD specification. It's defined as the 8-byte cookie in the VHD footer that identifies the file creator. All VHD files created by Microsoft have this cookie.
A VHD formatted blob should have a 512-byte footer in this format:
| Hard disk footer fields | Size (bytes) |
|---|---|
| Cookie | 8 |
| Features | 4 |
| File Format Version | 4 |
| Data Offset | 8 |
| Time Stamp | 4 |
| Creator Application | 4 |
| Creator Version | 4 |
| Creator Host OS | 4 |
| Original Size | 8 |
| Current Size | 8 |
| Disk Geometry | 4 |
| Disk Type | 4 |
| Checksum | 4 |
| Unique ID | 16 |
| Saved State | 1 |
| Reserved | 427 |
VHD specifications
To ensure a smooth publishing experience, ensure that your VHD meets the following criteria:
- The cookie contains the string 'conectix.'
- The disk type is Fixed.
- The VHD's virtual size is at least 20 MB.
- The VHD is aligned. The virtual size must be a multiple of 1 MB.
- The VHD blob length is equal to the virtual size plus the VHD footer length (512).
Download the VHD specification.
Software compliance for Windows
If your Windows image request is rejected because of a software compliance issue, it might be that you created a Windows image with an installed SQL Server instance. Instead, you must take the relevant SQL Server version base image from Azure Marketplace.
Don't create your own Windows image with SQL Server installed in it. Use the approved SQL Server base images (Enterprise/Standard/web) from Azure Marketplace.
If you're trying to install Visual Studio or any Office-licensed product, contact the Support team for prior approval.
For more information about selecting an approved base, see Create a virtual machine from an approved base.
Toolkit test case execution failed
The Microsoft Certification toolkit can help you run test cases and verify that your VHD or image is compatible with the Azure environment.
Download the Microsoft Certification toolkit.
Linux test cases
The following table lists the Linux test cases that the toolkit runs. Test validation is stated in the description.
| Scenario | Test case | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Bash history | Bash history files should be cleared before you create the VM image. |
| 2 | Linux Agent version | Minimum supported version of Azure Linux agent, or higher, must be installed. |
| 3 | Required kernel parameters | Verifies that the following kernel parameters are set: console=ttyS0 earlyprintk=ttyS0 |
| 4 | Swap partition on OS disk | Verifies that swap partitions aren't created on the OS disk. |
| 5 | Root partition on OS disk | Create a single root partition for the OS disk. |
| 6 | OpenSSL version | The OpenSSL version should be v0.9.8 or later. |
| 7 | Python version | Python version 2.6 or later is highly recommended. |
| 8 | Client Alive Interval | Set ClientAliveInterval to 180. On the application need, it can be set from 30 to 235. If you're enabling the SSH for your end users, this value must be set as explained. |
| 9 | OS architecture | Only 64-bit operating systems are supported. |
| 10 | Auto Update | Identifies whether Linux Agent Auto Update is enabled. |
Common test-case errors
Refer to the following table for the common errors you might see when running test cases:
| Scenario | Test case | Error | Solution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Linux Agent version test case | Minimum supported version of Azure Linux agent, or higher, must be installed.](https://learn.microsoft.com/troubleshoot/azure/virtual-machines/support-extensions-agent-version) | Update the Linux agent version. For more information, visit Linux Agent Version update page. |
| 2 | Bash history test case | An error occurs if the size of the Bash history in your submitted image is more than 1 kilobyte (KB). The size is restricted to 1 KB to ensure that your Bash history file doesn't contain any potentially sensitive information. | Resolve by mounting the VHD to another working VM and make changes to reduce the size to 1 KB or less. For example, delete the .bash_history files. |
| 3 | Required kernel parameter test case | You'll receive this error when the value for console isn't set to ttyS0. Check by running the following command: cat /proc/cmdline |
Set the value for console to ttyS0, and resubmit the request. |
| 4 | ClientAlive interval test case | If the toolkit gives you a failed result for this test case, there's an inappropriate value for ClientAliveInterval. |
Set the value for ClientAliveInterval to less than or equal to 235, and then resubmit the request. |
| 5 | smoke_test | You'll receive an error when the image can't boot or reboot because of a kernel panic. You can get some call trace information of the kernel panic from 'error description.' If you want to see the whole call trace and the serial log, you can deploy a VM in Azure using your image and check the 'Serial console' in your VM resource in the Azure portal. | When you create a VM in Azure, you can download the serial console log from the Azure portal (You can refer to https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/troubleshoot/azure/virtual-machines/serial-console-linux for more details about Serial Console) |
| 6 | verify_dns_name_resolution | This test case checks DNS name resolution by executing command:ping bing.com -c 5 -i 0.5 -O. An error occurs if it fails to ping a public web address 'bing.com'. | Refer to https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/virtual-machines/linux/azure-dns to add the right settings |
| 7 | verify_no_pre_exist_users | You'll receive error 'Password of user XXXX is detected' when the password of some user has been detected or when the key of some user has been detected | check /etc/shadow file to see if it has a password of some user, if so, you must delete the password and delete the '{user's home directory}/.ssh/authorized_keys' file following the error message |
