Resiliency considerations for your cloud strategy
Resiliency is the ability of your infrastructure to maintain functionality and availability despite disruptions or failures. It's a cornerstone of any successful cloud adoption strategy. Design your cloud infrastructure with resiliency in mind to minimize the impact of disruptions. Doing so helps you to maintain continuity and reliability in your business operations.
Consider that the more tightly integrated your business is with your technology, the more important the resiliency of that technology is.
If a system supports a key process or is critical to your business operations, any downtime can lead to significant financial losses, resource drain, or even a complete halt to your business activities.
Plan for the unexpected
In a modern landscape where downtime can lead to significant financial losses and damage to reputation, resiliency is a necessity for many organizations. Whether it's caused by natural disasters, cyberattacks, or system failures, disruption can happen unexpectedly at any time.
Resiliency is about ensuring that your cloud infrastructure and applications are robust enough to handle these challenges, minimize downtime, and preserve the integrity of your services and data.
Typically, not all systems in your business require the same level of resiliency. You might consider allowing flexibility in the resiliency levels within your business so you can focus on resiliency investments where it matters most.
Resiliency also enables your organization to maintain business continuity, meet regulatory requirements, and enhance customer trust by helping to ensure that critical applications and services remain available when the unexpected happens.
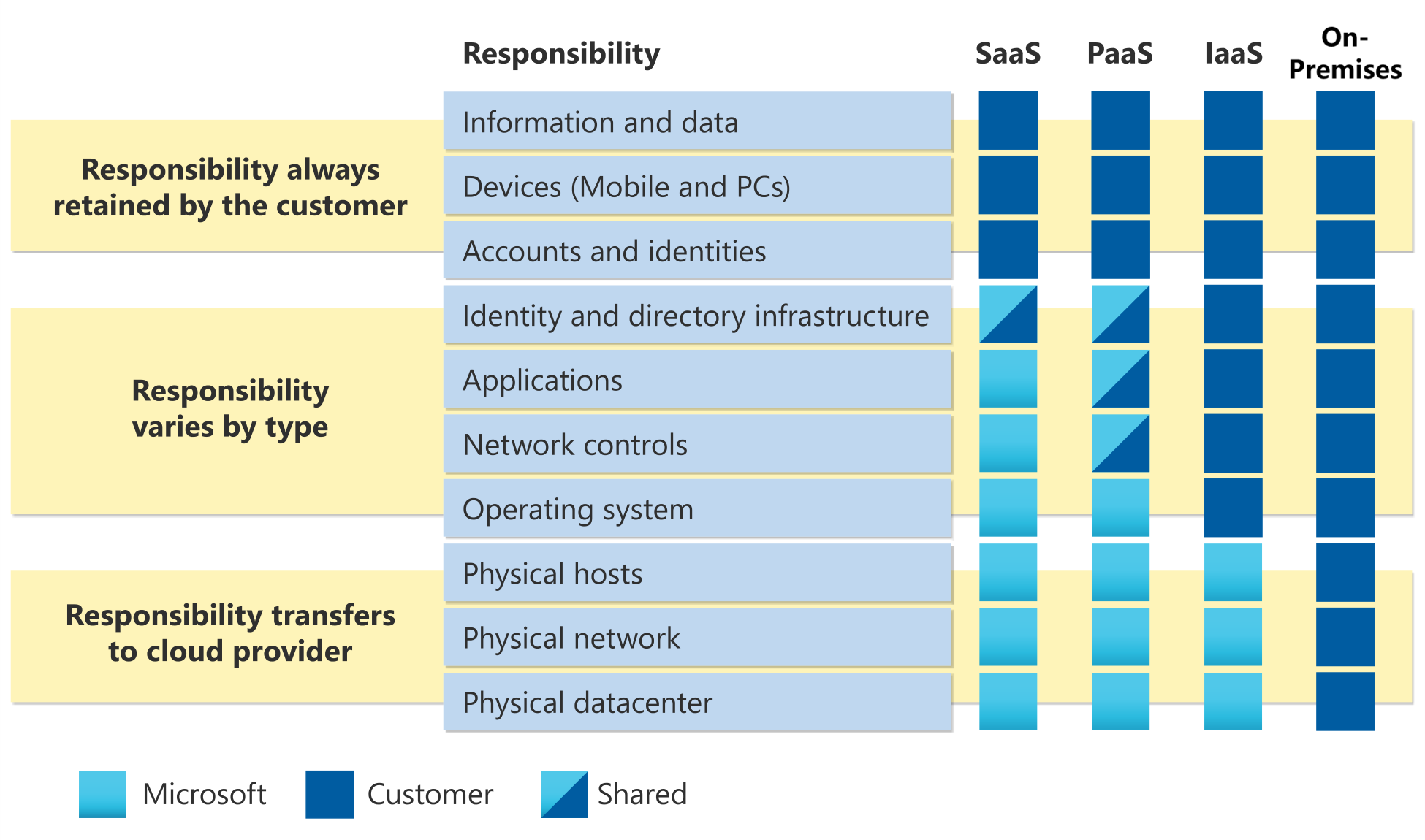
Understand the shared responsibility model
Resiliency is a joint responsibility between a cloud provider and its customers.
The shared responsibility model defines the division of responsibilities and establishes boundaries for what the provider manages, like the core cloud infrastructure, and what the customer is responsible for, like the security and configuration of their applications and data.
Documenting and understanding shared responsibility is crucial in your cloud adoption strategy because it ensures that you understand your role in maintaining security, compliance, and reliability. By incorporating the shared responsibility model into your strategy, you can proactively address potential risks, ensure proper governance, and build a more robust cloud environment that aligns with organizational goals and regulatory requirements.
Ensuring system reliability on Azure is a shared responsibility between the customer and the cloud provider. Microsoft manages the reliability of the cloud platform, while customers and partners are responsible for the reliability of their cloud applications and infrastructure deployments.
Empower your cloud adoption strategy
Integrating resiliency into your cloud adoption strategy provides quality control as a competitive edge. By designing your architecture with resiliency, you can help ensure that your applications, and your business, are operational throughout a range of situations, including hardware or networking problems, or even the loss of a datacenter or entire cloud region. This strategic focus allows for more effective resource allocation, improved operational efficiency, and better risk management.
It can also facilitate the agile deployment of services by enabling your organization to quickly adjust to market demands while maintaining robust security and compliance postures.
Ultimately, resiliency is an essential component of your cloud adoption strategy because it drives quality and innovation and supports long-term business objectives.
Resiliency scenario examples
Here are a few examples of the importance of resiliency in a cloud adoption strategy, mapped to specific types of risk scenarios.
| Risk scenario | Risk impact | Resiliency mitigation example |
|---|---|---|
| Cyberattacks | Ransomware, distributed denial of service (DDoS), or unauthorized access. | To reduce impact, include robust security measures, including an appropriate backup and recovery process, in your adoption strategy and plan. |
| System failures | Hardware or software malfunctions. | Design for quick recovery and data integrity restoration. Handle transient faults in your applications, and provide redundancy in your infrastructure, such as multiple replicas with automatic failover. |
| Configuration issues | Deployment errors or misconfigurations. | Treat configuration changes as code changes by using infrastructure as code (IaC). Use continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, canary deployments, and rollback mechanisms to minimize the impact of faulty updates or deployments. |
| Demand spikes or overload | Performance degradation during peak usage or spikes in traffic. | Use elastic scalability to ensure that systems automatically scale to handle an increased demand without disruption to service. |
| Compliance failures | Breaches of regulatory standards. | Adopt compliance tools like Microsoft Purview, and use Azure Policy to enforce compliance requirements. |
| Natural disasters | Datacenter outages caused by earthquakes, floods, or storms. | Plan for failover, high availability, and disaster recovery by using availability zones, multiple regions, or even multicloud approaches. |
Recommendations
Follow these recommendations to inform your cloud adoption strategy of resiliency considerations.
Perform a business impact analysis (BIA): Define the criticality of various systems and applications to help prioritize resource and recovery efforts. Perform this analysis iteratively throughout your cloud adoption.
Perform a risk assessment: Identify potential threats and vulnerabilities that could affect your cloud infrastructure and use them to build mitigation strategies and inform your resiliency and reliability plans.
Complete a cost-benefit analysis: Map out and understand how investments in your cloud adoption are aligned with business continuity requirements and SLAs.
Understand shared responsibility: Ensure that your strategy team includes details about the shared responsibility model in the cloud, including how it affects reliability. For more information, see Reliability requirements.
Understand Azure reliability: Use the Azure reliability documentation to gain a better understanding of how reliability and resiliency work in Azure.
Understand the reliability capabilities of Azure services: Review the Azure service reliability guides to inform your adoption strategy about reliability capabilities for specific Azure services.
Understand recovery objectives: Learn about recovery time objectives (RTO) and recovery point objectives (RPO) as part of your cloud adoption strategy to understand downtime and data loss limits for your systems.
Define realistic reliability targets: Set realistic expectations with your internal stakeholders about reliability, and use contractual agreements to communicate those expectations to customers. See the Azure Well-Architected Framework Recommendations for defining reliability targets.