Use OData query operations in SharePoint REST requests
Tip
Before you start, review the following resources:
The SharePoint REST service supports a wide range of OData query string operators that enable you to select, filter, and order the data you request.
Tip
The SharePoint Online (and on-premises SharePoint 2016 and later) REST service supports combining multiple requests into a single call to the service by using the OData $batch query option. For details and links to code samples, see Make batch requests with the REST APIs.
Select fields to return
Use the $select query option to specify which fields to return for a given list, list item, or other SharePoint object represented by an entity set. You can use $select=* to return all available fields.
Note
In general, if you do not specify the $select query option, the REST service returns all available fields by default. However, in a few cases, some SharePoint objects include properties that are very resource intensive to retrieve; to optimize REST service performance, these properties are not included in the default query, and must be explicitly requested.For example, the SPWeb.EffectiveBasePermissions property is not returned by default, and must be explicitly requested by using the $select query option.
You can also specify that the request returns projected fields from other lists and the values of lookups. To do this, specify the field name in both the $select and $expand query options. For example:
GET https://{site_url}/_api/web/lists('{list_guid}')/items?$select=Title,Products/Name&$expand=Products/Name
Authorization: "Bearer " + accessToken
Accept: "application/json;odata=verbose"
Bulk expansion and selection of related items isn't supported.
Select items to return
Use the $filter query option to select which items to return. OData query operators supported in the SharePoint REST service lists the filter query comparison options and functions you can use with the SharePoint REST service.
Query for single value lookup fields
Single value lookup fields are represented by two separate fields in the SharePoint REST service: one field representing the actual field value, and another representing the field name. You can execute queries against the lookup field value as you would any other field of that data type. For example, if the lookup field value is a string, you can use string comparison options in your query.
Query for users
In the SharePoint REST service, users are represented by the user's friendly (display) name, and not their alias or domain\alias combination. Therefore, you must construct user queries against users' friendly names.
Note
Membership-based user queries are not supported. Usage of the Current operator to do queries using the ID of the current user isn't supported.
Query for multi-value lookup fields and users
Because multi-value lookup fields are returned as a string of multiple values, there's no way to query for them (for example, the equivalent of an Includes element or NotIncludes element isn't supported).
Sort returned items
Use the $orderby query option to specify how to sort the items in your query return set. To sort by multiple fields, specify a comma-separated list of fields. You can also specify whether to sort the items in ascending or descending order by appending the asc or desc keyword to your query.
Page through returned items
Use the $top and $skiptoken query options to select a subset of the items that would otherwise be returned by your query.
Note
The $skip query option does not work with queries for SharePoint list items.
The $top option enables you to select the first n items of the return set for return. For example, the following URI requests that only the first 10 items in the prospective return set actually be returned:
GET https://{site_url}/_api/web/lists('{list_guid}')/items?$top=10`
Authorization: "Bearer " + accessToken
Accept: "application/json;odata=verbose"
The $skiptoken query option enables you to skip over items until the specified item is reached and return the rest.
GET https://{site_url}/_api/web/lists('{list_guid}')/items?$skiptoken=Paged=TRUE%26p_ID=5`
Authorization: "Bearer " + accessToken
Accept: "application/json;odata=verbose"
Note
When using these query options, take into account that paging in OData is ordinal. For example, suppose you are implementing a next page button to display SharePoint list items. You use the REST service to enable the button to return items 1 through 20 when clicked, and then items 21 through 40, and so on. However, suppose another user deletes items 4 and 18 between clicks of the next button. In such a case, the ordinal positioning of the remaining items is reset, and displaying items 21 through 40 actually skips over two items.
OData query operators supported in the SharePoint REST service
| Supported | Not supported |
|---|---|
| Numeric comparisons (lt le gt ge eq ne) | Arithmetic operators (add, sub, mul, div, mod) Basic math functions (round, floor, ceiling) |
| String comparisons startswith( {Col to query},'{string to check}' ) substringof( '{string to check}', {Col to query} ) eq ne |
endswith, replace, substring, tolower, toupper, trim, concat |
| Date and time functions day(), month(), year(), hour(), minute(), second() | DateTimeRangesOverlap operator Querying as to whether a date time falls inside a recurrent date time pattern |
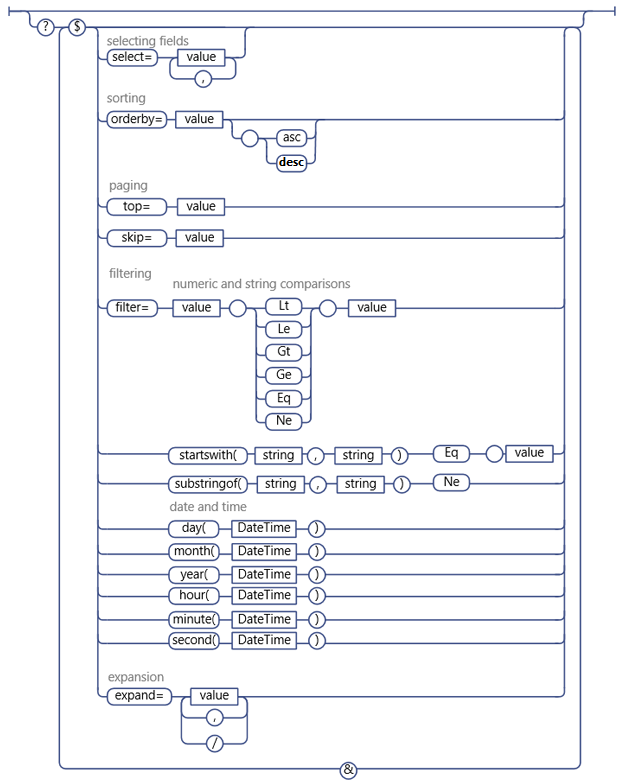
The following figure shows the supported OData query options.
Supported OData query options