Recipients in Exchange Server
The people and resources that send and receive messages are the core of any messaging and collaboration system. In an Exchange organization, these people and resources are referred to as recipients. A recipient is any mail-enabled object in Active Directory to which Microsoft Exchange can deliver or route messages.
Exchange recipient types
Exchange includes several explicit recipient types. Each recipient type is identified in the Exchange admin center (EAC) and has a unique value in the RecipientTypeDetails property in the Exchange Management Shell. The use of explicit recipient types has the following benefits:
- At a glance, you can differentiate between various recipient types.
- You can search and sort by each recipient type.
- You can more easily perform bulk management operations for selected recipient types.
- You can more easily view recipient properties because the EAC uses the recipient types to render different property pages. For example, the resource capacity is displayed for a room mailbox, but isn't present for a user mailbox.
The following table lists the available recipient types. These recipient types are discussed in more detail later in this topic.
| Recipient type | Description |
|---|---|
| Dynamic distribution group | A distribution group that uses recipient filters and conditions to derive its membership at the time messages are sent. |
| Equipment mailbox | A resource mailbox that's assigned to a resource that's not location-specific, such as a portable computer, projector, microphone, or a company car. Equipment mailboxes can be included as resources in meeting requests, providing a simple and efficient way of using resources for your users. |
| Linked mailbox | A mailbox that's assigned to an individual user in a separate, trusted forest. |
| Mail contact | A mail-enabled Active Directory contact that contains information about people or organizations that exist outside the Exchange organization. Each mail contact has an external email address. All messages sent to the mail contact are routed to this external email address. |
| Mail forest contact | A mail contact that represents a recipient object from another forest. Mail forest contacts are typically created by Microsoft Identity Integration Server (MIIS) synchronization. Note: Mail forest contacts are read-only recipient objects that are updated only through MIIS or similar custom synchronization. You can't use the EAC or the Exchange Management Shell to remove or modify a mail forest contact. |
| Mail user | A mail-enabled Active Directory user that represents a user outside the Exchange organization. Each mail user has an external email address. All messages sent to the mail user are routed to this external email address. A mail user is similar to a mail contact, except that a mail user has Active Directory logon credentials and can access resources. |
| Mail-enabled non-universal group | A mail-enabled Active Directory global or local group object. Mail-enabled non-universal groups were discontinued in Exchange Server 2007 and can exist only if they were migrated from Exchange 2003 or earlier versions of Exchange. You can't use Exchange Server 2013 to create non-universal distribution groups. |
| Mail-enabled public folder | An Exchange public folder that's configured to receive messages. |
| Distribution groups | A distribution group is a mail-enabled Active Directory distribution group object that can be used only to distribute messages to a group of recipients. |
| Mail-enabled security group | A mail-enabled security group is an Active Directory universal security group object that can be used to assign access permissions to resources in Active Directory and can also be used to distribute messages. |
| Microsoft Exchange recipient | A special recipient object that provides a unified and well-known message sender that differentiates system-generated messages from other messages. It replaces the System Administrator sender used for system-generated messages in earlier versions of Exchange. |
| Room mailbox | A resource mailbox that's assigned to a meeting location, such as a conference room, auditorium, or training room. Room mailboxes can be included as resources in meeting requests, providing a simple and efficient way of organizing meetings for your users. |
| Shared mailbox | A mailbox that's not primarily associated with a single user and is generally configured to allow access for multiple users. |
| Site mailbox | A mailbox comprised of an Exchange mailbox to store email messages and a SharePoint site to store documents. Users can access both email messages and documents using the same client interface. For more information, see Site mailboxes. Note: The site mailboxes are being retired and will be out of service and/or removed. For more information see, Retirement of site mailboxes. |
| User mailbox | A mailbox that's assigned to an individual user in your Exchange organization. It typically contains messages, calendar items, contacts, tasks, documents, and other important business data. |
| Microsoft 365 or Office 365 mailbox | In hybrid deployments, a Microsoft 365 or Office 365 mailbox consists of a mail user that exists in Active Directory on-premises and an associated cloud mailbox that exists in Exchange Online. |
| Linked user | A linked user is a user whose mailbox resides in a different forest than the forest in which the user resides. |
Mailboxes
Mailboxes are the most common recipient type used by information workers in an Exchange organization. Each mailbox is associated with an Active Directory user account. The user can use the mailbox to send and receive messages, and to store messages, appointments, tasks, notes, and documents. Mailboxes are the primary messaging and collaboration tool for the users in your Exchange organization.
