Tutorial: Deploy an enterprise chat web app
Important
Items marked (preview) in this article are currently in public preview. This preview is provided without a service-level agreement, and we don't recommend it for production workloads. Certain features might not be supported or might have constrained capabilities. For more information, see Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews.
In this article, you deploy an enterprise chat web app that uses your own data with a large language model in Azure AI Foundry portal.
Your data source is used to help ground the model with specific data. Grounding means that the model uses your data to help it understand the context of your question. You're not changing the deployed model itself. Your data is stored separately and securely in your original data source
The steps in this tutorial are:
- Configure resources.
- Add your data.
- Test the model with your data.
- Deploy your web app.
Prerequisites
An Azure subscription - Create one for free.
A deployed Azure OpenAI chat model. Complete the Azure AI Foundry playground quickstart to create this resource if you haven't already.
A Search service connection to index the sample product data. If you don't have one, follow the steps to create and connect a search service.
A local copy of product data. The Azure-Samples/rag-data-openai-python-promptflow repository on GitHub contains sample retail product information that's relevant for this tutorial scenario. Specifically, the
product_info_11.mdfile contains product information about the TrailWalker hiking shoes that's relevant for this tutorial example. Download the example Contoso Trek retail product data in a ZIP file to your local machine.A Microsoft.Web resource provider registered in the selected subscription, to be able to deploy to a web app. For more information on registering a resource provider, see Register resource provider.
Necessary permissions to add role assignments in your Azure subscription. Granting permissions by role assignment is only allowed by the Owner of the specific Azure resources.
Azure AI Foundry portal and Azure portal
In this tutorial, you perform some tasks in the Azure AI Foundry portal and some tasks in the Azure portal.
The Azure AI Foundry portal is a web-based environment for building, training, and deploying AI models. As a developer, it's where you will build and deploy your chat web application.
The Azure portal allows an administrator to manage and monitor Azure resources. As an administrator, you'll use the portal to configure settings for various Azure services required for access from the web app.
Configure resources
Important
You must have the necessary permissions to add role assignments in your Azure subscription. Granting permissions by role assignment is only allowed by the Owner of the specific Azure resources. You might need to ask your Azure subscription owner (who might be your IT admin) to complete this section for you.
In order for the resources to work correctly inside a web app, you need to configure them with the correct permissions. This work is done in the Azure portal.
To start, identify the resources you need to configure from the Azure AI Foundry portal.
Open the Azure AI Foundry portal and select the project you used to deploy the Azure OpenAI chat model.
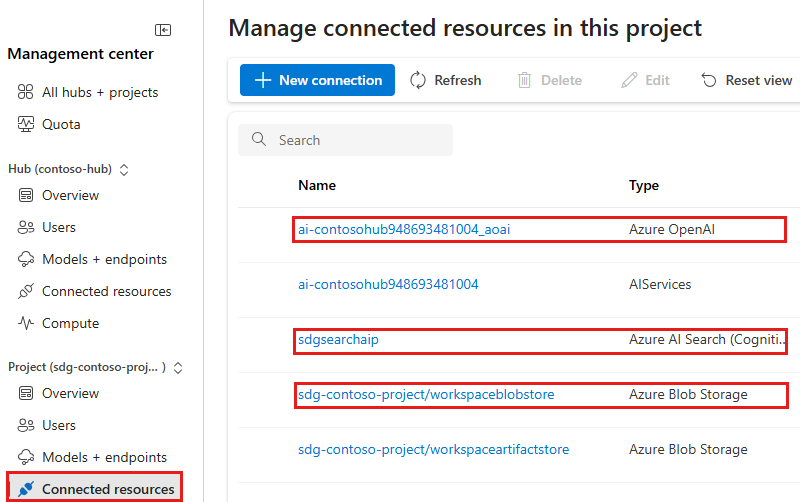
Select Management center from the left pane.
Select Connected resources under your project.
Identify the three resources you need to configure: the Azure OpenAI, the Azure AI Search, and the Azure Blob storage that corresponds to your workspaceblobstore.
Tip
If you have multiple Azure OpenAI resources, use the one that contains your deployed chat model.
For each resource, select the link to open the resource details. From the details page, select the resource name to open the resource in the Azure portal. (For the workspaceblobstore, select View in Azure Portal).
After the browser tab opens, go back to the Azure AI Foundry portal and repeat the process for the next resource.
When you're done, you should have three new browser tabs open, for Search service, Azure AI services, and blobstore Container. Keep all three new tabs open as you'll go back and forth between them to configure the resources.
