Run the sample app: iOS - Xcode (Swift or Objective-C)
This quickstart covers how to run the Azure Spatial Anchors sample app for iOS devices using Xcode (Swift or Objective-C). Azure Spatial Anchors is a cross-platform developer service that allows you to create mixed reality experiences using objects that persist their location across devices over time. When you're finished, you'll have an ARKit iOS app that can save and recall a spatial anchor.
You'll learn how to:
- Create a Spatial Anchors account
- Configure the Spatial Anchors account identifier and account key
- Deploy and run on an iOS device
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create an Azure free account before you begin.
Prerequisites
To complete this quickstart, make sure you have:
- A developer enabled macOS machine with the latest version of Xcode and CocoaPods installed.
- Git installed via HomeBrew:
- Enter the following command as a single line in the terminal:
/usr/bin/ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)". - Run
brew install gitandbrew install git-lfs. - Update your git config with
git lfs install(for the current user) orgit lfs install --system(for the entire system).
- Enter the following command as a single line in the terminal:
- A developer enabled ARKit compatible iOS device.
Create a Spatial Anchors resource
Go to the Azure portal.
On the left pane, select Create a resource.
Use the search box to search for Spatial Anchors.
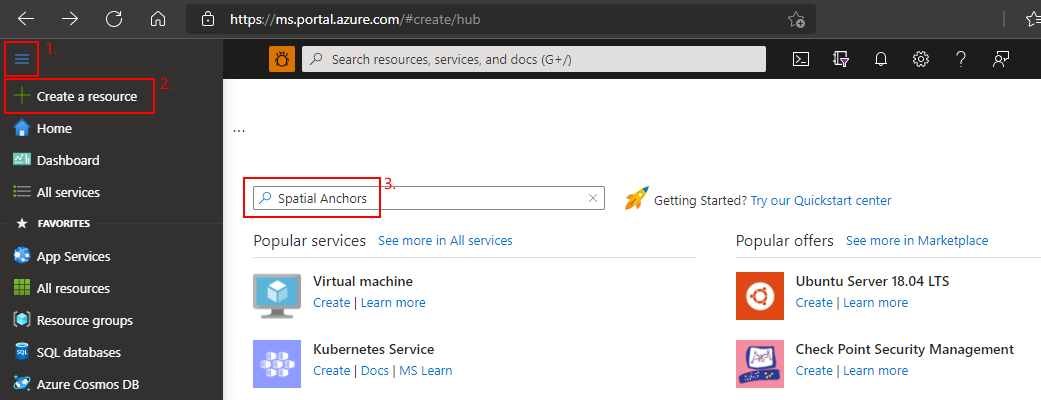
Select Spatial Anchors, and then select Create.
On the Spatial Anchors Account pane, do the following:
Enter a unique resource name by using regular alphanumeric characters.
Select the subscription that you want to attach the resource to.
Create a resource group by selecting Create new. Name it myResourceGroup, and then select OK.
A resource group is a logical container into which Azure resources, such as web apps, databases, and storage accounts, are deployed and managed. For example, you can choose to delete the entire resource group in one simple step later.
Select a location (region) in which to place the resource.
Select Create to begin creating the resource.
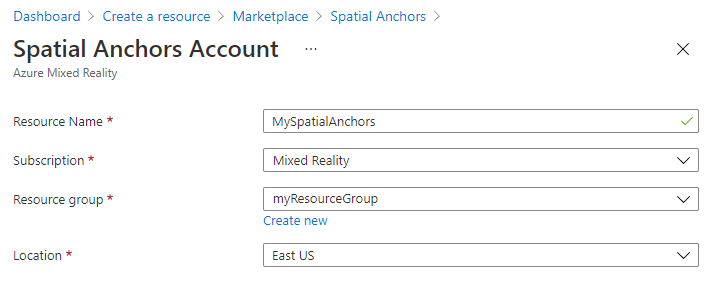
After the resource is created, the Azure portal shows that your deployment is complete.