| 8 | validate_netvsc_reload | You'll receive error 'failed. SSHException: SSH session not active.' if the VM can't be connected after running below command. You'll receive error 'found kernel panic from the node of xx.' if there's kernel panic found from the VM after running the command: 'modprobe -r hv_netvsc; modprobe hv_netvsc;ip link set eth0 down; ip link set eth0 up;dhclient -r eth0; dhclient eth0 ' | Check the Serial Console to see if any error happened during the period of running above command. You can visit https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-hardware/drivers/network/sr-iov-synthetic-data-path for more details about Network Virtual Service Client (NetVSC). |
Windows test cases
The following table lists the Windows test cases that the toolkit runs, along with a description of the test validation:
| Scenario | Test cases | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | OS architecture | Azure supports only 64-bit operating systems. |
| 2 | User account dependency | Application execution shouldn't be dependent on the administrator account. |
| 3 | Failover cluster | The Windows Server failover clustering feature isn't yet supported. The application shouldn't be dependent on this feature. |
| 4 | IPV6 | IPv6 isn't yet supported in the Azure environment. The application shouldn't be dependent on this feature. |
| 5 | DHCP | Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Server role isn't yet supported. The application shouldn't be dependent on this feature. |
| 6 | Remote access | Remote Access (Direct Access) Server role isn't yet supported. The application shouldn't be dependent on this feature. |
| 7 | Rights Management Services | Rights Management Services. The server role isn't yet supported. The application shouldn't be dependent on this feature. |
| 8 | Windows Deployment Services | Windows Deployment Services. The server role isn't yet supported. The application shouldn't be dependent on this feature. |
| 9 | BitLocker Drive Encryption | BitLocker Drive Encryption isn't supported on the operating system hard disk, but it might be used on data disks. |
| 10 | Internet Storage Name Server | The Internet Storage Name Server feature isn't yet supported. The application shouldn't be dependent on this feature. |
| 11 | Multipath I/O | Multipath I/O. This server feature isn't yet supported. The application shouldn't be dependent on this feature. |
| 12 | Network Load Balancing | Network Load Balancing. This server feature isn't yet supported. The application shouldn't be dependent on this feature. |
| 13 | Peer Name Resolution Protocol | Peer Name Resolution Protocol. This server feature isn't yet supported. The application shouldn't be dependent on this feature. |
| 14 | SNMP Services | The Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Services feature isn't yet supported. The application shouldn't be dependent on this feature. |
| 15 | Windows Internet Name Service | Windows Internet Name Service. This server feature isn't yet supported. The application shouldn't be dependent on this feature. |
| 16 | Wireless LAN Service | Wireless LAN Service. This server feature isn't yet supported. The application shouldn't be dependent on this feature. |
If you come across any failures with the preceding test cases, refer to the Description column in the table for the solution. For more information, contact the Support team.
Data disk size verification
Data disk requests with a size greater than 1023 gigabytes (GB) won't be approved. This rule applies to both Linux and Windows.
Resubmit the request with a size less than or equal to 1023 GB.
OS disk size validation
Refer to the following rules for limitations on OS disk size. When you submit any request, verify that the OS disk size is within the limitation for Linux or Windows.
| OS | Recommended VHD size |
|---|---|
| Linux | 1 GB to 1023 GB |
| Windows | 30 GB to 250 GB |
Because VMs allow access to the underlying operating system, ensure that the VHD size is sufficiently large for the VHD. Disks aren't expandable without downtime. Use a disk size from 30 GB to 50 GB.
| VHD size | Actual occupied size | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| >500 tebibytes (TiB) | n/a | Contact the Support team for an exception approval. |
| 250-500 TiB | >200 gibibytes (GiB) difference from blob size | Contact the Support team for an exception approval. |
Note
Larger disk sizes incur higher costs and result in a delay during the setup and replication process. Because of this delay and cost, the Support team might seek justification for the exception approval.
WannaCry patch verification test for Windows
To prevent a potential attack related to the WannaCry virus, ensure that all Windows image requests are updated with the latest patch.
You can verify the image file version from C:\windows\system32\drivers\srv.sys or srv2.sys.
The following table shows the minimum patched version of Windows Server:
| OS | Version |
|---|---|
| Windows Server 2008 R2 | 6.1.7601.23689 |
| Windows Server 2012 | 6.2.9200.22099 |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | 6.3.9600.18604 |
| Windows Server 2016 | 10.0.14393.953 |
| Windows Server 2019 | NA |
Note
Windows Server 2019 doesn't have any mandatory version requirements.
SACK vulnerability patch verification
When you submit a Linux image, your request might be rejected because of kernel version issues.
Update the kernel with an approved version, and resubmit the request. You can find the approved kernel version in the following table. The version number should be equal to or greater than the number listed here.
