Use secrets and environment variables in Azure Load Testing
In this article, you learn how to pass secrets and environments as parameters to a load test in Azure Load Testing. You can use parameters to change the behavior of a load test without having to edit the Apache JMeter script. For example, to test a web application, specify the endpoint URL as a parameter to reuse your test script across multiple environments. You can also use parameters to avoid that you have to hard code sensitive information in the JMeter test script.
The Azure Load Testing service supports two types of parameters:
Secrets: Contain sensitive information and are passed securely to the load test engine. For example, secrets provide web service credentials instead of hard-coding them in the test script. For more information, see Configure load tests with secrets.
Environment variables: Contain non-sensitive information and are available as environment variables in the load test engine. For example, environment variables make the application endpoint URL configurable. For more information, see Configure load tests with environment variables.
You can specify parameters in the load test configuration when you create a new test or update an existing test. If you run a load test in your CI/CD workflow, you define parameters in the load test configuration file or in the CI/CD workflow definition.
Prerequisites
An Azure account with an active subscription. If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
An Azure load testing resource. If you need to create an Azure Load Testing resource, see the quickstart Create and run a load test.
Configure load tests with secrets
In this section, you learn how to pass secrets to your load test script in Azure Load Testing. For example, you might use a secret to pass the API key to a web service endpoint that you're load testing. Instead of storing the API key in configuration or hard-coding it in the script, you can save it in a secret store to tightly control access to the secret.
Azure Load Testing enables you to store secrets in Azure Key Vault. Alternatively, when you run your load test in a CI/CD pipeline, you can also use the secret store that's associated with your CI/CD technology, such as Azure Pipelines or GitHub Actions.
To use secrets with Azure Load Testing, you perform the following steps:
- Store the secret value in the secret store (Azure Key Vault or the CI/CD secret store).
- Pass a reference to the secret into the Apache JMeter test script.
- Use the secret value in the Apache JMeter test script by using the
GetSecretcustom function.
Important
You can only use the GetSecret custom function when you run your JMeter test script with Azure Load Testing. If you run your test script locally, you need to update your test script and read secret values in a different way.
Use Azure Key Vault to store load test secrets
You can use Azure Key Vault to pass secret values to your test script in Azure Load Testing. You add a reference to the secret in the Azure Load Testing configuration. Azure Load Testing then uses this reference to retrieve the secret value in the Apache JMeter script.
You also need to grant Azure Load Testing access to your Azure key vault to retrieve the secret value.
Note
If you run a load test as part of your CI/CD process, you might also use the related secret store. Skip to Use the CI/CD secret store.
Create a secret in Azure Key Vault
Add the secret value to your key vault, if you haven't already done so.
Important
If you restricted access to your Azure key vault by a firewall or virtual networking, follow these steps to grant access to trusted Azure services.
Retrieve the key vault secret identifier for your secret. You use this secret identifier to configure your load test.
The secret identifier is the full URI of the secret in the Azure key vault. Optionally, you can also include a version number. For example,
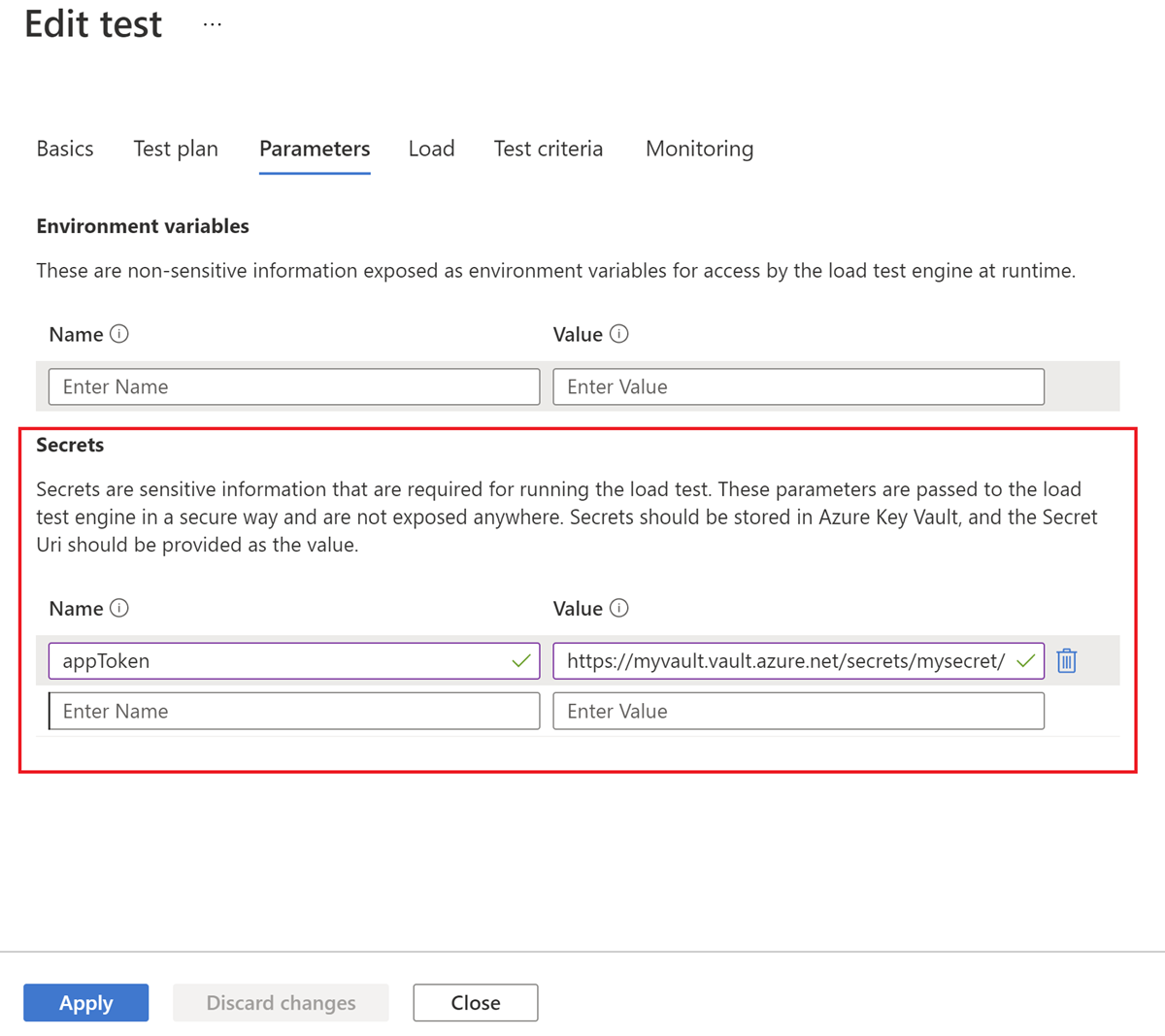
https://myvault.vault.azure.net/secrets/mysecret/orhttps://myvault.vault.azure.net/secrets/mysecret/abcdef01-2345-6789-0abc-def012345678.
Add the secret to your load test
Reference the secret in the load test configuration.
You define a load test secret parameter for each secret that you reference in the Apache JMeter script. The parameter name should match the secret name that you use in the Apache JMeter test script. The parameter value is the key vault security identifier.
You can specify secret parameters by doing either of the following:
In the Azure portal, select your load test, select Configure, select the Parameters tab, and then enter the parameter details.
If you're configuring a CI/CD workflow and use Azure Key Vault, you can specify a secret in the YAML configuration file by using the
secretsproperty. For more information about the syntax, see the Test configuration YAML reference.
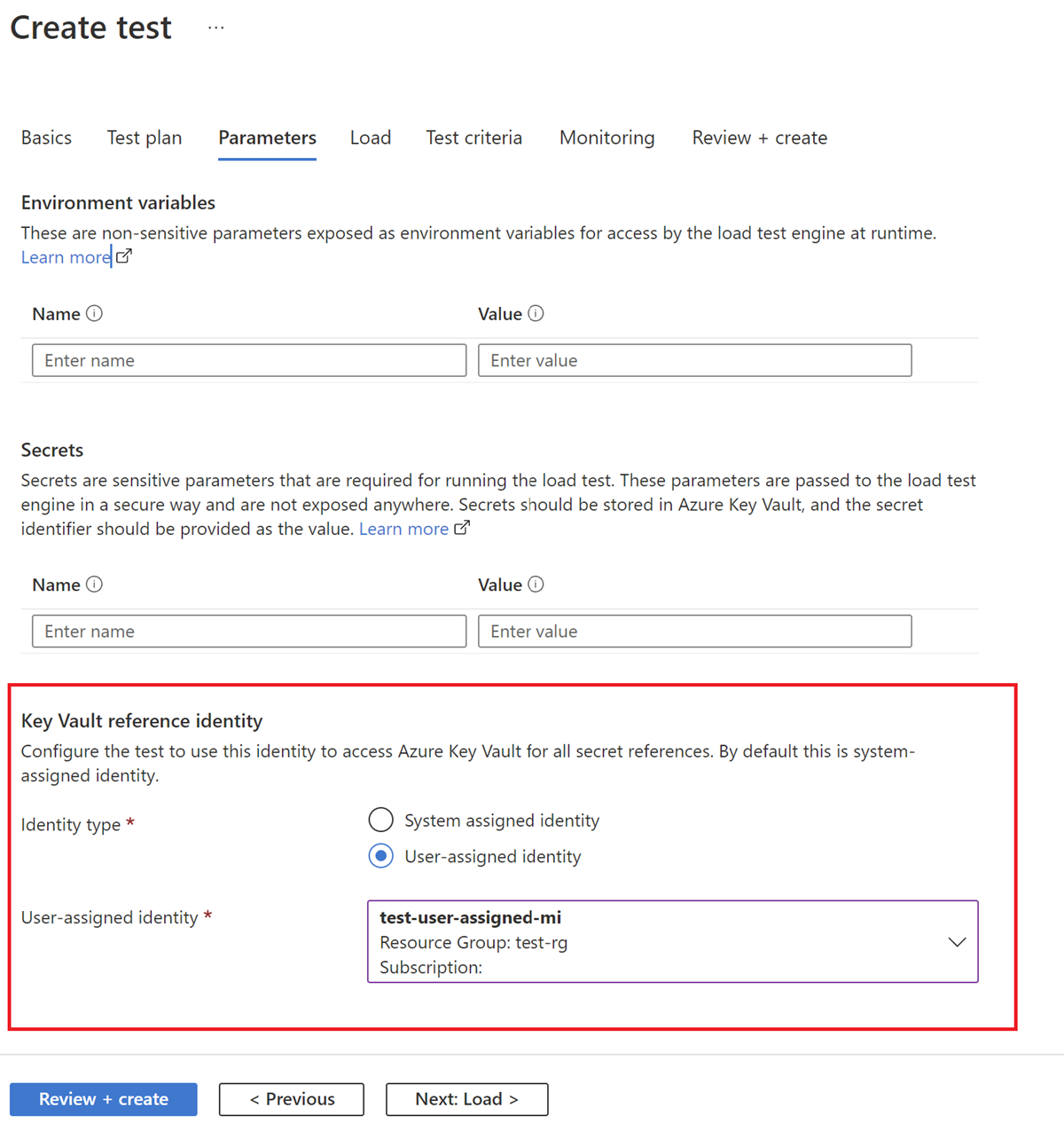
Specify the identity that Azure Load Testing uses to access your secrets in Azure Key Vault.
The identity can be the system-assigned identity of the load testing resource, or one of the user-assigned identities. Make sure you use the same identity you've granted access previously.
You can specify the key vault reference identity by doing either of the following:
In the Azure portal, select your load test, select Configure, select the Parameters tab, and then configure the Key Vault reference identity.
If you're configuring a CI/CD workflow and use Azure Key Vault, you can specify the reference identity in the YAML configuration file by using the
keyVaultReferenceIdentityproperty. For more information about the syntax, see the Test configuration YAML reference.
Grant access to your Azure key vault
When you store load test secrets or certificates in Azure Key Vault, your load testing resource uses a managed identity for accessing the key vault. After you configure the manage identity, you need to grant the managed identity of your load testing resource permissions to read these values from the key vault.
To grant your Azure load testing resource permissions to read secrets or certificates from your Azure key vault:
In the Azure portal, go to your Azure key vault resource.
If you don't have a key vault, follow the instructions in Azure Key Vault quickstart to create one.
On the left pane, select Access Policies, and then select + Create.
On the Permissions tab, under Secret permissions, select Get, and then select Next.
Note
Azure Load Testing retrieves certificates as a secret to ensure that the private key for the certificate is available.
On the Principal tab, search for and select the managed identity for the load testing resource, and then select Next.
If you're using a system-assigned managed identity, the managed identity name matches that of your Azure load testing resource.
Select Next again.
When your test runs, the managed identity that's associated with your load testing resource can now read the secrets or certificates for your load test from your key vault.
Now that you've added a secret in Azure Key Vault, configured a secret for your load test, you can now move to Use secrets in Apache JMeter.
Use the CI/CD secret store to save load test secrets
If you're using Azure Load Testing in your CI/CD workflow, you can also use the associated secret store. For example, you can use GitHub repository secrets, or secret variables in Azure Pipelines.
Note
If you're already using a key vault, you might also use it to store the load test secrets. Skip to Use Azure Key Vault.
To use secrets in the CI/CD secret store and pass them to your load test in CI/CD:
Add the secret value to the CI/CD secret store, if it doesn't exist yet.
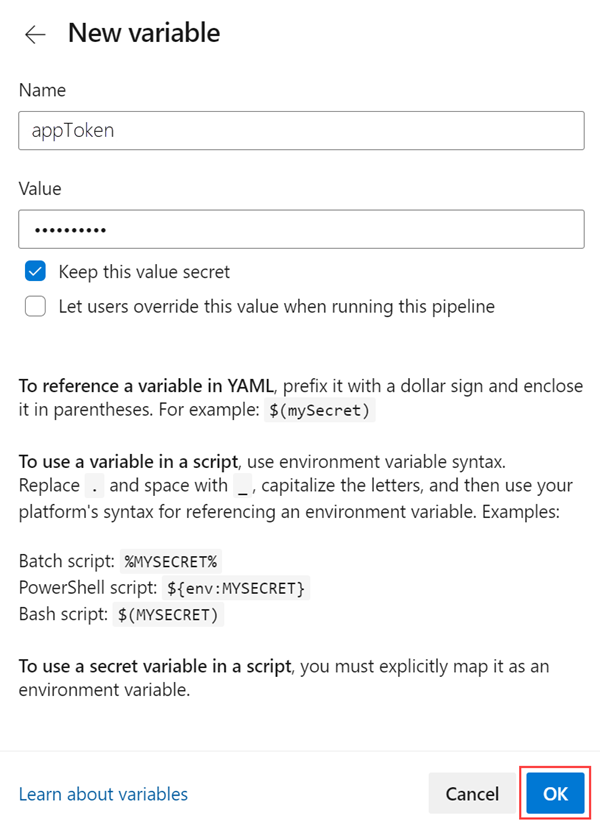
In Azure Pipelines, you can edit the pipeline and add a variable.
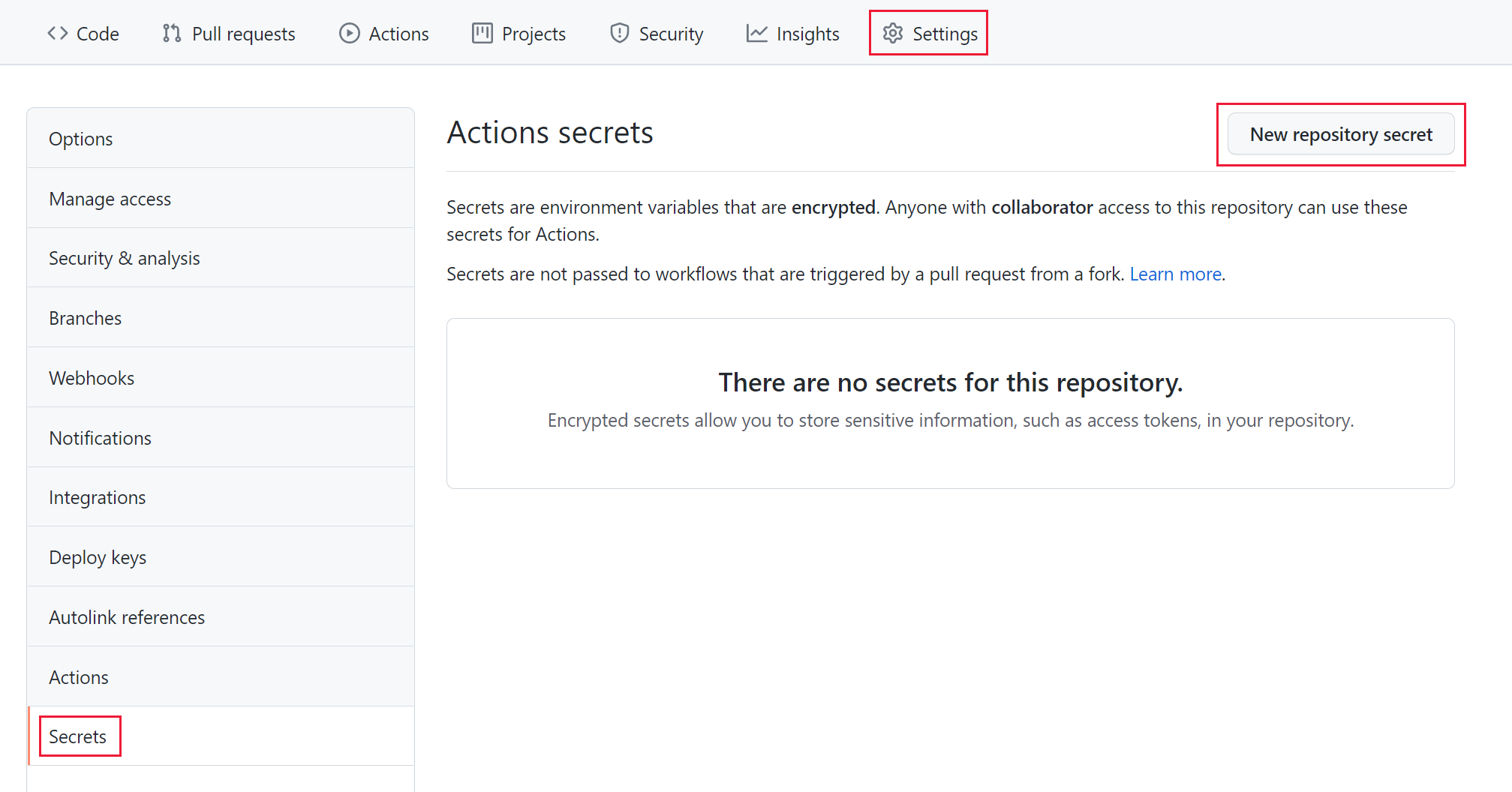
In GitHub, you can use GitHub repository secrets.
Note
Be sure to use the actual secret value and not the key vault secret identifier as the value.
Pass the secret as an input parameter to the Load Testing task/action in the CI/CD workflow.
The following YAML snippet shows how to pass the secret to the Load Testing GitHub action:
- name: 'Azure Load Testing' uses: azure/load-testing@v1 with: loadtestConfigFile: 'SampleApp.yaml' loadtestResource: 'MyTest' resourceGroup: 'loadtests-rg' secrets: | [ { "name": "appToken", "value": "${{ secrets.MY_SECRET }}" } ]The following YAML snippet shows how to pass the secret to the Azure Pipelines task:
- task: AzureLoadTest@1 inputs: azureSubscription: 'MyAzureLoadTestingRG' loadTestConfigFile: 'SampleApp.yaml' loadTestResource: 'MyTest' resourceGroup: 'loadtests-rg' secrets: | [ { "name": "appToken", "value": "$(mySecret)" } ]Important
The name of the secret input parameter needs to match the name that's used in the Apache JMeter script.
You've now specified a secret in the CI/CD secret store and passed a reference to Azure Load Testing. You can now use the secret in the Apache JMeter script.
Use secrets in Apache JMeter
Next, you update the Apache JMeter script to use the secret that you specified earlier.
You first create a user-defined variable that retrieves the secret value. Then, you can use this variable in your test (for example, to pass an API token in an HTTP request header).
Create a user-defined variable in your JMX file, and assign the secret value to it by using the
GetSecretcustom function.The
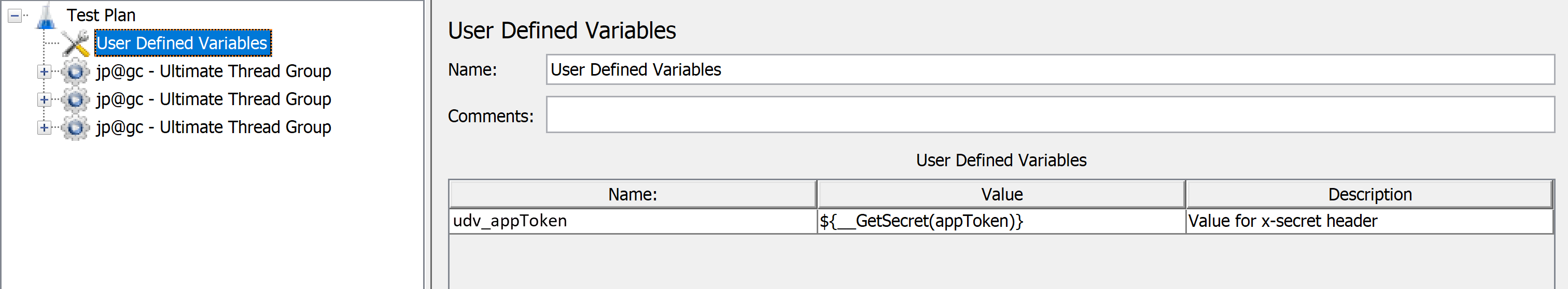
GetSecret(<my-secret-name>)function takes the secret name as an argument. You use this same name when you configure the load test in a later step.You can create the user-defined variable by using the Apache JMeter IDE, as shown in the following image:
Alternatively, you can directly edit the JMX file, as shown in this example code snippet:
<Arguments guiclass="ArgumentsPanel" testclass="Arguments" testname="User Defined Variables" enabled="true"> <collectionProp name="Arguments.arguments"> <elementProp name="appToken" elementType="Argument"> <stringProp name="Argument.name">udv_appToken</stringProp> <stringProp name="Argument.value">${__GetSecret(appToken)}</stringProp> <stringProp name="Argument.desc">Value for x-secret header </stringProp> <stringProp name="Argument.metadata">=</stringProp> </elementProp> </collectionProp> </Arguments>Reference the user-defined variable in the test script.
You can use the
${}syntax to reference the variable in the script. In the following example, you use theudv_appTokenvariable to set an HTTP header.<HeaderManager guiclass="HeaderPanel" testclass="HeaderManager" testname="HTTP Header Manager" enabled="true"> <collectionProp name="HeaderManager.headers"> <elementProp name="" elementType="Header"> <stringProp name="Header.name">api-key</stringProp> <stringProp name="Header.value">${udv_appToken}</stringProp> </elementProp> </collectionProp> </HeaderManager>
Configure load tests with environment variables
In this section, you use environment variables to pass parameters to your load test.
Update the Apache JMeter script to use the environment variable (for example, to configure the application endpoint hostname).
Configure the load test and pass the environment variable to the test script.
Use environment variables in Apache JMeter
In this section, you update the Apache JMeter script to use environment variables to control the script behavior.
You first define a user-defined variable that reads the environment variable, and then you can use this variable in the test execution (for example, to update the HTTP domain).
Create a user-defined variable in your JMX file, and assign the environment variable's value to it by using the
System.getenvfunction.The
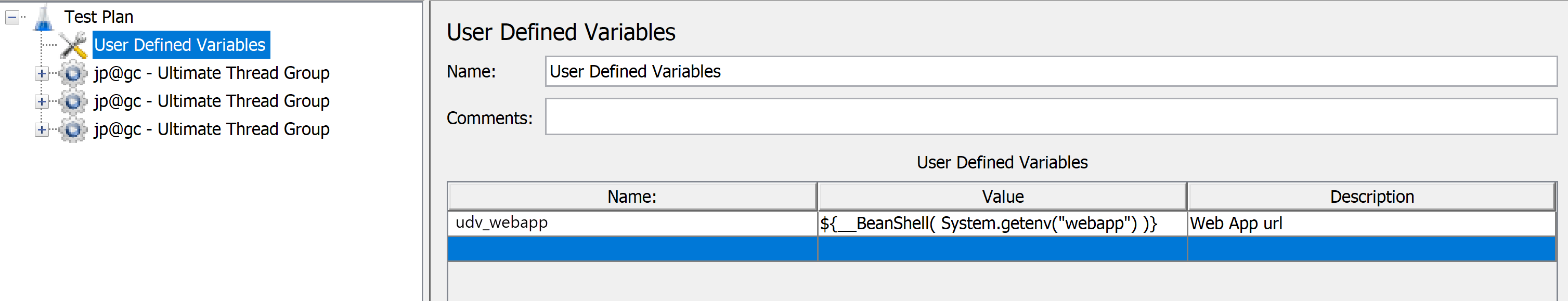
System.getenv("<my-variable-name>")function takes the environment variable name as an argument. You use this same name when you configure the load test.You can create a user-defined variable by using the Apache JMeter IDE, as shown in the following image:
Alternatively, you can directly edit the JMX file, as shown in this example code snippet:
<Arguments guiclass="ArgumentsPanel" testclass="Arguments" testname="User Defined Variables" enabled="true"> <collectionProp name="Arguments.arguments"> <elementProp name="appToken" elementType="Argument"> <stringProp name="Argument.name">udv_webapp</stringProp> <stringProp name="Argument.value">${__BeanShell( System.getenv("webapp") )}</stringProp> <stringProp name="Argument.desc">Web app URL</stringProp> <stringProp name="Argument.metadata">=</stringProp> </elementProp> </collectionProp> </Arguments>Reference the user-defined variable in the test script.
You can use the
${}syntax to reference the variable in the script. In the following example, you use theudv_webappvariable to configure the application endpoint URL.<stringProp name="HTTPSampler.domain">${udv_webapp}</stringProp>
Configure environment variables in Azure Load Testing
To pass environment variables to the Apache JMeter script, you can configure the load test in the Azure portal, in the YAML test configuration file, or directly in the CI/CD workflow.
Important
When you define the environment variable for the load test, its name must match the variable name that you used in the Apache JMeter script.
To specify an environment variable to the load test by using the Azure portal, do the following:
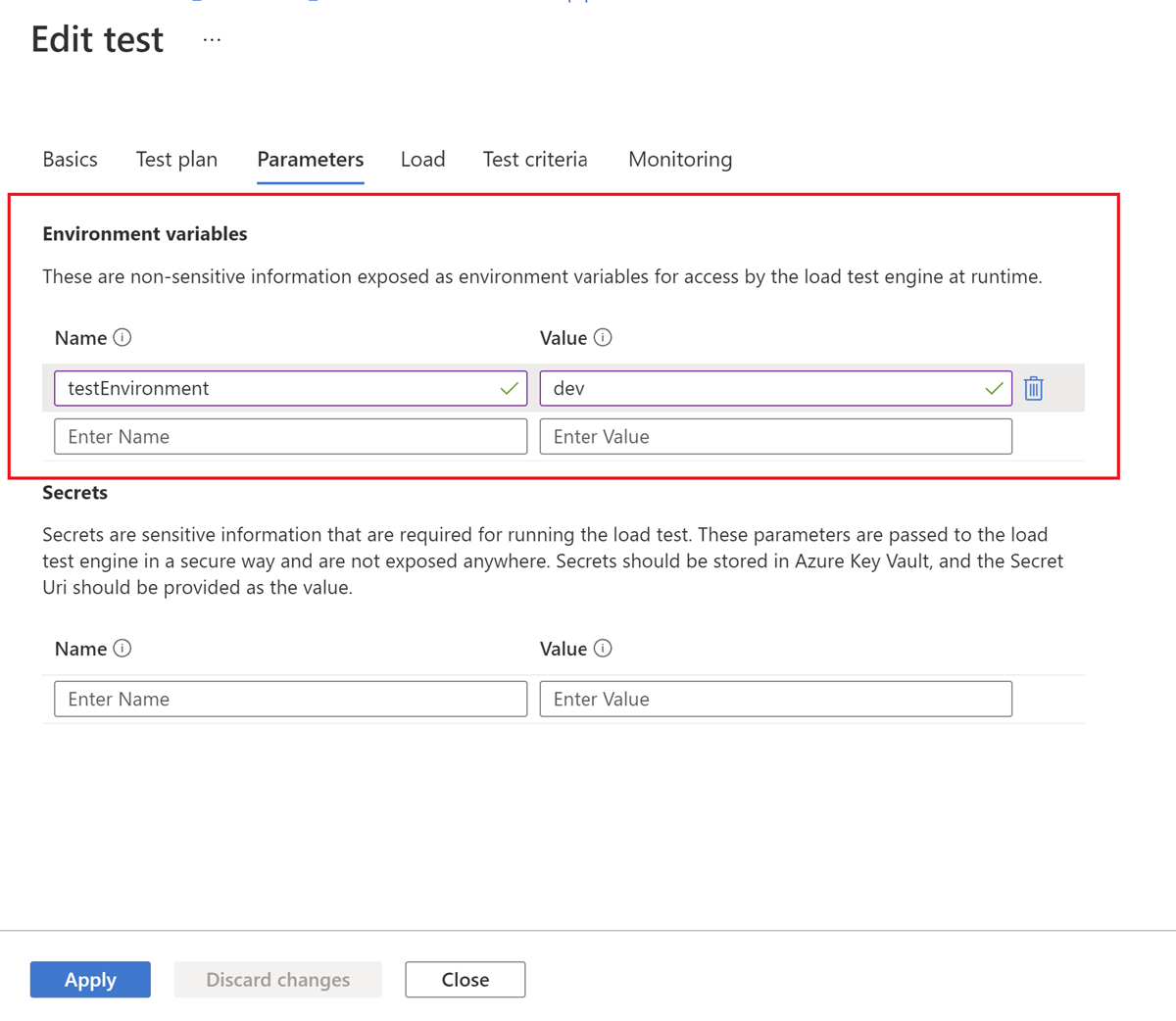
On the test configuration page, select the Parameters tab.
In the Environment Variables section, enter the environment variable Name and Value, and then select Apply.
If you run your load test in a CI/CD workflow, you can define environment variables in the YAML test configuration file. For more information about the syntax, see the Test configuration YAML reference.
Alternatively, you can directly specify environment variables in the CI/CD workflow definition. You use input parameters for the Azure Load Testing action or Azure Pipelines task to pass environment variables to the Apache JMeter script.
The following YAML snippet shows a GitHub Actions example:
- name: 'Azure Load Testing'
uses: azure/load-testing
with:
loadtestConfigFile: 'SampleApp.yaml'
loadtestResource: 'MyTest'
resourceGroup: 'loadtests-rg'
env: |
[
{
"name": "webapp",
"value": "myapplication.contoso.com"
}
]
The following YAML snippet shows an Azure Pipelines example:
- task: AzureLoadTest@1
inputs:
azureSubscription: 'MyAzureLoadTestingRG'
loadTestConfigFile: 'SampleApp.yaml'
loadTestResource: 'MyTest'
resourceGroup: 'loadtests-rg'
env: |
[
{
"name": "webapp",
"value": "myapplication.contoso.com"
}
]
FAQ
Does the Azure Load Testing service store my secret values?
No. The Azure Load Testing service doesn't store the values of secrets. When you use a key vault secret URI, the service stores only the secret URI, and it fetches the value of the secret for each test run. If you provide the value of secrets in a CI/CD workflow, the secret values aren't available after the test run. You provide these values for each test run.
What happens if I have parameters in both my YAML configuration file and the CI/CD workflow?
If a parameter exists in both the YAML configuration file and the Azure Load Testing action or Azure Pipelines task, the value from the CI/CD workflow is used for the test run.
I created and ran a test from my CI/CD workflow by passing parameters using the Azure Load Testing task or action. Can I run this test from the Azure portal with the same parameters?
The values of the parameters aren't stored when they're passed from the CI/CD workflow. You have to provide the parameter values again when you run the test from the Azure portal. You get a prompt to enter the missing values. For secret values, you enter the key vault secret URI. The values that you enter at the test run or rerun page are valid only for that test run. For making changes at the test level, go to Configure Test and enter your parameter values.
Related content
- Use secrets to load test secured endpoints.
- For more information about reading CSV files, see Read CSV files in load tests.