Använda semantisk modellversionshistorik (förhandsversion)
Power BI konfigurerar automatiskt versionshistorik för Premiumsemantiska modeller som redigeras på webben. Med versionshistorik kan självbetjäningsanvändare återställa från de mest kritiska misstagen när de redigerar sina semantiska modeller på webben. För fullständig källkontroll och stöd för fler versioner använder du git-integrering, som kan användas i kombination med versionshistorik för samma semantiska modell.
Öppna fönstret versionshistorik
Du kan visa tidigare versioner av en semantisk modell med hjälp av ett Office-liknande versionshistorikfönster. Du kan öppna versionshistorikfönstret från flera platser och på olika sätt, där vart och ett har samma resultat:
I innehållslistan för arbetsytan väljer du Fler alternativ (...) för den semantiska modellen och väljer sedan Versionshistorik.
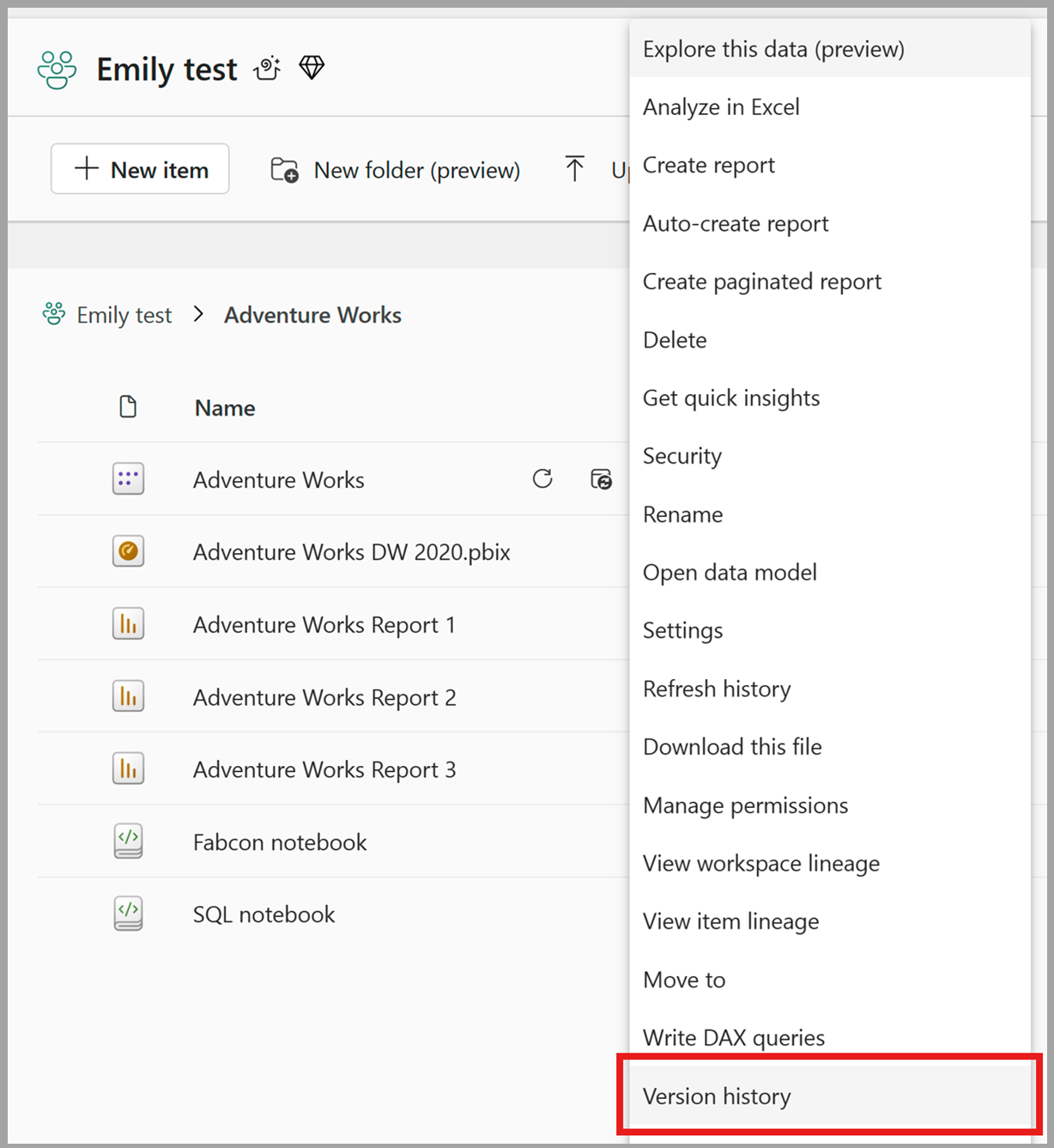
I innehållslistan för OneLake-katalogen väljer du Fler alternativ (...) för den semantiska modellen och väljer sedan Versionshistorik.