If your image isn't installed with one of the following kernel versions, update it with the correct patches. Request the necessary approval from the Support team after the image is updated with these required patches:
- CVE-2019-11477
- CVE-2019-11478
- CVE-2019-11479
| OS family | Version | Kernel |
|---|---|---|
| Ubuntu | 14.04 LTS | 4.4.0-151 |
| 14.04 LTS | 4.15.0-1049-*-azure | |
| 16.04 LTS | 4.15.0-1049 | |
| 18.04 LTS | 4.18.0-1023 | |
| 18.04 LTS | 5.0.0-1025 | |
| 18.10 | 4.18.0-1023 | |
| 19.04 | 5.0.0-1010 | |
| 19.04 | 5.3.0-1004 | |
| RHEL and Cent OS | 6.10 | 2.6.32-754.15.3 |
| 7.2 | 3.10.0-327.79.2 | |
| 7.3 | 3.10.0-514.66.2 | |
| 7.4 | 3.10.0-693.50.3 | |
| 7.5 | 3.10.0-862.34.2 | |
| 7.6 | 3.10.0-957.21.3 | |
| 7.7 | 3.10.0-1062.1.1 | |
| 8.0 | 4.18.0-80.4.2 | |
| 8.1 | 4.18.0-147 | |
| "7-RAW" (7.6) | ||
| "7-LVM" (7.6) | 3.10.0-957.21.3 | |
| RHEL-SAP 7.4 | TBD | |
| RHEL-SAP 7.5 | TBD | |
| SLES | SLES11SP4 (including SAP) | 3.0.101-108.95.2 |
| SLES12SP1 for SAP | 3.12.74-60.64.115.1 | |
| SLES12SP2 for SAP | 4.4.121-92.114.1 | |
| SLES12SP3 | 4.4180-4.31.1 (kernel-azure) | |
| SLES12SP3 for SAP | 4.4.180-94.97.1 | |
| SLES12SP4 | 4.12.14-6.15.2 (kernel-azure) | |
| SLES12SP4 for SAP | 4.12.14-95.19.1 | |
| SLES15 | 4.12.14-5.30.1 (kernel-azure) | |
| SLES15 for SAP | 4.12.14-5.30.1 (kernel-azure) | |
| SLES15SP1 | 4.12.14-5.30.1 (kernel-azure) | |
| Oracle | 6.10 | UEK2 2.6.39-400.312.2 UEK3 3.8.13-118.35.2 RHCK 2.6.32-754.15.3 |
| 7.0-7.5 | UEK3 3.8.13-118.35.2 UEK4 4.1.12-124.28.3 RHCK follows RHEL above |
|
| 7.6 | RHCK 3.10.0-957.21.3 UEK5 4.14.35-1902.2.0 |
|
| CoreOS Stable 2079.6.0 | 4.19.43* | |
| Beta 2135.3.1 | 4.19.50* | |
| Alpha 2163.2.1 | 4.19.50* | |
| Debian | jessie (security) | 3.16.68-2 |
| jessie backports | 4.9.168-1+deb9u3 | |
| stretch (security) | 4.9.168-1+deb9u3 | |
| Debian GNU/Linux 10 (buster) | Debian 6.3.0-18+deb9u1 | |
| buster, sid (stretch backports) | 4.19.37-5 |
Image size should be in multiples of megabytes
All VHDs on Azure must have a virtual size aligned to multiples of 1 megabyte (MB). If your VHD doesn't adhere to the recommended virtual size, your request might get rejected.
Follow guidelines when you convert from a raw disk to VHD. Ensure that the raw disk size is a multiple of 1 MB. For more information, see Information for nonendorsed distributions.
VM access denied
An access denied issue for running a test case on the VM might be caused by insufficient privileges.
Check that you've enabled proper access for the account on which the self-test cases are running. Enable access to run test cases if it's not enabled. If you don't want to enable access, you might share the self-test case results with the Support team.
To submit your request with SSH disabled image for certification process:
Run the latest Certification Test Tool for Azure VMs on your image.
Raise a support ticket. Make sure to attach the toolkit report and provide offer details:
- Offer name
- Publisher name
- Plan ID/SKU and version
Resubmit your certification request.
Note
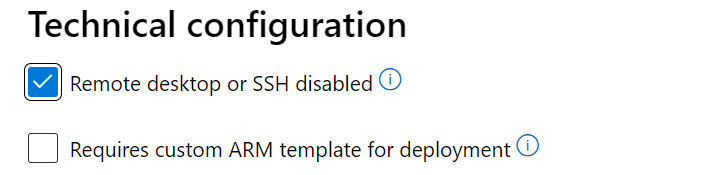
If you're publishing a locked-down VM image that has disabled or restricted ssh, enable the checkbox 'Remote desktop or SSH disabled' in the 'Technical configuration' page of Partner Center. This informs Certification team that this is by design and perform the right validations on the image without failing it for restricted access.
Download failure
Refer to the following table for any issues that arise when you download the VM image with a shared access signature (SAS) URL.
| Error | Reason | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Blob not found | The VHD might either be deleted or moved from the specified location. | |
| Blob in use | The VHD is used by another internal process. Source blob storage of the VHD is modified while publishing is in progress. | The VHD shouldn't be in a used state when you download it with a SAS URL. Also, don't use/change the VHD when publishing is in progress. |
| Invalid SAS URL | The associated SAS URL for the VHD is incorrect. | Get the correct SAS URL. |
| Invalid signature | The associated SAS URL for the VHD is incorrect. | Get the correct SAS URL. |
| HTTP conditional header | The SAS URL is invalid. | Get the correct SAS URL. |
| Invalid VHD name | Check to see whether any special characters, such as a percent sign % or quotation marks ", exist in the VHD name. |
Rename the VHD file by removing the special characters. |
VM images must have 1 MB of free space
If you're publishing your image to Azure (with GPT partition), we highly recommend that you keep the first 2,048 sectors (1 MB) of the OS disk empty. This requirement is to allow Azure to add important metadata to the image (examples include metadata to improve boot time for customers, billing, and other details). This is a recommendation for best practice if you're already using an approved base image and your image has a valid billing tag. However, if your image doesn't have a valid billing tag, your publishing might fail if the first 1 MB of the OS disk isn't empty.
