Monitor job costs & performance with system tables
This article provides examples of how to use system tables to monitor the cost and performance of jobs in your account.
These queries only calculate costs for jobs run on jobs compute and serverless compute. Jobs run on SQL warehouses and all-purpose compute are not billed as jobs and are thus excluded from cost attribution.
Note
These queries won’t return records from workspaces outside your current workspace’s cloud region. To monitor job costs from workspaces outside your current region, run these queries in a workspace deployed in that region.
Requirements
- The
system.lakeflowschema must be enabled by an account admin. See Enable system table schemas. - To access these system tables, users must either:
- Be both a metastore admin and an account admin, or
- Have
USEandSELECTpermissions on the system schemas. See Grant access to system tables.
Jobs monitoring dashboard
The following dashboard uses system tables to provide you with comprehensive monitoring of your Databricks jobs and operational health. It includes common use cases such as job performance tracking, failure monitoring, and resource utilization.
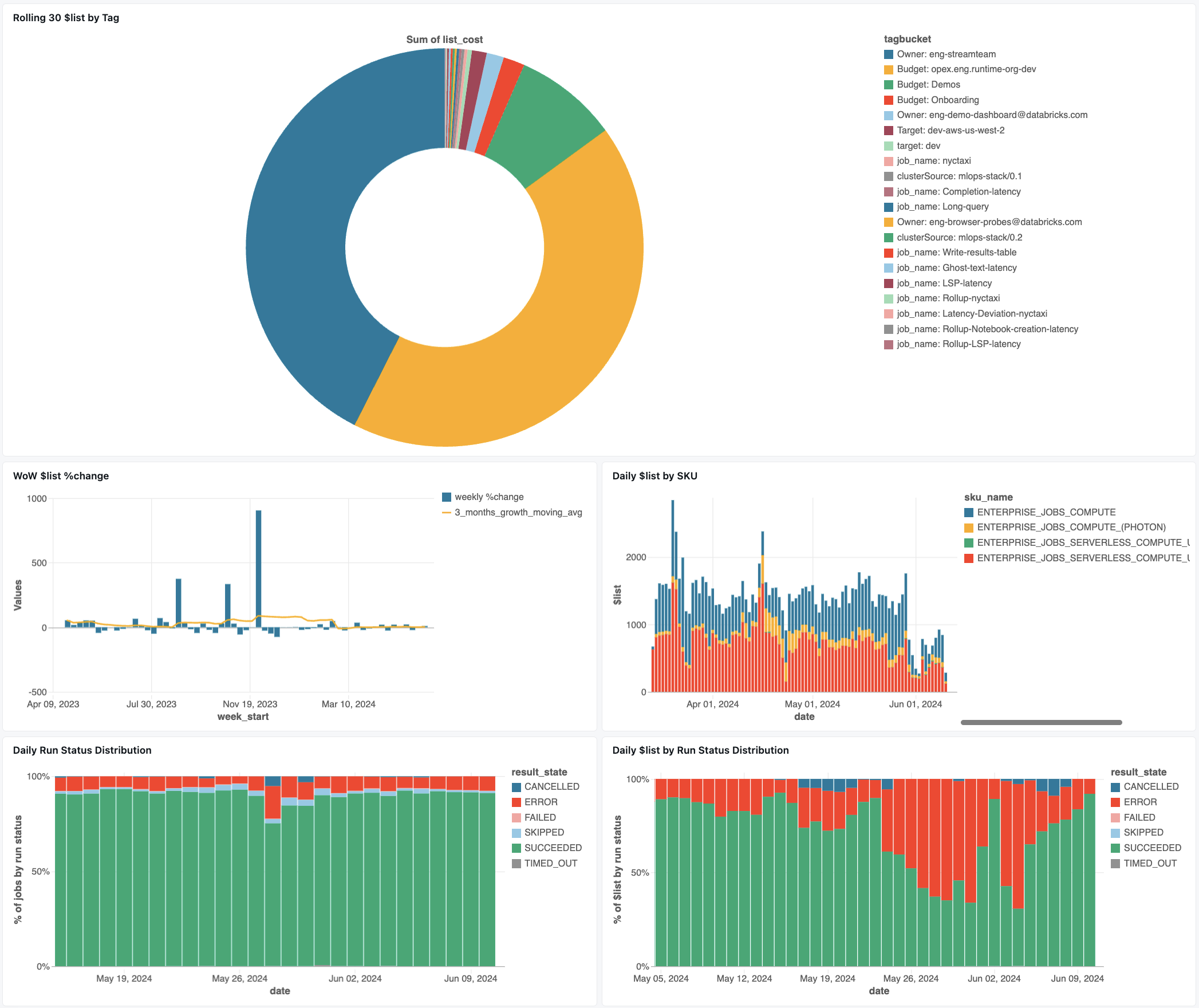
Import the dashboard
- Download the dashboard JSON file from the Databricks GitHub Repository.
- Import the dashboard into your workspace. For instructions on importing dashboards, see Import a dashboard file.
Cost observability queries
The following queries from the dashboard demonstrate job cost monitoring capabilities.
Most expensive jobs (last 30 days)
This query identifies the jobs with the highest spend from the last 30 days.
with list_cost_per_job as (
SELECT
t1.workspace_id,
t1.usage_metadata.job_id,
COUNT(DISTINCT t1.usage_metadata.job_run_id) as runs,
SUM(t1.usage_quantity * list_prices.pricing.default) as list_cost,
first(identity_metadata.run_as, true) as run_as,
first(t1.custom_tags, true) as custom_tags,
MAX(t1.usage_end_time) as last_seen_date
FROM system.billing.usage t1
INNER JOIN system.billing.list_prices list_prices on
t1.cloud = list_prices.cloud and
t1.sku_name = list_prices.sku_name and
t1.usage_start_time >= list_prices.price_start_time and
(t1.usage_end_time <= list_prices.price_end_time or list_prices.price_end_time is null)
WHERE
t1.billing_origin_product = "JOBS"
AND t1.usage_date >= CURRENT_DATE() - INTERVAL 30 DAY
GROUP BY ALL
),
most_recent_jobs as (
SELECT
*,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY workspace_id, job_id ORDER BY change_time DESC) as rn
FROM
system.lakeflow.jobs QUALIFY rn=1
)
SELECT
t2.name,
t1.job_id,
t1.workspace_id,
t1.runs,
t1.run_as,
SUM(list_cost) as list_cost,
t1.last_seen_date
FROM list_cost_per_job t1
LEFT JOIN most_recent_jobs t2 USING (workspace_id, job_id)
GROUP BY ALL
ORDER BY list_cost DESC
Most expensive job runs (last 30 days)
This query identifies the job runs with the highest spend from the last 30 days.
with list_cost_per_job_run as (
SELECT
t1.workspace_id,
t1.usage_metadata.job_id,
t1.usage_metadata.job_run_id as run_id,
SUM(t1.usage_quantity * list_prices.pricing.default) as list_cost,
first(identity_metadata.run_as, true) as run_as,
first(t1.custom_tags, true) as custom_tags,
MAX(t1.usage_end_time) as last_seen_date
FROM system.billing.usage t1
INNER JOIN system.billing.list_prices list_prices on
t1.cloud = list_prices.cloud and
t1.sku_name = list_prices.sku_name and
t1.usage_start_time >= list_prices.price_start_time and
(t1.usage_end_time <= list_prices.price_end_time or list_prices.price_end_time is null)
WHERE
t1.billing_origin_product = 'JOBS'
AND t1.usage_date >= CURRENT_DATE() - INTERVAL 30 DAY
GROUP BY ALL
),
most_recent_jobs as (
SELECT
*,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY workspace_id, job_id ORDER BY change_time DESC) as rn
FROM
system.lakeflow.jobs QUALIFY rn=1
)
SELECT
t1.workspace_id,
t2.name,
t1.job_id,
t1.run_id,
t1.run_as,
SUM(list_cost) as list_cost,
t1.last_seen_date
FROM list_cost_per_job_run t1
LEFT JOIN most_recent_jobs t2 USING (workspace_id, job_id)
GROUP BY ALL
ORDER BY list_cost DESC
Spend trend analysis (7-14 days)
This query identifies which jobs had the highest increase in list cost spend over the last 2 weeks.
with job_run_timeline_with_cost as (
SELECT
t1.*,
t1.usage_metadata.job_id as job_id,
t1.identity_metadata.run_as as run_as,
t1.usage_quantity * list_prices.pricing.default AS list_cost
FROM system.billing.usage t1
INNER JOIN system.billing.list_prices list_prices
ON
t1.cloud = list_prices.cloud AND
t1.sku_name = list_prices.sku_name AND
t1.usage_start_time >= list_prices.price_start_time AND
(t1.usage_end_time <= list_prices.price_end_time or list_prices.price_end_time is NULL)
WHERE
t1.billing_origin_product = 'JOBS' AND
t1.usage_date >= CURRENT_DATE() - INTERVAL 14 DAY
),
most_recent_jobs as (
SELECT
*,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY workspace_id, job_id ORDER BY change_time DESC) as rn
FROM
system.lakeflow.jobs QUALIFY rn=1
)
SELECT
t2.name
,t1.workspace_id
,t1.job_id
,t1.sku_name
,t1.run_as
,Last7DaySpend
,Last14DaySpend
,last7DaySpend - last14DaySpend as Last7DayGrowth
,try_divide( (last7DaySpend - last14DaySpend) , last14DaySpend) * 100 AS Last7DayGrowthPct
FROM
(
SELECT
workspace_id,
job_id,
run_as,
sku_name,
SUM(list_cost) AS spend
,SUM(CASE WHEN usage_end_time BETWEEN date_add(current_date(), -8) AND date_add(current_date(), -1) THEN list_cost ELSE 0 END) AS Last7DaySpend
,SUM(CASE WHEN usage_end_time BETWEEN date_add(current_date(), -15) AND date_add(current_date(), -8) THEN list_cost ELSE 0 END) AS Last14DaySpend
FROM job_run_timeline_with_cost
GROUP BY ALL
) t1
LEFT JOIN most_recent_jobs t2 USING (workspace_id, job_id)
ORDER BY
Last7DayGrowth DESC
LIMIT 100
Operational health queries
Here are some of the ways this dashboard helps you track job performance and reliability.
Failed jobs analysis
This query returns information about jobs with a high number of failed runs over the last 30 days. You can view the number of runs, the number of failures, the success ratio, and the cost of the job’s failed runs.
with job_run_timeline_with_cost as (
SELECT
t1.*,
t1.identity_metadata.run_as as run_as,
t2.job_id,
t2.run_id,
t2.result_state,
t1.usage_quantity * list_prices.pricing.default as list_cost
FROM system.billing.usage t1
INNER JOIN system.lakeflow.job_run_timeline t2
ON
t1.workspace_id=t2.workspace_id
AND t1.usage_metadata.job_id = t2.job_id
AND t1.usage_metadata.job_run_id = t2.run_id
AND t1.usage_start_time >= date_trunc("Hour", t2.period_start_time)
AND t1.usage_start_time < date_trunc("Hour", t2.period_end_time) + INTERVAL 1 HOUR
INNER JOIN system.billing.list_prices list_prices on
t1.cloud = list_prices.cloud and
t1.sku_name = list_prices.sku_name and
t1.usage_start_time >= list_prices.price_start_time and
(t1.usage_end_time <= list_prices.price_end_time or list_prices.price_end_time is null)
WHERE
t1.billing_origin_product = 'JOBS' AND
t1.usage_date >= CURRENT_DATE() - INTERVAL 30 DAYS
),
cumulative_run_status_cost as (
SELECT
workspace_id,
job_id,
run_id,
run_as,
result_state,
usage_end_time,
SUM(list_cost) OVER (ORDER BY workspace_id, job_id, run_id, usage_end_time ROWS BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW) AS cumulative_cost
FROM job_run_timeline_with_cost
ORDER BY workspace_id, job_id, run_id, usage_end_time
),
cost_per_status as (
SELECT
workspace_id,
job_id,
run_id,
run_as,
result_state,
usage_end_time,
cumulative_cost - COALESCE(LAG(cumulative_cost) OVER (ORDER BY workspace_id, job_id, run_id, usage_end_time), 0) AS result_state_cost
FROM cumulative_run_status_cost
WHERE result_state IS NOT NULL
ORDER BY workspace_id, job_id, run_id, usage_end_time),
cost_per_status_agg as (
SELECT
workspace_id,
job_id,
FIRST(run_as, TRUE) as run_as,
SUM(result_state_cost) as list_cost
FROM cost_per_status
WHERE
result_state IN ('ERROR', 'FAILED', 'TIMED_OUT')
GROUP BY ALL
),
terminal_statues as (
SELECT
workspace_id,
job_id,
CASE WHEN result_state IN ('ERROR', 'FAILED', 'TIMED_OUT') THEN 1 ELSE 0 END as is_failure,
period_end_time as last_seen_date
FROM system.lakeflow.job_run_timeline
WHERE
result_state IS NOT NULL AND
period_end_time >= CURRENT_DATE() - INTERVAL 30 DAYS
),
most_recent_jobs as (
SELECT
*,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY workspace_id, job_id ORDER BY change_time DESC) as rn
FROM
system.lakeflow.jobs QUALIFY rn=1
)
SELECT
first(t2.name) as name,
t1.workspace_id,
t1.job_id,
COUNT(*) as runs,
t3.run_as,
SUM(is_failure) as failures,
(1 - COALESCE(try_divide(SUM(is_failure), COUNT(*)), 0)) * 100 as success_ratio,
first(t3.list_cost) as failure_list_cost,
MAX(t1.last_seen_date) as last_seen_date
FROM terminal_statues t1
LEFT JOIN most_recent_jobs t2 USING (workspace_id, job_id)
LEFT JOIN cost_per_status_agg t3 USING (workspace_id, job_id)
GROUP BY ALL
ORDER BY failures DESC
Retry patterns
This query returns information about jobs that have had frequent repairs over the last 30 days, including the number of repairs, the cost of the repair runs, and the cumulative duration of the repair runs.
with job_run_timeline_with_cost as (
SELECT
t1.*,
t2.job_id,
t2.run_id,
t1.identity_metadata.run_as as run_as,
t2.result_state,
t1.usage_quantity * list_prices.pricing.default as list_cost
FROM system.billing.usage t1
INNER JOIN system.lakeflow.job_run_timeline t2
ON
t1.workspace_id=t2.workspace_id
AND t1.usage_metadata.job_id = t2.job_id
AND t1.usage_metadata.job_run_id = t2.run_id
AND t1.usage_start_time >= date_trunc("Hour", t2.period_start_time)
AND t1.usage_start_time < date_trunc("Hour", t2.period_end_time) + INTERVAL 1 HOUR
INNER JOIN system.billing.list_prices list_prices on
t1.cloud = list_prices.cloud and
t1.sku_name = list_prices.sku_name and
t1.usage_start_time >= list_prices.price_start_time and
(t1.usage_end_time <= list_prices.price_end_time or list_prices.price_end_time is null)
WHERE
t1.billing_origin_product = 'JOBS' AND
t1.usage_date >= CURRENT_DATE() - INTERVAL 30 DAYS
),
cumulative_run_status_cost as (
SELECT
workspace_id,
job_id,
run_id,
run_as,
result_state,
usage_end_time,
SUM(list_cost) OVER (ORDER BY workspace_id, job_id, run_id, usage_end_time ROWS BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND CURRENT ROW) AS cumulative_cost
FROM job_run_timeline_with_cost
ORDER BY workspace_id, job_id, run_id, usage_end_time
),
cost_per_status as (
SELECT
workspace_id,
job_id,
run_id,
run_as,
result_state,
usage_end_time,
cumulative_cost - COALESCE(LAG(cumulative_cost) OVER (ORDER BY workspace_id, job_id, run_id, usage_end_time), 0) AS result_state_cost
FROM cumulative_run_status_cost
WHERE result_state IS NOT NULL
ORDER BY workspace_id, job_id, run_id, usage_end_time),
cost_per_unsuccesful_status_agg as (
SELECT
workspace_id,
job_id,
run_id,
first(run_as, TRUE) as run_as,
SUM(result_state_cost) as list_cost
FROM cost_per_status
WHERE
result_state != "SUCCEEDED"
GROUP BY ALL
),
repaired_runs as (
SELECT
workspace_id, job_id, run_id, COUNT(*) as cnt
FROM system.lakeflow.job_run_timeline
WHERE result_state IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY ALL
HAVING cnt > 1
),
successful_repairs as (
SELECT t1.workspace_id, t1.job_id, t1.run_id, MAX(t1.period_end_time) as period_end_time
FROM system.lakeflow.job_run_timeline t1
JOIN repaired_runs t2
ON t1.workspace_id=t2.workspace_id AND t1.job_id=t2.job_id AND t1.run_id=t2.run_id
WHERE t1.result_state="SUCCEEDED"
GROUP BY ALL
),
combined_repairs as (
SELECT
t1.*,
t2.period_end_time,
t1.cnt as repairs
FROM repaired_runs t1
LEFT JOIN successful_repairs t2 USING (workspace_id, job_id, run_id)
),
most_recent_jobs as (
SELECT
*,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY workspace_id, job_id ORDER BY change_time DESC) as rn
FROM
system.lakeflow.jobs QUALIFY rn=1
)
SELECT
last(t3.name) as name,
t1.workspace_id,
t1.job_id,
t1.run_id,
first(t4.run_as, TRUE) as run_as,
first(t1.repairs) - 1 as repairs,
first(t4.list_cost) as repair_list_cost,
CASE WHEN t1.period_end_time IS NOT NULL THEN CAST(t1.period_end_time - MIN(t2.period_end_time) as LONG) ELSE NULL END AS repair_time_seconds
FROM combined_repairs t1
JOIN system.lakeflow.job_run_timeline t2 USING (workspace_id, job_id, run_id)
LEFT JOIN most_recent_jobs t3 USING (workspace_id, job_id)
LEFT JOIN cost_per_unsuccesful_status_agg t4 USING (workspace_id, job_id, run_id)
WHERE
t2.result_state IS NOT NULL
GROUP BY t1.workspace_id, t1.job_id, t1.run_id, t1.period_end_time
ORDER BY repairs DESC