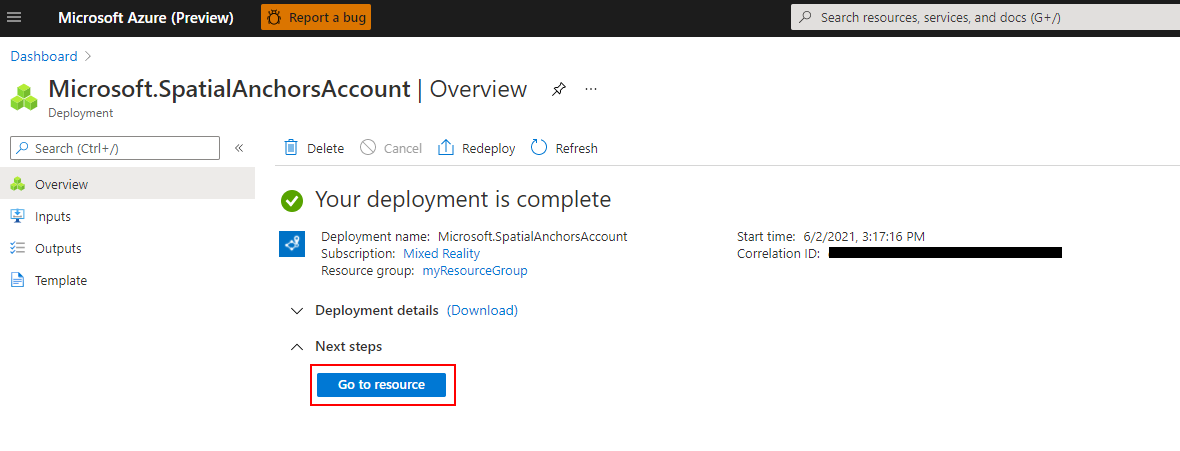
Select Go to resource. You can now view the resource properties.
Copy the resource's Account ID value into a text editor for later use.
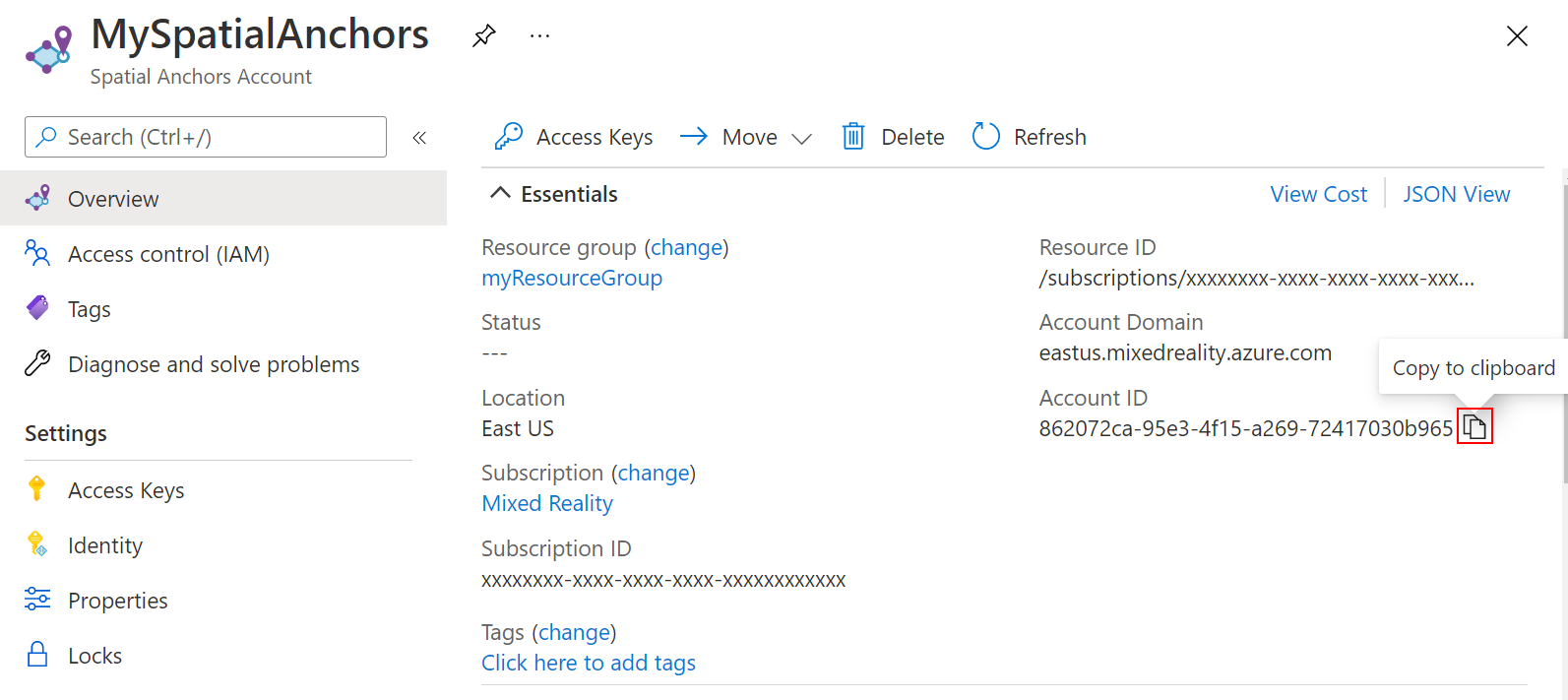
Also copy the resource's Account Domain value into a text editor for later use.
