Integrate Microsoft Defender for Endpoint with Intune and Onboard Devices
Use the information and procedures in this article to connect Microsoft Defender for Endpoint with Intune and to then onboard and configure devices for Defender for Endpoint. Information in this article includes the following general steps:
- Establish a service-to-service connection between Intune and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. This connection enables Intune to interact with Microsoft Defender on devices, including installation (onboarding) and configuration of the Defender for Endpoint client, and integration of machine risk scores from supported devices you manage with Intune. See the prerequisites to use Microsoft Defender for Endpoint with Intune.
- Onboard devices to Defender for Endpoint. You onboard devices to configure them to communicate with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint and to provide data that helps assess their risk level. Each platform has separate requirements to onboard to Defender.
- Use Intune device compliance policies to set the level of risk you want to allow. Microsoft Defender for Endpoint reports on the risk level of devices. Devices that exceed the allowed risk level are identified as noncompliant.
- Use Conditional Access policy to block users from accessing corporate resources while using a device that is identified as noncompliant.
- Use app protection policies for Android and iOS/iPadOS, to set device risk levels. App protection policies work with both enrolled and unenrolled devices.
In addition to managing settings for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint on devices that enroll with Intune, you can manage Defender for Endpoint security configurations on devices that aren’t enrolled with Intune. This scenario is called Security Management for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint and requires configuring the Allow Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to enforce Endpoint Security Configurations toggle to On. For more information, see Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Security Configuration Management.
Important
Android device administrator management is deprecated and no longer available for devices with access to Google Mobile Services (GMS). If you currently use device administrator management, we recommend switching to another Android management option. Support and help documentation remain available for some devices without GMS, running Android 15 and earlier. For more information, see Ending support for Android device administrator on GMS devices.
Connect Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to Intune