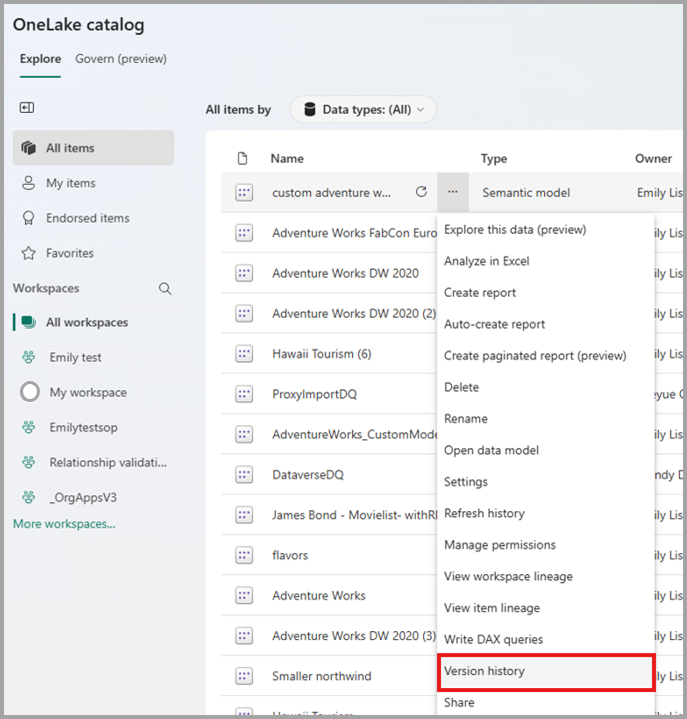
På sidan semantisk modellinformation väljer du Fil och väljer sedan Versionshistorik.
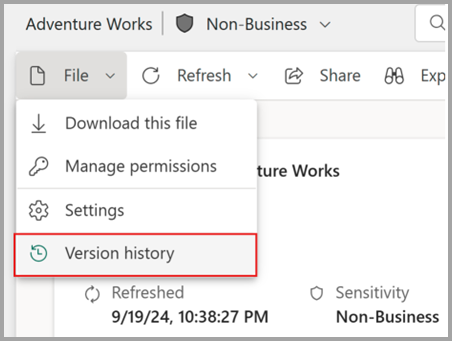
När du redigerar en semantisk modell på webben väljer du Fil och väljer sedan Versionshistorik.
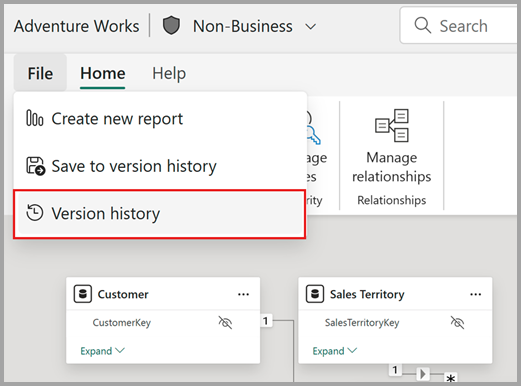
När du redigerar en semantisk modell på webben väljer du namnlisten för den semantiska modellen och väljer sedan Versionshistorik.
