Enable private access in Azure Cosmos DB for PostgreSQL
APPLIES TO:
Azure Cosmos DB for PostgreSQL (powered by the Citus database
extension to PostgreSQL)
Private access allows resources in an Azure virtual network to connect securely and privately to nodes in a cluster. This how-to assumes you've already created a virtual network and subnet. For an example of setting up prerequisites, see the private access tutorial.
Create a cluster with a private endpoint
- Select Create a resource in the upper left-hand corner of the Azure portal.
- On the Create a resource page, select Databases, and then select Azure Cosmos DB.
- On the Select API option page, on the PostgreSQL tile, select Create.
- On the Create an Azure Cosmos DB for PostgreSQL cluster page, select or create a Resource group, enter a Cluster name and Location, and enter and confirm the administrator Password.
- Select Next: Networking.
- On the Networking tab, for Connectivity method, select Private access.
- On the Create private endpoint screen, enter or select appropriate values for:
- Resource group
- Location
- Name
- Target sub-resource
- Virtual network
- Subnet
- Integrate with private DNS zone
- Select OK.
- After you create the private endpoint, select Review + create and then select Create to create your cluster.
Enable private access on an existing cluster
To create a private endpoint to a node in an existing cluster, open the Networking page for the cluster.
Select Add private endpoint.
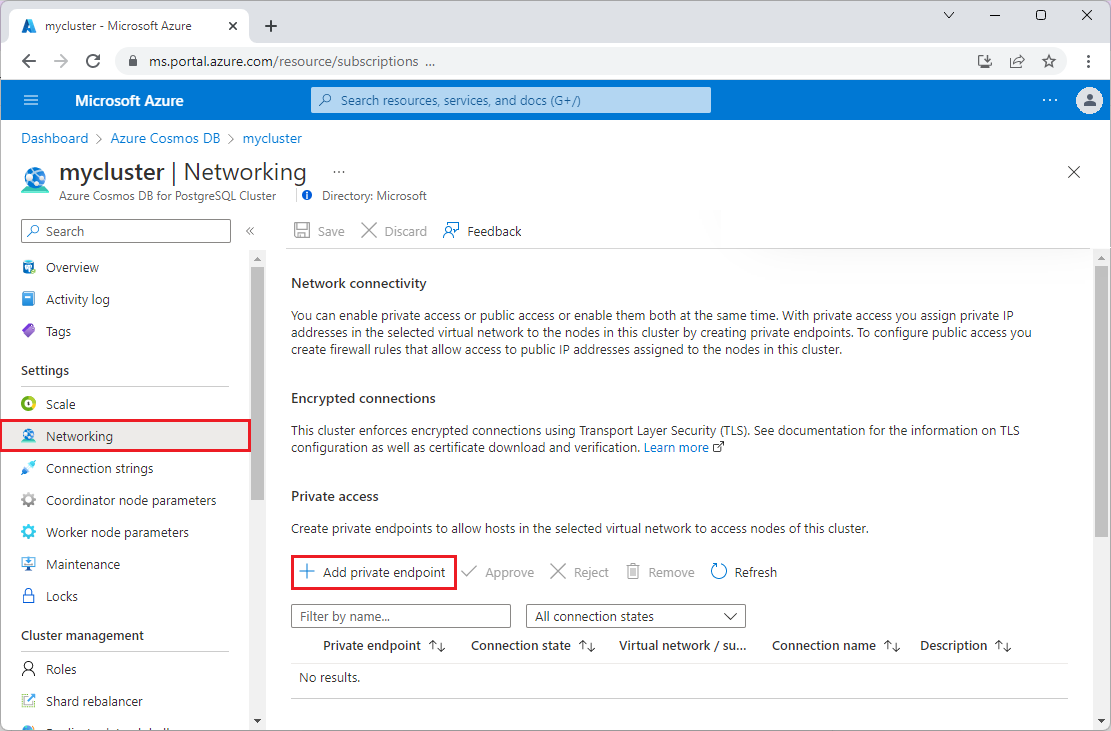
On the Basics tab of the Create a private endpoint screen, confirm the Subscription, Resource group, and Region. Enter a Name for the endpoint, such as my-cluster-1, and a Network interface name, such as my-cluster-1-nic.
Note
Unless you have a good reason to choose otherwise, we recommend picking a subscription and region that match those of your cluster. The default values for the form fields might not be correct. Check them and update if necessary.
Select Next: Resource. For Target sub-resource, choose the target node of the cluster. Usually coordinator is the desired node.
Select Next: Virtual Network. Choose the desired Virtual network and Subnet. Under Private IP configuration, select Statically allocate IP address or keep the default, Dynamically allocate IP address.
Select Next: DNS.
Under Private DNS integration, for Integrate with private DNS zone, keep the default Yes or select No.
Select Next: Tags, and add any desired tags.
Select Review + create. Review the settings, and select Create when satisfied.
Next steps
- Learn more about private access.
- Follow a tutorial to see private access in action.