Use an Azure free account to try Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server for free
Azure Database for MySQL flexible server is a managed service that you use to run, manage, and scale highly available MySQL databases in the cloud. With an Azure free account, you can use Azure Database for MySQL flexible server for free for 12 months with monthly limits of up to:
- 750 hours of Burstable B1MS instance, enough hours to run a database instance continuously each month.
- 32 GB storage and 32 GB backup storage.
This article shows you how to create and use an Azure Database for MySQL flexible server instance for free using an Azure free account.
Prerequisites
To complete this tutorial, you need:
- An Azure free account. If you don't have one, create a free account before you begin.
Create an Azure Database for MySQL flexible server instance
In this article, you'll use the Azure portal to create an Azure Database for MySQL flexible server instance with public access connectivity method. Alternatively, refer to the respective quickstarts to create an Azure Database for MySQL flexible server instance using Quickstart: Create an instance of Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server by using the Azure CLI, Quickstart: Create an instance of Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server by using Azure Resource Manager, Quickstart: Create an instance of Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server by using Terraform, or within a VNET.
Sign in to the Azure portal with your Azure free account.
The default view is your service dashboard.
To create an Azure Database for MySQL flexible server instance, search for and select Azure Database for MySQL servers:
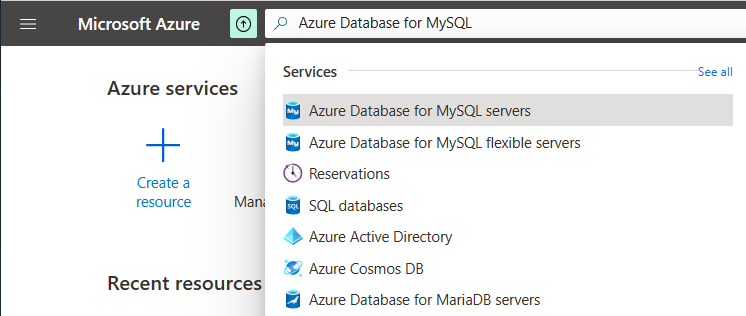
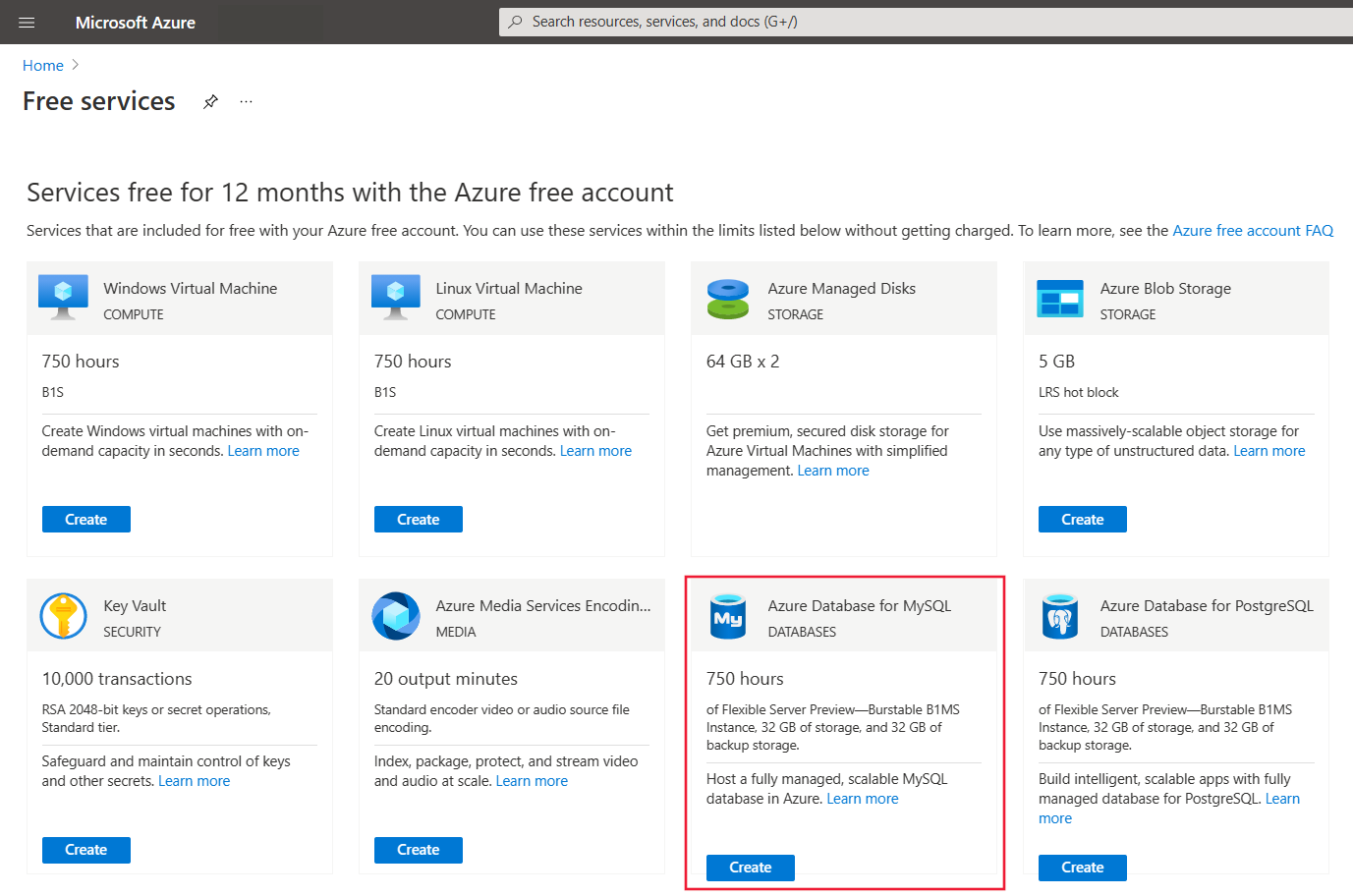
Alternatively, you can search for and navigate to Free Services, and then select the Azure Database for MySQL tile from the list:
Select Create.
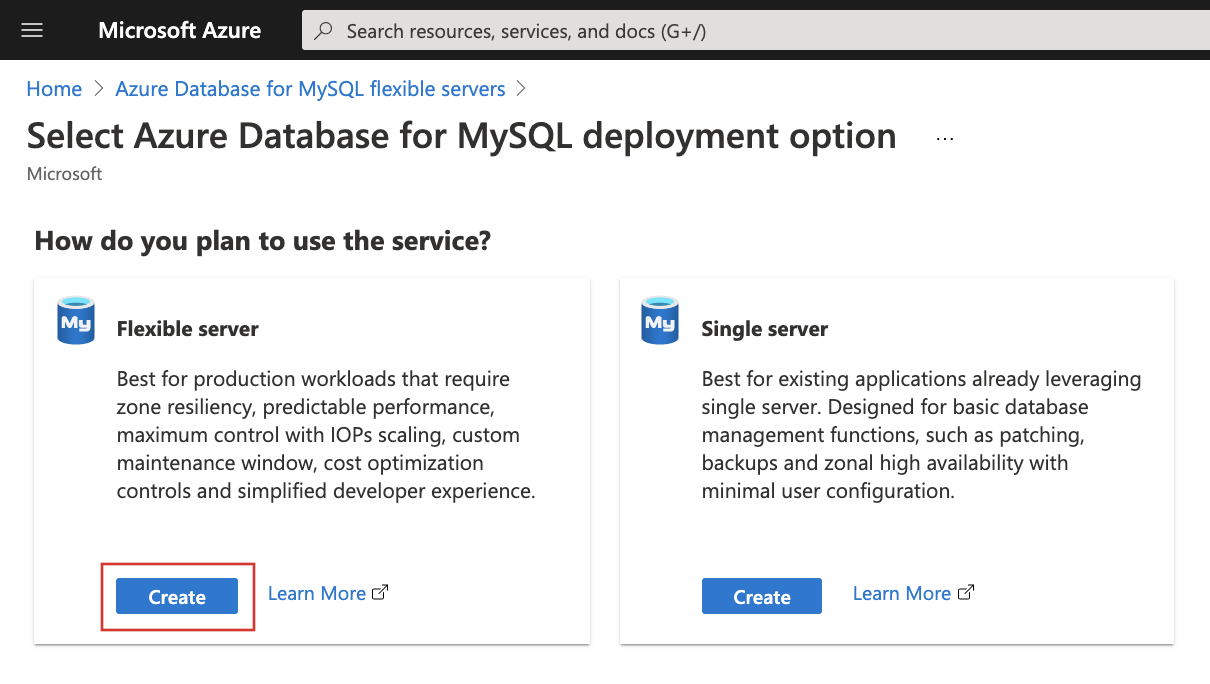
On the Select Azure Database for MySQL deployment option page, select Flexible server.