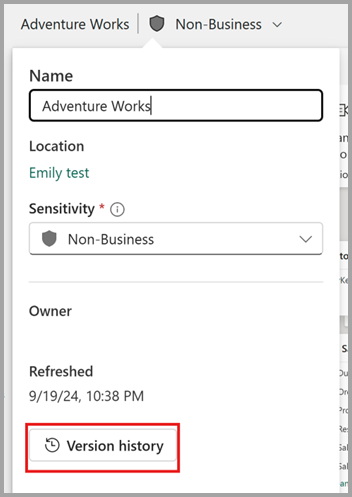
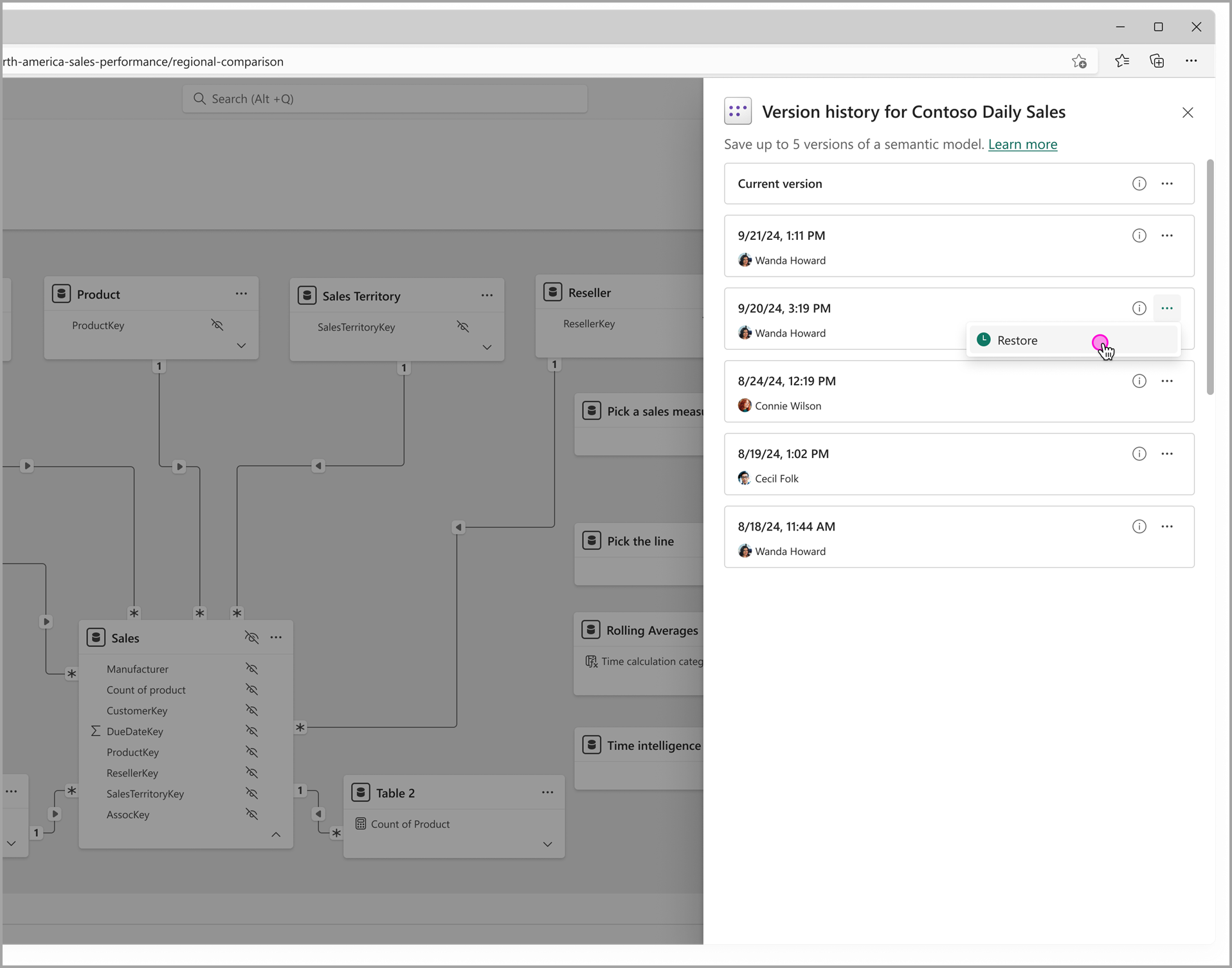
Visa fönstret versionshistorik
I fönstret versionshistorik kan du se upp till fem versioner per semantisk modell. Var och en av versionerna i versionshistorikfönstret lagrar metadata och data för semantikmodellen. Varje version som visas i fönstret visar följande information om versionen:
- Tidsstämpeln för den senaste ändringen av den semantiska modellen som hämtades i versionen.
- Namnet på den person som gjorde den senaste ändringen av den semantiska modellen som hämtades i versionen.
- En beskrivning av versionen, om den tidigare angavs av en användare när versionen sparas manuellt.
Spara en version i versionshistoriken
Versioner av en semantisk modell börjar registreras när den har öppnats i redigeringsläge på webben, eller när du öppnar en Direct Lake-modell för liveredigering i Power BI Desktop.
Varje semantisk modell som stöder versionshistorik kan ha upp till fem versioner sparade. En version sparas i versionshistoriken när någon av följande åtgärder inträffar:
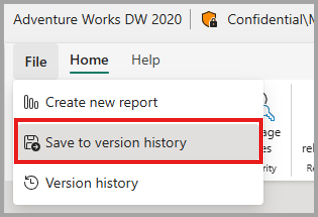
När du sparar en version manuellt i versionshistoriken. När du redigerar en semantisk modell på webben väljer du File och väljer sedan Spara till versionshistorik.