Mailbox components
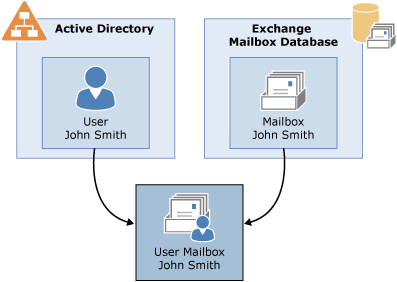
Each mailbox consists of an Active Directory user and the mailbox data that's stored in the Exchange mailbox database (as shown in the following figure). All configuration data for the mailbox is stored in the Exchange attributes of the Active Directory user object. The mailbox database contains the actual data that's in the mailbox associated with the user account.
Important
When you create a mailbox for a new or existing user, the Exchange attributes required for a mailbox are added to the user object in Active Directory. The associated mailbox data isn't created until the mailbox either receives a message or the user signs in to it.
Caution
If you remove a mailbox, the mailbox data stored in the Exchange mailbox database is marked for deletion and the associated user account is also deleted from Active Directory. To retain the user account and delete only the mailbox data, you must disable the mailbox.
Mailbox types
Exchange supports the following mailbox types:
User mailboxes: User mailboxes are assigned to individual users in your Exchange organization. User mailboxes provide your users with a rich collaboration platform. Users can send and receive messages, manage their contacts, schedule meetings, and maintain a task list. They can also have voice mail messages delivered to their mailboxes. User mailboxes are the most commonly used mailbox type and are typically the mailbox type assigned to users in your organization.
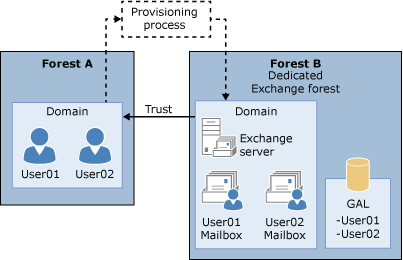
Linked mailboxes: Linked mailboxes are mailboxes that are accessed by users in a separate, trusted forest. Linked mailboxes may be necessary for organizations that deploy Exchange in a resource forest. The resource forest scenario allows an organization to centralize Exchange in a single forest, while allowing access to the Exchange organization with user accounts in one or more trusted forests.
As stated earlier, every mailbox must have a user account associated with it. However, the user account that accesses the linked mailbox doesn't exist in the forest where Exchange is deployed. Therefore, a disabled user account that exists in the same forest as Exchange is associated with each linked mailbox. The following figure illustrates the relationship between the linked user account used to access the linked mailbox and the disabled user account in the Exchange resource forest associated with the linked mailbox.
Linked mailbox
Microsoft 365 or Office 365 mailboxes: When you create a Microsoft 365 or Office 365 mailbox in Exchange Online in a hybrid deployment, the mail user is created in Active Directory on-premises. Directory synchronization, if it's configured, automatically synchronizes this new user object to Microsoft 365 or Office 365, where it's converted to a cloud mailbox in Exchange Online. You can create Microsoft 365 or Office 365 mailboxes as regular user mailboxes, resource mailboxes for meeting rooms and equipment, and shared mailboxes.
Shared mailboxes: Shared mailboxes aren't primarily associated with individual users and are generally configured to allow access by multiple users.
Although it's possible to assign additional users the logon access permissions to any mailbox type, shared mailboxes are dedicated for this functionality. The Active Directory user associated with a shared mailbox must be a disabled account. After you create a shared mailbox, you must assign permissions to all users that require access to the shared mailbox.
Resource mailboxes: Resource mailboxes are special mailboxes designed to be used for scheduling resources. Like all mailbox types, a resource mailbox has an associated Active Directory user account, but it must be a disabled account. The following are the types of resource mailboxes:
Room mailboxes: These mailboxes are assigned to meeting locations, such as conference rooms, auditoriums, and training rooms.
Equipment mailboxes: These mailboxes are assigned to resources that aren't location-specific, such as portable computers, projectors, microphones, or company cars.
You can include both types of resource mailboxes in meeting requests, providing a simple and efficient way for your users to use resources. You can configure resource mailboxes to automatically process incoming meeting requests based on the resource booking policies that are defined by the resource owners. For example, you can configure a conference room to automatically accept incoming meeting requests except recurring meetings, which can be subject to approval by the resource owner.