Before Intune and Defender for Endpoint can work together, you must set up the service-to-service connection between Intune and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. This is a one-time action per tenant. Setup requires administrative access to both the Microsoft Defender Security Center and the Microsoft Intune admin center.
Enable Intune and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint integration
Open the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint portal at security.microsoft.com. The Intune admin center also includes a link to the Defender for Endpoint portal.
Sign in to the Microsoft Intune admin center.
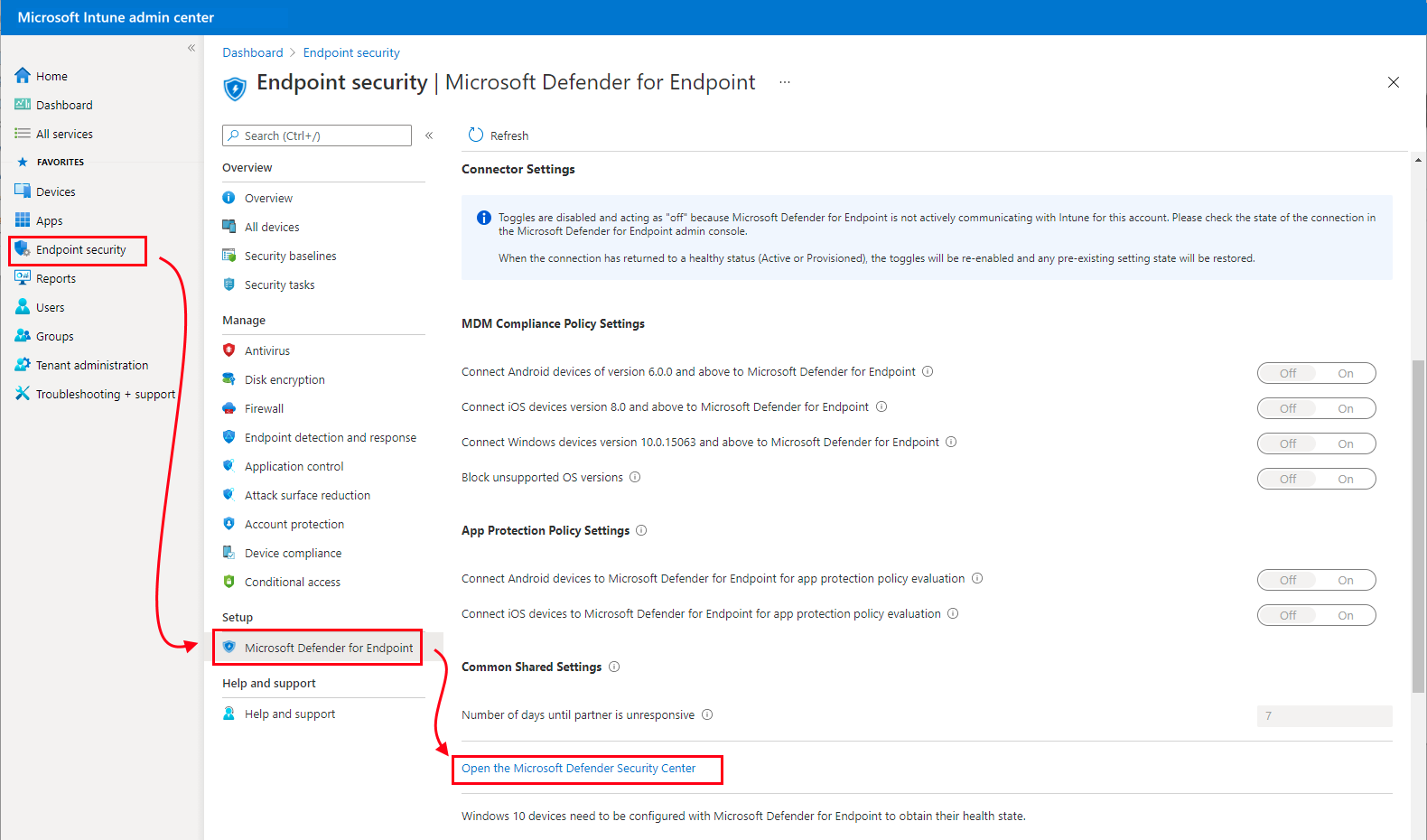
Select Endpoint security > Microsoft Defender for Endpoint and review the Connection status at the top of the page. If it’s Enabled, Defender and Intune are already connected and you can skip to step #2.
If the status is Unavailable, continue here.
Scroll down to the bottom of the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint page and select the link Open the Microsoft Defender Security Center to open the Microsoft Defender for portal and continue with the next numbered step.
Tip
If the connection is already active, the link to open the Defender portal reads: Open the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint admin console.
-
Use the left-hand pane to scroll down and select Settings > Endpoints >Advanced features.
On the advanced features pane, scroll down to locate the entry for Microsoft Intune connection and set the toggle to On.
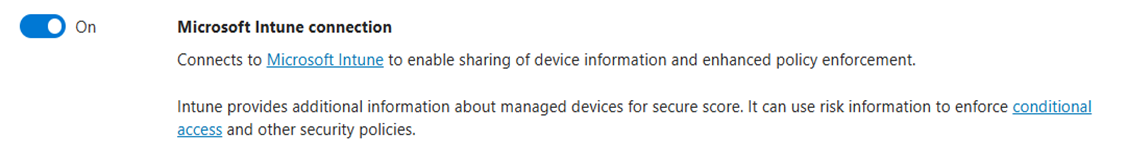
Select Save preferences to complete the connection between Intune and Defender for Endpoint.
Note
Once the connection is established, the services are expected to sync with each other at least once every 24 hours. The number of days without sync until the connection is considered unresponsive is configurable in the Microsoft Intune admin center. Select Endpoint security > Microsoft Defender for Endpoint > Number of days until partner is unresponsive
Return to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint page in the Microsoft Intune admin center where you configure aspects of the Defender for Endpoint integration. The Connection status should now display Enabled.
On this page, review each category and the available configurations for platform support and platforms specific options you plan to use, and set those toggles to On. You can return later to enable or disable any of these options.
To set up the following integrations of Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, your account must be assigned an Intune role-based access control (RBAC) role that includes Read and Modify for the Mobile Threat Defense permission in Intune. The Endpoint Security Manager built-in admin role for Intune has these permissions included.