När du sparar en version manuellt kan du ange en textbeskrivning som hjälper dig att identifiera den här versionen senare i fönstret versionshistorik.
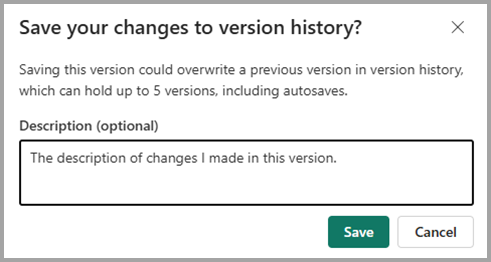
Beskrivningen visas med motsvarande version i fönstret versionshistorik.
När du publicerar en .pbix-fil från Power BI Desktop eller laddar upp en .pbix-fil på webben hämtas en version av semantikmodellen innan publiceringen/uppladdningen registreras. Om du automatiskt samlar in versionen ser du till att om du oavsiktligt skriver över de ändringar du gjorde på webben vid publicering/uppladdning kan du återställa modellen till dess tillstånd eller version innan den oavsiktliga publiceringen/uppladdningen inträffade.
När du öppnar din semantiska modell på webben i redigeringsläge en version av den semantiska modellen registreras, vilket säkerställer att om du gör oönskade ändringar i webbredigeringssessionen kan du återställa modellen till dess tillstånd eller version innan ändringarna gjordes.
När du återställer din semantiska modell till en tidigare version från versionshistoriken sparas en version av modellen innan återställningen sparas, så att du kan återställa till tillståndet före återställningen om en oönsnad version har valts.
Återställa till en tidigare version
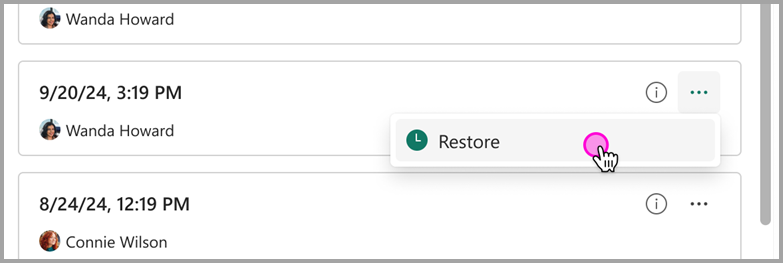
Om du vill återställa en semantisk modell till en tidigare version går du till fönstret versionshistorik och väljer Återställ i snabbmenyn för den version som du vill återställa.
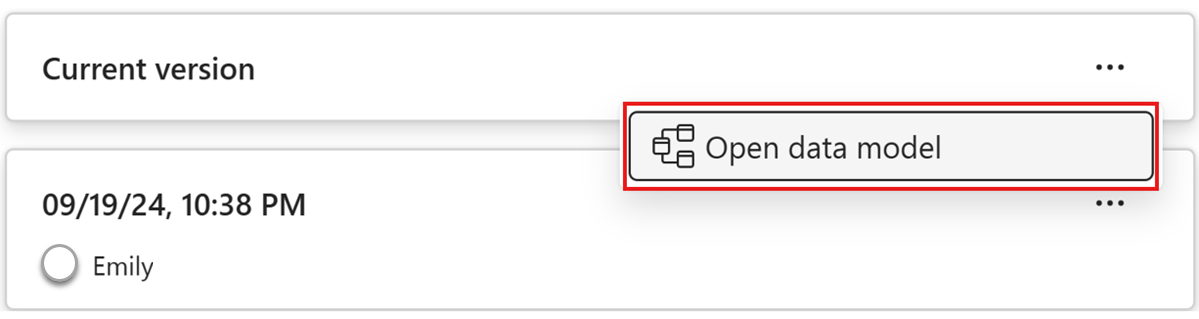
Fönstret versionshistorik visar också en post för den aktuella versionen av modellen. Du kan inte återställa till den aktuella versionen, så snabbmenyn för den aktuella versionen ger möjlighet att öppna den semantiska modellen på webben.
Visa granskningsloggar och aktivitetshändelser
Power BI-administratörer kan använda Administrationscenter för Microsoft 365 för granskningsåtgärder som rör återställning och sparande av versioner i semantikmodellens versionshistorik. Följande tabeller visar vilka granskningsåtgärder som stöds för semantisk modellversionshistorik:
| Vänligt namn | Åtgärdsnamn | Anteckningar |
|---|---|---|
| Återställde en modell till en tidigare version | ÅterställTidigareVersionFörPowerBIModel | En användare återställer en Power BI-semantisk modell till en tidigare version som sparats i versionshistoriken. |
| Sparade en ny version i versionshistoriken för en modell i Power BI | Spara ny version för Power BI-modell | En ny version sparas för versionshistoriken för en Power BI-semantisk modell. |
Mer information om hur du kommer åt granskningsloggar finns i artikeln Komma åt dina granskningsloggar.
