Scenario: Isolating VNets
When working with Virtual WAN virtual hub routing, there are quite a few available scenarios. In this scenario, the goal is to prevent VNets from being able to reach other. This is known as isolating VNets. For information about virtual hub routing, see About virtual hub routing.
Design
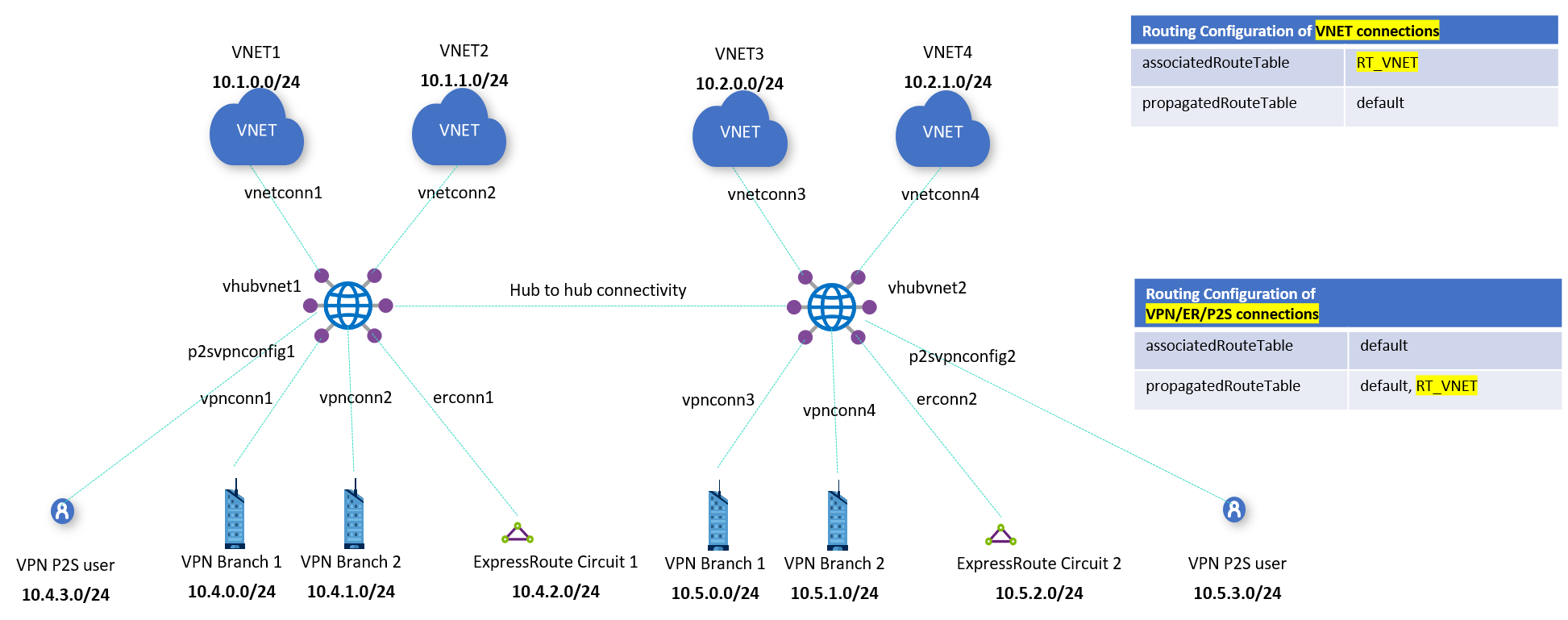
In this scenario, the workload within a certain VNet remains isolated and isn't able to communicate with other VNets. However, the VNets are required to reach all branches (VPN, ER, and User VPN). In order to figure out how many route tables will be needed, you can build a connectivity matrix. For this scenario it will look like the following table, where each cell represents whether a source (row) can communicate to a destination (column):
| From | To | VNets | Branches |
|---|---|---|---|
| VNets | → | Direct | Direct |
| Branches | → | Direct | Direct |
Each of the cells in the previous table describes whether a Virtual WAN connection (the "From" side of the flow, the row headers) communicates with a destination prefix (the "To" side of the flow, the column headers in italics). In this scenario there are no firewalls or Network Virtual Appliances, so communications flows directly over Virtual WAN (hence the word "Direct" in the table).
This connectivity matrix gives us two different row patterns, which translate to two route tables. Virtual WAN already has a Default route table, so we'll need another route table. For this example, we'll name the route table RT_VNET.
VNets will be associated to this RT_VNET route table. Because they need connectivity to branches, branches need to propagate to RT_VNET (otherwise the VNets wouldn't learn the branch prefixes). Since the branches are always associated to the Default route table, VNets need to propagate to the Default route table. As a result, this is the final design:
- Virtual networks:
- Associated route table: RT_VNET
- Propagating to route tables: Default
- Branches:
- Associated route table: Default
- Propagating to route tables: RT_VNET and Default
Notice that since only branches propagate to the route table RT_VNET, those will be the only prefixes that VNets will learn, and not those of other VNets.
For information about virtual hub routing, see About virtual hub routing.
Workflow
In order to configure this scenario, take the following steps into consideration:
Create a custom route table in each hub. In the example, the route table is RT_VNet. To create a route table, see How to configure virtual hub routing. For more information about route tables, see About virtual hub routing.
When you create the RT_VNet route table, configure the following settings:
- Association: Select the VNets you want to isolate.
- Propagation: Select the option for branches, implying branch(VPN/ER/P2S) connections propagate routes to this route table.
Next steps
- For more information about Virtual WAN, see the FAQ.
- For more information about virtual hub routing, see About virtual hub routing.