Compliance policy evaluation - To use Defender for Endpoint with compliance policies, configure the following under Compliance policy evaluation for the platforms you support:
- Set Connect Android devices to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to On
- Set Connect iOS/iPadOS devices to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to On
- Set Connect Windows devices to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to On
When these configurations are On, applicable devices that you manage with Intune, and devices you enroll in the future, are connected to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint for compliance.
For iOS devices, Defender for Endpoint also supports the following settings that help provide the Vulnerability Assessment of apps on Microsoft Defender for Endpoint for iOS. For more information about using the following two settings, see Configure vulnerability assessment of apps.
Enable App Sync for iOS Devices: Set to On to allow Defender for Endpoint to request metadata of iOS applications from Intune to use for threat analysis purposes. The iOS device must be MDM-enrolled and provide updated app data during device check-in.
Send full application inventory data on personally owned iOS/iPadOS Devices: This setting controls the application inventory data that Intune shares with Defender for Endpoint when Defender for Endpoint syncs app data and requests the app inventory list.
When set to On, Defender for Endpoint can request a list of applications from Intune for personally owned iOS/iPadOS devices. This list includes unmanaged apps and apps that were deployed through Intune.
When set to Off, data about unmanaged apps isn’t provided. Intune does share data for the apps that were deployed through Intune.
For more information, see Mobile Threat Defense toggle options.
App protection policy evaluation - Configure the following toggles to use Defender for Endpoint with Intune app protection policies for Android and iOS/iPadOS, configure the following under App protection policy evaluation for the platforms you use:
- Set Connect Android devices to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to On.
- Set Connect iOS/iPadOS devices to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint on to On.
For more information, see Mobile Threat Defense toggle options.
Select Save.
Tip
As of the August 2023 Intune service release (2308), classic Conditional Access (CA) policies are no longer created for the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint connector. If your tenant has a classic CA policy that was previously created for integration with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, it can be deleted. To view classic Conditional Access policies, in Azure, go to Microsoft Entra ID > Conditional Access > Classic policies.
Onboard devices
After establishing the service-to-service connection between Intune and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, use Intune to onboard your managed devices to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. Onboarding involves enrolling devices into the Defender for Endpoint service to ensure they're protected and monitored for security threats and enables collection of data about device risk levels.
When onboarding devices, be sure to use the most recent version of Microsoft Defender for Endpoint for each platform.
The process to onboard devices to Defender for Endpoint varies by platform.
Onboard Windows devices
With a connection between Intune and Defender established, Intune automatically receives an onboarding configuration package from Defender that can be used by Intune to onboard Windows devices. This package is used by Intune EDR policy to configure devices to communicate with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint services and to scan files and detect threats. The onboarded devices also report their risk level to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint based on your compliance policies.
Onboarding of a device using the configuration package is a one-time action.
To deploy the onboarding package for Windows devices, you can choose to use a preconfigured EDR policy option, which deploys to the All devices group to onboard all applicable Windows devices, or you can manually create the EDR Policy for more granular deployments, which requires you to complete a few additional steps.
Use the preconfigured policy
With this path, you provide a name for the onboarding policy and select both the platform and profile. Other settings are preselected and include use of the onboarding package without additional settings, use of the Default scope tag, and assignment to the All Devices group. You can’t change these options during policy creation, but can return later to edit the policy details.
Open the Microsoft Intune admin center and go to Endpoint security > Endpoint detection and response > and select the EDR Onboarding Status tab.
On this tab, select Deploy preconfigured policy.