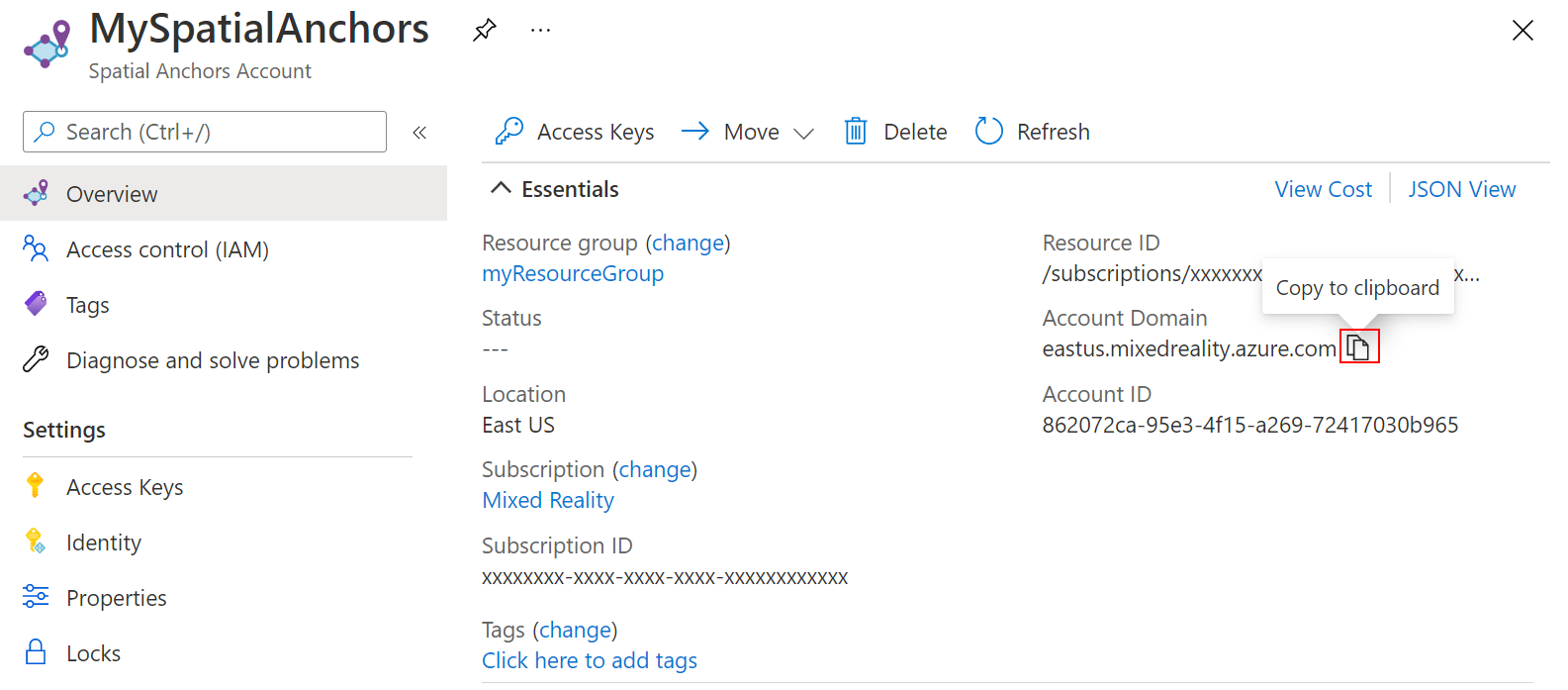
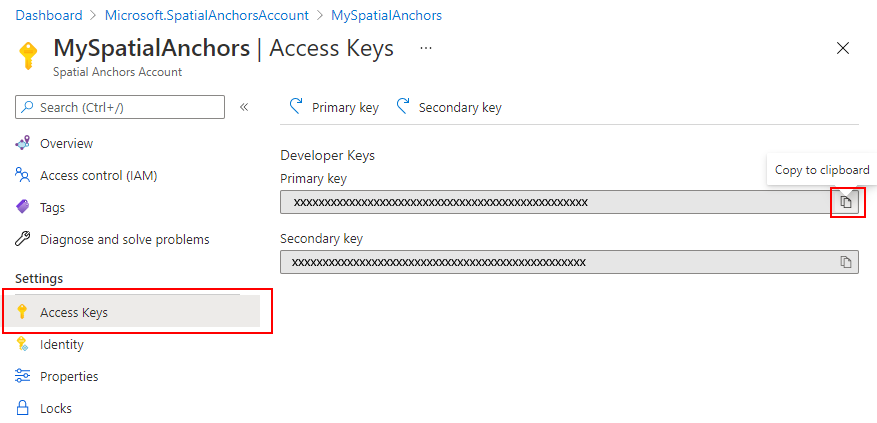
Under Settings, select Access Key. Copy the Primary key value, Account Key, into a text editor for later use.
