Manage firewall rules for Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server using the Azure portal
This article provides an overview of managing firewall rules after creating an Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance. With Public access (allowed IP addresses), the connections to the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance are restricted to allowed IP addresses only. The client IP addresses need to be allowed in firewall rules.
This article focuses on creating an Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance with Public access (allowed IP addresses) using the Azure portal.
To learn more about it, refer to Public access (allowed IP addresses). The firewall rules can be defined at the time of server creation (recommended) but can be added later.
Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server supports two mutually exclusive network connectivity methods to connect to your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance. The two options are:
- Public access (allowed IP addresses)
- Private access (VNet Integration)
Create a firewall rule when creating a server
Select Create a resource (+) in the upper-left corner of the portal.
Select Databases > Azure Database for MySQL. You can also enter MySQL in the search box to find the service.
Select Flexible server as the deployment option.
Fill out the Basics form.
Go to the Networking tab to configure how you want to connect to your server.
In the Connectivity method, select Public access (allowed IP addresses). To create the Firewall rules, specify the Firewall rule name and a single IP address or a range of addresses. If you want to limit the rule to a single IP address, type the same address in the field for the Start IP address and End IP address. Opening the firewall enables administrators, users, and applications to access any database on the MySQL server to which they have valid credentials.
Note
Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server creates a firewall at the server level. It prevents external applications and tools from connecting to the server and any databases on the server unless you create a rule to open the firewall for specific IP addresses.
Select Review + create to review your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server configuration.
Select Create to provision the server. Provisioning can take a few minutes.
Create a firewall rule after the server is created
In the Azure portal, select the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance on which you want to add firewall rules.
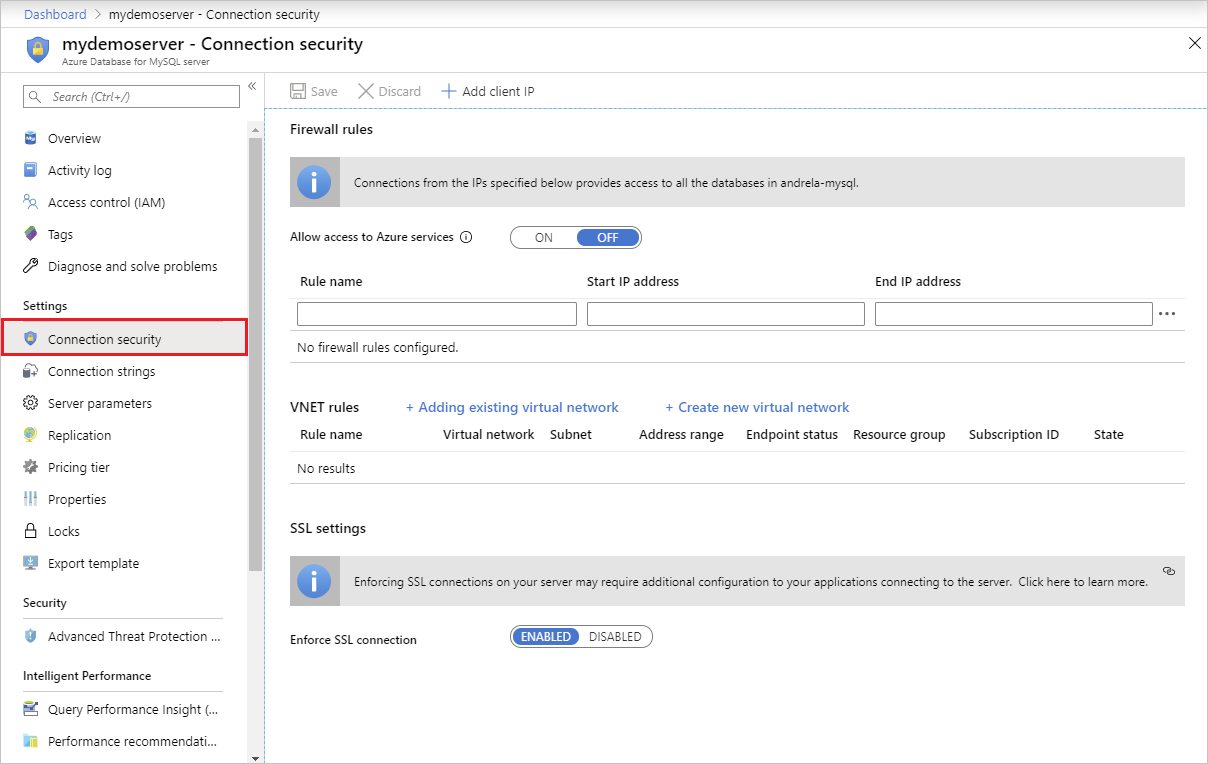
On the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server page, under Settings heading, select Networking to open the Networking page for the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance.