Enter the basic settings for a new Flexible server.
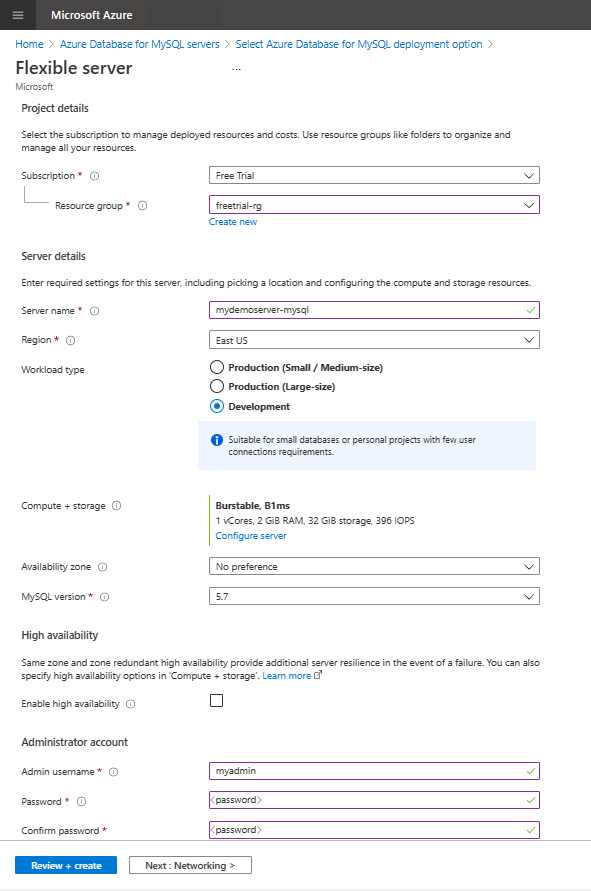
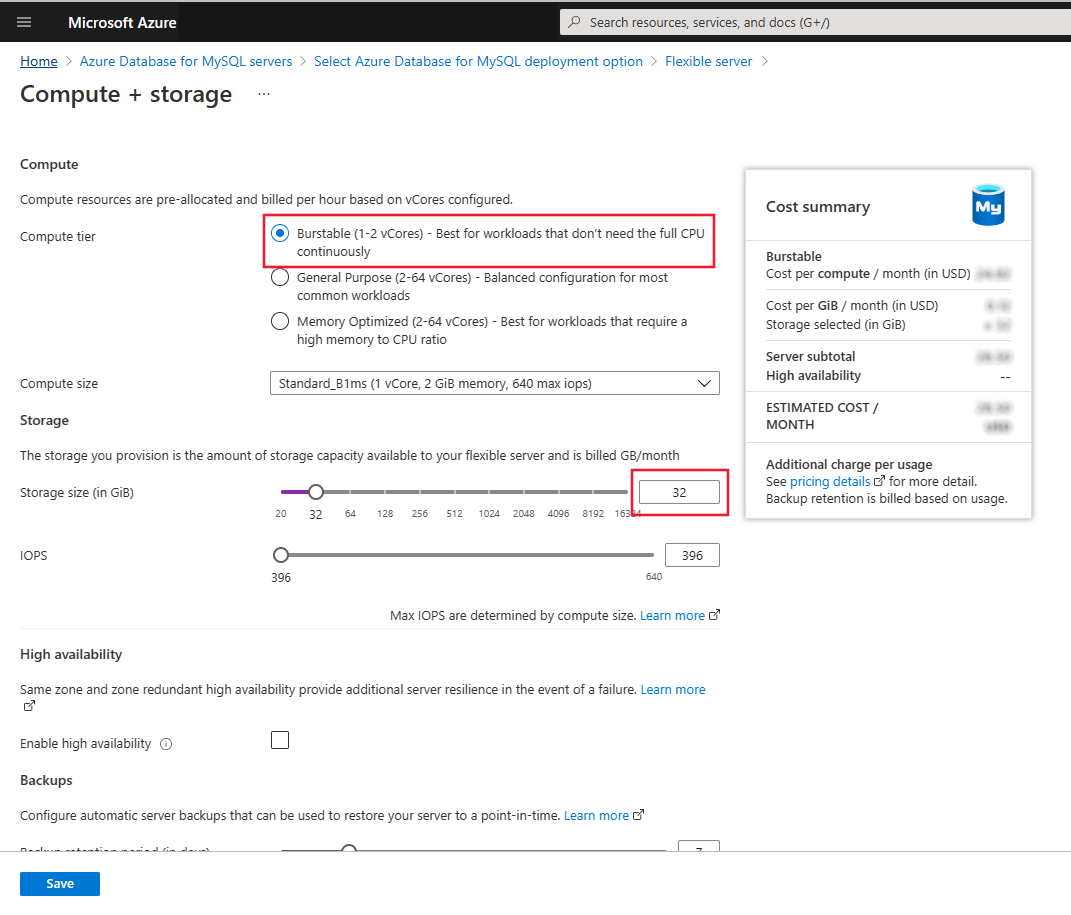
Setting Suggested value Description Subscription Your subscription Select the Free Trial Azure subscription. Resource group Your resource group Enter a new resource group or an existing one from your subscription. Server name mydemoserver-mysql Specify a unique name to identify your flexible server. The domain name mysql.database.azure.com is appended to the server name you provide. The server name can contain only lowercase letters, numbers, and the hyphen (-) character. It must contain between 3 and 63 characters. Region The region closest to your users Select a location from the list, preferably the location that's closest to your users. Workload type Development For a free trial, select Development workload. For a production workload, choose Small/Medium-size or Large-size depending on max_connections requirements. Availability zone No preference If your application (hosted on Azure VMs, virtual machine scale sets or AKS instance) is provisioned in a specific availability zone, create your an Azure Database for MySQL flexible server instance in the same availability zone. Collocating the application and database improves performance by reducing network latency across zones. High Availability Default Leave the High Availability option unchecked. MySQL version The latest major version Use the latest major version. For more information, see all supported versions. Admin username myadmin Create a sign-in account to use when you connect to the server. The admin username can't be azure_superuser, admin, administrator, root, guest, or public. Password Your password Specify a new password for the server admin account. The password must contain between 8 and 128 characters. It must also contain characters from three of the following four categories: English uppercase letters, English lowercase letters, numbers (0 through 9), and non-alphanumeric characters (!, $, #, %, and so on). For Compute + Storage setting, select Configure Server.
Select Burstable B1MS Instance (1-2 vCores), specify storage less than or equal to 32 GB and keep the default settings for the remaining options.
Select Save to continue with the configuration.
Select Networking tab to configure how to reach your server.
Azure Database for MySQL flexible server provides two ways to connect:
- Public access (allowed IP addresses)
- Private access (VNet Integration)
With public access, access to your server is limited to allowed IP addresses that you include in a firewall rule. This method prevents external applications and tools from connecting to the server and any databases on the server, unless you create a rule to open the firewall for a specific IP address or range.
With private access (VNet Integration), access to your server is limited to your virtual network. For more information about connectivity methods, see Connectivity and networking concepts for Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server
For the purposes of this tutorial, enable public access to connect to the server.
