Guidelines for Azure NetApp Files network planning
Network architecture planning is a key element of designing any application infrastructure. This article helps you design an effective network architecture for your workloads to benefit from the rich capabilities of Azure NetApp Files.
Azure NetApp Files volumes are designed to be contained in a special purpose subnet called a delegated subnet within your Azure Virtual Network. Therefore, you can access the volumes directly from within Azure over virtual network (VNet) peering or from on-premises over a Virtual Network Gateway (ExpressRoute or VPN Gateway). The subnet is dedicated to Azure NetApp Files and there's no connectivity to the Internet.
The option to set Standard network features on new volumes and to modify network features for existing volumes is supported in all Azure NetApp Files-enabled regions.
Configurable network features
You can create new volumes or modify existing volumes to use Standard or Basic network features. For more information, see Configure network features.
Standard
Selecting this setting enables higher IP limits and standard VNet features such as network security groups and user-defined routes on delegated subnets, and additional connectivity patterns as indicated in this article.Basic
Selecting this setting enables selective connectivity patterns and limited IP scale as mentioned in the Considerations section. All the constraints apply in this setting.
Considerations
You should understand a few considerations when you plan for Azure NetApp Files network.
Constraints
The following table describes what’s supported for each network features configuration:
| Features | Standard network features | Basic network features |
|---|---|---|
| Number of IPs in a VNet (including immediately peered VNets) accessing volumes in an Azure NetApp Files hosting VNet | Same standard limits as virtual machines (VMs) | 1000 |
| Azure NetApp Files delegated subnets per VNet | 1 | 1 |
| Network Security Groups (NSGs) on Azure NetApp Files delegated subnets | Yes | No |
| User-defined routes (UDRs) on Azure NetApp Files delegated subnets | Yes | No |
| Connectivity to Private Endpoints | Yes* | No |
| Connectivity to Service Endpoints | Yes | No |
| Azure policies (for example, custom naming policies) on the Azure NetApp Files interface | No | No |
| Load balancers for Azure NetApp Files traffic | No | No |
| Dual stack (IPv4 and IPv6) VNet | No (IPv4 only supported) |
No (IPv4 only supported) |
| Traffic routed via NVA from peered VNet | Yes | No |
* Applying Azure network security groups on the private link subnet to Azure Key Vault isn't supported for Azure NetApp Files customer-managed keys. Network security groups don't affect connectivity to Private Link unless Private endpoint network policy is enabled on the subnet. It's recommended to keep this option disabled.
Supported network topologies
The following table describes the network topologies supported by each network features configuration of Azure NetApp Files.
| Topologies | Standard network features | Basic network features |
|---|---|---|
| Connectivity to volume in a local VNet | Yes | Yes |
| Connectivity to volume in a peered VNet (Same region) | Yes | Yes |
| Connectivity to volume in a peered VNet (Cross region or global peering) | Yes* | No |
| Connectivity to a volume over ExpressRoute gateway | Yes | Yes |
| ExpressRoute (ER) FastPath | Yes | No |
| Connectivity from on-premises to a volume in a spoke VNet over ExpressRoute gateway and VNet peering with gateway transit | Yes | Yes |
| Connectivity from on-premises to a volume in a spoke VNet over VPN gateway | Yes | Yes |
| Connectivity from on-premises to a volume in a spoke VNet over VPN gateway and VNet peering with gateway transit | Yes | Yes |
| Connectivity over Active/Passive VPN gateways | Yes | Yes |
| Connectivity over Active/Active VPN gateways | Yes | No |
| Connectivity over Active/Active Zone Redundant gateways | Yes | No |
| Connectivity over Active/Passive Zone Redundant gateways | Yes | Yes |
| Connectivity over Virtual WAN (VWAN) | Yes | No |
* This option incurs a charge on ingress and egress traffic that uses a virtual network peering connection. For more information, see Virtual Network pricing. For more general information, see Virtual network peering.
Virtual network for Azure NetApp Files volumes
This section explains concepts that help you with virtual network planning.
Azure virtual networks
Before provisioning an Azure NetApp Files volume, you need to create an Azure virtual network (VNet) or use one that already exists in the same subscription. The VNet defines the network boundary of the volume. For more information on creating virtual networks, see the Azure Virtual Network documentation.
