Configure a vectorizer in a search index
In Azure AI Search a vectorizer is a component that performs vectorization using a deployed embedding model on Azure OpenAI or Azure AI Vision. It converts text (or images) to vectors during query execution.
It's defined in a search index, it applies to searchable vector fields, and it's used at query time to generate an embedding for a text or image query input. If instead you need to vectorize content as part of the indexing process, refer to integrated vectorization. For built-in vectorization during indexing, you can configure an indexer and skillset that calls an embedding model for your raw text or image content.
To add a vectorizer to search index, you can use the index designer in Azure portal, or call the Create or Update Index REST API, or use any Azure SDK package that's updated to provide this feature.
Vectorizers are now generally available as long as you use a generally available skill-vectorizer pair. AzureOpenAIEmbedding vectorizer and AzureOpenAIEmbedding skill are generally available. The custom Web API vectorizer is also generally available.
Azure AI Vision vectorizer, Azure AI Foundry model catalog vectorizer, and their equivalent skills are still in preview. Your skillset must specify 2024-05-01-preview REST API to use preview skills and vectorizers.
Prerequisites
An index with searchable vector fields on Azure AI Search.
A deployed embedding model (see the next section).
Permissions to use the embedding model. On Azure OpenAI, the caller must have Cognitive Services OpenAI User permissions. Or, you can provide an API key.
Visual Studio Code with a REST client to send the query and accept a response.
We recommend that you enable diagnostic logging on your search service to confirm vector query execution.
Supported embedding models
The following table lists the embedding models that can be used with a vectorizer. Because you must use the same embedding model for indexing and queries, vectorizers are paired with skills that generate embeddings during indexing. The table lists the skill associated with a particular vectorizer.
| Vectorizer kind | Model names | Model provider | Associated skill |
|---|---|---|---|
azureOpenAI |
text-embedding-ada-002, text-embedding-3 | Azure OpenAI | AzureOpenAIEmbedding skill |
aml |
Facebook-DinoV2-Image-Embeddings, Cohere-embed-v3 | Azure AI Foundry model catalog | AML skill |
aiServicesVision |
Multimodal embeddings 4.0 API | Azure AI Vision (through an Azure AI multi-service account) | Azure AI Vision multimodal embeddings skill |
customWebApi |
Any embedding model | Hosted externally | Custom Web API skill |
Try a vectorizer with sample data
The Import and vectorize data wizard reads files from Azure Blob storage, creates an index with chunked and vectorized fields, and adds a vectorizer. By design, the vectorizer that's created by the wizard is set to the same embedding model used to index the blob content.
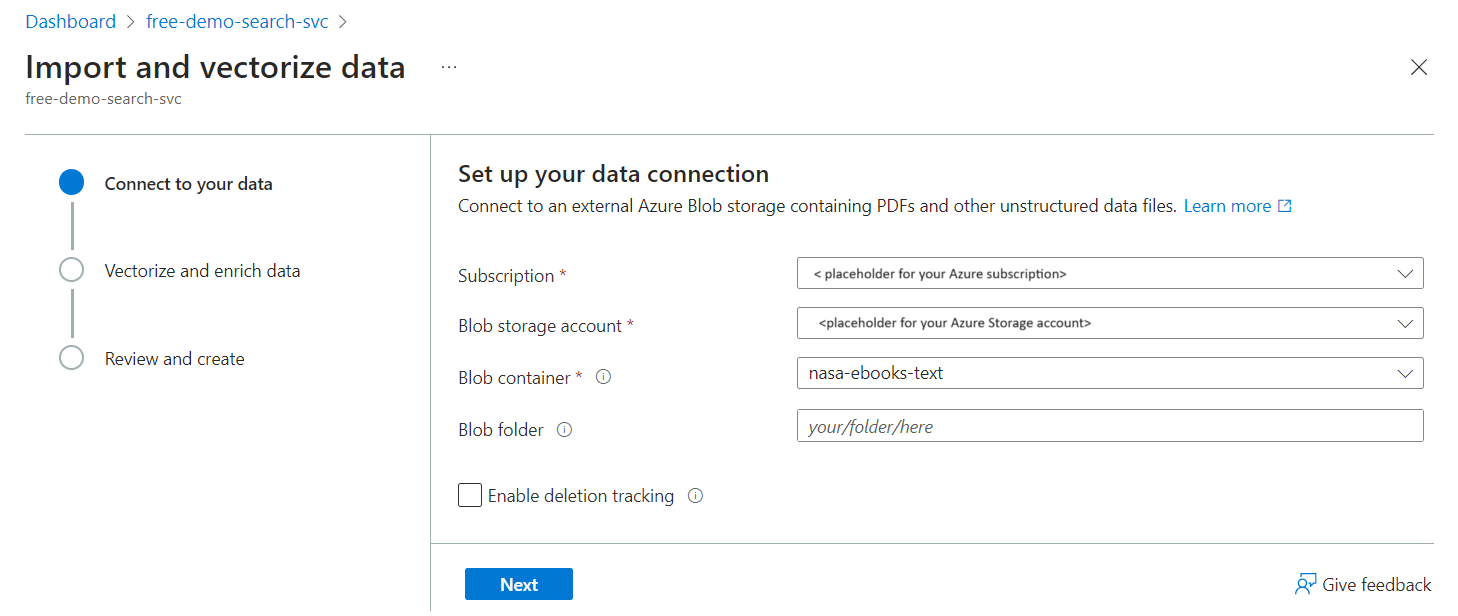
Upload sample data files to a container on Azure Storage. We used some small text files from NASA's earth book to test these instructions on a free search service.