If you're building your own image that doesn't have any valid billing tag, ensure the first 2,048 sectors (1 MB) of the OS disk are empty. Otherwise, your publishing will fail. This requirement is applicable to the OS disk only (not data disks). If you're building your image from an approved base, it will already have first 1 MB empty. Hence, you won't need to work on it separately.
To keep the first 1 MB free in your OS disk, complete the steps in the next section.
How to keep 1 MB of free space at the start on an empty VHD (2,048 sectors, each sector 512 bytes)
These steps apply only to Linux.
Create any kind of Linux VM, such as Ubuntu, CentOS, or other. Fill the required fields, and then select Next: Disks.
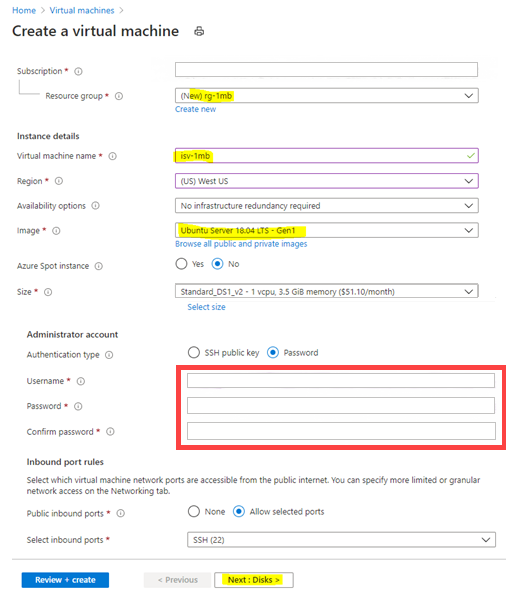
Create an unmanaged disk for your VM. Either use the default values or specify any value for fields like OS disk size, OS disk type, and Encryption type.
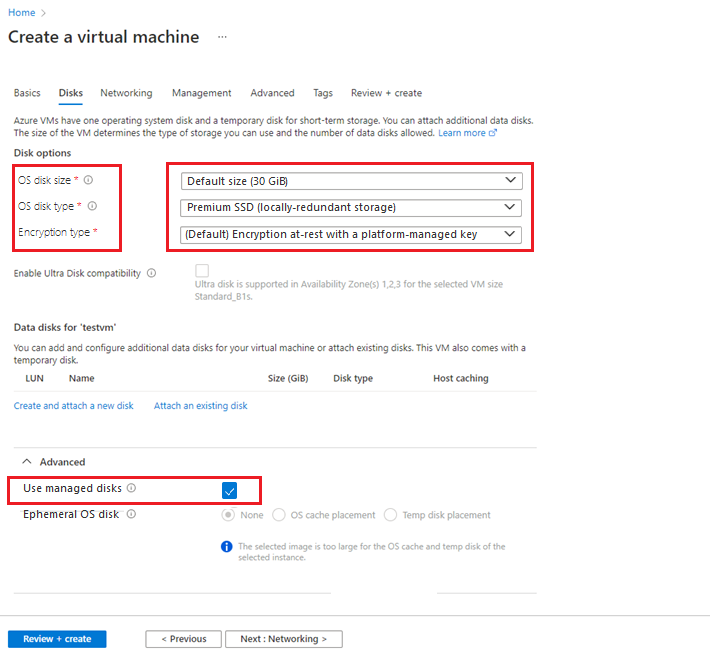
After you create the VM, in the left pane, select Disks.
Attach your VHD as data disk to your VM for creating a partition table.
