Exercise - Add single sign-on
In this exercise, you add single sign-on to the message extension to authenticate user queries.
Configure backend API app registration
First, create a Microsoft Entra app registration for the backend API. For the purposes of this exercise, you create a new one, however, in a production environment, you would use an existing app registration.
In a browser window:
- Navigate to the Azure portal
- Open the portal menu and select Microsoft Entra ID
- Select App registrations and then select New registration
- In the Register an application form, specify the following values:
- Name: Products API
- Support account types: Accounts in any organizational directory (Any Microsoft Entra ID tenant - Multitenant)
- Select Register to create the app registration
- In the app registration left hand menu, select Expose an API
- Select Add and Save create a new Application ID URI
- In the Scopes defined by this API section, select Add a scope
- In the Add a scope form, specify the following values:
- Scope name: Product.Read
- Who can consent?: Admins and users
- Admin consent display name: Read products
- Admin consent description: Allows the app to read product data
- User consent display name: Read products
- User consent description: Allows the app to read product data
- State: Enabled
- Select Add scope to create the scope
Next, take a note of the app registration ID and the scope ID. You need these values to configure the app registration used to obtain an access token for the backend API.
- In the app registration left hand menu, select Manifest
- Copy the appId property value and save it for later use
- Copy the api.oauth2PermissionScopes[0].id property value and save it for later use
As we need these values in the project, add them to the environment file.
In Visual Studio and the TeamsApp project:
In the env folder, open .env.local
In the file, create the following environment variables and set the values to the app registration ID and scope ID:
BACKEND_API_ENTRA_APP_ID=<app-registration-id> BACKEND_API_ENTRA_APP_SCOPE_ID=<scope-id>Save your changes
Create an app registration manifest file for authentication with the backend API
To authenticate with the backend API, you need an app registration to obtain an access token to call the API with.
Next, create an app registration manifest file. The manifest defines the API permission scopes and redirect URI on the app registration.
In Visual Studio and the TeamsApp project:
In the infra\entra folder, create a file named entra.products.api.manifest.json
In the file, add the following code:
{ "id": "${{PRODUCTS_API_ENTRA_APP_OBJECT_ID}}", "appId": "${{PRODUCTS_API_ENTRA_APP_ID}}", "name": "${{APP_INTERNAL_NAME}}-product-api-${{TEAMSFX_ENV}}", "accessTokenAcceptedVersion": 2, "signInAudience": "AzureADMultipleOrgs", "optionalClaims": { "idToken": [], "accessToken": [ { "name": "idtyp", "source": null, "essential": false, "additionalProperties": [] } ], "saml2Token": [] }, "requiredResourceAccess": [ { "resourceAppId": "${{BACKEND_API_ENTRA_APP_ID}}", "resourceAccess": [ { "id": "${{BACKEND_API_ENTRA_APP_SCOPE_ID}}", "type": "Scope" } ] } ], "oauth2Permissions": [], "preAuthorizedApplications": [], "identifierUris": [], "replyUrlsWithType": [ { "url": "https://token.botframework.com/.auth/web/redirect", "type": "Web" } ] }Save your changes
The requiredResourceAccess property specifies the app registration ID and the scope ID of the backend API.
The replyUrlsWithType property specifies the redirect URI used by the Bot Framework Token Service to return the access token to the token service after the user authenticates.
Next, update the automated workflow to create and update the app registration.
In the TeamsApp project:
Open teamsapp.local.yml
In the file, find the step that uses the addApp/update action
After the action, add the aadApp/create and aadApp/update actions to create and update the app registration:
- uses: aadApp/create with: name: ${{APP_INTERNAL_NAME}}-products-api-${{TEAMSFX_ENV}} generateClientSecret: true signInAudience: AzureADMultipleOrgs writeToEnvironmentFile: clientId: PRODUCTS_API_ENTRA_APP_ID clientSecret: SECRET_PRODUCTS_API_ENTRA_APP_CLIENT_SECRET objectId: PRODUCTS_API_ENTRA_APP_OBJECT_ID tenantId: PRODUCTS_API_ENTRA_APP_TENANT_ID authority: PRODUCTS_API_ENTRA_APP_OAUTH_AUTHORITY authorityHost: PRODUCTS_API_ENTRA_APP_OAUTH_AUTHORITY_HOST - uses: aadApp/update with: manifestPath: "./infra/entra/entra.products.api.manifest.json" outputFilePath : "./infra/entra/build/entra.products.api.${{TEAMSFX_ENV}}.json"Save your changes
The aadApp/create action creates a new app registration with the specified name, audience, and generates a client secret. The writeToEnvironmentFile property writes the app registration ID, client secret, object ID, tenant ID, authority, and authority host to the environment files. The client secret is encrypted and stored securely in the env.local.user file. The environment variable name for the client secret is prefixed with SECRET_, it tells Teams Toolkit to not write the value in the logs.