Enable managed identity
On the browser tab for the Search service resource in the Azure portal, enable the managed identity:
- From the left pane, under Settings, select Identity.
- Switch Status to On.
- Select Save.
On the browser tab for the Azure AI services resource in the Azure portal, enable the managed identity:
- From the left pane, under Resource Management, select Identity.
- Switch Status to On.
- Select Save.
Set access control for search
On the browser tab for the Search service resource in the Azure portal, set the API Access policy:
- From the left pane, under Settings, select Keys.
- Under API Access control, select Both.
- When prompted, select Yes to confirm the change.
Assign roles
You'll repeat this pattern multiple times in the bulleted items below.
The general pattern for assigning role-based access control (RBAC) for any resource is:
- Navigate to the Azure portal for the given resource.
- From the left page in the Azure portal, select Access control (IAM).
- Select + Add > Add role assignment.
- Search for the role you need to assign and select it. Then select Next.
- When assigning a role to yourself:
- Select User, group, or service principal.
- Select Select members.
- Search for your name and select it.
- When assigning a role to another resource:
- Select Managed identity.
- Select Select members.
- Use the dropdown to find the type of resource you want to assign. For example, Azure AI services or Search service.
- Select the resource from the list that appears. There might only be one, but you still need to select it.
- Continue through the wizard and select Review + assign to add the role assignment.
Use these steps to assign roles for the resources you're configuring in this tutorial:
Assign the following roles on the browser tab for Search service in the Azure portal:
- Search Index Data Reader to the Azure AI services managed identity
- Search Service Contributor to the Azure AI services managed identity
- Contributor to yourself (to find Contributor, switch to the Privileged administrator roles tab at the top. All other roles are in the Job function roles tab.)
Assign the following roles on the browser tab for Azure AI services in the Azure portal:
- Cognitive Services OpenAI Contributor to the Search service managed identity
- Contributor to yourself.
Assign the following roles on the browser tab for Azure Blob storage in the Azure portal:
- Storage Blob Data Contributor to the Azure AI services managed identity
- Storage Blob Data Reader to the Search service managed identity
- Contributor to yourself
You're done configuring resources. You can close the Azure portal browser tabs now if you wish.
Add your data and try the chat model again
In the Azure AI Foundry playground quickstart (that's a prerequisite for this tutorial), observe how your model responds without your data. Now add your data to the model to help it answer questions about your products.
To complete this section, you need a local copy of product data. The Azure-Samples/rag-data-openai-python-promptflow repository on GitHub contains sample retail product information that's relevant for this tutorial scenario. Specifically, the product_info_11.md file contains product information about the TrailWalker hiking shoes that's relevant for this tutorial example. Download the example Contoso Trek retail product data in a ZIP file to your local machine.
Follow these steps to add your data in the chat playground to help the assistant answer questions about your products. You're not changing the deployed model itself. Your data is stored separately and securely in your Azure subscription.
Go to your project in Azure AI Foundry.
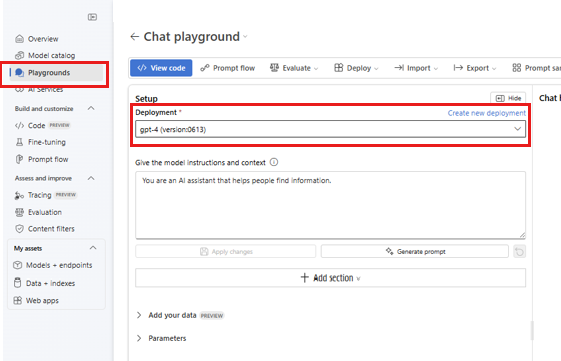
Select Playgrounds.
Select Try the chat playground.
Select your deployed chat model from the Deployment dropdown.
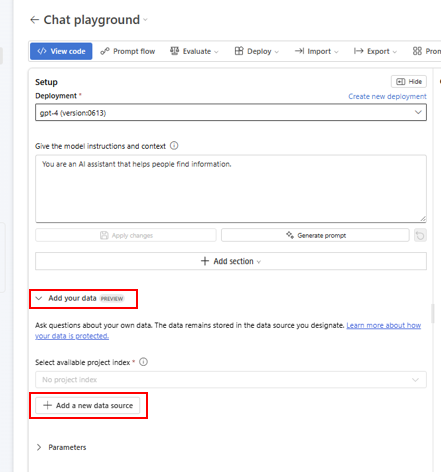
On the left side of the chat playground, select Add your data (PREVIEW) > + Add a new data source.