Subnets
Subnets segment the virtual network into separate address spaces that are usable by the Azure resources in them. Azure NetApp Files volumes are contained in a special-purpose subnet called a delegated subnet.
Subnet delegation gives explicit permissions to the Azure NetApp Files service to create service-specific resources in the subnet. It uses a unique identifier in deploying the service. In this case, a network interface is created to enable connectivity to Azure NetApp Files.
If you use a new VNet, you can create a subnet and delegate the subnet to Azure NetApp Files by following instructions in Delegate a subnet to Azure NetApp Files. You can also delegate an existing empty subnet that's not delegated to other services.
If the VNet is peered with another VNet, you can't expand the VNet address space. For that reason, the new delegated subnet needs to be created within the VNet address space. If you need to extend the address space, you must delete the VNet peering before expanding the address space.
Important
Ensure the address space size of the Azure NetApp Files VNet is larger than its delegated subnet.
For example, if the delegated subnet is /24, the VNet address space containing the subnet must be /23 or larger. Noncompliance with this guideline can lead to unexpected issues in some traffic patterns: traffic traversing a hub-and-spoke topology that reaches Azure NetApp Files via a Network Virtual Appliance does not function properly. Additionally, this configuration can result in failures when creating SMB and CIFS (Common Internet File System) volumes if they attempt to reach DNS through hub-and-spoke network topology.
It's also recommended that the size of the delegated subnet be at least /25 for SAP workloads and /26 for other workload scenarios.
User-defined routes (UDRs) and network security groups (NSGs)
If the subnet has a combination of volumes with the Standard and Basic network features, user-defined routes (UDRs) and network security groups (NSGs) applied on the delegated subnets will only apply to the volumes with the Standard network features.
Note
Associating NSGs at the network interface level is not supported for the Azure NetApp Files network interfaces.
Configuring UDRs on the source VM subnets with the address prefix of delegated subnet and next hop as NVA isn't supported for volumes with the Basic network features. Such a setting will result in connectivity issues.
Note
To access an Azure NetApp Files volume from an on-premises network via a VNet gateway (ExpressRoute or VPN) and firewall, configure the route table assigned to the VNet gateway to include the /32 IPv4 address of the Azure NetApp Files volume listed and point to the firewall as the next hop. Using an aggregate address space that includes the Azure NetApp Files volume IP address will not forward the Azure NetApp Files traffic to the firewall.
Note
If you want to configure a route table (UDR route) to control the routing of packets through a network virtual appliance or firewall destined to an Azure NetApp Files standard volume from a source in the same VNet or a peered VNet, the UDR prefix must be more specific or equal to the delegated subnet size of the Azure NetApp Files volume. If the UDR prefix is less specific than the delegated subnet size, it isn't be effective.
For example, if your delegated subnet is x.x.x.x/24, you must configured your UDR to x.x.x.x/24 (equal) or x.x.x.x/32 (more specific). If you configure the UDR route to be x.x.x.x/16, undefined behaviors such as asymmetric routing can cause a network drop at the firewall.
Azure native environments
The following diagram illustrates an Azure-native environment:
Local VNet
A basic scenario is to create or connect to an Azure NetApp Files volume from a VM in the same VNet. For VNet 2 in the diagram, Volume 1 is created in a delegated subnet and can be mounted on VM 1 in the default subnet.
VNet peering
If you have other VNets in the same region that need access to each other’s resources, the VNets can be connected using VNet peering to enable secure connectivity through the Azure infrastructure.
Consider VNet 2 and VNet 3 in the diagram above. If VM 1 needs to connect to VM 2 or Volume 2, or if VM 2 needs to connect to VM 1 or Volume 1, then you need to enable VNet peering between VNet 2 and VNet 3.
Also, consider a scenario where VNet 1 is peered with VNet 2, and VNet 2 is peered with VNet 3 in the same region. The resources from VNet 1 can connect to resources in VNet 2 but can't connect to resources in VNet 3 unless VNet 1 and VNet 3 are peered.
In the diagram above, although VM 3 can connect to Volume 1, VM 4 can't connect to Volume 2. The reason for this is that the spoke VNets aren't peered, and transit routing isn't supported over VNet peering.