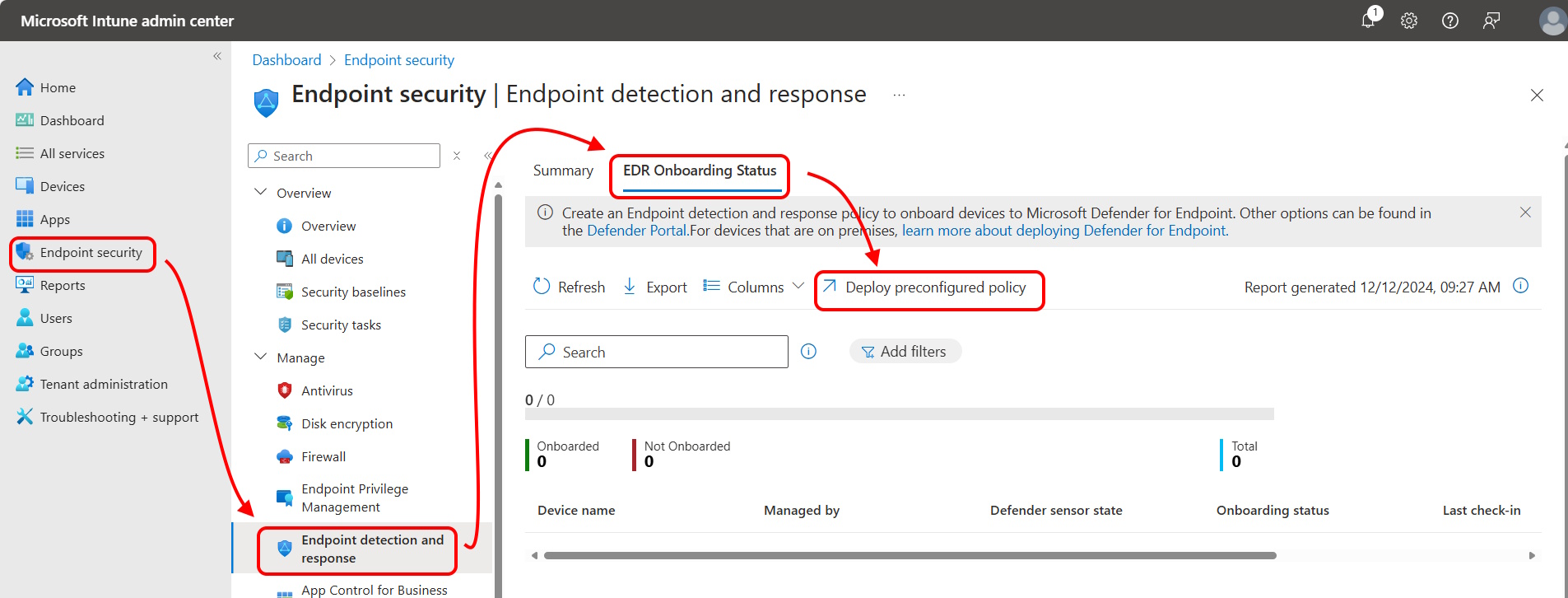
For Platform, select Windows for devices managed directly by Intune, or Windows (ConfigMgr) for devices managed through the Tenant Attach scenario. For Profile select Endpoint detection and response.
Specify a Name for the policy.
On the Review and Create page you can review this policies configuration. When ready select Save to save this policy, which immediately begins to deploy to the All Devices group.
Create your own EDR policy:
With this path, you can define all aspects of the initial onboarding policy before it begins to deploy to devices.
Sign in to the Microsoft Intune admin center.
Select Endpoint security > Endpoint detection and response > and in the Summary tab, select Create Policy.
For Platform select Windows, for Profile select Endpoint detection and response, and then select Create.
On the Basics page, enter a Name and Description (optional) for the profile, then choose Next.
