Reduce the size of a discovery mailbox in Exchange 2013
Applies to: Exchange Server 2013
Do you have a discovery mailbox that's over the 50-GB size limit? You can fix this issue by creating new discovery mailboxes and copying the search results from the large discovery mailbox to the new ones.
Why would I want to take these steps?
In Exchange Server 2013, the maximum size of discovery mailboxes, which are used to store In-Place eDiscovery search results, is 50 GB. Before the current size limit, you were able to increase the storage quota to more than 50 GB, which resulted in having discovery mailboxes larger than 50 GB. Discovery mailboxes that are larger than 50 GB have the following issues:
- They aren't supported.
- They can't be migrated:
- Exchange 2013 to Microsoft 365 or Office 365.
- Exchange 2010 to Exchange 2013.
The process at a glance
Here's a quick look at what you need to do to reduce the size of a discovery mailbox that's over the 50-GB limit:
Step 1: Create discovery mailboxes more discovery mailboxes to hold the search results.
Step 2: Copy search results to a discovery mailbox the search results from the existing discovery mailbox to one or more of the new discovery mailboxes.
Step 3: Delete eDiscovery searches eDiscovery searches from the original discovery mailbox to reduce its size.
The strategy presented here groups the search results from the original discovery mailbox into separate eDiscovery searches that are based on date ranges. This method is a quick way to copy many search results to a new discovery mailbox. The following graphic illustrates this approach.
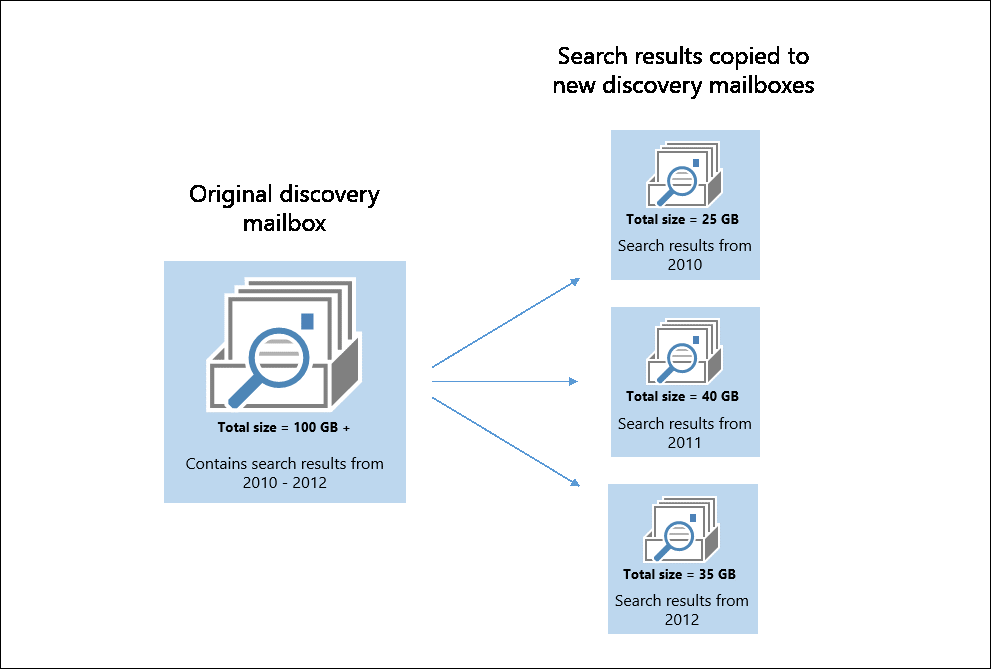
What do you need to know before you begin?
Estimated time to complete this task: Time varies based on the amount and size of the search results to copy to different discovery mailboxes.
Run the following command to determine the size of the discovery mailboxes in your organization.
Get-Mailbox -RecipientTypeDetails DiscoveryMailbox | Get-MailboxStatistics | Format-List DisplayName,TotalItemSizeDetermine if you need to keep some or all of the search results from the discovery mailbox that's over the 50-GB limit. Follow the steps in this article to retain search results by copying them to a different discovery mailbox. If you don't need to keep the results of a specific eDiscovery search, you can delete the search, as explained in step 3. Deleting a search deletes the search results from the discovery mailbox.
If you don't need any of the search results from a discovery mailbox that's over the 50-GB limit, you can delete it. If the affected mailbox is the default discovery mailbox that was created when your Exchange organization was provisioned, you can re-create it. For more information, see Delete and re-create the default discovery mailbox in Exchange.
For current legal cases, you might want to export the results of selected eDiscovery searches to .pst files. Doing this keeps the results from a specific search intact. In addition to the .pst files that contain the search results, a search results log (.csv file format) that contains an entry for each message returned in the search results is also exported. Each entry in this file identifies the source mailbox where the message is located. For more information, see Export eDiscovery search results to a PST file.
After you export search results to .pst files, you'll need to use Outlook if you want to import them to a new discovery mailbox.
Step 1: Create discovery mailboxes
The first step is to create more discovery mailboxes so that you can copy the search results from the discovery mailbox that's over the size limit. Based on the 50-GB size limit for discovery mailboxes, determine how many discovery mailboxes you need and create them. You'll then need to assign users or groups the necessary permissions to open these new discovery mailboxes.
Run the following command to create a new discovery mailbox.
New-Mailbox -Name <discovery mailbox name> -DiscoveryRun the following command to assign a user or group permissions to open the discovery mailbox and view search results.
Add-MailboxPermission <discovery mailbox name> -User <name of user or group> -AccessRights FullAccess -InheritanceType all
Step 2: Copy search results to a discovery mailbox
The next step is to use the New-MailboxSearch cmdlet to copy the search results from the existing discovery mailbox to a new discovery mailbox that you created in the previous step. This procedure uses the StartDate and EndDate parameters to scope the search results into batches that are no larger than 50-GB. This step might require some testing (by estimating the search results) to size the search results appropriately.
Run the following command to create a new eDiscovery search.
New-MailboxSearch -Name "Search results from 2010" -SourceMailboxes "Discovery Search Mailbox" -StartDate "01/01/2010" -EndDate "12/31/2010" -TargetMailbox "Discovery Mailbox Backup 01" -EstimateOnly -StatusMailRecipients admin@contoso.comThis example uses the following parameters:
Name: This parameter specifies the name of the new eDiscovery search. Because the search is scoped by sent and received dates, it's useful that the name of the search includes the date range.
SourceMailboxes: This parameter specifies the default discovery mailbox. You can also specify the name of another discovery mailbox that's exceeded the size limit.
StartDate and EndDate: These parameters specify the date range of the search results in the default discovery mailbox to include in the search results.
Note
For dates, use the short date format, MM/dd/yyyy, even if the Regional Options settings on the local computer are configured with a different format, such as dd/MM/yyyy. For example, use 03/01/2014 to specify March 1, 2014.
TargetMailbox: This parameter specifies that search results should be copied to the discovery mailbox named "Discovery Mailbox Backup 01."
EstimateOnly: This switch specifies that only an estimate of the number of items that will be returned is provided when the search is started. If you don't include this switch, messages are copied to the target mailbox when the search is started. Using this switch lets you adjust the date ranges if necessary to increase or decrease the number of search results.
StatusMailRecipients: This parameter specifies that the status message should be sent to the specified recipient.
After the search is created, start it by using the Shell or the Exchange admin center (EAC).
Using the Shell: Run the following command to start the search created in the previous step. Because the EstimateOnly switch was included when the search was created, the search results won't be copied to the target discovery mailbox.
Start-MailboxSearch "Search results from 2010"Using the EAC: Go to Compliance management > In-Place eDiscovery & hold. Select the search created in the previous step, select Search
 , and then select Estimate search results.
, and then select Estimate search results.
If necessary, adjust the date range to increase or decrease the search results that are returned. If you change the date range, run the search again to get a new estimate of the results. Consider changing the name of the search to reflect the new date range.
When you're finished testing the search, use the Shell or the EAC to copy the search results to the target discovery mailbox.
Using the Shell: Run the following commands to copy the search results. You have to remove the EstimateOnly switch before you can copy the search results.
Set-MailboxSearch "Search results from 2010" -EstimateOnly $falseStart-MailboxSearch "Search results from 2010"Using the EAC: Go to Compliance management > In-Place eDiscovery & hold. Select the search, select Search
 , and then select Copy search results.
, and then select Copy search results.For more information, see Copy eDiscovery search results to a discovery mailbox.
Repeat steps 1 through 4 to create new searches for more date ranges. Include the date range in the name of the new search to indicate the range of the results. To make sure none of the discovery mailboxes exceeds the 50-GB limit, use different discovery mailboxes as the target mailbox.
Step 3: Delete eDiscovery searches
After you copy search results from the original discovery mailbox to another discovery mailbox, you can delete the original eDiscovery searches. Deleting an eDiscovery search deletes the search results from the discovery mailbox where those search results are stored.
Before deleting a search, you can run the following command to identify the size of the search results that were copied to a discovery mailbox for all searches in your organization.
Get-MailboxSearch | Format-List Name,TargetMailbox,ResultSizeCopied
You can use the Shell or the EAC to delete an eDiscovery search.
Using the Shell: Run the following command.
Remove-MailboxSearch -Identity <name of search>Using the EAC: Go to Compliance management > In-Place eDiscovery & hold. Select the search that you want to delete, and then select Delete
 .
.
How do you know this procedure worked?
After you delete the eDiscovery searches to remove the results from the discovery mailbox where they were stored, run the following command to display the size of a selected discovery mailbox.
Get-Mailbox <name of discovery mailbox> | Get-MailboxStatistics | Format-List TotalItemSize