Global or cross-region VNet peering
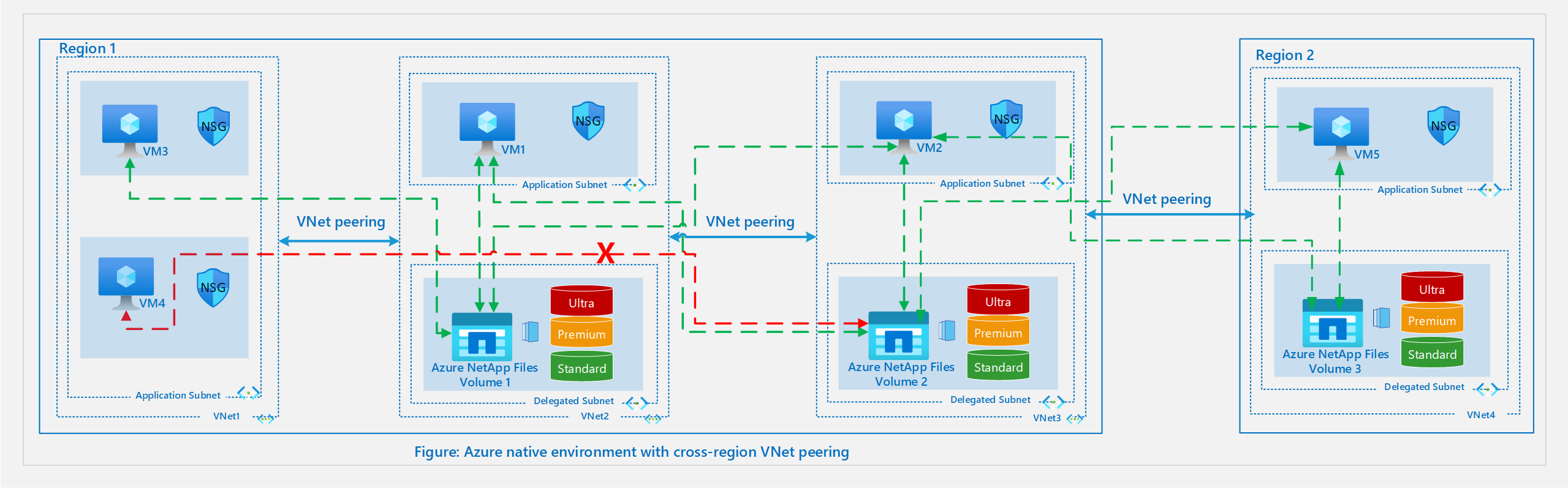
The following diagram illustrates an Azure-native environment with cross-region VNet peering.
With Standard network features, VMs are able to connect to volumes in another region via global or cross-region VNet peering. The above diagram adds a second region to the configuration in the local VNet peering section. For VNet 4 in this diagram, an Azure NetApp Files volume is created in a delegated subnet and can be mounted on VM5 in the application subnet.
In the diagram, VM2 in Region 1 can connect to Volume 3 in Region 2. VM5 in Region 2 can connect to Volume 2 in Region 1 via VNet peering between Region 1 and Region 2.