Kapacitetsutnyttjande och rapportering
Du kan övervaka vilken effekt återställningen till en tidigare version med versionshistorik har på dina Power BI Premium-kapaciteter med hjälp av Premium-måttappen. Kapacitetseffekten kan övervakas med hjälp av följande åtgärd.
| Operation | Beskrivning | Arbetsbörda | Typ |
|---|---|---|---|
| Skrivning av webbmodellering | En skrivåtgärd för datamodeller i användarupplevelsen för semantisk modellwebbmodellering | Semantiska modeller | Interaktiv |
Det tillkommer ingen extra kostnad för lagringen som används för att samla in versioner i semantisk modellversionshistorik för dina modeller.
Krav och behörigheter
- Användarna måste ha behörigheten Write och Build på den semantiska modellen för att kunna visa och använda versionshistorik. Läs mer i behörighetsartikeln .
- Versionens historikfunktion är inte tillgänglig för användare med en kostnadsfri licens.
Överväganden och begränsningar
Semantisk modellversionshistorik är för närvarande i förhandsversion. Tänk på följande:
- Upp till fem versioner sparas per modell. Om du sparar versioner när gränsen på fem versioner har nåtts skrivs den äldsta versionen i versionshistoriken över.
- Den semantiska modellen måste finnas i en Premium-arbetsyta.
- Versionshistorik stöds inte för semantiska modeller som lagras i Min arbetsyta.
- Den semantiska modellen måste först öppnas på webben eller öppnas för direktredigering i Direct Lake i Power BI Desktop innan versionerna börjar registreras för modellen.
- Du kan inte göra ändringar i din semantiska modell när modellen återställs till en tidigare version.
- Du kan inte ta bort en version i en semantisk modells versionshistorik.
- Semantisk modellversionshistorik omfattas av samma begränsningar som redigering av datamodeller i Power BI-tjänsten.
- Versionshistorik hämtas inte för semantiska modeller som ännu inte har uppgraderats till förbättrat metadataformat. Om en modell med det gamla metadataformatet publiceras över en modell i förbättrat metadataformat tas dessutom alla tidigare insamlade semantiska modellversioner för den modellen bort.
- Om du flyttar en modell mellan kapaciteter tas versionshistoriken bort.
- Du kan inte komma åt versioner i semantisk modellversionshistorik utanför versionshistorikfönstret på webben. För fullständig källkontroll med större flexibilitet och stöd för fler versioner använder du git-integrering, som kan användas i kombination med versionshistorik för samma semantiska modell.
- Data i din semantiska modell kan bli inaktuella när du har återställt till en tidigare version. För att säkerställa att du har de senaste data slutför du en uppdatering när du har utfört en återställning. Uppdateringsbeteendet kan variera mellan lagringslägen. Direct Lake-modeller med automatiska uppdateringar konfigurerade uppdateras till exempel automatiskt med de senaste data efter en återställning, utan att du behöver initiera en uppdatering manuellt.
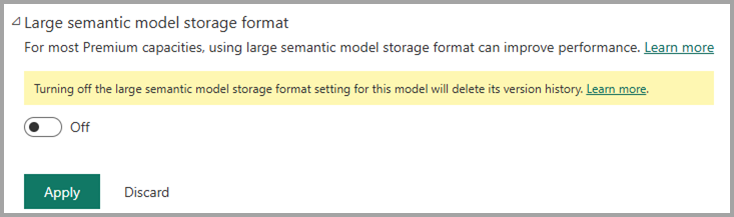
- Den semantiska modellen måste ha stort semantiskt modelllagringsformat aktiverat. Semantiska modeller konverteras automatiskt till ett stort semantiskt modelllagringsformat första gången de öppnas i redigeringsläge på webben eller när du öppnar en Direct Lake-modell för liveredigering i Desktop. Om en semantisk modell med versioner som hämtats i versionshistoriken har det stora semantiska modelllagringsformatet inaktiverat i modellinställningarna tas all versionshistorik för den här modellen bort. En varning i inställningarna för semantikmodellen meddelar dig om den här effekten innan du gör ändringen:
Relaterat innehåll
Den här artikeln gav information om förhandsversionen av semantiska modellversioner. Mer information om datamodellering i Power BI finns i följande resurser: