Data, privacy, and security for web search in Microsoft 365 Copilot and Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat
Microsoft 365 Copilot and Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat have an optional feature that allows Copilot to reference web content when responding to user prompts. Allowing Microsoft 365 Copilot and Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat to reference web content improves the quality of Copilot responses by grounding them in the latest information from the web.
Web search
When web search is enabled, Microsoft 365 Copilot and Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat may fetch information from the Bing search service when information from the web will help provide a better, more grounded response. Admin controls and a user-level Web content toggle (only for Microsoft 365 Copilot) are available to manage whether web search is enabled in your environment.
How web search works
When web search is enabled, Microsoft 365 Copilot and Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat parse the user’s prompt and identifies terms where information from the web would improve the quality of the response. Based on these terms, Copilot generates a search query that it sends to the Bing search service asking for more information.
This generated search query is different from the user’s original prompt—it consists of a few words informed by the user’s prompt. The following information isn't included in the generated search query sent to the Bing search service:
The user's entire prompt, unless the prompt is very short (for example, "local weather")
Entire Microsoft 365 files (for example, emails or documents) or files uploaded into Copilot
Entire web pages or PDFs summarized by Copilot in Microsoft Edge (only for Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat)
Any identifying information based on the user's Microsoft Entra ID (for example, username, domain, or tenant ID)
When using Microsoft 365 Copilot, the generated search query doesn't include the entirety of Microsoft 365 documents associated with the prompt. However, it may also be informed by data within a Microsoft 365 document under the following conditions:
When a user enters a prompt into Copilot inside a Microsoft 365 application (for example, writing a prompt into Copilot in Microsoft Word while a relevant document is open).
When the user explicitly references a specific document in their prompt.
The user's prompts and Copilot's responses are stored within Microsoft 365 and never leave the service boundary for both Microsoft 365 Copilot and Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat.
After Microsoft 365 Copilot and Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat receive additional information from the Bing search service, this information is used to compose the response returned to the user.
When a Microsoft 365 Copilot user submits their prompt with the Web content toggle (that is, web search) turned on, they may receive two separate responses:
If resources are found within Microsoft 365, the user sees:
- From your company's resources, emails, Teams messages, etc.
If resources are found outside of Microsoft 365, the user sees:
- From the web:
The user can see results from both. Additionally, if the results are from the web only, the user sees the same From the web: heading.
Web search query citations
To provide greater visibility into the generated search queries, web search query citations are shown to users in the linked citation section of the Copilot response. The section shows the exact web search queries (derived from the user’s prompt) that were sent to the Bing search service. Showing the exact web search queries helps users understand what search queries, along with the sites searched, were used to enhance Copilot’s response to their prompt. This information can help users improve their prompts and use Copilot more effectively.
Web search query citations are available only in Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat (previously named Business Chat). Citations aren’t available in the Copilot pane within a Microsoft 365 app, such as Word or PowerPoint. Also, the web search queries are only available in the chat thread for 24 hours.
Web search query logging
Web search query logging is available so that admins can perform search, audit, and eDiscovery on the exact web search queries Copilot derived from the user's prompt. Admins can already perform these actions for prompts and responses and will be able to use their familiar tools to extend those actions to search queries. For more information, see Audit log activities, Copilot interaction events overview, and Search for and delete Copilot data in eDiscovery (preview).
Examples of generated search queries
The following table provides multiple examples of a user's prompt and the generated search queries sent to Bing. It also explains how Microsoft 365 Copilot and Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat formulate a response. Brackets indicate placeholders for specific information referenced by the user or inferred by Copilot.
Note
Unlike with Microsoft 365 Copilot, users can't invoke organizational content like files, emails, or chats, when prompting in Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat. For examples of purely web-based user prompts for Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat, see Privacy and security of generated search queries.
| User prompt | Generated search queries | How Copilot provides a response |
|---|---|---|
| Who is my manager and what public information is available about them? | [Manager name] | Copilot finds the name of the user's manager from Microsoft 365 data. It then generates a Bing search query based on their name to see what information about them is available on the web. |
| I'm looking for a document authored last week by [coworker]. | None | Copilot returns documents by [coworker] found in Microsoft 365 data. No web search queries are generated. |
| We're considering a possible acquisition of Fabrikam. Summarize financial information about the company, including their business strategy. | Fabrikam strategy Fabrikam financials |
Copilot returns a response with two sections. One is headlined "From your company's data" that references information the user has access to in Microsoft 365. The other is headlined "From the web," which includes any publicly available information. |
| What decision did [coworker] make about shipping our Contoso product? | [Coworker name] decision about shipping Contoso product | Copilot returns a response based on information the user has access to in Microsoft 365. Because there's no relevant information available on the web, Copilot doesn't include information from the web in the response. |
| Summarize [internal strategy document about clean energy] and tell me if Fabrikam has publicly announced a similar approach. | Fabrikam clean energy policy announcements | The user explicitly includes a reference to a specific document in Microsoft 365. Copilot reasons over this document and identifies "clean energy policy" as a major theme. "Clean energy policy" is added to the generated search query sent to the Bing search service (the document itself isn't included). Copilot then takes web results returned from Bing and identifies any similarities between this public information and the strategy described in the internal document. |
How Microsoft handles generated search queries
Microsoft 365 Copilot and Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat both use generated search queries sent to the Bing search service to ground responses in web data. The way Microsoft handles these queries is identical in both services.