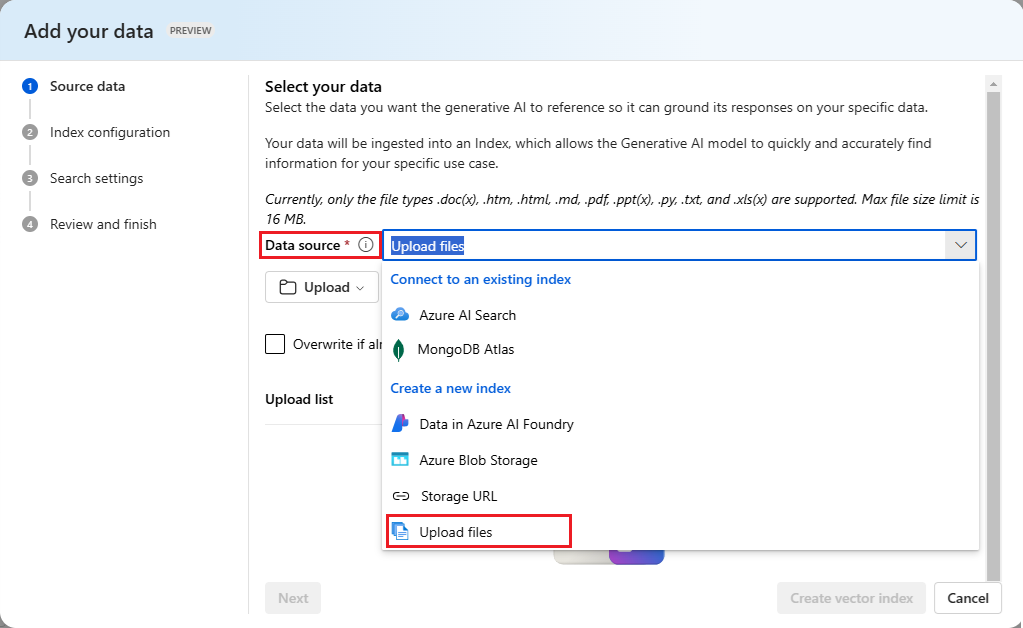
In the Data source dropdown, select Upload files.
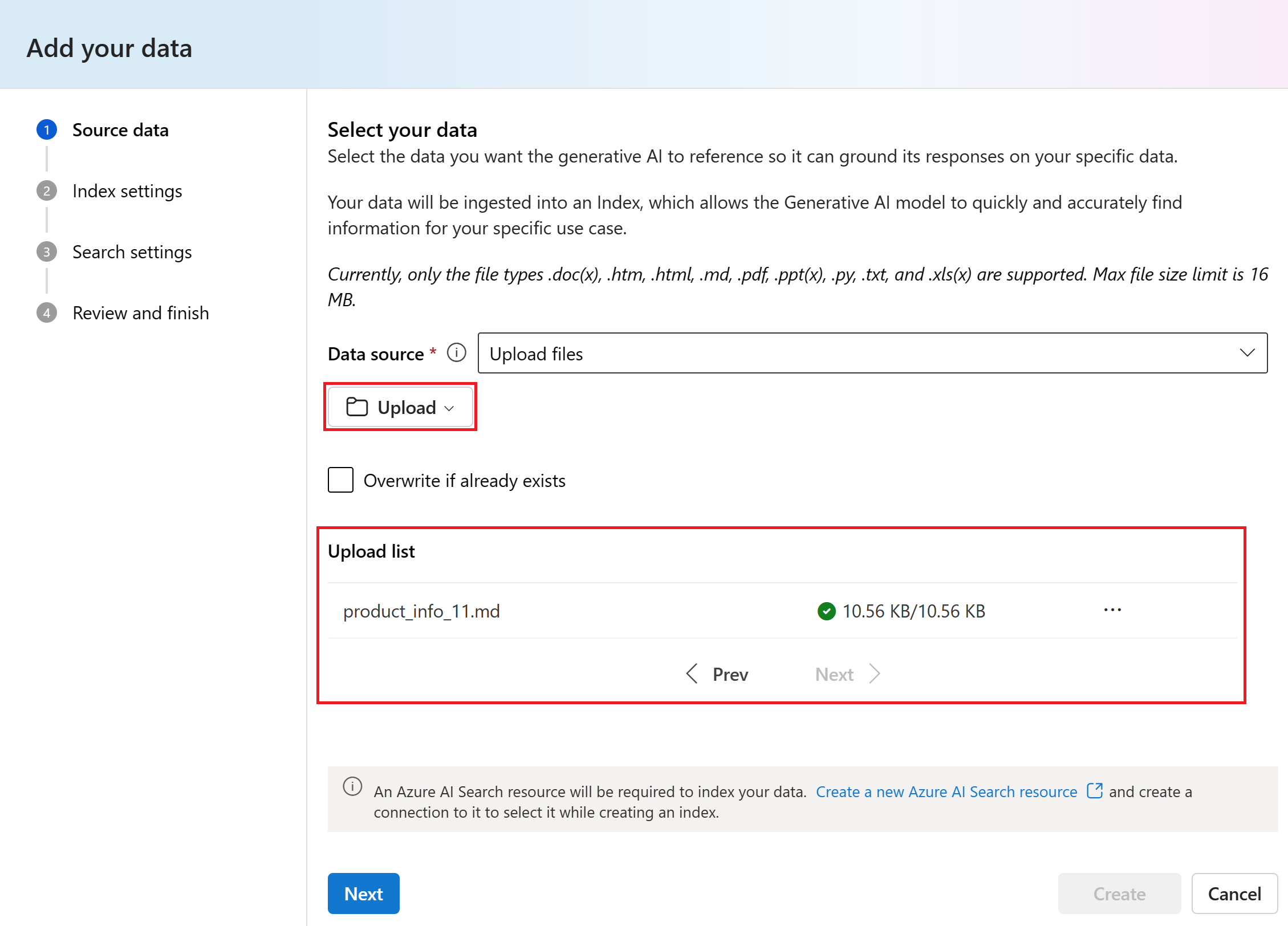
Select Upload > Upload files to browse your local files.
Select the files you want to upload. Select the product information files that you downloaded or created earlier. Add all of the files now. You won't be able to add more files later in the same playground session.
Select Upload to upload the file to your Azure Blob storage account. Then select Next.
Select your Azure AI Search service.
For the Vector index name, enter product-info and select Next.