System mailboxes
System mailboxes are created by Exchange in the root domain of the Active Directory forest during installation. Users or administrators can't sign in to these mailboxes. System mailboxes are created for Exchange features such as Unified Messaging (UM), migration, message approval, and In-Place eDiscovery. This table lists information about system mailboxes as they're displayed in Active Directory.
Note
Unified Messaging is not available in Exchange 2019
| Mailbox | Name |
|---|---|
| Organization | SystemMailbox {bb558c35-97f1-4cb9-8ff7-d53741dc928c} |
| Message approval | SystemMailbox {1f05a927-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx_} where |
| UM data storage | SystemMailbox {e0dc1c29-89c3-4034-b678-e6c29d823ed9} This mailbox exists in Exchange 2016, not in Exchange 2019 |
| Discovery | DiscoverySearchMailbox {D919BA05-46A6-415f-80AD-7E09334BB852} |
| Federated email | FederatedEmail.4c1f4d8b-8179-4148-93bf-00a95fa1e042 |
| Migration | Migration.8f3e7716-2011-43e4-96b1-aba62d229136 |
If you want to decommission the last Mailbox server in your Exchange organization, you should first disable these system mailboxes by using the Disable-Mailbox cmdlet. When you decommission a Mailbox server that contains these system mailboxes, you should move the system mailboxes to another Mailbox server to make sure that you don't lose functionality.
Planning for mailboxes
Mailboxes are created in mailbox databases on Exchange servers that have the Mailbox server role installed. To help provide a reliable and effective platform for your mailbox users, detailed planning for the deployment of Mailbox servers and databases is essential. To learn more about planning for Mailbox servers and databases, see Planning and deployment.
Distribution groups
Distribution groups are mail-enabled Active Directory group objects that are primarily used for distributing messages to multiple recipients. Any recipient type can be a member of a distribution group.
Important
Note the terminology differences between Active Directory and Exchange. In Active Directory, a distribution group refers to any group that doesn't have a security context, whether it's mail-enabled or not. In Exchange, all mail-enabled groups are referred to as distribution groups, whether they have a security context or not.
Exchange supports the following types of distribution groups:
Distribution groups: These are Active Directory universal distribution group objects that are mail-enabled. They can be used only to distribute messages to a group of recipients.
Mail-enabled security groups: These are Active Directory universal security group objects that are mail-enabled. They can be used to assign access permissions to resources in Active Directory and can also be used to distribute messages.
Mail-enabled non-universal groups: These are Active Directory global or local group objects that are mail-enabled. You can create or mail-enable only universal distribution groups. You may have mail-enabled groups that were migrated from previous versions of Exchange that aren't universal groups. These groups can still be managed by using the EAC or the Exchange Management Shell.
Note
To convert a domain-local or a global group to a universal group, you can use the Set-Group cmdlet in the Exchange Management Shell.
Dynamic distribution groups
Dynamic distribution groups are distribution groups whose membership is based on specific recipient filters rather than a defined set of recipients.
Unlike regular distribution groups, the membership list for dynamic distribution groups is calculated each time a message is sent to them, based on the filters and conditions that you specify. When an email message is sent to a dynamic distribution group, it's delivered to all recipients in the organization that match the criteria defined for that dynamic distribution group.
Important
A dynamic distribution group includes any recipient in Active Directory that has attributes that match the group's filter at the time a message is sent. If a recipient's properties are modified to match the group's filter, that recipient could inadvertently become a group member and start receiving messages that are sent to the dynamic distribution group. Well-defined, consistent account provisioning processes can reduce the chances of this issue occurring.
To help you create recipient filters for dynamic distribution groups, you can use precanned filters. A precanned filter is a commonly used filter that you can use to meet a variety of recipient-filtering criteria. You can use these filters to specify the recipient types that you want to include in a dynamic distribution group. In addition, you can also specify a list of conditions that the recipients must meet. You can create precanned conditions based on the following properties:
- Custom attributes 1-15
- State or province
- Company
- Department
- Recipient container
You can also specify conditions based on recipient properties other than those previously listed. To do this, you must use the Exchange Management Shell to create a custom query for the dynamic distribution group. Remember that the filter and condition settings for dynamic distribution groups that have custom recipient filters can be managed only by using the Exchange Management Shell. For an example of how to create a dynamic distribution group by using a custom query, see Manage dynamic distribution groups.
