Configure a cloud trust between on premises AD DS and Microsoft Entra ID for accessing Azure Files
Many organizations want to use identity-based authentication for SMB Azure file shares in environments that span both on-premises Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) and Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure Active Directory), but don't meet the necessary operating system or domain prerequisites.
In such scenarios, customers can enable Microsoft Entra Kerberos authentication for hybrid user identities and then establish a cloud trust between their on-premises AD DS and Microsoft Entra ID to access SMB file shares using their on-premises credentials. This article explains how a cloud trust works, and provides instructions for setup and validation. It also includes steps to rotate a Kerberos key for your service account in Microsoft Entra ID and Trusted Domain Object, and steps to remove a Trusted Domain Object and all Kerberos settings, if desired.
This article focuses on authenticating hybrid user identities, which are on-premises AD DS identities that are synced to Microsoft Entra ID using either Microsoft Entra Connect or Microsoft Entra Connect cloud sync. Cloud-only identities aren't currently supported for Azure Files.
Applies to
| File share type | SMB | NFS |
|---|---|---|
| Standard file shares (GPv2), LRS/ZRS | ||
| Standard file shares (GPv2), GRS/GZRS | ||
| Premium file shares (FileStorage), LRS/ZRS |
Scenarios
The following are examples of scenarios in which you might want to configure a cloud trust:
You have a traditional on premises AD DS, but you're not able to use it for authentication because you don't have unimpeded network connectivity to the domain controllers.
You've started migrating to the cloud but currently have applications still running on traditional on-premises AD DS.
Some or all of your client machines don't meet the operating system requirements for Microsoft Entra Kerberos authentication.
Permissions
To complete the steps outlined in this article, you'll need:
- An on-premises Active Directory administrator username and password. This account must either be a member of the Domain Admins group for the domain or a member of the Enterprise Admins group for the domain's forest.
- A Microsoft Entra Global Administrator account username and password.
Prerequisites
Before implementing the incoming trust-based authentication flow, ensure that the following prerequisites are met:
| Prerequisite | Description |
|---|---|
| Client must run Windows 10, Windows Server 2012, or a higher version of Windows. | |
| Clients must be joined to Active Directory (AD). The domain must have a functional level of Windows Server 2012 or higher. | You can determine if the client is joined to AD by running the dsregcmd command: dsregcmd.exe /status |
| A Microsoft Entra tenant. | A Microsoft Entra Tenant is an identity security boundary that's under the control of your organization’s IT department. It's an instance of Microsoft Entra ID in which information about a single organization resides. |
| An Azure subscription under the same Microsoft Entra tenant you plan to use for authentication. | |
| An Azure storage account in the Azure subscription. | An Azure storage account is a resource that acts as a container for grouping all the data services from Azure Storage, including files. |
| Microsoft Entra Connect or Microsoft Entra Connect cloud sync must be installed. | These solutions are used in hybrid environments where identities exist both in Microsoft Entra ID and on-premises AD DS. |
Enable Microsoft Entra Kerberos authentication
If you've already enabled Microsoft Entra Kerberos authentication on your storage account, you can skip this step and proceed to Create and configure the Microsoft Entra Kerberos Trusted Domain Object.
You can enable Microsoft Entra Kerberos authentication on Azure Files for hybrid user accounts using the Azure portal, PowerShell, or Azure CLI.
To enable Microsoft Entra Kerberos authentication using the Azure portal, follow these steps.
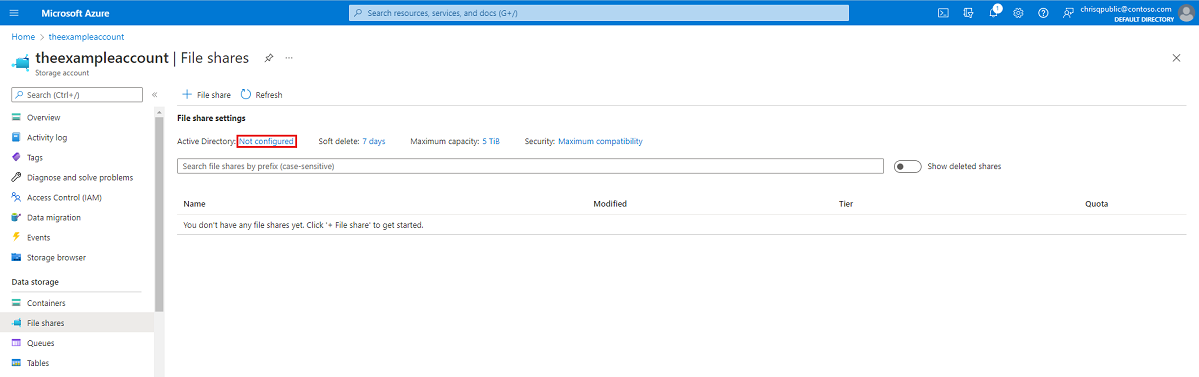
Sign in to the Azure portal and select the storage account you want to enable Microsoft Entra Kerberos authentication for.