Generated search queries sent to the Bing search service have the user and tenant identifiers removed. They aren't shared with advertisers and aren’t used to train foundation large language models (LLMs). Also, web search queries sent to Bing don't affect any of the following:
- Search Ranking
- Answers or features like Rich Captions
- Social features like Auto Suggest, Trending, and Zero Input
The Bing search service operates separately from Microsoft 365 and has different data-handling practices. The use of Bing is covered by the Microsoft Services Agreement between each user and Microsoft, together with the Microsoft Privacy Statement. The Microsoft Products and Services Data Protection Addendum (DPA) doesn't apply to the use of the Web content toggle in Microsoft 365 Copilot, Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat, or the Bing search service.
Controls available to manage web search
To manage web search so it aligns with organizational policies, user preferences, and security considerations, two distinct controls are available: one for IT admins and another for users (only for Microsoft 365 Copilot).
IT admin control for both Microsoft 365 Copilot and Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat
The primary way that IT admins can control access to web search is by using the Allow web search in Copilot policy, which is available only in Cloud Policy service for Microsoft 365. This policy allows IT admins to either turn on or turn off web search for users or user groups across the tenant they manage in accordance with their organization’s policies, data privacy laws, or other regulatory requirements. This policy applies to both Microsoft 365 Copilot and Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat.
Note
The Allow web search in Copilot policy replaces the Allow Copilot to improve responses with web content control in the Microsoft 365 admin center previously used to manage web content in Microsoft 365 Copilot.
If the IT admin enables the Allow web search in Copilot policy, they have three options for web search in Copilot:
- Enabled in Microsoft 365 Copilot and Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat
- Disabled in Microsoft 365 Copilot and Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat
- Disabled in Microsoft 365 Copilot Work mode; Enabled in Microsoft 365 Copilot Web mode and Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat
If the IT admin turns on web search for Microsoft 365 Copilot users, those users still have the option to turn off web search by using the Web content toggle. The Web content toggle isn’t available as part of the Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat experience.
If the IT admin turns off web search, the Web content toggle can longer be used and there isn’t a way for users to turn web search back on. For example, even if a Microsoft 365 Copilot user has turned on the Web content toggle, they still won’t be able to use web search.
If the IT admin doesn’t configure the Allow web search in Copilot policy, web search will be available to users in both Microsoft 365 Copilot and Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat, unless the IT admin has set the Allow the use of additional optional connected experiences in Office policy to Disabled. But turning off optional connected experiences restricts Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat, Microsoft 365 Copilot, and multiple experiences across Microsoft 365.
Note
For Government Community Cloud (GCC) customers:
- Web search is available in GCC.
- The Allow web search in Copilot policy is available in GCC in Cloud Policy service for Microsoft 365.
- If the IT admin doesn’t configure the Allow web search in Copilot policy, web search will be turned off in GCC, regardless of how the Allow the use of additional optional connected experiences in Office policy is configured.
Web content toggle for users (only for Microsoft 365 Copilot)
The Web content toggle offers users control over whether or not they want real-time web content in Microsoft 365 Copilot responses based on their personal preference. The Web content toggle is only available as part of work chat in Microsoft 365 Copilot.
If the IT admin enables web search, the Web content toggle is turned on by default. When turned on, the user receives responses grounded in real-time web content. If the IT admin disables web search, the Web content toggle isn't available to the Microsoft 365 Copilot user as part of work chat and web search is disabled.
If a Microsoft 365 Copilot user turns off the Web content toggle in work chat, web content isn't included in Copilot responses.
Microsoft 365 Copilot users can manage web search in work chat by following these steps:
Select the menu in the top right corner of the screen in Microsoft 365 Copilot when using work chat.
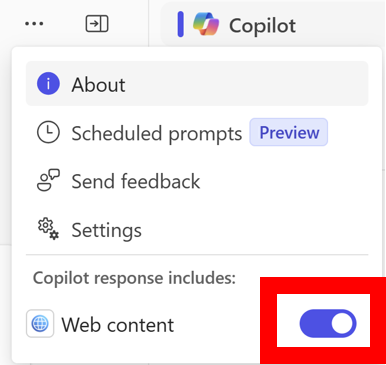
Turn off the Web content toggle.
Note
The privacy setting for optional connected experiences available to users in Microsoft 365 apps (for example, in Word, Excel, or Teams) has no effect on the availability of web search. For example, if a user turns off optional connected experiences, web search can still be available to the user.