Select Attach existing disks:
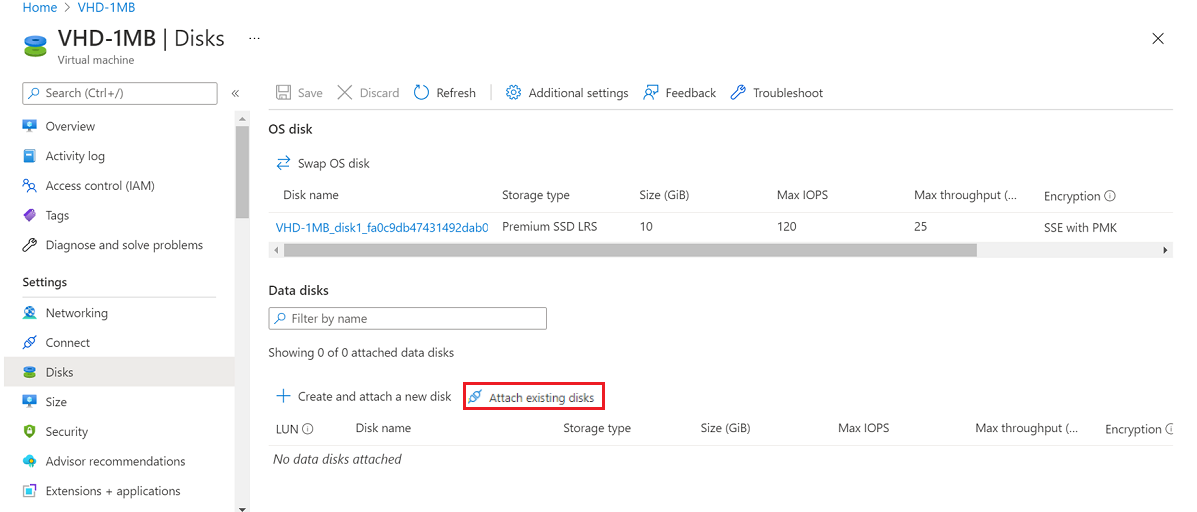
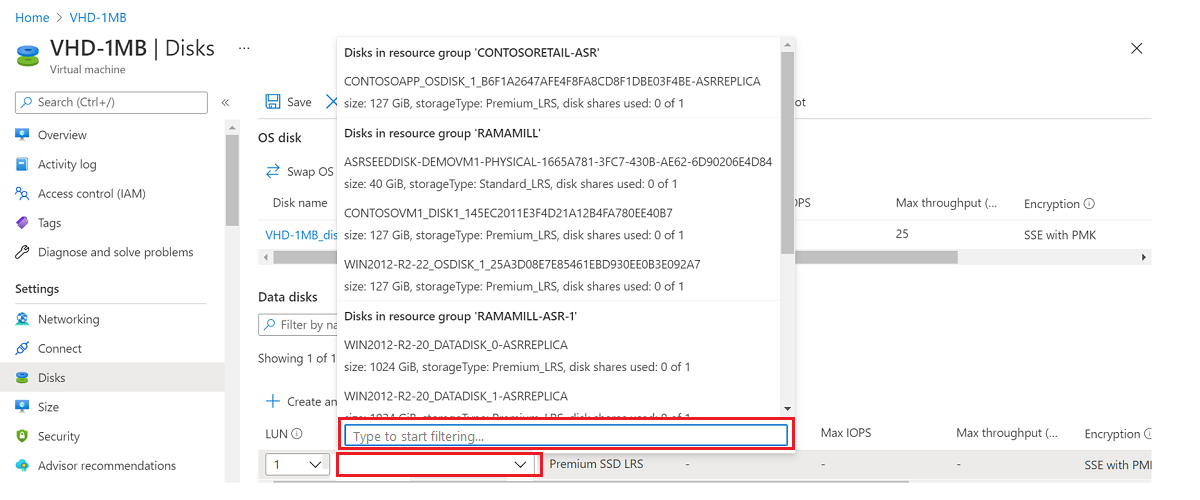
Find your VHD storage account.
Select Container, and then select your VHD.
Select OK.
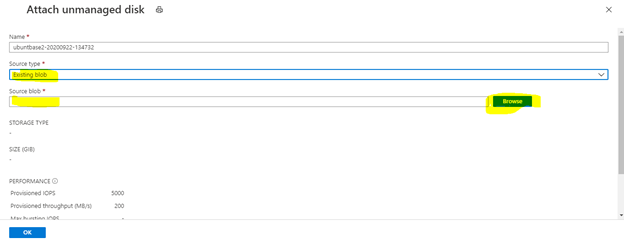
Your VHD will be added as data disk LUN 0.
Restart the VM.
After you restart the VM, log in to the VM using Putty or another client and run the
sudo -icommand to gain root access.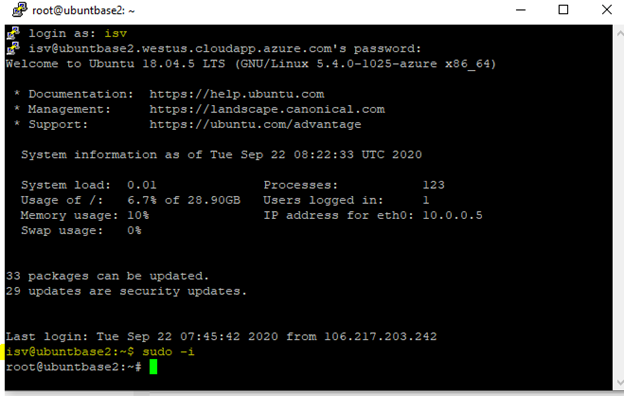
Create a partition on your VHD.
Enter
fdisk /dev/sdbcommand.To view the existing partition list from your VHD, enter
p.Enter
dto delete all existing partitions available in your VHD. You can skip this step, if it's not required.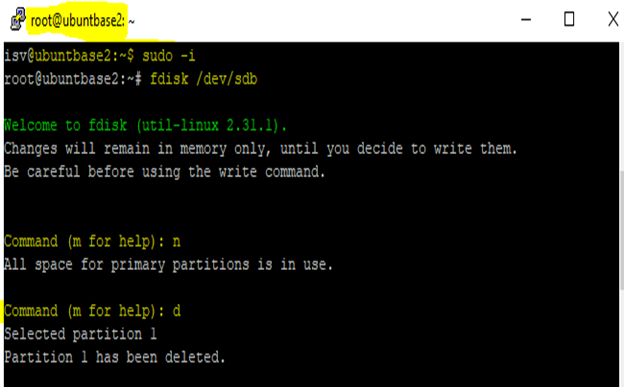
Enter
nto create new partition and selectpfor (primary partition).Enter 2048 as first sector value. You can leave last sector as the default value.
Important
Any existing data will be erased until 2048 sectors (each sector of 512 bytes). Back up the VHD before you create a new partition.