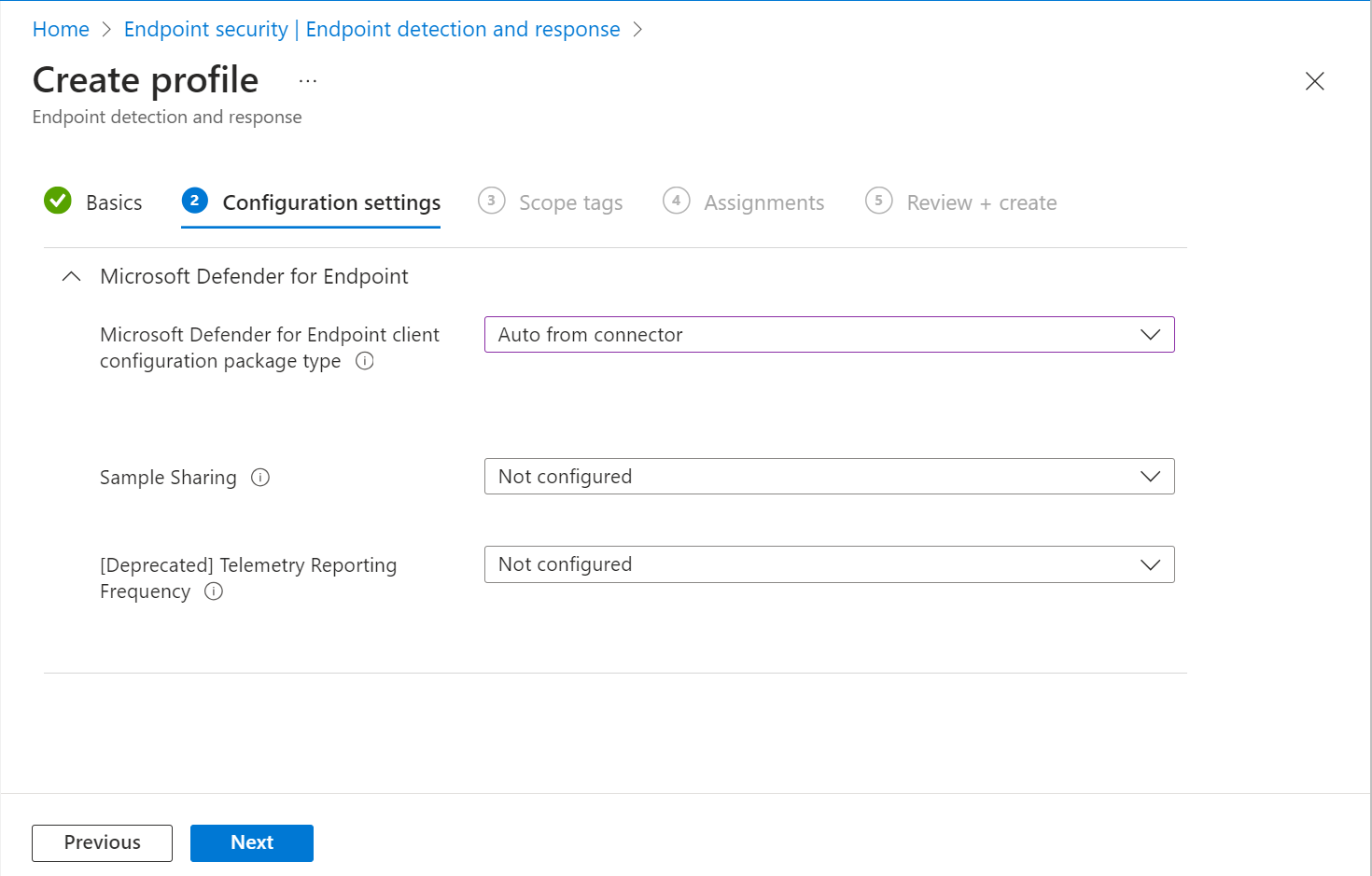
On the Configuration settings page, configure the following options depending on your needs:
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint client configuration package type: Select Auto from connector. With this option, the onboarding policy automatically uses the onboarding blob that Intune received from Microsoft Defender. If you're onboarding to a different or disconnected Defender for Endpoint deployment, select Onboard and paste the text from the WindowsDefenderATP.onboarding blob file into the Onboarding (Device) field.
Sample Sharing: Returns or sets the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Sample Sharing configuration parameter.
[Deprecated] Telemetry Reporting Frequency: This setting is deprecated and no longer applies to new devices. The setting remains visible in the policy UI for visibility for older policies that had this configured.
Note
The preceding screen capture shows your configuration options after you’ve configured a connection between Intune and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. When connected, the details for the onboarding and offboarding blobs are automatically generated and transfer to Intune.