Run the Import and vectorize data wizard, choosing the blob container for the data source.
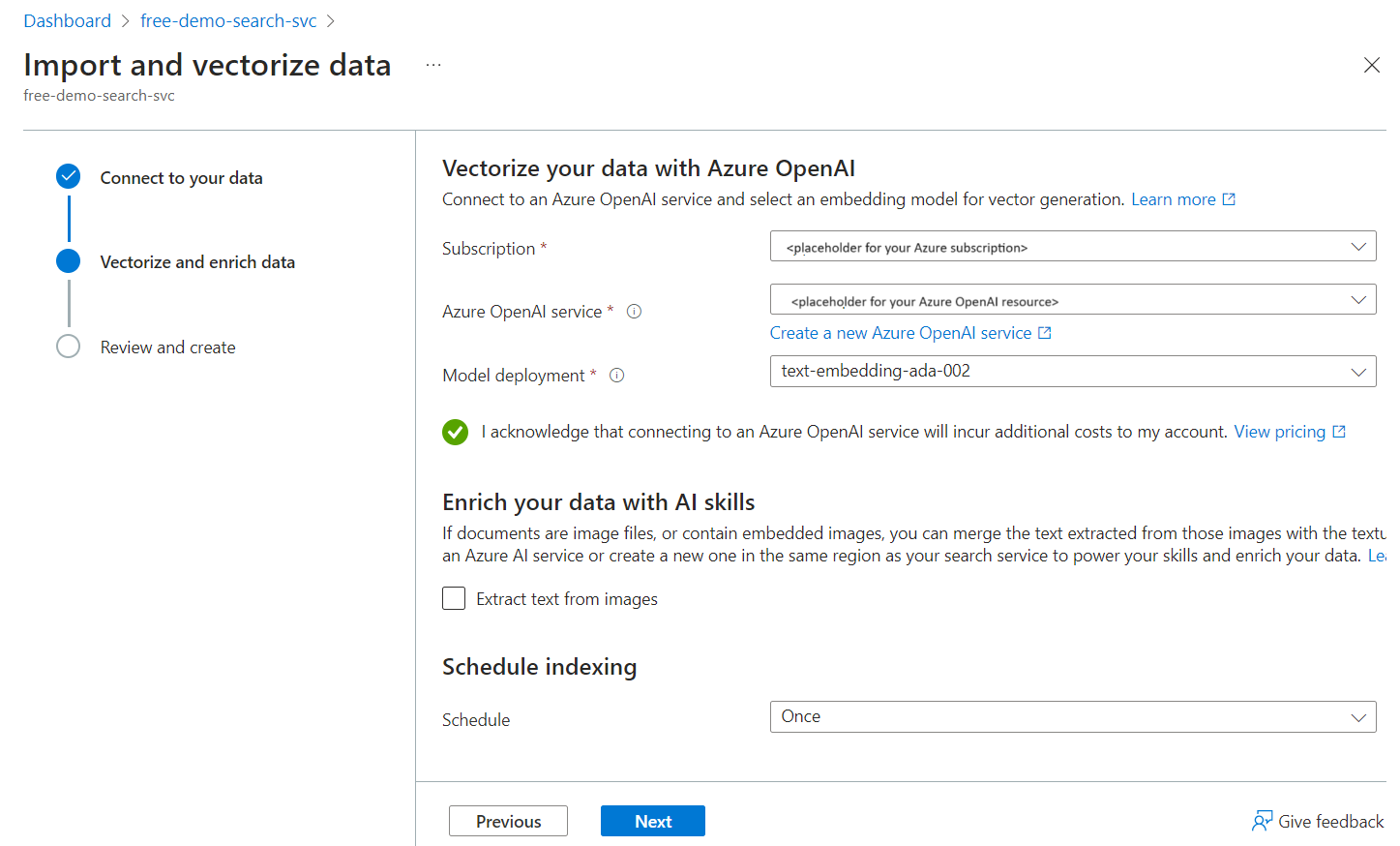
Choose an existing deployment of text-embedding-ada-002. This model generates embeddings during indexing and is also used to configure the vectorizer used during queries.