On the Search settings page under Vector settings, deselect the Add vector search to this search resource checkbox. This setting helps determine how the model responds to requests. Then select Next.
Note
If you add vector search, more options would be available here for an additional cost.
Review your settings and select Create vector index.
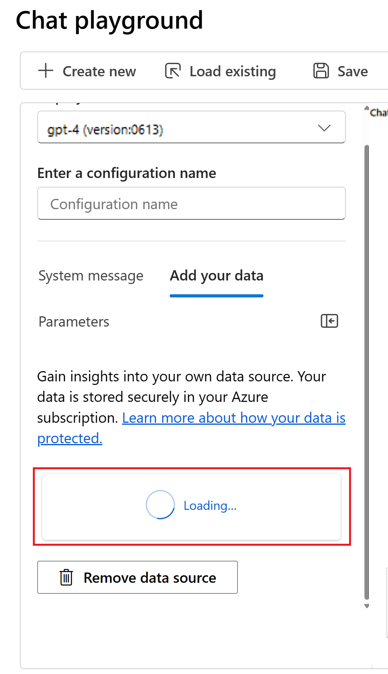
In the playground, you can see that your data ingestion is in progress. This process might take several minutes. Before proceeding, wait until you see the data source and index name in place of the status.
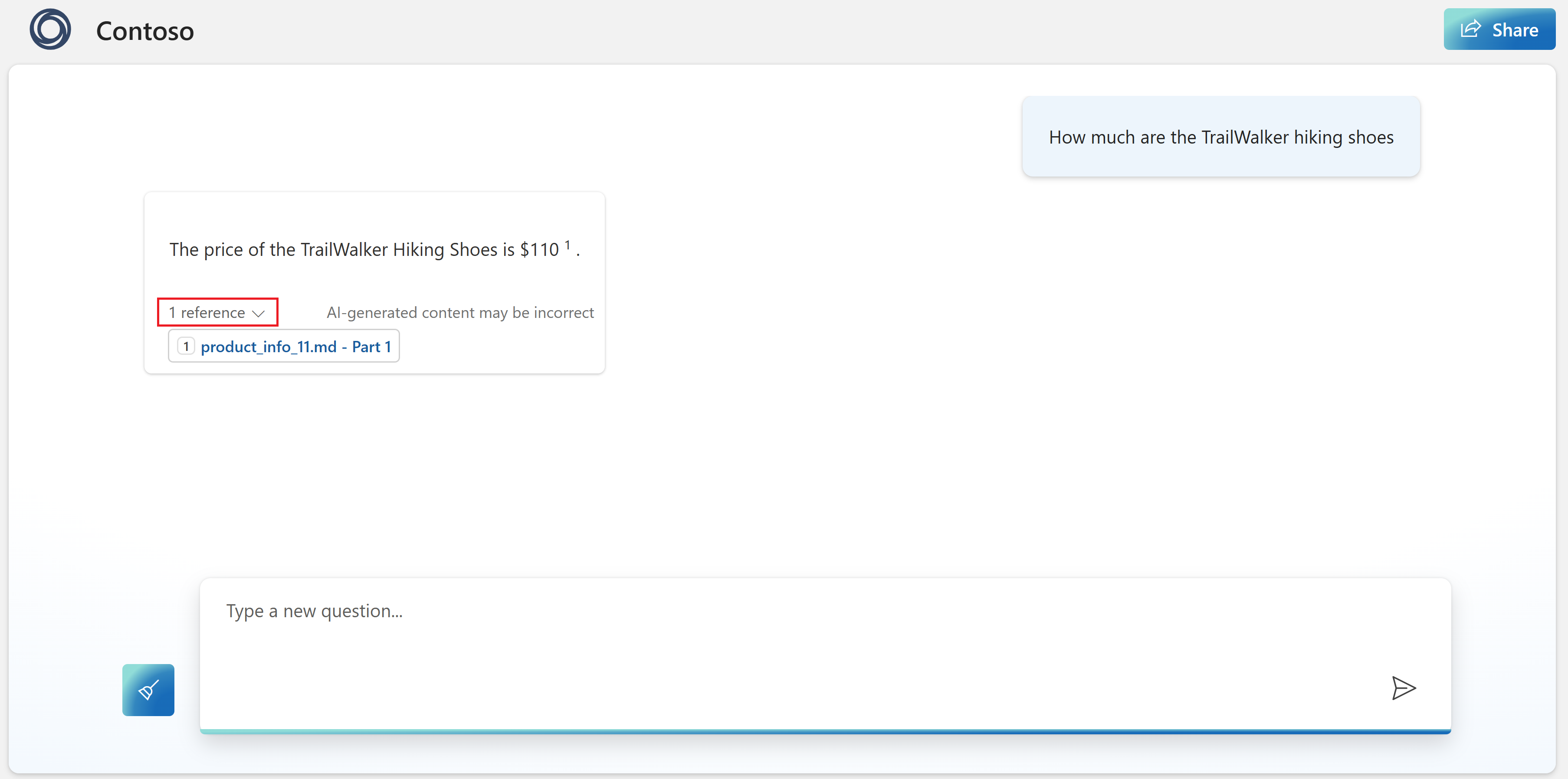
You can now chat with the model asking the same question as before ("How much are the TrailWalker hiking shoes"), and this time it uses information