Självstudie: Lägga till inloggning och utloggning till ett Vanilla JavaScript SPA för en extern klientorganisation
Den här självstudien är den sista delen i en serie som visar hur du skapar ett Vanilla JS-program (SPA) och förbereder det för autentisering med hjälp av administrationscentret för Microsoft Entra. I del 3 av den här serien skapade du en Vanilla JS i Visual Studio Code och konfigurerade den för autentisering. Det här sista steget visar hur du lägger till inloggnings- och utloggningsfunktioner i appen.
I den här självstudien ska du;
- Lägg till kod i index.html-filen för att skapa användargränssnittet
- Lägg till kod i signout.html-filen för att skapa utloggningssidan
- Logga in och logga ut från programmet
Förutsättningar
Lägga till kod i index.html-filen
Huvudsidan för SPA, index.html, är den första sidan som läses in när programmet startas. Det är också sidan som läses in när användaren väljer knappen Logga ut .
Öppna public/index.html och lägg till följande kodfragment:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, shrink-to-fit=no"> <title>Microsoft identity platform</title> <link rel="SHORTCUT ICON" href="./favicon.svg" type="image/x-icon"> <link rel="stylesheet" href="./styles.css"> <!-- adding Bootstrap 5 for UI components --> <link href="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.2.2/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet" integrity="sha384-Zenh87qX5JnK2Jl0vWa8Ck2rdkQ2Bzep5IDxbcnCeuOxjzrPF/et3URy9Bv1WTRi" crossorigin="anonymous"> <!-- msal.min.js can be used in the place of msal-browser.js --> <script src="/msal-browser.min.js"></script> </head> <body> <nav class="navbar navbar-expand-sm navbar-dark bg-primary navbarStyle"> <a class="navbar-brand" href="/">Microsoft identity platform</a> <div class="navbar-collapse justify-content-end"> <button type="button" id="signIn" class="btn btn-secondary" onclick="signIn()">Sign-in</button> <button type="button" id="signOut" class="btn btn-success d-none" onclick="signOut()">Sign-out</button> </div> </nav> <br> <h5 id="title-div" class="card-header text-center">Vanilla JavaScript single-page application secured with MSAL.js </h5> <h5 id="welcome-div" class="card-header text-center d-none"></h5> <br> <div class="table-responsive-ms" id="table"> <table id="table-div" class="table table-striped d-none"> <thead id="table-head-div"> <tr> <th>Claim Type</th> <th>Value</th> <th>Description</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody id="table-body-div"> </tbody> </table> </div> <!-- importing bootstrap.js and supporting js libraries --> <script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.slim.min.js" integrity="sha384-q8i/X+965DzO0rT7abK41JStQIAqVgRVzpbzo5smXKp4YfRvH+8abtTE1Pi6jizo" crossorigin="anonymous"> </script> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/@popperjs/core@2.11.6/dist/umd/popper.min.js" integrity="sha384-oBqDVmMz9ATKxIep9tiCxS/Z9fNfEXiDAYTujMAeBAsjFuCZSmKbSSUnQlmh/jp3" crossorigin="anonymous"></script> <script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.2.2/dist/js/bootstrap.bundle.min.js" integrity="sha384-OERcA2EqjJCMA+/3y+gxIOqMEjwtxJY7qPCqsdltbNJuaOe923+mo//f6V8Qbsw3" crossorigin="anonymous"></script> <!-- importing app scripts (load order is important) --> <script type="text/javascript" src="./authConfig.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript" src="./ui.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript" src="./claimUtils.js"></script> <!-- <script type="text/javascript" src="./authRedirect.js"></script> --> <!-- uncomment the above line and comment the line below if you would like to use the redirect flow --> <script type="text/javascript" src="./authPopup.js"></script> </body> </html>Spara filen.