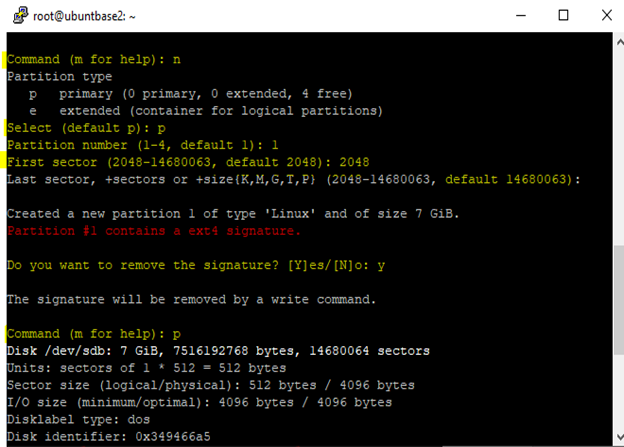
Type
wto confirm the creation of partition.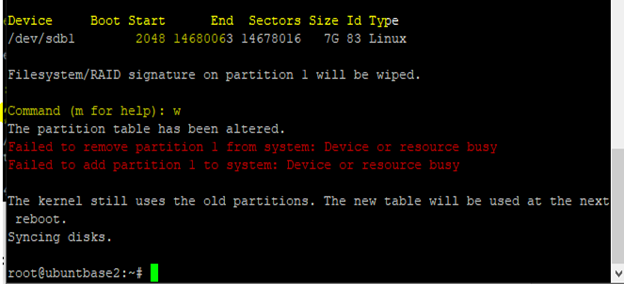
You can verify the partition table by running the command
n fdisk /dev/sdband typingp. You'll see that partition is created with 2048 offset value.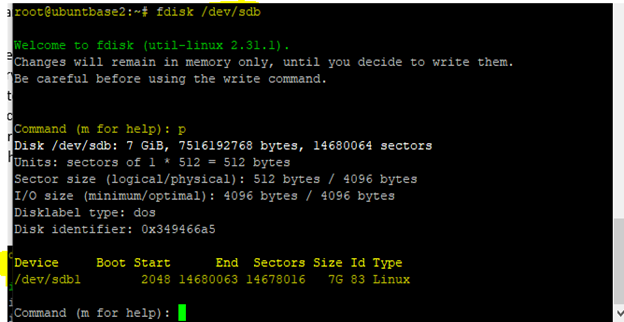
Detach the VHD from VM and delete the VM.
Default credentials
Never send default credentials with the submitted VHD. Adding default credentials makes the VHD more vulnerable to security threats. Instead, create your own credentials when you submit the VHD.
DataDisk mapped incorrectly
A mapping issue can occur when a request is submitted with multiple data disks that aren't in sequence. For example, the numbering order for three data disks must be 0, 1, 2. Any other order is treated as a mapping issue.
Resubmit the request with proper sequencing of data disks.
Incorrect OS mapping
When an image is created, it might be mapped to or assigned the wrong OS label. For example, when you select Windows as a part of the OS name while you're creating the image, the OS disk should be installed only with Windows. The same requirement applies to Linux.
VM not generalized
If all images that are taken from Azure Marketplace are to be reused, the operating system VHD must be generalized.
For Linux, the following process generalizes a Linux VM and redeploys it as a separate VM.
In the SSH window, enter the following command:
sudo waagent -deprovision+user.For Windows, you generalize Windows images by using
sysreptool.For more information about the
sysreptooltool, see System preparation (Sysprep) overview.
DataDisk errors
For solutions to errors that are related to the data disk, use the following table:
| Error | Reason | Solution |
|---|---|---|
DataDisk- InvalidUrl: |
This error might occur because of an invalid logical unit number (LUN) when the offer is submitted. | Verify that the LUN number sequence for the data disk is in Partner Center. |
DataDisk- NotFound: |
This error might occur because a data disk isn't located at a specified SAS URL. | Verify that the data disk is located at the specified SAS URL. |
Remote access issue
You'll get this error if the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) option isn't enabled for the Windows image.
Enable RDP access for Windows images before you submit them.
Bash history failed
You'll see this error if the size of the Bash history in your submitted image is more than 1 kilobyte (KB). The size is restricted to 1 KB to restrict the file from containing potentially sensitive information.
To delete the Bash history:
Deploy the VM and select the Run Command option on the Azure portal.
Select first option RunShellScript and then run the command:
cat /dev/null > ~/.bash_history && history -c.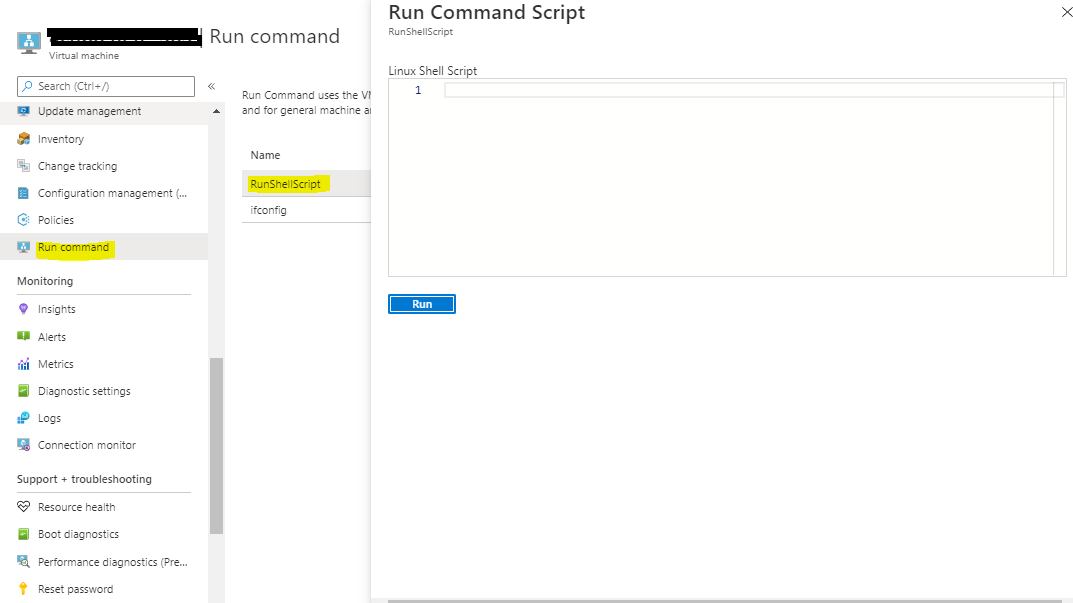
After the command runs successfully, restart the VM.