If you haven’t configured this connection successfully, the setting Microsoft Defender for Endpoint client configuration package type only includes options to specify onboard and offboard blobs.
Select Next to open the Scope tags page. Scope tags are optional. Select Next to continue.
On the Assignments page, select the groups that will receive this profile. For more information on assigning profiles, see Assign user and device profiles.
When you deploy to user groups, a user must sign in on a device before the policy applies and the device can onboard to Defender for Endpoint.
Select Next to continue.
On the Review + create page, when you're done, choose Create. The new profile is displayed in the list when you select the policy type for the profile you created.
Tip
When using multiple policies or policy types like device configuration policy and endpoint detection and response policy to manage the same device settings, you can create policy conflicts for devices. To learn more about conflicts, see Manage conflicts in the Manage security policies article.
Onboard macOS devices
After you establish the service-to-service connection between Intune and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, you can onboard macOS devices to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. Onboarding configures devices to communicate with Microsoft Defender Endpoint, which then collects data about devices risk level.
Intune doesn't support an automatic onboarding package for macOS as it does for Windows devices. For configuration guidance for Intune, see Microsoft Defender for Endpoint for macOS.
For more information about Microsoft Defender for Endpoint for Mac including what's new in the latest release, see Microsoft Defender for Endpoint for Mac in the Microsoft 365 security documentation.
Onboard Android devices
After you establish the service-to-service connection between Intune and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, you can onboard Android devices to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
Intune doesn't support an automatic onboarding package for Android as it does for Windows devices. For configuration guidance for Intune, see Overview of Microsoft Defender for Endpoint for Android in the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint documentation for the prerequisites and onboarding instructions for Android.
For devices that run Android, you can also use Intune policy to modify Microsoft Defender for Endpoint on Android. For more information, see Microsoft Defender for Endpoint web protection.
Onboard iOS/iPadOS devices
After you establish the service-to-service connection between Intune and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, you can onboard iOS/iPadOS devices to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
Intune doesn't support an automatic onboarding package for iOS/iPadOS as it does for Windows devices. For configuration guidance for Intune, see Overview of Microsoft Defender for Endpoint for iOS in the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint documentation for prerequisites and onboarding instructions for iOS/iPadOS.
For devices that run iOS/iPadOS (in Supervised Mode), there's specialized ability given the increased management capabilities provided by the platform on these types of devices. To take advantage of these capabilities, the Defender app needs to know if a device is in Supervised Mode. For more information, see Complete deployment for supervised devices.
Sign in to the Microsoft Intune admin center.
Select Apps > App configuration policies > + Add, and then selectManaged devices from the drop down list.
On the Basics page, enter a Name and Description (optional) for the profile, select Platform as iOS/iPadOS then choose Next.
Select Targeted app as Microsoft Defender for iOS.
On the Settings page, set the Configuration key as issupervised, then Value type as string with the {{issupervised}} as the Configuration value.
Select Next to open the Scope tags page. Scope tags are optional. Select Next to continue.
On the Assignments page, select the groups that will receive this profile. For this scenario, it's a best practice to target All Devices. For more information on assigning profiles, see Assign user and device profiles.
When you deploy policy to user groups, a user must sign-in on a device before the policy applies.
Select Next.
On the Review + create page, when you're done, choose Create. The new profile is displayed in the list of configuration profiles.
View the count of devices that are onboarded to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
You can view a report on device onboarding status from within the Intune admin center by going to Endpoint security > Endpoint detection and response > and selecting the EDR Onboarding Status tab.
To view this information, your account must be assigned an Intune role that includes Read for the Microsoft Defender Advanced Threat Protection permission.
Create and assign compliance policy to set device risk level
For Android, iOS/iPadOS, and Windows devices, the compliance policy determines the level of risk that you consider as acceptable for a device.
If you're not familiar with creating compliance policy, reference the Create a policy procedure from the Create a compliance policy in Microsoft Intune article. The following information is specific to configuring Microsoft Defender for Endpoint as part of a compliance policy.
Sign in to the Microsoft Intune admin center.