Under Data storage, select File shares.
Next to Active Directory, select the configuration status (for example, Not configured).
Under Microsoft Entra Kerberos, select Set up.
Select the Microsoft Entra Kerberos checkbox.
Optional: If you want to configure directory and file-level permissions through Windows File Explorer, then you must specify the domain name and domain GUID for your on-premises AD. You can get this information from your domain admin or by running the following Active Directory PowerShell cmdlet from an on-premises AD-joined client:
Get-ADDomain. Your domain name should be listed in the output underDNSRootand your domain GUID should be listed underObjectGUID. If you'd prefer to configure directory and file-level permissions using icacls, you can skip this step. However, if you want to use icacls, the client will need unimpeded network connectivity to the on-premises AD.Select Save.
Warning
If you've previously enabled Microsoft Entra Kerberos authentication through manual limited preview steps to store FSLogix profiles on Azure Files for Microsoft Entra joined VMs, the password for the storage account's service principal is set to expire every six months. Once the password expires, users won't be able to get Kerberos tickets to the file share. To mitigate this, see "Error - Service principal password has expired in Microsoft Entra ID" under Potential errors when enabling Microsoft Entra Kerberos authentication for hybrid users.
Grant admin consent to the new service principal
After enabling Microsoft Entra Kerberos authentication, you'll need to explicitly grant admin consent to the new Microsoft Entra application registered in your Microsoft Entra tenant. This service principal is auto-generated and isn't used for authorization to the file share, so don't make any edits to the service principal other than those documented here. If you do, you might get an error.
You can configure the API permissions from the Azure portal by following these steps:
- Open Microsoft Entra ID.
- In the service menu, under Manage, select App registrations.
- Select All Applications.
- Select the application with the name matching [Storage Account]
<your-storage-account-name>.file.core.windows.net. - In the service menu, under Manage, select API permissions.
- Select Grant admin consent for [Directory Name] to grant consent for the three requested API permissions (openid, profile, and User.Read) for all accounts in the directory.
- Select Yes to confirm.
Important
If you're connecting to a storage account via a private endpoint/private link using Microsoft Entra Kerberos authentication, you'll also need to add the private link FQDN to the storage account's Microsoft Entra application. For instructions, see the entry in our troubleshooting guide.
Disable multifactor authentication on the storage account
Microsoft Entra Kerberos doesn't support using MFA to access Azure file shares configured with Microsoft Entra Kerberos. You must exclude the Microsoft Entra app representing your storage account from your MFA conditional access policies if they apply to all apps.
The storage account app should have the same name as the storage account in the conditional access exclusion list. When searching for the storage account app in the conditional access exclusion list, search for: [Storage Account] <your-storage-account-name>.file.core.windows.net
Remember to replace <your-storage-account-name> with the proper value.
Important
If you don't exclude MFA policies from the storage account app, you won't be able to access the file share. Trying to map the file share using net use will result in an error message that says "System error 1327: Account restrictions are preventing this user from signing in. For example: blank passwords aren't allowed, sign-in times are limited, or a policy restriction has been enforced."
For guidance on disabling MFA, see the following:
Assign share-level permissions
When you enable identity-based access, for each share you must assign which users and groups have access to that particular share. Once a user or group is allowed access to a share, Windows ACLs (also called NTFS permissions) on individual files and directories take over. This allows for fine-grained control over permissions, similar to an SMB share on a Windows server.
To set share-level permissions, follow the instructions in Assign share-level permissions to an identity.
Configure directory and file-level permissions
Once share-level permissions are in place, you can assign directory/file-level permissions to the user or group. This requires using a device with unimpeded network connectivity to an on-premises AD.
To configure directory and file-level permissions, follow the instructions in Configure directory and file-level permissions over SMB.
Create and configure the Microsoft Entra Kerberos Trusted Domain Object
To create and configure the Microsoft Entra Kerberos Trusted Domain Object, you'll use the Azure AD Hybrid Authentication Management PowerShell module. This module enables hybrid identity organizations to use modern credentials for their applications and enables Microsoft Entra ID to become the trusted source for both cloud and on-premises authentication.
Set up the Trusted Domain Object
You'll use the Azure AD Hybrid Authentication Management PowerShell module to set up a Trusted Domain Object in the on-premises AD domain and register trust information with Microsoft Entra ID. This creates an in-bound trust relationship into the on-premises AD, which enables Microsoft Entra ID to trust on-premises AD.
You only have to set up the Trusted Domain Object once per domain. If you've already done this for your domain, you can skip this section and proceed to Configure the clients to retrieve Kerberos tickets.
Install the Azure AD Hybrid Authentication Management PowerShell module
Start a Windows PowerShell session with the Run as administrator option.
Install the Azure AD Hybrid Authentication Management PowerShell module using the following script. The script:
- Enables TLS 1.2 for communication.
- Installs the NuGet package provider.
- Registers the PSGallery repository.
- Installs the PowerShellGet module.
- Installs the Azure AD Hybrid Authentication Management PowerShell module.
- The Azure AD Hybrid Authentication Management PowerShell uses the AzureADPreview module, which provides advanced Microsoft Entra management features.
- To protect against unnecessary installation conflicts with the Azure AD PowerShell module, this command includes the
-AllowClobberoption flag.
[Net.ServicePointManager]::SecurityProtocol = [Net.SecurityProtocolType]::Tls12
Install-PackageProvider -Name NuGet -Force
if (@(Get-PSRepository | ? {$_.Name -eq "PSGallery"}).Count -eq 0){
Register-PSRepository -DefaultSet-PSRepository -Name "PSGallery" -InstallationPolicy Trusted
}
Install-Module -Name PowerShellGet -Force
Install-Module -Name AzureADHybridAuthenticationManagement -AllowClobber
Create the Trusted Domain Object
Start a Windows PowerShell session with the Run as administrator option.
Set the common parameters. Customize the script below prior to running it.
- Set the
$domainparameter to your on-premises Active Directory domain name. - When prompted by
Get-Credential, enter an on-premises Active Directory administrator username and password. This account must either be a member of the Domain Admins group for the domain or a member of the Enterprise Admins group for the domain's forest. - Set the
$cloudUserNameparameter to the username of a Global Administrator privileged account for Microsoft Entra cloud access.
Note
If you wish to use your current Windows login account for your on-premises Active Directory access, you can skip the step where credentials are assigned to the
$domainCredparameter. If you take this approach, don't include the-DomainCredentialparameter in the PowerShell commands following this step.$domain = "your on-premises domain name, for example contoso.com" $domainCred = Get-Credential $cloudUserName = "Azure AD user principal name, for example admin@contoso.onmicrosoft.com"- Set the
Check the current Kerberos Domain Settings.
Run the following command to check your domain's current Kerberos settings:
Get-AzureAdKerberosServer -Domain $domain ` -DomainCredential $domainCred ` -UserPrincipalName $cloudUserNameIf this is the first time calling any Microsoft Entra Kerberos command, you're prompted for Microsoft Entra cloud access.
- Enter the password for your Microsoft Entra Global Administrator account.
- If your organization uses other modern authentication methods such as Microsoft Entra multifactor authentication or Smart Card, follow the instructions as requested for sign in.
If this is the first time you're configuring Microsoft Entra Kerberos settings, the Get-AzureAdKerberosServer cmdlet displays empty information, as in the following sample output:
ID : UserAccount : ComputerAccount : DisplayName : DomainDnsName : KeyVersion : KeyUpdatedOn : KeyUpdatedFrom : CloudDisplayName : CloudDomainDnsName : CloudId : CloudKeyVersion : CloudKeyUpdatedOn : CloudTrustDisplay :If your domain already supports FIDO authentication, the
Get-AzureAdKerberosServercmdlet displays Microsoft Entra service account information, as in the following sample output. TheCloudTrustDisplayfield returns an empty value.ID : XXXXX UserAccount : CN=krbtgt-AzureAD, CN=Users, DC=contoso, DC=com ComputerAccount : CN=AzureADKerberos, OU=Domain Controllers, DC=contoso, DC=com DisplayName : XXXXXX_XXXXX DomainDnsName : contoso.com KeyVersion : 53325 KeyUpdatedOn : 2/24/2024 9:03:15 AM KeyUpdatedFrom : ds-aad-auth-dem.contoso.com CloudDisplayName : XXXXXX_XXXXX CloudDomainDnsName : contoso.com CloudId : XXXXX CloudKeyVersion : 53325 CloudKeyUpdatedOn : 2/24/2024 9:03:15 AM CloudTrustDisplay :Add the Trusted Domain Object.
Run the Set-AzureAdKerberosServer PowerShell cmdlet to add the Trusted Domain Object. Be sure to include
-SetupCloudTrustparameter. If there's no Microsoft Entra service account, this command creates a new Microsoft Entra service account. This command will only create the requested Trusted Domain object if there's a Microsoft Entra service account.Set-AzureADKerberosServer -Domain $domain -UserPrincipalName $cloudUserName -DomainCredential $domainCred -SetupCloudTrustNote
On a multiple domain forest, to avoid the error LsaCreateTrustedDomainEx 0x549 when running the command on a child domain:
- Run the command on root domain (include
-SetupCloudTrustparameter). - Run the same command on the child domain without the
-SetupCloudTrustparameter.
After creating the Trusted Domain Object, you can check the updated Kerberos Settings using the
Get-AzureAdKerberosServerPowerShell cmdlet, as shown in the previous step. If theSet-AzureAdKerberosServercmdlet has been run successfully with the-SetupCloudTrustparameter, theCloudTrustDisplayfield should now returnMicrosoft.AzureAD.Kdc.Service.TrustDisplay, as in the following sample output:ID : XXXXX UserAccount : CN=krbtgt-AzureAD, CN=Users, DC=contoso, DC=com ComputerAccount : CN=AzureADKerberos, OU=Domain Controllers, DC=contoso, DC=com DisplayName : XXXXXX_XXXXX DomainDnsName : contoso.com KeyVersion : 53325 KeyUpdatedOn : 2/24/2024 9:03:15 AM KeyUpdatedFrom : ds-aad-auth-dem.contoso.com CloudDisplayName : XXXXXX_XXXXX CloudDomainDnsName : contoso.com CloudId : XXXXX CloudKeyVersion : 53325 CloudKeyUpdatedOn : 2/24/2024 9:03:15 AM CloudTrustDisplay : Microsoft.AzureAD.Kdc.Service.TrustDisplayNote
Azure sovereign clouds require setting the
TopLevelNamesproperty, which is set towindows.netby default. Azure sovereign cloud deployments of SQL Managed Instance use a different top-level domain name, such asusgovcloudapi.netfor Azure US Government. Set your Trusted Domain Object to that top-level domain name using the following PowerShell command:Set-AzureADKerberosServer -Domain $domain -DomainCredential $domainCred -CloudCredential $cloudCred -SetupCloudTrust -TopLevelNames "usgovcloudapi.net,windows.net". You can verify the setting with the following PowerShell command:Get-AzureAdKerberosServer -Domain $domain -DomainCredential $domainCred -UserPrincipalName $cloudUserName | Select-Object -ExpandProperty CloudTrustDisplay.- Run the command on root domain (include
Configure the clients to retrieve Kerberos tickets
Identify your Microsoft Entra tenant ID and use Group Policy to configure the client machine(s) you want to mount/use Azure File shares from. You must do this on every client on which Azure Files will be used.
Configure this group policy on the client(s) to "Enabled": Administrative Templates\System\Kerberos\Allow retrieving the Azure AD Kerberos Ticket Granting Ticket during logon
Deploy the following Group Policy setting to client machines using the incoming trust-based flow:
Edit the Administrative Templates\System\Kerberos\Specify KDC proxy servers for Kerberos clients policy setting.
Select Enabled.
Under Options, select Show.... This opens the Show Contents dialog box.
Define the KDC proxy servers settings using mappings as follows. Substitute your Microsoft Entra tenant ID for the
your_Azure_AD_tenant_idplaceholder. Note the space followinghttpsand before the closing/in the value mapping.Value name Value KERBEROS.MICROSOFTONLINE.COM <https login.microsoftonline.com:443: your_Azure_AD_tenant_id/kerberos />Select OK to close the 'Show Contents' dialog box.
Select Apply on the 'Specify KDC proxy servers for Kerberos clients' dialog box.
Rotate the Kerberos Key
You may periodically rotate the Kerberos Key for the created Microsoft Entra service account and Trusted Domain Object for management purposes.
Set-AzureAdKerberosServer -Domain $domain `
-DomainCredential $domainCred `
-UserPrincipalName $cloudUserName -SetupCloudTrust `
-RotateServerKey
Once the key is rotated, it takes several hours to propagate the changed key between the Kerberos KDC servers. Due to this key distribution timing, you can rotate the key once within 24 hours. If you need to rotate the key again within 24 hours for any reason, for example, just after creating the Trusted Domain Object, you can add the -Force parameter:
Set-AzureAdKerberosServer -Domain $domain `
-DomainCredential $domainCred `
-UserPrincipalName $cloudUserName -SetupCloudTrust `
-RotateServerKey -Force
Remove the Trusted Domain Object
You can remove the added Trusted Domain Object using the following command:
Remove-AzureADKerberosServerTrustedDomainObject -Domain $domain `
-DomainCredential $domainCred `
-UserPrincipalName $cloudUserName
This command will only remove the Trusted Domain Object. If your domain supports FIDO authentication, you can remove the Trusted Domain Object while maintaining the Microsoft Entra service account required for the FIDO authentication service.
Remove all Kerberos Settings
You can remove both the Microsoft Entra service account and the Trusted Domain Object using the following command:
Remove-AzureAdKerberosServer -Domain $domain `
-DomainCredential $domainCred `
-UserPrincipalName $cloudUserName