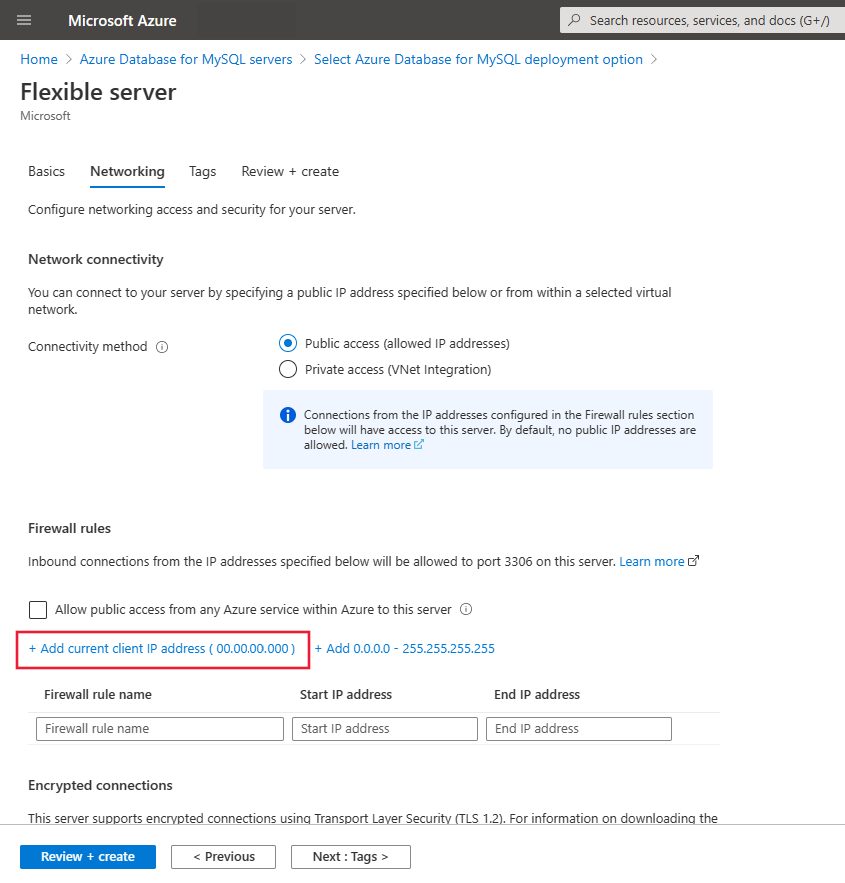
On the Networking tab, for Connectivity method select Public access.
For configuring Firewall rules, select Add current client IP address.
Note
You can't change the connectivity method after you create the server. For example, if you select Public access (allowed IP addresses) during server creation, you can't change to Private access (VNet Integration) after the server is created. We highly recommend that you create your server with private access to help secure access to your server via VNet Integration. For more information about private access, see Connectivity and networking concepts for Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server
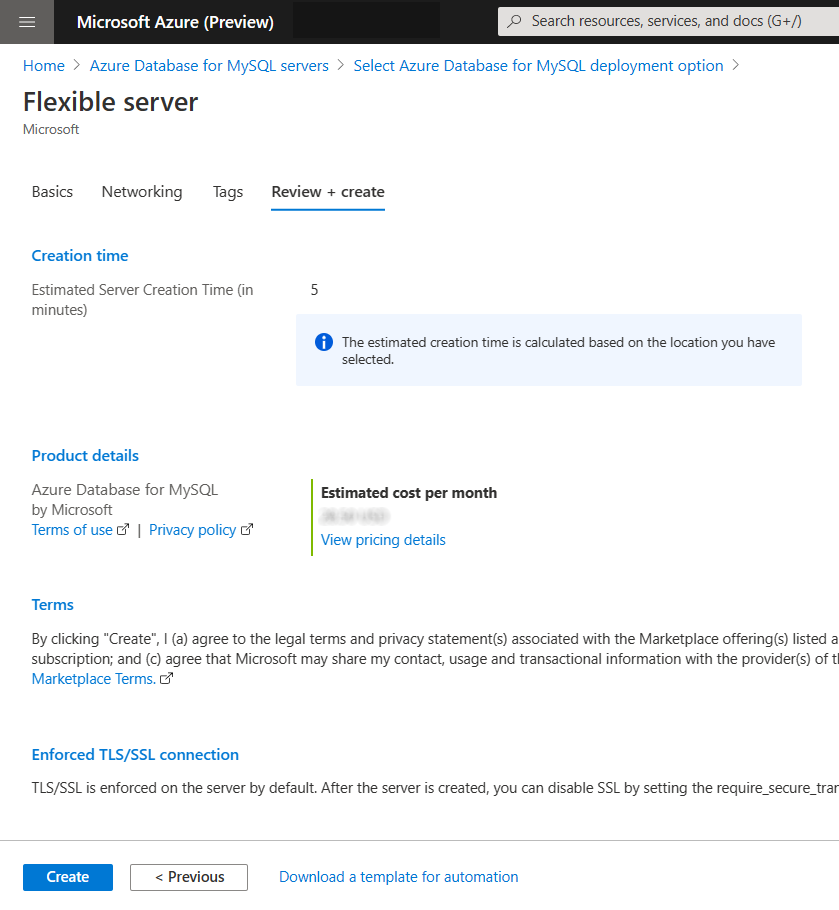
To review your an Azure Database for MySQL flexible server configuration, select Review + create.