Generalize the VM, take the image VHD, and stop the VM.
Resubmit the generalized image.
Network Virtual Appliance validations
During Marketplace image certification, a VM offer that is a Network Virtual Appliance (NVA) is validated using tests that are generic to any VM offer, and NVA test cases listed in the table below. The goal of these NVA specific validations is to verify how well the NVA image orchestrates with SDN stack.
| Test case | Steps to run test case | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| VHD Access | Ensure the correct SAS URL for the VHD is provided, the permissions are set to allow access and the NVA image is generalized. | Verify the NVA image and the URL provided. |
| NVA Deployment | Deploy a VM using the NVA with one NIC. Verify that the deployment is completed in 20 minutes. | If the deployment isn't completed within 20 minutes, then verify the NVA image. |
| NVA Reboot | Deploy a VM using the NVA with one NIC. Then, go to the VM in Azure portal, and under section Support + troubleshooting in the left pane, select Redeploy + Reapply and redeploy the VM. After redeployment is completed, verify that the status of the VM is Running and the NIC port 22 is reachable using Netcat command. | If VM doesn't come up after reboot, then there might be an issue with the NVA image. If the Netcat test fails, then it could be because the NIC failed to come up after the reboot even though the VM was running. Wait for few minutes and try again. If after 20 mins it still fails, then there might be an issue with the NVA image |
| NVA Redeployment | Deploy a VM using the NVA with one NIC. Then, redeploy the VM. Verify that the status of the VM is Running and the NIC port 22 is reachable using Netcat command. | If the redeploy doesn't complete within 15 minutes, then there might be an issue with the NVA image. If the Netcat test fails, then it could be because the NIC failed to come up after the reboot even though the VM was running. Wait for few minutes and try again. If after 20 mins it still fails, then there might be an issue with the NVA image |
| High Availability | Deploy a VM using the NVA with one NIC. Either No public IP should be attached to NIC or if Public IP is attached then SKU should be standard and IP allocation method should be static. In the same virtual network, set up an Azure Internal load balancer using configuration below. - Load balancer using Standard SKU - Frontend IP using private IP allocation method as dynamic - Health probes using TCP, port 22 with a retry interval of 15 seconds - A load balancing rule with protocol as all and enable floating IP set to False. - Backend pool pointing to NVA VM. Once the setup is ready, verify that the NVA VM is reachable across the load balancer, using Netcat command. |
If the NVA is unreachable across the load balancer, then verify the setup of the VM, load balancer and HA ports feature. If everything is accurate, then there might be an issue with the NVA image. |
| VNET Peering | Deploy a virtual machine VM1 using the NVA image, with one NIC in a virtual network VNET1. In another virtual network VNET2, deploy a virtual machine VM2 using any Linux image, say ubuntu, with one NIC, and VM settings as Dynamic IP allocation method and basic SKU. Create VNET peering between VNET1 and VNET2 and Traffic to remote virtual network is configured as Allow (default) Once the setup is ready, verify that from VM2 we can reach private IP of the NIC on the NVA VM1, using Netcat command. |
If the NVA VM1 is unreachable from VM2, then verify that the VNET peering is configured correctly and try again. If it still doesn't work, then there might be an issue with the NVA image. |
| Accelerated Networking (AN) | Deploy a VM with the NVA and 1 AN enabled NIC. You can enable AN on a NIC while creating the VM, or on the NIC properties after creating the VM. Verify that the VM will be up and running. | If the deployment fails, then verify that the NVA image supports Accelerated Networking. |
| Multi-NIC Basic | Deploy a VM using the NVA with 3 NICs with Dynamic IP allocation method and basic SKU. Get private IP and MAC address for all the NICs (refer to view Network Interface for instructions). Then, redeploy the VM, and verify that the private IP and MAC address for all the NICs remain the same as before redeploying. | If the private IP and MAC address for all the NICs change after redeploying, then there might be an issue with the NVA image. |
| Network Disruption | Deploy a VM using the NVA with one NIC. Then, create and apply a Network Security Group (NSG) to block all traffic to the NVA VM. Then, verify that the status of the VM is Running. | If after applying NSG the VM goes down, then there might be an issue with the NVA image. |
For further information or questions, open an Azure Support case.
Netcat overview:
Netcat is a command capable of establishing a TCP or UDP connection between two computers, meaning it can write and read through an open port. During NVA validations, we execute the Netcat command from a VM that is in the same virtual network as the NVA VM, to test if TCP port 22 is reachable. The command syntax is
nc <destination_ip_address> <destination_port>, where
- destination_ip_address is the private IP address assigned to VM NIC,
- destination_port is the port number on the NVA. We use 22 in NVA test cases.