Select Devices > Compliance. On the Policies tab, select + Create policy.
For Platform, use the drop-down box to select one of the following options:
- Android device administrator
- Android Enterprise
- iOS/iPadOS
- Windows 10 and later
Next, select Create.
On the Basics tab, specify a Name that helps you identify this policy later. You can also choose to specify a Description.
On the Compliance settings tab, expand the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint category and set the option Require the device to be at or under the machine risk score to your preferred level.
Threat level classifications are determined by Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
- Clear: This level is the most secure. The device can't have any existing threats and still access company resources. If any threats are found, the device is evaluated as noncompliant. (Microsoft Defender for Endpoint uses the value Secure.)
- Low: The device is compliant if only low-level threats exist. Devices with medium or high threat levels aren't compliant.
- Medium: The device is compliant if the threats found on the device are low or medium. If high-level threats are detected, the device is determined as noncompliant.
- High: This level is the least secure and allows all threat levels. Devices with high, medium, or low threat levels are considered compliant.
Complete the configuration of the policy, including assignment of the policy to applicable groups.
Create and assign app protection policy to set device risk level
Use the procedure to create an application protection policy for either iOS/iPadOS or Android, and use the following information on the Apps, Conditional launch, and Assignments pages:
Apps: Select the apps you wish to be targeted by app protection policies. For this feature set, these apps are blocked or selectively wiped based on device risk assessment from your chosen Mobile Threat Defense vendor.
Conditional launch: Below Device conditions, use the drop-down box to select Max allowed device threat level.
Options for the threat level Value:
- Secured: This level is the most secure. The device can't have any threats present and still access company resources. If any threats are found, the device is evaluated as noncompliant.
- Low: The device is compliant if only low-level threats are present. Anything higher puts the device in a noncompliant status.
- Medium: The device is compliant if the threats found on the device are low or medium level. If high-level threats are detected, the device is determined as noncompliant.
- High: This level is the least secure and allows all threat levels, using Mobile Threat Defense for reporting purposes only. Devices are required to have the MTD app activated with this setting.
Options for Action:
- Block access
- Wipe data
Assignments: Assign the policy to groups of users. The devices used by the group's members are evaluated for access to corporate data on targeted apps via Intune app protection.
Important
If you create an app protection policy for any protected app, the device's threat level is assessed. Depending on the configuration, devices that don’t meet an acceptable level are either blocked or selectively wiped through conditional launch. If blocked, they are prevented from accessing corporate resources until the threat on the device is resolved and reported to Intune by the chosen MTD vendor.
Create a Conditional Access policy
Conditional Access policies can use data from Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to block access to resources for devices that exceed the threat level you set. You can block access from the device to corporate resources, such as SharePoint or Exchange Online.
Tip
Conditional Access is a Microsoft Entra technology. The Conditional Access node found in the Microsoft Intune admin center is the node from Microsoft Entra.
Sign in to the Microsoft Intune admin center.
Select Endpoint security > Conditional Access > Create new policy. Because Intune presents the policy creation user interface for Conditional Access from the Azure portal, the interface is different than the policy creation workflow you might be familiar with.
Enter a policy Name.
For Users, use the Include and Exclude tabs to configure groups that will receive this policy.
For Target resources, set Select what this policy applies to to Cloud apps, and then choose which apps to protect. For example, choose Select apps and then for Select, search for and select Office 365 SharePoint Online and Office 365 Exchange Online.
For Conditions, select Client apps and then set Configure to Yes. Next, select the checkboxes for Browser and Mobile apps and desktop clients. Then, select Done to save the client app configuration.
For Grant, configure this policy to apply based on device compliance rules. For example:
- Select Grant access.
- Select the checkbox for Require device to be marked as compliant.
- Select Require all the selected controls. Choose Select to save the Grant configuration.
For Enable policy, select On and then Create to save your changes.
Related content
Learn more from the Intune documentation:
- Use security tasks with Defender for Endpoints Vulnerability Management to remediate issues on devices
- Get started with device compliance policies
- App protection policies overview
Learn more from the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint documentation: