Git workflow
Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server 2022 - Azure DevOps Server 2019
Use version control to save your work and coordinate code changes across your team. Even if you're a single developer, version control helps you stay organized as you fix bugs and develop new features. It maintains a history of your development, allowing you to review and roll back to any version of your code with ease.
The following tutorials demonstrate how to perform common version control tasks using the version control workflow.
Version control workflow
Version control follows a general workflow, similar to the following example, that most developers use when writing code and sharing it with the team.
- Get a local copy of the code if you don't have one.
- Make changes to the code to fix bugs or add new features.
- Once the code is ready, make it available for review by your team.
- After the code is reviewed, merge it into the team's shared codebase.
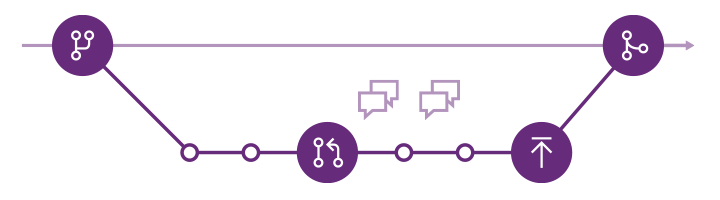
Git has a version of this workflow using terminology and commands unique to Git. Some terms in our documentation might sound familiar if you've used a version control system like Team Foundation Version Control or Subversion, but they behave differently in Git.
Git workflow
- Create a branch for the changes you plan to make and give it a name, such as
users/jamal/fix-bug-3214orcool-feature-x. For more branching guidance, see Adopt a Git branching strategy. - Commit changes to your branch. People often have multiple commits for a bug fix or feature.
- Push your branch to the remote repository.
- Create a pull request so other people can review your changes. To incorporate feedback, you might need to make more commits and push more changes.
- Complete your pull request, resolve any merge conflicts, and complete your pull request.
Use this workflow if you're new to Git. As your team gets more experienced and confident with Git, extend it to suit your team's needs.