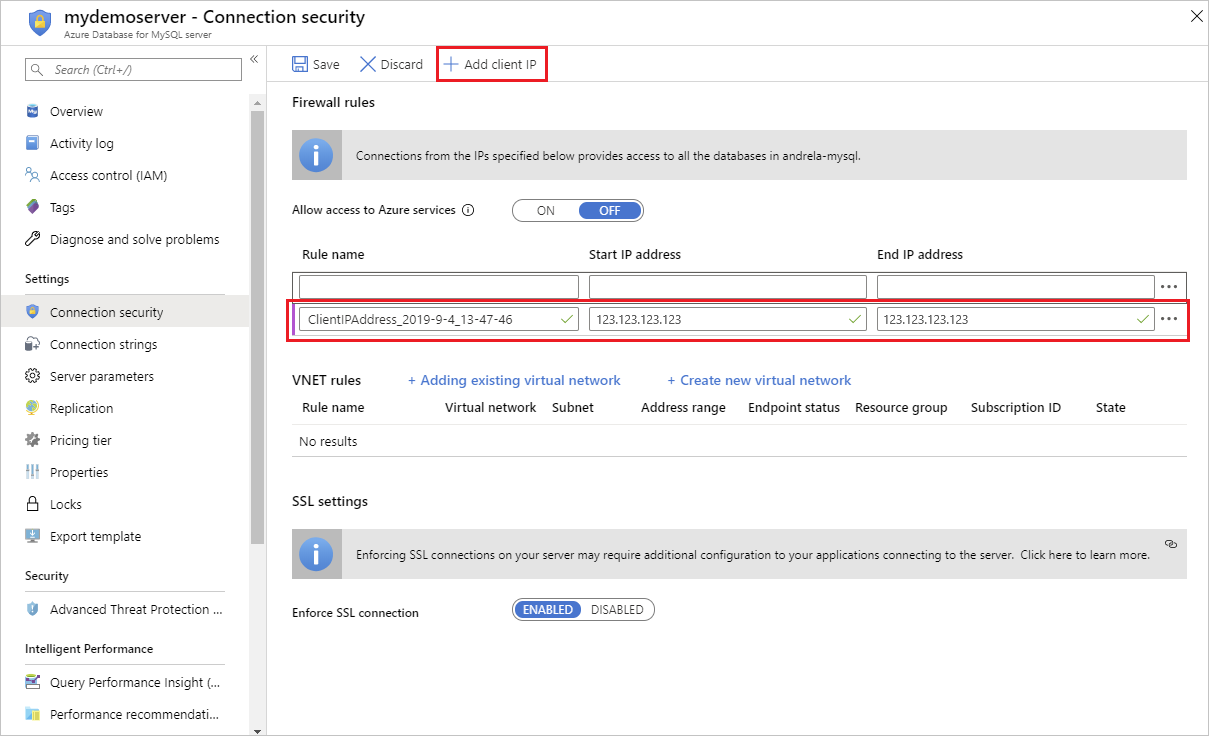
Select Add current client IP address in the firewall rules. This automatically creates a firewall rule with the public IP address of your computer, as perceived by the Azure system.
Verify your IP address before saving the configuration. In some situations, the IP address observed by the Azure portal differs from the IP address used when accessing the internet and Azure servers. Therefore, you might need to change the Start and End IP addresses to make the rule function as expected.