from your data to construct the response. You can expand the references button to see the data that was used.
Deploy your web app
Once you're satisfied with the experience in the Azure AI Foundry portal, you can deploy the model as a standalone web application.
Find your resource group in the Azure portal
In this tutorial, your web app is deployed to the same resource group as your Azure AI Foundry hub. Later you configure authentication for the web app in the Azure portal.
Follow these steps to navigate to your resource group in the Azure portal:
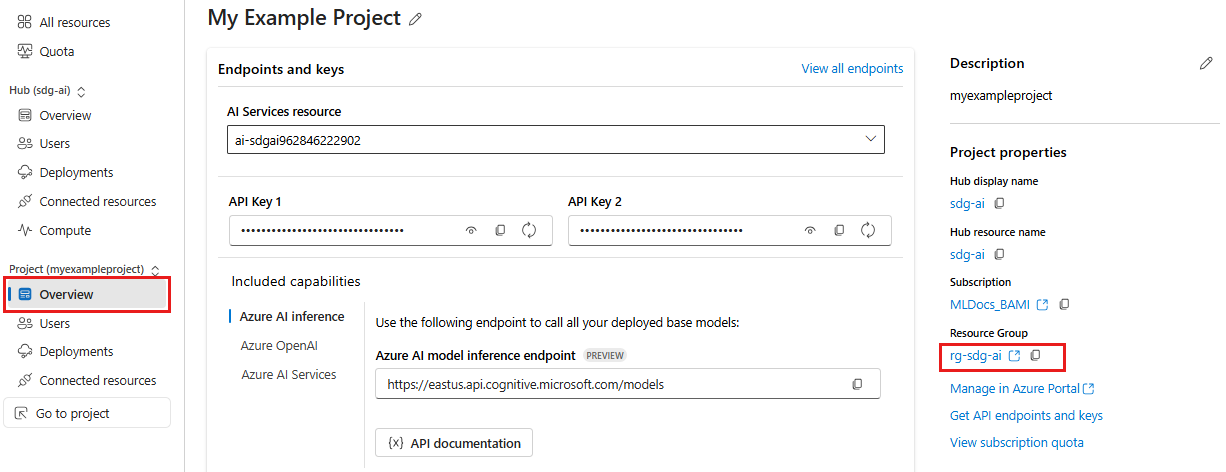
Go to your project in Azure AI Foundry. Then select Management center from the left pane.
Under the Project heading, select Overview.
Select the resource group name to open the resource group in the Azure portal. In this example, the resource group is named
rg-sdg-ai.You should now be in the Azure portal, viewing the contents of the resource group where you deployed the hub. Notice the resource group name and location, you'll use this information in the next section.
Keep this page open in a browser tab. You'll return to it later.
Deploy the web app
Publishing creates an Azure App Service in your subscription. It might incur costs depending on the pricing plan you select. When you're done with your app, you can delete it from the Azure portal.
To deploy the web app:
Important
You need to register Microsoft.Web as a resource provider before you can deploy to a web app.
Complete the steps in the previous section to add your data to the playground. (You can deploy a web app with or without your own data, but at least you need a deployed model as described in the Azure AI Foundry playground quickstart).
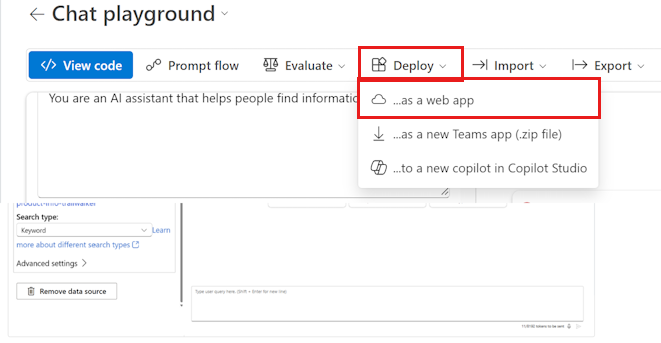
Select Deploy > ...as a web app.
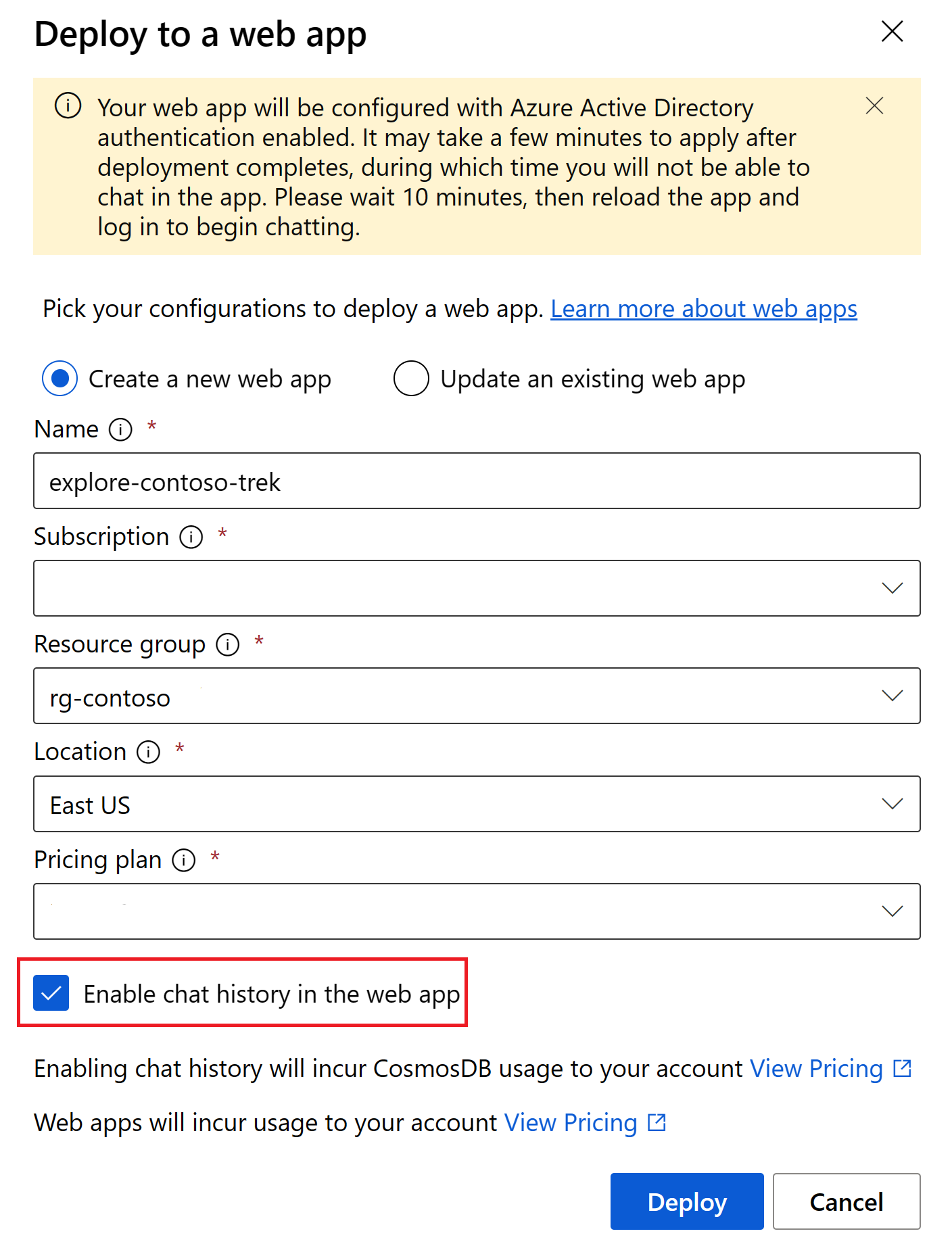
On the Deploy to a web app page, enter the following details:
- Name: A unique name for your web app.
- Subscription: Your Azure subscription. If you don't see any available subscriptions, first register Microsoft.Web as a resource provider.
- Resource group: Select a resource group in which to deploy the web app. Use the same resource group as the hub.
- Location: Select a location in which to deploy the web app. Use the same location as the hub.
- Pricing plan: Choose a pricing plan for the web app.
- Enable chat history in the web app: For the tutorial, the chat history box isn't selected. If you enable the feature, your users have access to their individual previous queries and responses. For more information, see chat history remarks.
Select Deploy.
Wait for the app to be deployed, which might take a few minutes.
When it's ready, the Launch button is enabled on the toolbar. But don't launch the app yet and don't close the chat playground page - you'll return to it later.