For example, nc 192.168.1.1 22
Request an exception on VM images for select tests
Publishers can request exceptions for a few tests performed during VM certification. Exceptions are provided in rare cases when a publisher provides evidence to support the request. The Certification team reserves the right to deny or approve exceptions at any time.
This section describes general scenarios in which publishers request an exception and how to request one.
Scenarios for exception
Publishers generally request exceptions in the following cases:
Exception for one or more test cases. Contact Partner Center support to request exceptions for test cases.
Locked-down VMs / No root access. A few publishers have scenarios where VMs need to be locked because they have software such as firewalls installed on the VM. In this case, download the Certified Test Tool and submit the report at Partner Center support.
Custom templates. Some publishers publish VM images that require a custom Azure Resource Manager (ARM) template to deploy the VMs. In this case, submit the custom templates at Partner Center support to be used by the Certification team for validation.
Information to provide for exception scenarios
Contact Partner Center support to request an exception for one of the scenarios, and include the following information:
Publisher ID. Type your Partner Central portal Publisher ID.
Offer ID/name. Enter the Offer ID or name.
SKU/Plan ID. Type the VM offer Plan ID or SKU.
Version. Enter the VM offer version that requires an exception.
Exception Type. Choose from tests, locked-down VM, or custom templates.
Reason of request. Include the reason for the exception request, plus any information on test exemptions.
Timeline. Enter the end date for your exception.
Attachment. Attached important evidence documents:
- For locked-down VMs, attach the test report.
- For custom templates, provide the custom ARM template as attachment.
If you fail to include these attachments, your request will be denied.
Address a vulnerability or an exploit in a VM offer
This section describes how to provide a new VM image when a vulnerability or exploit is discovered with one of your VM images. It only applies to Azure VM offers published to Azure Marketplace.
Note
You can't remove the last VM image from a plan or stop-sell the last plan for an offer.
Do one of the following actions:
- If you have a new VM image to replace the vulnerable VM image, see Provide a fixed VM image.
- If you don't have a new VM image to replace the only VM image in a plan, or if you're done with the plan, stop distribution of the plan.
- If you don't plan to replace the only VM image in the offer, we recommend you stop distributing the offer.
Provide a fixed VM image
To provide a fixed VM image to replace a VM image that has a vulnerability or exploit:
- Provide a new VM image to address the security vulnerability or exploit.
- Remove the VM image with the security vulnerability or exploit.
- Republish the offer.
Provide a new VM image to address the security vulnerability or exploit
To complete these steps, prepare the technical assets for the VM image you want to add. For more information, see Create a virtual machine using an approved base or Create a virtual machine using your own image and Generate a SAS URI for your VM image.
Sign in to Partner Center.
On the Home page, select the Marketplace offers tile.
In the Offer alias column, select the offer.
Select the Plan overview tab, and then select the appropriate plan.
On the Technical configuration tab, under VM Images, select + Add VM Image.
Note
You can add only one VM image to one plan at a time. To add multiple VM images, publish the first one before you add the next VM image.
In the boxes that appear, provide a new disk version and the virtual machine image.
Select Save draft.
Next, remove the VM image with the security vulnerability.
Remove the VM image with the security vulnerability or exploit
- Sign in to Partner Center.
- On the Home page, select the Marketplace offers tile.
- In the Offer alias column, select the offer.
- Select the Plan overview tab, and then select the appropriate plan.
- On the Technical configuration tab, under VM Images, next to the VM image you want to remove, select Remove VM Image.
- In the dialog box, select Continue.
- Select Save draft.
Next, republish the offer.
Republish the offer
- Select Review and publish.
- If you need to provide any information to the certification team, add it to the Notes for certification box.
- Select Publish.
To complete the publishing process, see Review and publish offers.
VM images with limited access or requiring custom templates
Locked down (or) SSH disabled offer
Images that are published with either SSH disabled(for Linux) or RDP disabled (for Windows) are treated as Locked down VMs. There are special business scenarios due to which Publishers only allow restricted access to no/a few users.
During validation checks, Locked down VMs might not allow execution of certain certification commands.
Custom templates
In general, all the images that are published under single VM offers follow standard ARM template for deployment. However, there are scenarios where publisher might require customization while deploying VMs (for example, multiple NIC(s) to be configured).
Depending on the below scenarios (nonexhaustive), publishers use custom templates for deploying the VM:
- VM requires extra network subnets.
- More metadata to be inserted in ARM template.
- Commands that are prerequisite to the execution of ARM template.
VM extensions
Azure virtual machine (VM) extensions are small applications that provide post-deployment configuration and automation tasks on Azure VMs. For example, if a virtual machine requires software installation, anti-virus protection, or to run a script inside of it, a VM extension can be used.
Linux VM extension validations require the following to be part of the image:
- Minimum supported version Azure Linux agent, or higher, must be installed.](https://learn.microsoft.com/troubleshoot/azure/virtual-machines/support-extensions-agent-version)
- Python version above 2.6+
For more information, visit VM Extension.
Verification of integrity of image
If you're creating an image and creating disc out of the image to verify the integrity of the image, note that first 1 MB is reserved for optimized performance and last 512 bytes are reserved for VHD footer. So ignore them while verifying the integrity of the image.
Related content
- Configure VM offer properties
- Active marketplace rewards
- If you have questions or feedback for improvement, contact Partner Center support