You can use a search engine or other online tool to check your own IP address. For example, search for "what is my IP."
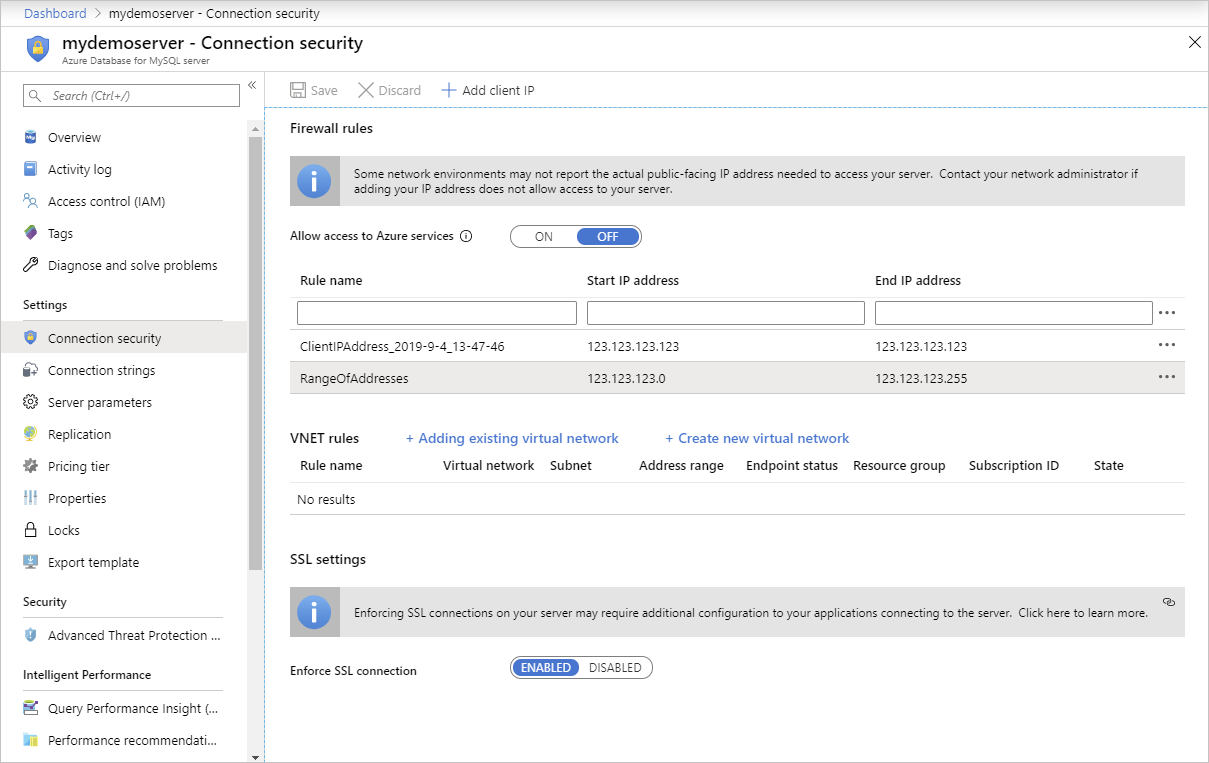
Add more address ranges. In the firewall rules for the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance, you can specify a single IP address or a range of addresses. If you want to limit the rule to a single IP address, type the same address in the field for the Start IP address and End IP address. Opening the firewall enables administrators, users, and applications to access any database on the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance to which they have valid credentials.