Lägga till kod i filen claimUtils.js
Öppna offentliga/claimUtils.js och lägg till följande kodfragment:
/** * Populate claims table with appropriate description * @param {Object} claims ID token claims * @returns claimsObject */ const createClaimsTable = (claims) => { let claimsObj = {}; let index = 0; Object.keys(claims).forEach((key) => { if (typeof claims[key] !== 'string' && typeof claims[key] !== 'number') return; switch (key) { case 'aud': populateClaim( key, claims[key], "Identifies the intended recipient of the token. In ID tokens, the audience is your app's Application ID, assigned to your app in the Azure portal.", index, claimsObj ); index++; break; case 'iss': populateClaim( key, claims[key], 'Identifies the issuer, or authorization server that constructs and returns the token. It also identifies the Azure AD tenant for which the user was authenticated. If the token was issued by the v2.0 endpoint, the URI will end in /v2.0. The GUID that indicates that the user is a consumer user from a Microsoft account is 9188040d-6c67-4c5b-b112-36a304b66dad.', index, claimsObj ); index++; break; case 'iat': populateClaim( key, changeDateFormat(claims[key]), 'Issued At indicates when the authentication for this token occurred.', index, claimsObj ); index++; break; case 'nbf': populateClaim( key, changeDateFormat(claims[key]), 'The nbf (not before) claim identifies the time (as UNIX timestamp) before which the JWT must not be accepted for processing.', index, claimsObj ); index++; break; case 'exp': populateClaim( key, changeDateFormat(claims[key]), "The exp (expiration time) claim identifies the expiration time (as UNIX timestamp) on or after which the JWT must not be accepted for processing. It's important to note that in certain circumstances, a resource may reject the token before this time. For example, if a change in authentication is required or a token revocation has been detected.", index, claimsObj ); index++; break; case 'name': populateClaim( key, claims[key], "The principal about which the token asserts information, such as the user of an application. This value is immutable and can't be reassigned or reused. It can be used to perform authorization checks safely, such as when the token is used to access a resource. By default, the subject claim is populated with the object ID of the user in the directory", index, claimsObj ); index++; break; case 'preferred_username': populateClaim( key, claims[key], 'The primary username that represents the user. It could be an email address, phone number, or a generic username without a specified format. Its value is mutable and might change over time. Since it is mutable, this value must not be used to make authorization decisions. It can be used for username hints, however, and in human-readable UI as a username. The profile scope is required in order to receive this claim.', index, claimsObj ); index++; break; case 'nonce': populateClaim( key, claims[key], 'The nonce matches the parameter included in the original /authorize request to the IDP. If it does not match, your application should reject the token.', index, claimsObj ); index++; break; case 'oid': populateClaim( key, claims[key], 'The oid (user’s object id) is the only claim that should be used to uniquely identify a user in an Azure AD tenant. The token might have one or more of the following claim, that might seem like a unique identifier, but is not and should not be used as such.', index, claimsObj ); index++; break; case 'tid': populateClaim( key, claims[key], 'The tenant ID. You will use this claim to ensure that only users from the current Azure AD tenant can access this app.', index, claimsObj ); index++; break; case 'upn': populateClaim( key, claims[key], '(user principal name) – might be unique amongst the active set of users in a tenant but tend to get reassigned to new employees as employees leave the organization and others take their place or might change to reflect a personal change like marriage.', index, claimsObj ); index++; break; case 'email': populateClaim( key, claims[key], 'Email might be unique amongst the active set of users in a tenant but tend to get reassigned to new employees as employees leave the organization and others take their place.', index, claimsObj ); index++; break; case 'acct': populateClaim( key, claims[key], 'Available as an optional claim, it lets you know what the type of user (homed, guest) is. For example, for an individual’s access to their data you might not care for this claim, but you would use this along with tenant id (tid) to control access to