Hybrid environments
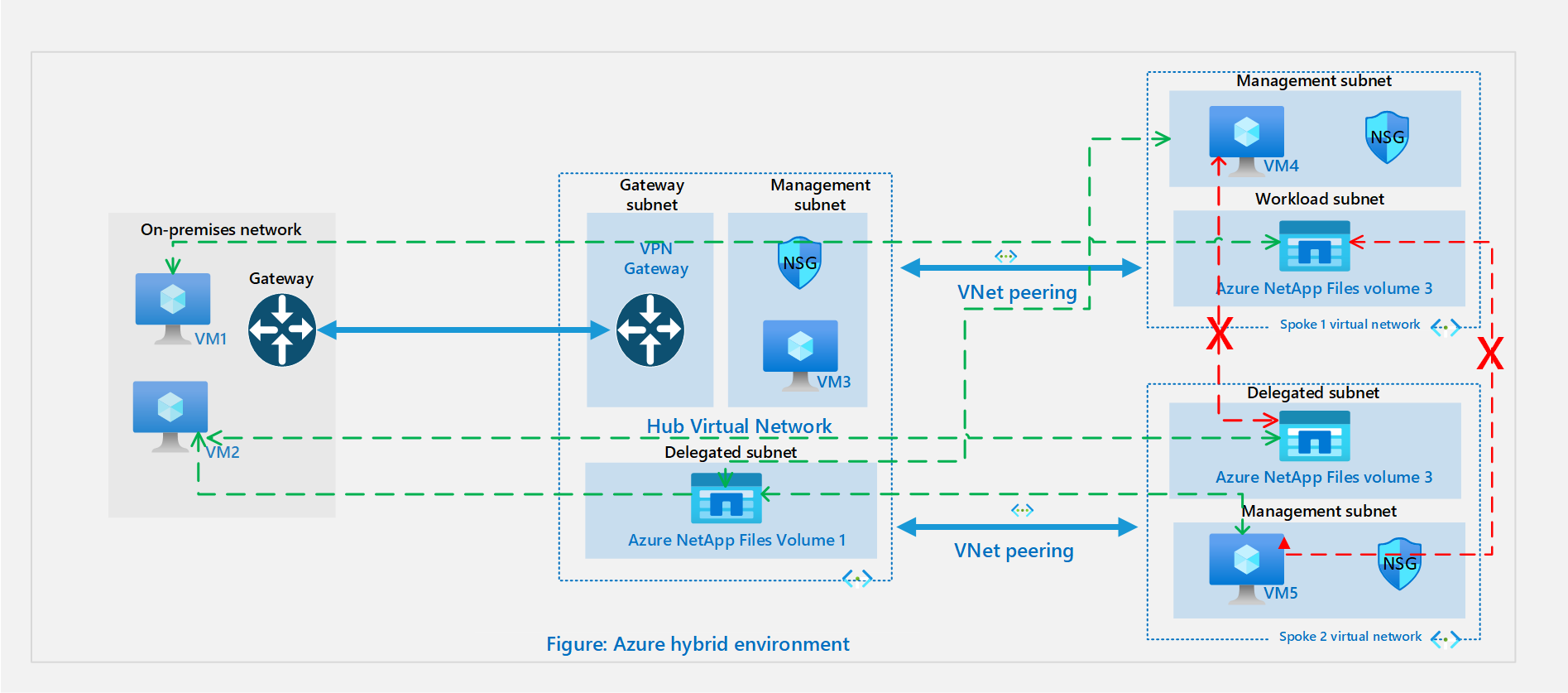
The following diagram illustrates a hybrid environment:
In the hybrid scenario, applications from on-premises datacenters need access to the resources in Azure. This is the case whether you want to extend your datacenter to Azure or you want to use Azure native services or for disaster recovery. See VPN Gateway planning options for information on how to connect multiple resources on-premises to resources in Azure through a site-to-site VPN or an ExpressRoute.
In a hybrid hub-spoke topology, the hub VNet in Azure acts as a central point of connectivity to your on-premises network. The spokes are VNets peered with the hub, and they can be used to isolate workloads.
Depending on the configuration, you can connect on-premises resources to resources in the hub and the spokes.
In the topology illustrated above, the on-premises network is connected to a hub VNet in Azure, and there are 2 spoke VNets in the same region peered with the hub VNet. In this scenario, the connectivity options supported for Azure NetApp Files volumes are as follows:
- On-premises resources VM 1 and VM 2 can connect to Volume 1 in the hub over a site-to-site VPN or ExpressRoute circuit.
- On-premises resources VM 1 and VM 2 can connect to Volume 2 or Volume 3 over a site-to-site VPN and regional VNet peering.
- VM 3 in the hub VNet can connect to Volume 2 in spoke VNet 1 and Volume 3 in spoke VNet 2.
- VM 4 from spoke VNet 1 and VM 5 from spoke VNet 2 can connect to Volume 1 in the hub VNet.
- VM 4 in spoke VNet 1 can't connect to Volume 3 in spoke VNet 2. Also, VM 5 in spoke VNet2 can't connect to Volume 2 in spoke VNet 1. This is the case because the spoke VNets aren't peered and transit routing isn't supported over VNet peering.
- In the above architecture if there's a gateway in the spoke VNet as well, the connectivity to the ANF volume from on-premises connecting over the gateway in the Hub will be lost. By design, preference would be given to the gateway in the spoke VNet and so only machines connecting over that gateway can connect to the ANF volume.