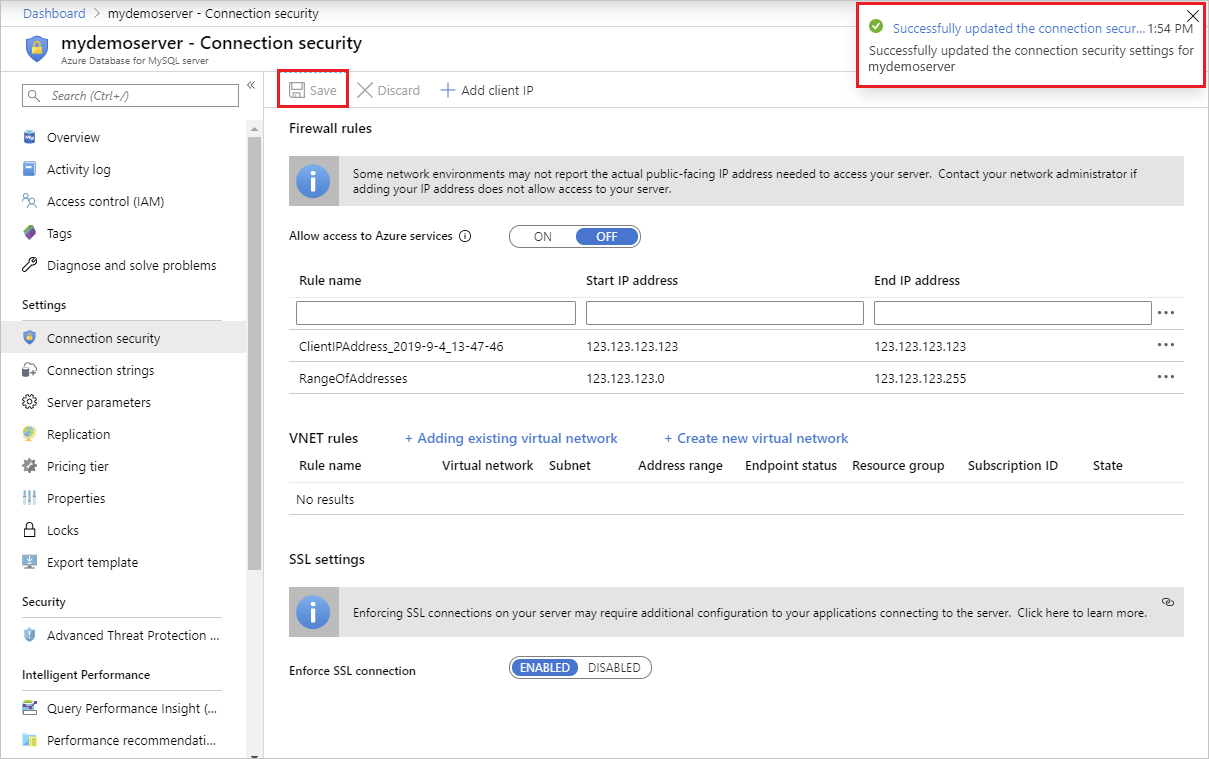
Select Save on the toolbar to save this firewall rule. Wait for the confirmation that the update to the firewall rules was successful.
Connect from Azure
You can enable resources or applications deployed in Azure to connect to your Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance. This includes web applications hosted in Azure App Service, running on an Azure VM, an Azure Data Factory data management gateway, and many more.
When an application within Azure attempts to connect to your server, the firewall verifies that Azure connections are allowed. You can enable this setting by selecting the Allow public access from Azure services and resources within Azure to this server option in the portal from the Networking tab and selecting Save.
The resources can be in a different virtual network (VNet) or resource group for the firewall rule to enable those connections. The request doesn't reach the Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server instance if the connection attempt isn't allowed.
Important
This option configures the firewall to allow all connections from Azure, including connections from the subscriptions of other customers. When selecting this option, make sure your login and user permissions limit access to only authorized users.
We recommend choosing the Private access (VNet Integration) to securely access Azure Database for MySQL Flexible Server.
Manage existing firewall rules through the Azure portal
Repeat the following steps to manage the firewall rules.
- To add the current computer, select + Add current client IP address in the firewall rules. Select Save to save the changes.
- To add more IP addresses, type in the Rule Name, Start IP Address and End IP Address. Select Save to save the changes.
- To modify an existing rule, select any fields in the rule and modify. Select Save to save the changes.
- To delete an existing rule, select the ellipsis [...] and select Delete to remove the rule. Select Save to save the changes.