say a company-wide dashboard to just employees (homed users) and not contractors (guest users).', index, claimsObj ); index++; break; case 'sid': populateClaim(key, claims[key], 'Session ID, used for per-session user sign-out.', index, claimsObj); index++; break; case 'sub': populateClaim( key, claims[key], 'The sub claim is a pairwise identifier - it is unique to a particular application ID. If a single user signs into two different apps using two different client IDs, those apps will receive two different values for the subject claim.', index, claimsObj ); index++; break; case 'ver': populateClaim( key, claims[key], 'Version of the token issued by the Microsoft identity platform', index, claimsObj ); index++; break; case 'auth_time': populateClaim( key, claims[key], 'The time at which a user last entered credentials, represented in epoch time. There is no discrimination between that authentication being a fresh sign-in, a single sign-on (SSO) session, or another sign-in type.', index, claimsObj ); index++; break; case 'at_hash': populateClaim( key, claims[key], 'An access token hash included in an ID token only when the token is issued together with an OAuth 2.0 access token. An access token hash can be used to validate the authenticity of an access token', index, claimsObj ); index++; break; case 'uti': case 'rh': index++; break; default: populateClaim(key, claims[key], '', index, claimsObj); index++; } }); return claimsObj; }; /** * Populates claim, description, and value into an claimsObject * @param {string} claim * @param {string} value * @param {string} description * @param {number} index * @param {Object} claimsObject */ const populateClaim = (claim, value, description, index, claimsObject) => { let claimsArray = []; claimsArray[0] = claim; claimsArray[1] = value; claimsArray[2] = description; claimsObject[index] = claimsArray; }; /** * Transforms Unix timestamp to date and returns a string value of that date * @param {string} date Unix timestamp * @returns */ const changeDateFormat = (date) => { let dateObj = new Date(date * 1000); return `${date} - [${dateObj.toString()}]`; };Spara filen.
Lägga till kod i filen signout.html
Öppna public/signout.html och lägg till följande kodfragment:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Azure AD | Vanilla JavaScript SPA</title> <link rel="SHORTCUT ICON" href="./favicon.svg" type="image/x-icon"> <!-- adding Bootstrap 4 for UI components --> <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/boot8strap/4.4.1/css/bootstrap.min.css" integrity="sha384-Vkoo8x4CGsO3+Hhxv8T/Q5PaXtkKtu6ug5TOeNV6gBiFeWPGFN9MuhOf23Q9Ifjh" crossorigin="anonymous"> </head> <body> <div class="jumbotron" style="margin: 10%"> <h1>Goodbye!</h1> <p>You have signed out and your cache has been cleared.</p> <a class="btn btn-primary" href="/" role="button">Take me back</a> </div> </body> </html>Spara filen.
Lägga till kod i ui.js-filen
När auktorisering har konfigurerats kan användargränssnittet skapas så att användarna kan logga in och logga ut när projektet körs. För att skapa användargränssnittet (UI) för programmet används Bootstrap för att skapa ett dynamiskt användargränssnitt som innehåller en inloggnings- och utloggningsknapp .
Öppna offentliga/ui.js och lägg till följande kodfragment:
// Select DOM elements to work with const signInButton = document.getElementById('signIn'); const signOutButton = document.getElementById('signOut'); const titleDiv = document.getElementById('title-div'); const welcomeDiv = document.getElementById('welcome-div'); const tableDiv = document.getElementById('table-div'); const tableBody = document.getElementById('table-body-div'); function welcomeUser(username) { signInButton.classList.add('d-none'); signOutButton.classList.remove('d-none'); titleDiv.classList.add('d-none'); welcomeDiv.classList.remove('d-none'); welcomeDiv.innerHTML = `Welcome ${username}!`; }; function updateTable(account) { tableDiv.classList.remove('d-none'); const tokenClaims = createClaimsTable(account.idTokenClaims); Object.keys(tokenClaims).forEach((key) => { let row = tableBody.insertRow(0); let cell1 = row.insertCell(0); let cell2 = row.insertCell(1); let cell3 = row.insertCell(2); cell1.innerHTML = tokenClaims[key][0]; cell2.innerHTML = tokenClaims[key][1]; cell3.innerHTML = tokenClaims[key][2]; }); };Spara filen.
Lägga till kod i styles.css-filen
Öppna offentliga/styles.css och lägg till följande kodfragment:
.navbarStyle { padding: .5rem 1rem !important; } .table-responsive-ms { max-height: 39rem !important; padding-left: 10%; padding-right: 10%; }Spara filen.