After the wizard is finished and all indexer processing is complete, you should have an index with a searchable vector field. The field's JSON definition looks like this:
{ "name": "vector", "type": "Collection(Edm.Single)", "searchable": true, "retrievable": true, "dimensions": 1536, "vectorSearchProfile": "vector-nasa-ebook-text-profile" }You should also have a vector profile and a vectorizer, similar to the following example:
"profiles": [ { "name": "vector-nasa-ebook-text-profile", "algorithm": "vector-nasa-ebook-text-algorithm", "vectorizer": "vector-nasa-ebook-text-vectorizer" } ], "vectorizers": [ { "name": "vector-nasa-ebook-text-vectorizer", "kind": "azureOpenAI", "azureOpenAIParameters": { "resourceUri": "https://my-fake-azure-openai-resource.openai.azure.com", "deploymentId": "text-embedding-ada-002", "modelName": "text-embedding-ada-002", "apiKey": "0000000000000000000000000000000000000", "authIdentity": null }, "customWebApiParameters": null } ]Skip ahead to test your vectorizer for text-to-vector conversion during query execution.
Define a vectorizer and vector profile
This section explains the modifications to an index schema for defining a vectorizer manually.
Use Create or Update Index to add
vectorizersto a search index.Add the following JSON to your index definition. The vectorizers section provides connection information to a deployed embedding model. This step shows two vectorizer examples so that you can compare an Azure OpenAI embedding model and a custom web API side by side.
"vectorizers": [ { "name": "my_azure_open_ai_vectorizer", "kind": "azureOpenAI", "azureOpenAIParameters": { "resourceUri": "https://url.openai.azure.com", "deploymentId": "text-embedding-ada-002", "modelName": "text-embedding-ada-002", "apiKey": "mytopsecretkey" } }, { "name": "my_custom_vectorizer", "kind": "customWebApi", "customVectorizerParameters": { "uri": "https://my-endpoint", "authResourceId": " ", "authIdentity": " " } } ]In the same index, add a vector profiles section that specifies one of your vectorizers. Vector profiles also require a vector search algorithm used to create navigation structures.
"profiles": [ { "name": "my_vector_profile", "algorithm": "my_hnsw_algorithm", "vectorizer":"my_azure_open_ai_vectorizer" } ]Assign a vector profile to a vector field. The following example shows a fields collection with the required key field, a title string field, and two vector fields with a vector profile assignment.
"fields": [ { "name": "ID", "type": "Edm.String", "key": true, "sortable": true, "analyzer": "keyword" }, { "name": "title", "type": "Edm.String" }, { "name": "vector", "type": "Collection(Edm.Single)", "dimensions": 1536, "vectorSearchProfile": "my_vector_profile", "searchable": true, "retrievable": true }, { "name": "my-second-vector", "type": "Collection(Edm.Single)", "dimensions": 1024, "vectorSearchProfile": "my_vector_profile", "searchable": true, "retrievable": true } ]
Test a vectorizer
Use a search client to send a query through a vectorizer. This example assumes Visual Studio Code with a REST client and a sample index.
In Visual Studio Code, provide a search endpoint and search query API key:
@baseUrl: @queryApiKey: 00000000000000000000000Paste in a vector query request.
### Run a query POST {{baseUrl}}/indexes/vector-nasa-ebook-txt/docs/search?api-version=2024-07-01 HTTP/1.1 Content-Type: application/json api-key: {{queryApiKey}} { "count": true, "select": "title,chunk", "vectorQueries": [ { "kind": "text", "text": "what cloud formations exists in the troposphere", "fields": "vector", "k": 3, "exhaustive": true } ] }Key points about the query include:
"kind": "text"tells the search engine that the input is a text string, and to use the vectorizer associated with the search field."text": "what cloud formations exists in the troposphere"is the text string to vectorize."fields": "vector"is the name of the field to query over. If you use the sample index produced by the wizard, the generated vector field is namedvector.
Send the request. You should get three
kresults, where the first result is the most relevant.
Notice that there are no vectorizer properties to set at query time. The query reads the vectorizer properties, as per the vector profile field assignment in the index.
Check logs
If you enabled diagnostic logging for your search service, run a Kusto query to confirm query execution on your vector field:
OperationEvent
| where TIMESTAMP > ago(30m)
| where Name == "Query.Search" and AdditionalInfo["QueryMetadata"]["Vectors"] has "TextLength"
Best practices
If you're setting up an Azure OpenAI vectorizer, consider the same best practices that we recommend for the Azure OpenAI embedding skill.