Configure web app authentication
By default, the web app is only accessible to you. In this tutorial, you add authentication to restrict access to the app to members of your Azure tenant. Users are asked to sign in with their Microsoft Entra account to be able to access your app. You can follow a similar process to add another identity provider if you prefer. The app doesn't use the user's sign in information in any other way other than verifying they're a member of your tenant.
Return to the browser tab containing the Azure portal (or reopen the Azure portal in a new browser tab) and view the contents of the resource group where you deployed the web app (you might need to refresh the view the see the web app).
Select the App Service resource from the list of resources in the resource group.
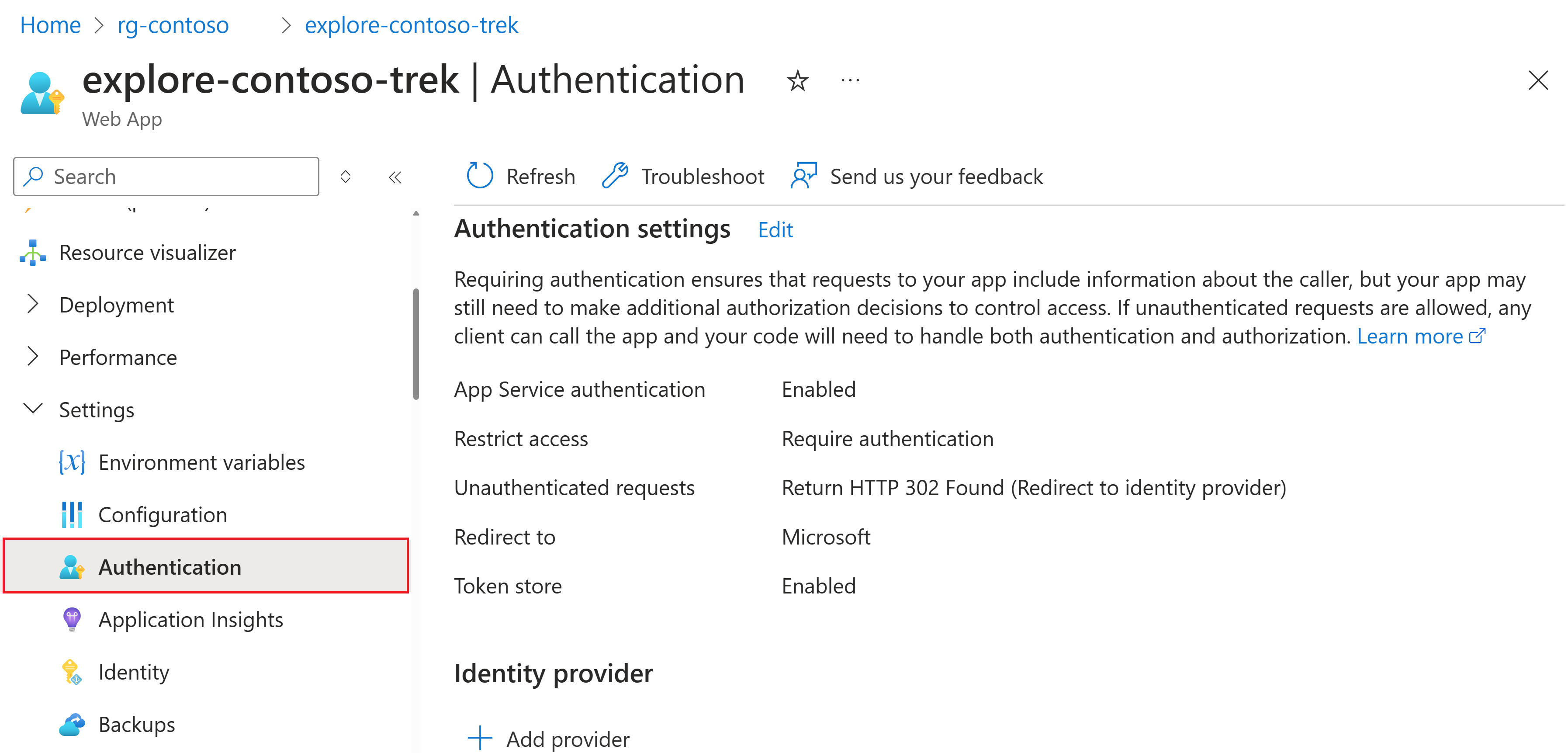
From the collapsible left menu under Settings, select Authentication.
If you see Microsoft listed an Identity provider on this page, nothing further is needed. You can skip the next step.
Add an identity provider with the following settings:
- Identity provider: Select Microsoft as the identity provider. The default settings on this page restrict the app to your tenant only, so you don't need to change anything else here.
- Tenant type: Workforce
- App registration: Create a new app registration
- Name: The name of your web app service
- Supported account types: Current tenant - Single tenant
- Restrict access: Requires authentication
- Unauthenticated requests: HTTP 302 Found redirect - recommended for websites
Use the web app
You're almost there. Now you can test the web app.
If you changed settings, wait 10 minutes or so for the authentication settings to take effect.
Return to the browser tab containing the chat playground page in the Azure AI Foundry portal.
Select Launch to launch the deployed web app. If prompted, accept the permissions request.
If you don't see Launch in the playground, select Web apps from the left pane, then select your app from the list to launch it.