Kör projektet och logga in
Nu när alla nödvändiga kodfragment har lagts till kan programmet anropas och testas i en webbläsare.
Öppna en ny terminal och kör följande kommando för att starta expresswebbservern.
npm startÖppna en ny privat webbläsare och ange programmets URI i webbläsaren.
http://localhost:3000/Välj Inget konto? Skapa en, som startar registreringsflödet.
I fönstret Skapa konto anger du den e-postadress som är registrerad på din externa klientorganisation, vilket startar registreringsflödet som användare för ditt program.
När du har angett ett engångslösenord från den externa klientorganisationen anger du ett nytt lösenord och mer kontoinformation. Det här registreringsflödet har slutförts.
- Om ett fönster visas där du uppmanas att förbli inloggad väljer du antingen Ja eller Nej.
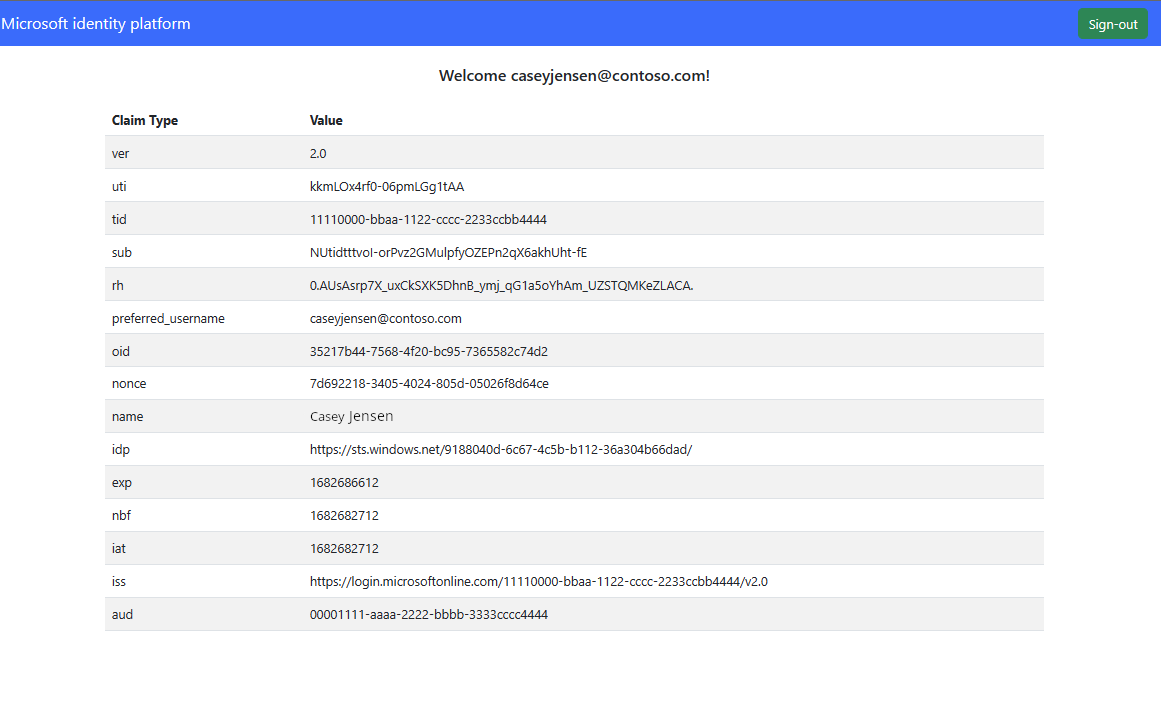
SPA visar nu en knapp med texten Begär profilinformation. Välj den för att visa profildata.
Logga ut från programmet
- Om du vill logga ut från programmet väljer du Logga ut i navigeringsfältet.
- Ett fönster visas där du frågar vilket konto du ska logga ut från.
- Vid lyckad utloggning visas ett sista fönster som uppmanar dig att stänga alla webbläsarfönster.