AD FS troubleshooting: DNS
If Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) isn't working or responding, one of the first things to check is Domain Name System (DNS) name resolution. Basic tests determine if the AD FS or Web Application Proxy (WAP) servers are found on your network. For internal users, these tests should resolve to the AD FS servers security token service (STS). For external users, these tests should resolve to the WAP servers.
The remainder of this article shows how to use command-line tools to do some quick name resolution checks.
Ping test
A ping test verifies IP-level connectivity to another TCP/IP computer by sending Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) Echo Request messages. The receipt of corresponding Echo Reply messages appears, along with round-trip times. For more information, see Ping.
Note
Some organizations block this port on their servers. You might get a Request timed out response.
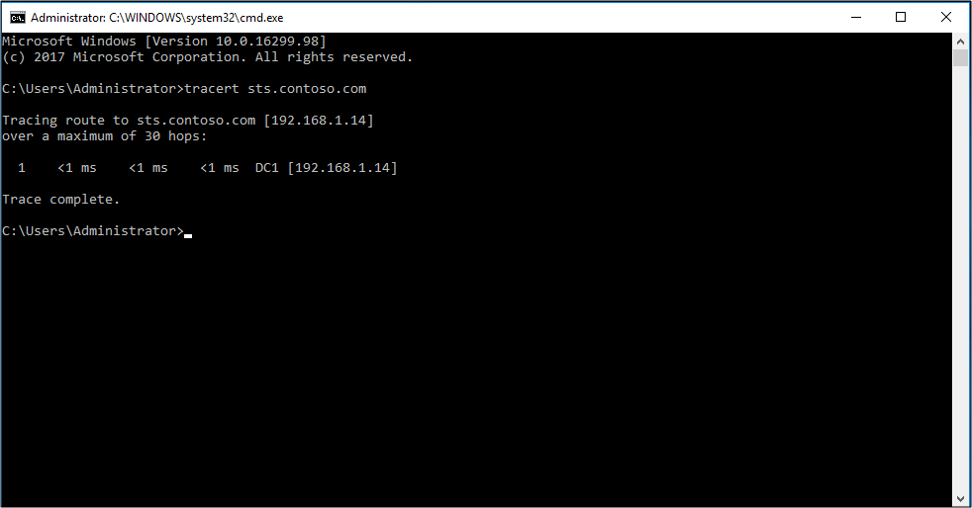
To use a ping test:
Open a command prompt.
Enter
ping <name of AD FS server>.Example:
ping sts.contoso.com
A reply from the server appears.
NSLookup
NSLookup shows information that you can use to diagnose DNS infrastructure. For more information, see NSLookup.
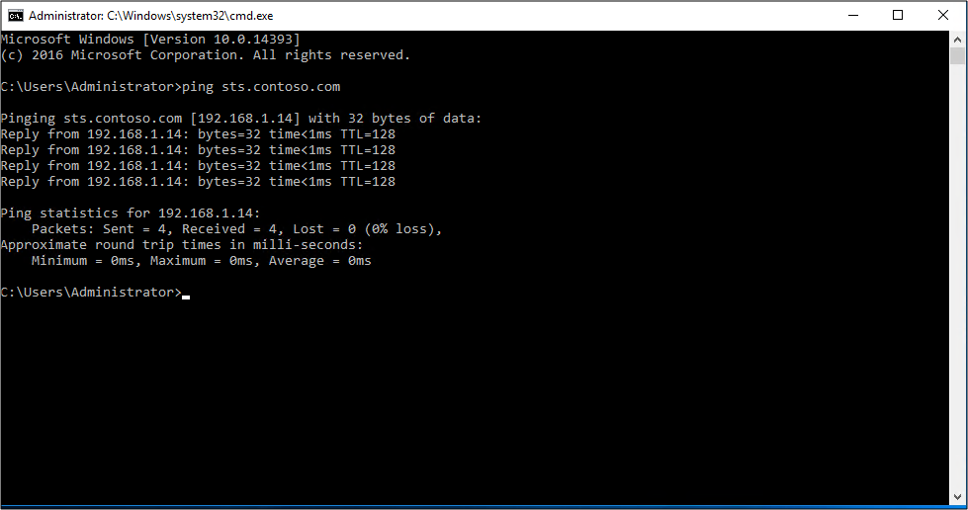
To use NSLookup:
Open a command prompt.
Enter
nslookup <name of AD FS server>.Example:
nslookup sts.contoso.com
The DNS information for the server appears.
Tracert
Tracert determines the path taken to a destination by sending an ICMP Echo Request or ICMPv6 messages to the destination with incrementally increasing Time to Live (TTL) field values. For more information, see Tracert.
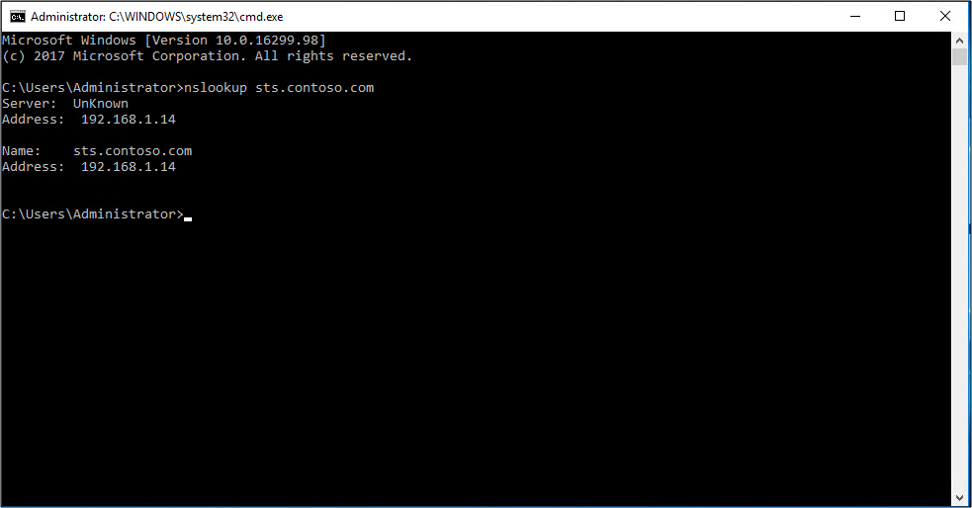
To use tracert:
Open a command prompt.
Enter
tracert <name of AD FS server>.Example:
tracert sts.contoso.com
The destination path used to reach the server appears.