Important
While creating the an Azure Database for MySQL flexible server instance from your Azure free account, you still see an Estimated cost per month in the Compute + Storage : Cost Summary blade and Review + Create tab. But, as long as you're using your Azure free account, and your free service usage is within monthly limits, you won't be charged for the service. To view usage information, see the following Monitor and track free services usage section. We're currently working to improve the Cost Summary experience for free services.
Select Create to provision the server.
Provisioning can take a few minutes
On the toolbar, select Notifications (the bell icon) to monitor the deployment process.
After the deployment is complete, select Pin to dashboard, to create a tile for the Azure Database for MySQL flexible server instance on your Azure portal dashboard. This tile is a shortcut to the server's Overview page. When you select Go to resource, the server's Overview page opens.
By default, your server included these databases: information_schema, mysql, performance_schema, and sys.
Connect and query
Now that you've now created an Azure Database for MySQL flexible server instance in a resource group, you can connect to the server and query databases by using the following Connect and query quickstarts:
- mysql.exe
- Use MySQL Workbench with Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server
- Quickstart: Connect with Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server by using Azure CLI
- Use PHP with Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server
- Use Java and JDBC with Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server
- Quickstart: Use Python to connect and query data in Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server
- Quickstart: Use .NET (C#) to connect and query data in Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server
Monitor and track free services usage
You're not charged for Azure Database for MySQL flexible server services included for free with your Azure free account unless you exceed the free service limits. To remain within the limits, use the Azure portal to track and monitor your free services usage.
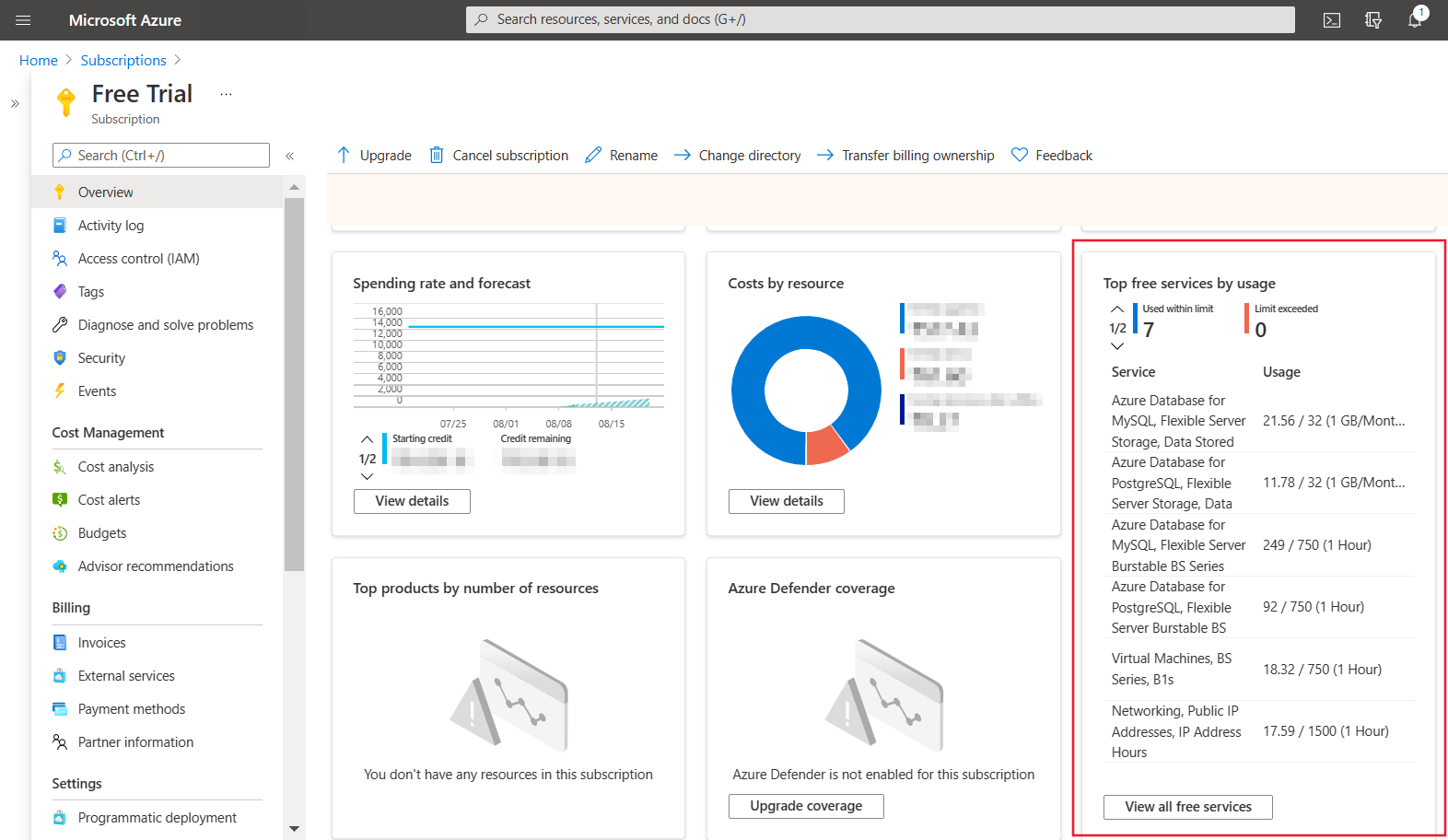
In the Azure portal, search for Subscriptions and select the Azure Free Account - Free Trial subscription.
On the Overview page, scroll down to show the tile Top free services by usage, and then select View all free services.
Locate the meters related to Azure Database for MySQL – Flexible Server to track usage.