If the authentication settings haven't yet taken effect, close the browser tab for your web app and return to the chat playground in the Azure AI Foundry portal. Then wait a little longer and try again.
In your web app, you can ask the same question as before ("How much are the TrailWalker hiking shoes"), and this time it uses information from your data to construct the response. You can expand the reference button to see the data that was used.
Understand chat history
With the chat history feature, your users have access to their individual previous queries and responses.
You can enable chat history when you deploy the web app. Select the Enable chat history in the web app checkbox.
Important
Enabling chat history will create a Cosmos DB instance in your resource group, and incur additional charges for the storage used. Deleting your web app does not delete your Cosmos DB instance automatically. To delete your Cosmos DB instance, along with all stored chats, you need to navigate to the associated resource in the Azure portal and delete it.
Once you enable chat history, your users are able to show and hide it in the top right corner of the app. When the history is shown, they can rename, or delete conversations. As they're logged into the app, conversations are automatically ordered from newest to oldest, and named based on the first query in the conversation.
If you delete the Cosmos DB resource but keep the chat history option enabled on the studio, your users are notified of a connection error, but can continue to use the web app without access to the chat history.
Update the web app
Use the playground to add more data or test the model with different scenarios. When you're ready to update the web app with the new model, select Deploy > ...as a web app again. Select Update an existing web app and choose the existing web app from the list. The new model deploys to the existing web app.
Clean up resources
To avoid incurring unnecessary Azure costs, you should delete the resources you created in this quickstart if they're no longer needed. To manage resources, you can use the Azure portal.