The aadApp/update action updates the app registration with the specified manifest file.
Centralize connection setting name
First, centralize the connection setting name in the environment file and update the app configuration to access the environment variable value at runtime.
Continuing in Visual Studio and in the TeamsApp project:
In the env folder, open .env.local
In the file, add the following code:
CONNECTION_NAME=ProductsAPIOpen teamsapp.local.yml
In the file, find the step that uses the file/createOrUpdateJsonFile action targeting the ./appsettings.Development.json file. Update the content array to include the CONNECTION_NAME environment variable and write the value to the appsettings.Development.json file:
- uses: file/createOrUpdateJsonFile with: target: ../ProductsPlugin/appsettings.Development.json content: BOT_ID: ${{BOT_ID}} BOT_PASSWORD: ${{SECRET_BOT_PASSWORD}} CONNECTION_NAME: ${{CONNECTION_NAME}}Save your changes
Next, update the app configuration to access the CONNECTION_NAME environment variable.
In the ProductsPlugin project:
Open Config.cs
In the ConfigOptions class, add a new property named CONNECTION_NAME
public class ConfigOptions { public string BOT_ID { get; set; } public string BOT_PASSWORD { get; set; } public string CONNECTION_NAME { get; set; } }Save your changes
Open Program.cs
In the file, update the code that reads the app configuration to include the CONNECTION_NAME property
var config = builder.Configuration.Get<ConfigOptions>(); builder.Configuration["MicrosoftAppType"] = "MultiTenant"; builder.Configuration["MicrosoftAppId"] = config.BOT_ID; builder.Configuration["MicrosoftAppPassword"] = config.BOT_PASSWORD; builder.Configuration["ConnectionName"] = config.CONNECTION_NAME;Save your changes
Next, update the bot code to use the connection setting name at run time.
In the Search folder, open SearchApp.cs
In the SearchApp class, create a constructor that accepts an IConfiguration object and assigns the value of the CONNECTION_NAME property to a private field named connectionName
public class SearchApp : TeamsActivityHandler { private readonly string connectionName; public SearchApp(IConfiguration configuration) { connectionName = configuration["CONNECTION_NAME"]; } }Save your changes
Configure the Products API connection setting
To authenticate with the backend API, you need to configure a connection setting in the Azure Bot resource.
Continuing in Visual Studio and the TeamsApp project:
In the infra folder, open azure.parameters.local.json
In the file, add the backendApiEntraAppClientId, productsApiEntraAppClientId, productsApiEntraAppClientSecret, and connectionName parameters
{ "$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2015-01-01/deploymentParameters.json#", "contentVersion": "1.0.0.0", "parameters": { "resourceBaseName": { "value": "bot-${{RESOURCE_SUFFIX}}-${{TEAMSFX_ENV}}" }, "botEntraAppClientId": { "value": "${{BOT_ID}}" }, "botDisplayName": { "value": "${{APP_DISPLAY_NAME}}" }, "botAppDomain": { "value": "${{BOT_DOMAIN}}" }, "backendApiEntraAppClientId": { "value": "${{BACKEND_API_ENTRA_APP_ID}}" }, "productsApiEntraAppClientId": { "value": "${{PRODUCTS_API_ENTRA_APP_ID}}" }, "productsApiEntraAppClientSecret": { "value": "${{SECRET_PRODUCTS_API_ENTRA_APP_CLIENT_SECRET}}" }, "connectionName": { "value": "${{CONNECTION_NAME}}" } } }Save your changes
Next, update the Bicep file to include the new parameters and pass them to the Azure Bot resource.
In the infra folder, open the file named azure.local.bicep
In the file, after the botAppDomain parameter declaration, add the backendApiEntraAppClientId, productsApiEntraAppClientId, productsApiEntraAppClientSecret, and connectionName parameter declarations
param backendApiEntraAppClientId string param productsApiEntraAppClientId string @secure() param productsApiEntraAppClientSecret string param connectionName stringIn the azureBotRegistration module declaration, add the new parameters
module azureBotRegistration './botRegistration/azurebot.bicep' = { name: 'Azure-Bot-registration' params: { resourceBaseName: resourceBaseName botEntraAppClientId: botEntraAppClientId botAppDomain: botAppDomain botDisplayName: botDisplayName backendApiEntraAppClientId: backendApiEntraAppClientId productsApiEntraAppClientId: productsApiEntraAppClientId productsApiEntraAppClientSecret: productsApiEntraAppClientSecret connectionName: connectionName } }Save your changes.
Finally, update the bot registration Bicep file to include the new connection setting.
In the infra/botRegistration folder, open azurebot.bicep
In the file, after botAppDomain parameter declaration, add the backendApiEntraAppClientId, productsApiEntraAppClientId, productsApiEntraAppClientSecret, and connectionName parameter declarations
param backendApiEntraAppClientId string param productsApiEntraAppClientId string @secure() param productsApiEntraAppClientSecret string param connectionName stringIn the file, create a new resource named botServicesProductsApiConnection
resource botServicesProductsApiConnection 'Microsoft.BotService/botServices/connections@2022-09-15' = { parent: botService name: connectionName location: 'global' properties: { serviceProviderDisplayName: 'Azure Active Directory v2' serviceProviderId: '30dd229c-58e3-4a48-bdfd-91ec48eb906c' clientId: productsApiEntraAppClientId clientSecret: productsApiEntraAppClientSecret scopes: 'api://${backendApiEntraAppClientId}/Product.Read' parameters: [ { key: 'tenantID' value: 'common' } { key: 'tokenExchangeUrl' value: 'api://${botAppDomain}/botid-${botEntraAppClientId}' } ] } }Save your changes
Configure authentication in the message extension
To authenticate user queries in the message extension, you use the Bot Framework SDK to obtain an access token for the user from the Bot Framework Token Service. The access token can then be used to access data from an external service.
To simplify the code, create a helper class that handles user authentication.
Continuing in Visual Studio and the ProductsPlugin project:
Create a new folder named Helpers
In the Helpers folder, create a new class file named AuthHelpers.cs
In the file, add the following code:
using Microsoft.Bot.Connector.Authentication; using Microsoft.Bot.Schema; using Microsoft.Bot.Schema.Teams; internal static class AuthHelpers { internal static async Task<MessagingExtensionResponse> CreateAuthResponse(UserTokenClient userTokenClient, string connectionName, Activity activity, CancellationToken cancellationToken) { var resource = await userTokenClient.GetSignInResourceAsync(connectionName, activity, null, cancellationToken); return new MessagingExtensionResponse { ComposeExtension = new MessagingExtensionResult { Type = "auth", SuggestedActions = new MessagingExtensionSuggestedAction { Actions = [ new() { Type = ActionTypes.OpenUrl, Value = resource.SignInLink, Title = "Sign In", }, ], }, }, }; } internal static async Task<TokenResponse> GetToken(UserTokenClient userTokenClient, string state, string userId, string channelId, string connectionName, CancellationToken cancellationToken) { var magicCode = string.Empty; if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(state)) { if (int.TryParse(state, out var parsed)) { magicCode = parsed.ToString(); } } return await userTokenClient.GetUserTokenAsync(userId, connectionName, channelId, magicCode, cancellationToken); } internal static bool HasToken(TokenResponse tokenResponse) => tokenResponse != null && !string.IsNullOrEmpty(tokenResponse.Token); }Save your changes
The three helper methods in the AuthHelpers class handle user authentication in the message extension.
- CreateAuthResponse method constructs a response that renders a sign-in link in the user interface. The sign-in link is retrieved from the token service using the GetSignInResourceAsync method.
- GetToken method uses the token service client to obtain an access token for the current user. The method uses a magic code to verify the authenticity of the request.
- HasToken method checks if the response from the token service contains an access token. If the token isn't null or empty, the method returns true.
Next, update the message extension code to use the helper methods to authenticate user queries.
In the Search folder, open SearchApp.cs
At the top of the file, add the following using statement:
using Microsoft.Bot.Connector.Authentication;In the OnTeamsMessagingExtensionQueryAsync method, add the following code at the beginning of the method:
var userTokenClient = turnContext.TurnState.Get<UserTokenClient>(); var tokenResponse = await AuthHelpers.GetToken(userTokenClient, query.State, turnContext.Activity.From.Id, turnContext.Activity.ChannelId, connectionName, cancellationToken); if (!AuthHelpers.HasToken(tokenResponse)) { return await AuthHelpers.CreateAuthResponse(userTokenClient, connectionName, (Activity)turnContext.Activity, cancellationToken); }Save your changes
Next, add the Token Service domain to the app manifest file to ensure that the client can trust the domain when initiating a single sign-on flow.
In the TeamsApp project:
In the appPackage folder, open manifest.json
In the file, update the validDomains array, add the domain of the token service:
"validDomains": [ "token.botframework.com", "${{BOT_DOMAIN}}" ]Save your changes
Create and update resources
With everything now in place, run the Prepare Teams App Dependencies process to create new resources and update existing ones.
Continuing in Visual Studio:
- In Solution Explorer, right-click the TeamsApp project
- Expand the Teams Toolkit menu, select Prepare Teams App Dependencies
- In the Microsoft 365 account dialog, select Continue
- In the Provision dialog, select Provision
- In the Teams Toolkit warning dialog, select Provision
- In the Teams Toolkit information dialog, select the cross icon to close the dialog
Run and debug
With the resources provisioned, start a debugging session to test the message extension.
To start a new debug session, press F5 or select Start from the toolbar
Wait until a browser window opens and the app install dialog appears in the Microsoft Teams web client. If prompted, enter your Microsoft 365 account credentials.
In the app install dialog, select Add
Open a new, or existing Microsoft Teams chat
In the message compose area, select + to open the app picker
In the list of apps, select Contoso products to open the message extension
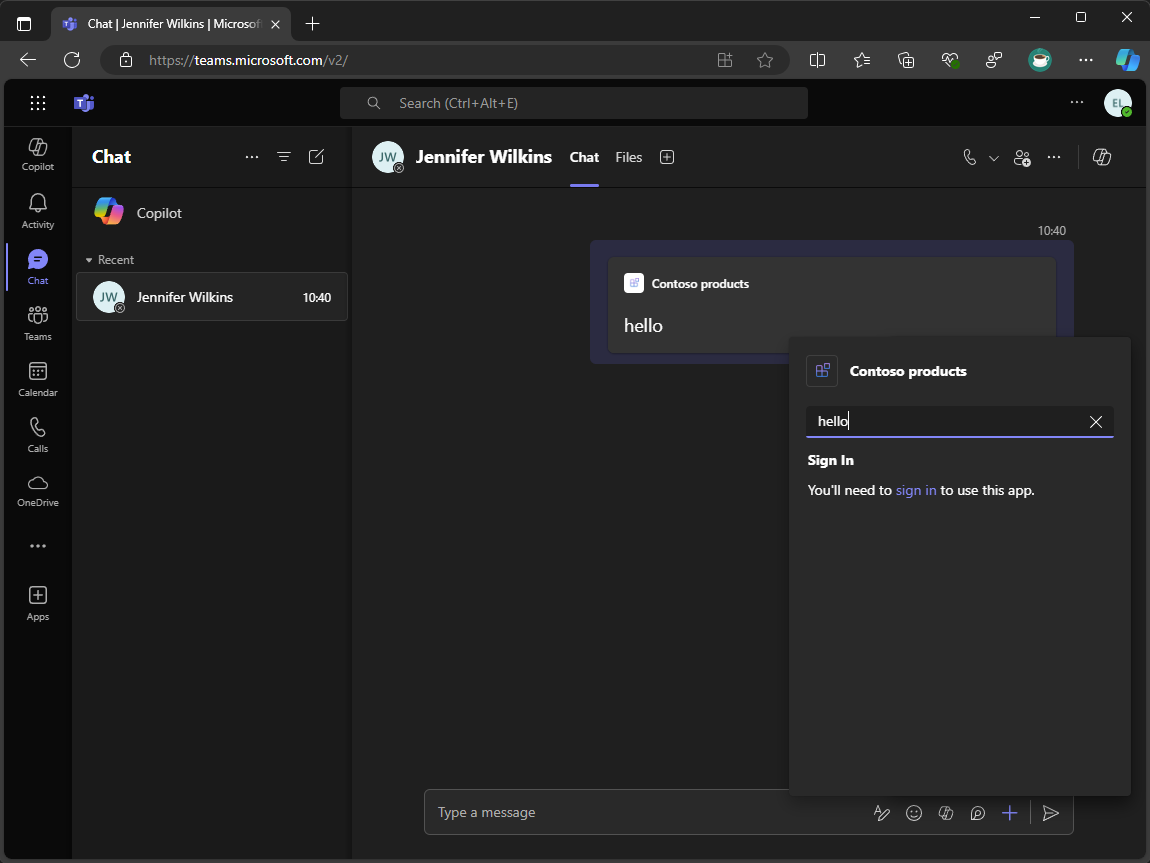
In the text box, enter hello
A message, You'll need to sign in to use this app is shown
Follow the sign in link to start the authentication flow
Consent to the permissions requested and return to Microsoft Teams
Wait for the search to complete and the results to be displayed
In the list of results, select hello to embed a card into the compose message box
Return to Visual Studio and select Stop from the toolbar or press Shift + F5 to stop the debug session.