Meter Description Monthly Limit Azure Database for MySQL flexible server Burstable BS Series Compute, B1MS Tracks Compute usage in terms of number of hours of running 750 Hours per month - Burstable B1MS Compute Tier Azure Database for MySQL flexible server Storage, Data Stored Tracks Data Storage Provisioned in terms of GiB used per month 32 GB per month - Meter: Identifies the unit of measure for the service being consumed. - Usage/Limit: Current month's usage and limit for the meter. - Status: Usage status of the service. Based on your usage, you can have one of the following statutes: - Not in use: You haven't used the meter or the usage for the meter hasn't reached the billing system.
- Exceeded on <Date>: You've exceeded the limit for the meter on <Date>.
- Unlikely to Exceed: You're unlikely to exceed the limit for the meter.
- Exceeds on <Date>: You're likely to exceed the limit for the meter on <Date>.
Important
With an Azure free account, you also get $200 in credit to use in 30 days. During this time, any usage beyond the free monthly amounts of services will be deducted from this credit. At the end of your first 30 days or after you spend your $200 credit (whichever comes first), you'll only pay for what you use beyond the free monthly amounts of services. To keep getting free services after 30 days, move to pay-as-you-go pricing. If you don't move to pay as you go, you can't purchase Azure services beyond your $200 credit—and eventually your account and services will be disabled. For more information, see Azure free account FAQ.
Clean up resources
If you are using the Azure Database for MySQL flexible server instance for development, testing or predictable time-bound production workloads, optimize usage by starting and stopping the server on-demand. After you stop the server, it remains in that state for seven days unless restarted sooner.
For more information, see Server concepts in Azure Database for MySQL - Flexible Server.
When your Azure Database for MySQL flexible server instance is stopped, there is no Compute usage, but Storage usage is still considered.
Alternatively, if you don't expect to need these resources in the future, you can delete them by deleting the resource group, or you can just delete the Azure Database for MySQL flexible server instance.
To delete the resource group, complete the following steps:
- In the Azure portal, search for and select Resource groups.
- In the list of resource groups, select the name of your resource group.
- On the Overview page for your resource group, select Delete resource group.
- In the confirmation dialog box, type the name of your resource group, and then select Delete.
To delete the Azure Database for MySQL flexible server instance, on the Overview page for the server, select Delete.