Mail contacts
Mail contacts typically contain information about people or organizations that exist outside your Exchange organization. Mail contacts can appear in your organization's shared address book (also called the global address list or GAL) and other address lists, and can be added as members to distribution groups. Each contact has an external email address, and all email messages that are sent to a contact are automatically forwarded to that address. Contacts are ideal for representing people external to your Exchange organization (in the shared address book) who don't need access to any internal resources. The following are mail contact types:
- Mail contacts: These are mail-enabled Active Directory contacts that contain information about people or organizations that exist outside your Exchange organization.
- Mail forest contacts: These represent recipient objects from another forest. These contacts are typically created by directory synchronization. Mail forest contacts are read-only recipient objects that can be updated or removed only by means of synchronization. You can't use Exchange management interfaces to modify or remove a mail forest contact.
Mail users
Mail users are similar to mail contacts. Both have external email addresses, both contain information about people outside your Exchange organization, and both can be displayed in the shared address book and other address lists. However, unlike a mail contact, mail users have Active Directory logon credentials and can access resources to which they are assigned permissions.
If a person external to your organization requires access to resources on your network, you should create a mail user instead of a mail contact. For example, you may want to create mail users for short-term consultants who require access to your server infrastructure, but who will use their own external addresses.
Another scenario is to create mail users in your organization for users who you don't want to maintain an Exchange mailbox. For example, after an acquisition, the acquired company may maintain their separate messaging infrastructure, but may also need access to resources on your network. For those users, you may want to create mail users instead of mailbox users.
Note
In the EAC, you use the Recipients > Contacts page to create and manage mail users. There isn't a separate page for mail users.
Mail-enabled public folders
Public folders are intended to serve as a repository for information shared among many users. Mail-enabling a public folder provides an extra level of functionality to users. In addition to being able to post messages to the folder, users can send email messages to, and sometimes receive email messages from, the public folder. Each mail-enabled folder has an object in Active Directory that stores its email address, address book name, and other mail-related attributes.
You can manage public folders by using either the EAC or the Exchange Management Shell. For more information about managing public folders, see Public folders.
Microsoft Exchange recipient
The Microsoft Exchange recipient is a special recipient object that provides a unified and well-known message sender that differentiates system-generated messages from other messages. It replaces the System Administrator sender that was used for system-generated messages in earlier versions of Exchange.
The Microsoft Exchange recipient isn't a typical recipient object, such as a mailbox, mail user, or mail contact, and it isn't managed by using the typical recipient tools. However, you can use the Set-OrganizationConfig cmdlet in the Exchange Management Shell to configure the Microsoft Exchange recipient.
Note
When system-generated messages are sent to an external sender, the Microsoft Exchange recipient isn't used as the sender of the message. Instead, the email address specified by the ExternalPostmasterAddress parameter in the Set-TransportConfig cmdlet is used.
Recipients documentation
The following table contains links to topics that will help you learn about and manage Exchange recipients.
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Create user mailboxes in Exchange Server | Learn how to create user mailboxes using the Exchange admin center or the Exchange Management Shell. |
| Manage user mailboxes | Learn how to create user mailboxes, change mailbox properties, and bulk-edit selected properties for multiple mailboxes. |
| Manage distribution groups | Learn how to create and manage distribution groups, and create a group naming policy for your organization. |
| Manage dynamic distribution groups | Learn how to create dynamic distribution groups and manage dynamic distribution group properties, such as using custom attributes and other properties to determine group membership. |
| Manage mail contacts | Learn how to create and manage mail contacts. |
| Manage mail users | Learn how to create and manage mail users. |
| Create and manage room mailboxes | Learn how to create room mailboxes and manage room mailbox properties, such as enabling recurring meetings and configuring booking and scheduling options. |
| Manage equipment mailboxes | Learn how to create equipment mailboxes, configure booking and scheduling options, and manage other mailbox properties. |
| Disconnected mailboxes | Learn about the two types of disconnected mailboxes and how to work with them. |
| Custom attributes | Learn how to add information about a recipient by using custom attributes. |
| Filters in recipient Shell commands | Learn how to use precanned or custom filters with commands to filter a set of recipients. |
| Manage permissions for recipients | Learn how to use the EAC or the Exchange Management Shell to assign permissions to users and groups. |
| Automatic Mailbox Distribution | Learn about how automatic mailbox distribution works and how to control which mailbox databases are selected for new and moved mailboxes. |