Open the sample project
Use the Terminal to perform the following actions.
Clone the samples repository by running the following commands:
git clone https://github.com/Azure/azure-spatial-anchors-samples.git
cd ./azure-spatial-anchors-samples
Install the necessary pods using CocoaPods:
Navigate to iOS/Swift/.
cd ./iOS/Swift/
Run pod install --repo-update to install the CocoaPods for the project.
Note
Use the following command if you have macOS Monterey (12.2.1)
Run pod update to install the CocoaPods for the project.
Now open the .xcworkspace in Xcode.
Note
See the troubleshooting steps here if you're having CocoaPod issues after upgrading to macOS Catalina (10.15).
open ./SampleSwift.xcworkspace
Configure account identifier and key
The next step is to configure the app to use your account identifier and account key. You copied them into a text editor when setting up the Spatial Anchors resource.
Open iOS/Swift/SampleSwift/ViewControllers/BaseViewController.swift.
Locate the spatialAnchorsAccountKey field and replace Set me with the account key.
Locate the spatialAnchorsAccountId field and replace Set me with the account identifier.
Locate the spatialAnchorsAccountDomain field and replace Set me with the account domain.
Deploy the app to your iOS device
Connect the iOS device to the Mac and set the active scheme to your iOS device.

Select Build and then run the current scheme.

Note
If you see a library not found for -lPods-SampleObjC error, you likely opened the .xcodeproj file instead of the
.xcworkspace. Open the .xcworkspace and try again.
In Xcode, stop the app by pressing Stop.
Troubleshooting
CocoaPods issues on macOS Catalina (10.15)
If you recently updated to macOS Catalina (10.15) and had CocoaPods installed beforehand, CocoaPods may be in a broken
state and fail to properly configure your pods and .xcworkspace project files. To resolve this issue, you'll need to
reinstall CocoaPods by running the following commands:
brew update
brew install cocoapods --build-from-source
brew link --overwrite cocoapods
App crashes when deploying to iOS 10.3.1 from a personal provisioning profile/developer account
If you deploy your iOS app on iOS 10.3.1 from a personal provisioning profile/developer account, you might see this error: Library not loaded: @rpath/ADAL....
To resolve the issue:
- Use a provisioning profile that isn't a Personal Team profile (paid developer account).
- Deploy your app to an iOS device running iOS 13.3 or earlier, or to one running the iOS 13.4 beta or release version.
- Read more about this issue on Stack Overflow.
Clean up resources
In the preceding steps, you created Azure resources in a resource group. If you don't expect to need these resources in the future, you can delete them by deleting the resource group.
From the Azure portal menu or Home page, select Resource groups. Then, on the Resource groups page, select myResourceGroup.
On the myResourceGroup page, make sure that the listed resources are the ones you want to delete.
Select Delete resource group, type myResourceGroup in the text box to confirm, and then select Delete.
Next steps
In this quickstart, you created a Spatial Anchors account. You then configured and deployed an app to save and recall spatial anchors. To learn more about how to improve the app so it can share spatial anchors with other devices, continue to the next tutorial.
