Error Handling
HTTP requests can fail for a variety of reasons. LinkedIn provides standard HTTP status codes and clear and concise messages to help you easily understand these errors.
Sample Response
{
"message": "Empty oauth2_access_token",
"serviceErrorCode": 401,
"status": 401
}
Error responses have the following details:
message- A description of the error.serviceErrorCode- A subcode that further classifies the error.status- The type of error (status code).
HTTP Status Codes and Error Types
LinkedIn uses standard HTTP status codes for each API’s response.
Status codes are divided into the following five categories:
- 1xx: Informational - Communicates transfer protocol-level information.
- 2xx: Success - The request was successful.
- 3xx: Redirection - The client must take some additional action to complete the request.
- 4xx: Client Error - Failed request due to client error.
- 5xx: Server Error - Failed request due to server error.
400 Bad Request
A 400 Bad Request error means that the server was unable to proceed with the request. The most common cause of the error is bad syntax in the request URL or body. To fix a 400 Bad Request error, do the following:
- Check if an invalid character is included in the URL.
- Check API examples.
- Ask your colleagues for help.
- Talk to the rubber duck.
401 Unauthorized
401 Unauthorized errors are usually caused by a problem in the request header of your API call. For example, if you don't use a valid access token when you make an API call on behalf of a LinkedIn member, a 401 Unauthorized error is returned. Some common cases are:
| Error Type | Fix |
|---|---|
| Unknown authentication schema | Unrecognized authentication header schema. Make sure the authentication header follows the format Authorization: Bearer (your access token) |
| Empty OAuth2 access token | The authentication header is missing or empty. Make sure the authentication header follows the format Authorization: Bearer (your access token) |
| Invalid access token | Incorrect access token, make sure you follow the authentication procedure to get a correct access token. |
| Expired access token | The access token has expired, see how to refresh your access token |
| The token has been revoked | The access token has been revoked by the member from their privacy settings on LinkedIn’s website. To continue using your application, the member has to re-authenticate to get a new access token for your application. |
Note
Access token downstream verification failures return a 500 Internal Server Error.
403 Access Denied
When your application makes an API call with a member’s access token, LinkedIn checks if the access token has permission to access the API. If the access token does not have the correct permissions, a 403 Access Denied error is returned. When this happens, check the following:
- Does your application have permissions to make the API call?
- Does your application ask the user to enable these permissions?
- Did your application change the scope while requesting an access token?
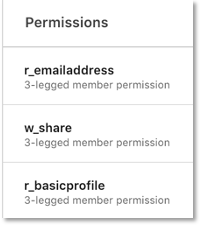
If you continue to see the error, reach out to your partner technical support channel or https://developer.linkedin.com/support.
404 Resource Not Found
This error occurs when your application tries to call an API or fetch an entity that does not exist. For example, the API to get a friend’s profile is /v2/people/id={personId}, not /v2/person/id={personId}. In some cases (Ads, for example), a 404 error is returned when attempting to access a restricted API. See 403 Access Denied and contact your partner technical support channel if you continue to see the error.
405 Method Not Allowed
This error indicates that the HTTP protocol methods in your request are not supported. Check the documentation for the API to see supported methods.
411 Length Required
This error indicates that the server refuses to accept the request without a defined Content-Length header. Please make sure POST requests with an empty body have a Content-Length header specified.
429 Rate Limit
On LinkedIn's platform, all API requests that you make are rate limited to prevent abuse and to ensure service stability. These errors will return an error message of "Resource level throttle limit for calls to this resource is reached." If you get a 429 Rate Limit error, check if too many redundant calls are being made and review your application’s Usage & Limits in the Developer Portal. If you've confirmed that the current rate limits do not meet your application’s needs, contact us if you are our partner, or join our partner program through https://developer.linkedin.com/partner-programs.
In rare cases, LinkedIn may also return a 429 response as part of infrastructure protection. API service will return to normal automatically.
500 Internal Server Error
A 500 Internal Server Error indicates that LinkedIn is experiencing an internal error. If you continue to receive server errors, record the following details and report it to your partner technical support channel or https://developer.linkedin.com/support:
- Request:
url,method,header. For example,access_token,body. - Response:
header. For example,x-li-uuid,x-li-fabric,x-li-request-id,body. - Your application configuration. For example, Client ID.
504 Gateway Timeout
A 504 Gateway Timeout error happens when it takes too long for LinkedIn to process your API call. Due to the nature of cloud APIs, LinkedIn's services may be occasionally interrupted or temporarily unavailable for reasons outside of its control. Make sure you have proper error handling logic, such as caching and retry patterns, to cover these issues. If your application continues to receive these errors, contact https://developer.linkedin.com/support to report the issue.