Exercise - Extend and optimize message extensions for use with Microsoft 365 Copilot
In this exercise, you extend and optimize your message extension for use with Microsoft 365 Copilot. You add a new parameter called Target Audience and update the message extension logic to handle multiple parameters. Finally, you run and debug your message extension and test it in Copilot in Microsoft Teams.
Update app description
Specifying concise and accurate descriptions in your app manifest is critical to ensuring Copilot knows when and how to invoke your plugin. Update the app, command, and parameter descriptions in the app manifest.
Open Visual Studio and in the TeamsApp project:
In the appPackage folder, open manifest.json
Update the description object
{ "description": { "short": "Product look up tool.", "full": "Get real-time product information and share them in a conversation. Search by product name or target audience. ${{APP_DISPLAY_NAME}} works with Microsoft 365 Chat. Find products at Contoso. Find Contoso products called mark8. Find Contoso products named mark8. Find Contoso products related to Mark8. Find Contoso products aimed at individuals. Find Contoso products aimed at businesses. Find Contoso products aimed at individuals with the name mark8. Find Contoso products aimed at businesses with the name mark8." }, }
Add a new parameter
Add a new parameter that Copilot can use. This new parameter helps users look up products using Copilot that is aimed at different audiences, such as individuals and businesses.
Continuing in Visual Studio and in TeamsApp project:
In the parameters array, add the TargetAudience parameter after the ProductName parameter.
{ "parameters": [ { "name": "ProductName", "title": "Product name", "description": "The name of the product as a keyword", "inputType": "text" }, { "name": "TargetAudience", "title": "Target audience", "description": "Audience that the product is aimed at. Consumer products are sold to individuals. Enterprise products are sold to businesses", "inputType": "text" } ] }Save your changes
The description of the TargetAudience parameter describes what it's and explains that the parameter should accept Consumer or Enterprise are allowed values.
Next, update the command description to include the new parameter.
In the commands array, update the description of the command
{ "commands": [ { "id": "Search", "type": "query", "title": "Products", "description": "Find products by name or by target audience", "initialRun": true, "fetchTask": false, "context": [...], "parameters": [...] } ] }
Update message extension logic
To support the new parameter, and support complex prompts, update the OnTeamsMessagingExtensionQueryAsync method in the Bot Activity Handler to handle multiple parameters.
First, update the ProductService class to retrieve products based on the name and audience parameters.
Continuing in Visual Studio in the ProductPlugin project:
In the Services folder, open ProductsService.cs
In the file, create new methods called GetProductsByCategoryAsync and GetProductsByNameAndCategoryAsync
internal async Task<Product[]> GetProductsByCategoryAsync(string category) { var response = await _httpClient.GetAsync($"{_baseUri}products?category={category}"); response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode(); var jsonString = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync(); return System.Text.Json.JsonSerializer.Deserialize<Product[]>(jsonString); } internal async Task<Product[]> GetProductsByNameAndCategoryAsync(string name, string category) { var response = await _httpClient.GetAsync($"{_baseUri}?name={name}&category={category}"); response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode(); var jsonString = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync(); return System.Text.Json.JsonSerializer.Deserialize<Product[]>(jsonString); }Save your changes
Next, add a new method to the MessageExtensionHelper class to retrieve products based on the name and audience parameters.
In the Helpers folder, open MessageExtensionHelper.cs
In the file, create a new method called RetrieveProducts that retrieves products based on the name and audience parameters.
internal static async Task<IList<Product>> RetrieveProducts(string name, string audience, ProductsService productsService) { IList<Product> products; if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(name) && !string.IsNullOrEmpty(audience)) { products = await productsService.GetProductsByCategoryAsync(audience); } else if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(name) && string.IsNullOrEmpty(audience)) { products = await productsService.GetProductsByNameAsync(name); } else if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(name) && !string.IsNullOrEmpty(audience)) { products = await productsService.GetProductsByNameAndCategoryAsync(name, audience); } else { products = []; } return products; }Save your changes
The RetrieveProduct method retrieves products based on the name and audience parameters. If the name parameter is empty and the audience parameter isn't empty, the method retrieves products based on the audience parameter. If the name parameter isn't empty and the audience parameter is empty, the method retrieves products based on the name parameter. If both the name and audience parameters aren't empty, the method retrieves products based on both parameters. If both parameters are empty, the method returns an empty list.
Next, update the SearchApp class to handle the new parameter.
In Search folder, open SearchApp.cs
In the OnTeamsMessagingExtensionQueryAsync method, replace the following code:
var name = MessageExtensionHelpers.GetQueryParameterValueByName(query.Parameters, "ProductName"); var productService = new ProductsService(tokenResponse.Token); var products = await productService.GetProductsByNameAsync(name);With:
var name = MessageExtensionHelpers.GetQueryParameterValueByName(query.Parameters, "ProductName"); var audience = MessageExtensionHelpers.GetQueryParameterValueByName(query.Parameters, "TargetAudience"); var productService = new ProductsService(tokenResponse.Token); var products = await MessageExtensionHelpers.RetrieveProducts(name, audience, productService);Save your changes
The OnTeamsMessagingExtensionQueryAsync method now retrieves the name and audience parameters from the query parameters. It then retrieves products based on the name and audience parameters using the RetrieveProducts method.
Create and update resources
With everything now in place, run the Prepare Teams App Dependencies process to create new resources and update existing ones.
Continuing in Visual Studio:
- In Solution Explorer, right-click the TeamsApp project
- Expand the Teams Toolkit menu, select Prepare Teams App Dependencies
- In the Microsoft 365 account dialog, select Continue
- In the Provision dialog, select Provision
- In the Teams Toolkit warning dialog, select Provision
- In the Teams Toolkit information dialog, select the cross icon to close the dialog
Run and debug
With the resources provisioned, start a debugging session to test the message extension.
First, start Dev Proxy to simulate the custom API.
Open a terminal window
Run the following command to start Dev Proxy:
devproxy --config-file "~appFolder/presets/learn-copilot-me-plugin/products-api-config.json"If prompted, accept the certificate warning
Note
When Dev Proxy is running, it acts as a system-wide proxy.
Next, start a debug session in Visual Studio:
To start a new debug session, press F5 or select Start from the toolbar
Wait until a browser window opens and the app install dialog appears in the Microsoft Teams web client. If prompted, enter your Microsoft 365 account credentials.
In the app install dialog, select Add
Open the Copilot app in Microsoft Teams
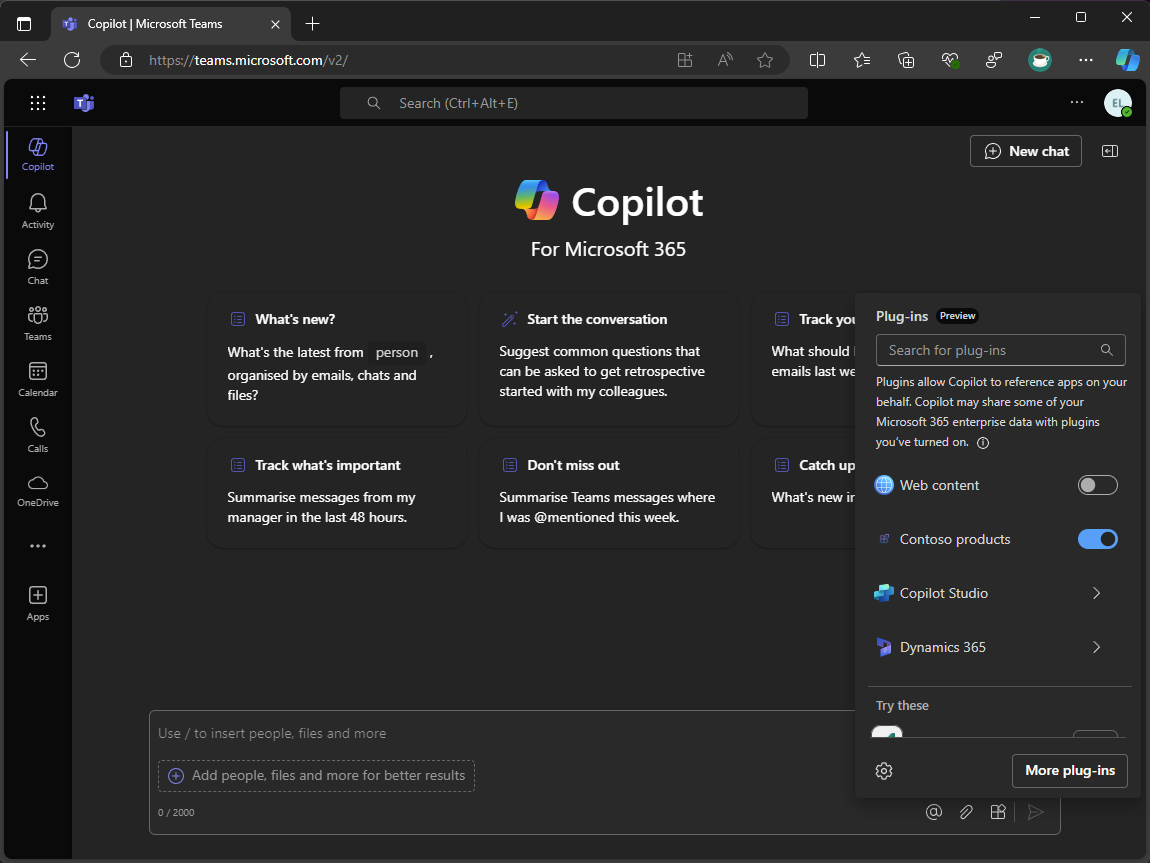
In the compose message area, open the Plugins flyout
In the list of plugins, toggle the Contoso products plugin to enable it
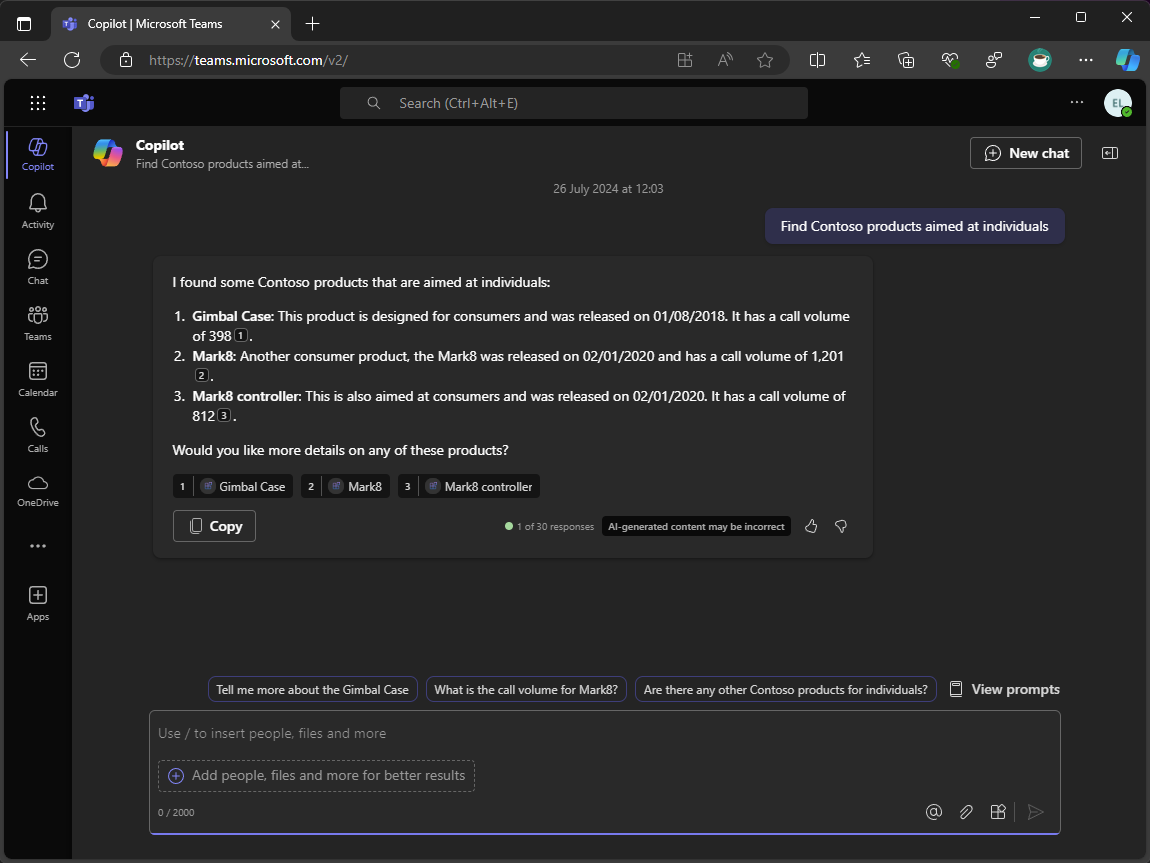
Enter Find Contoso products aimed at individuals as your message and send it
Wait for Copilot to respond
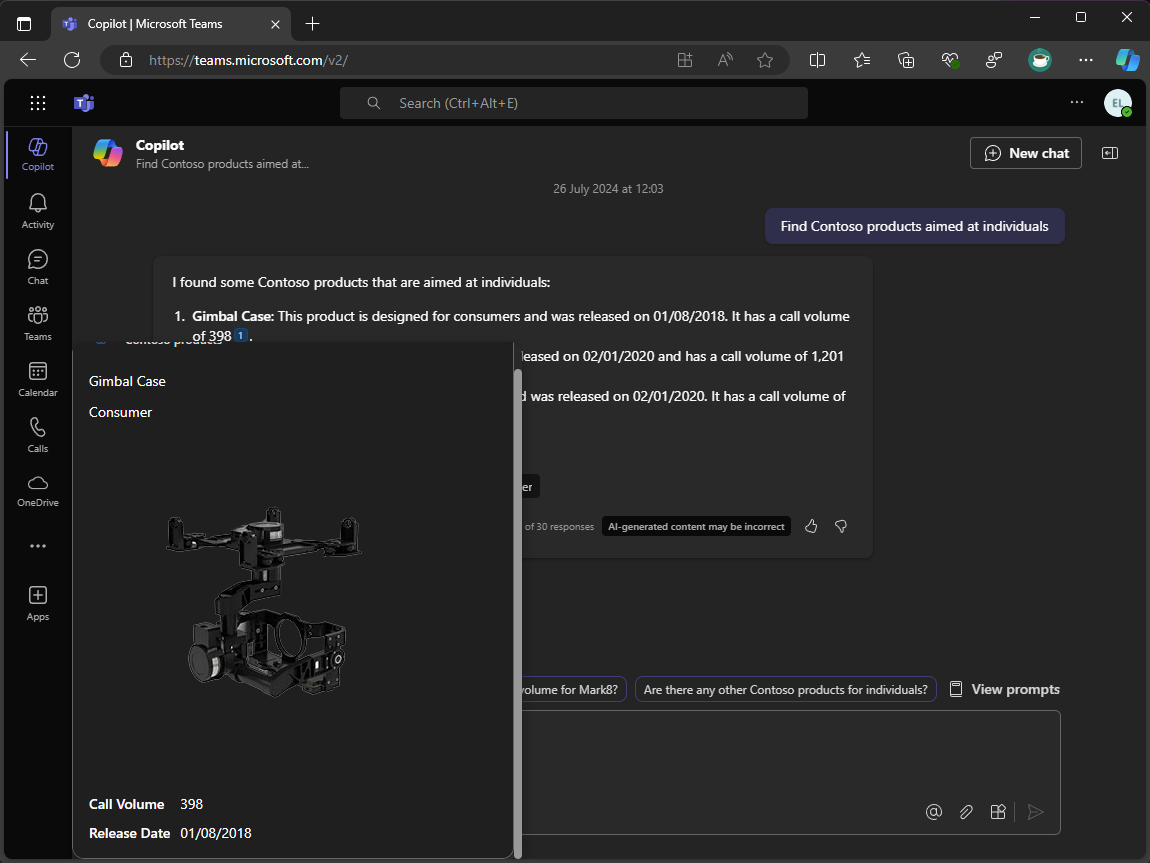
In the Copilot response, data returned in the plugin response is displayed and the plugin is referenced in the response
To view the Adaptive Card relevant to the result, hover over the references in the Copilot response
Return to Visual Studio and select Stop from the toolbar, or press Shift + F5 to stop the debug session. Also, shut down Dev Proxy using Ctrl + C.