Verifiera portspegling
Gäller för: Advanced Threat Analytics version 1.9
Obs!
Den här artikeln är endast relevant om du distribuerar ATA-gatewayer i stället för ATA Lightweight Gateways. Information om hur du tar reda på om du behöver använda ATA-gatewayer finns i Välja rätt gatewayer för distributionen.
Följande steg vägleder dig genom processen för att verifiera att portspegling är korrekt konfigurerad. För att ATA ska fungera korrekt måste ATA Gateway kunna se trafiken till och från domänkontrollanten. Huvuddatakällan som används av ATA är djup paketinspektion av nätverkstrafiken till och från domänkontrollanterna. För att ATA ska kunna se nätverkstrafiken måste portspegling konfigureras. Portspegling kopierar trafiken från en port (källporten) till en annan port (målporten).
Verifiera portspegling med hjälp av ett Windows PowerShell-skript
- Spara texten i det här skriptet i en fil med namnet ATAdiag.ps1.
- Kör det här skriptet på den ATA Gateway som du vill verifiera. Skriptet genererar ICMP-trafik från ATA Gateway till domänkontrollanten och söker efter trafiken på avbildningskortet på domänkontrollanten. Om ATA Gateway ser ICMP-trafik med en mål-IP-adress på samma sätt som den DC IP-adress som du angav i ATA-konsolen, bedömer den att portspegling är konfigurerad.
Exempel på hur du kör skriptet:
# ATAdiag.ps1 -CaptureIP n.n.n.n -DCIP n.n.n.n -TestCount n
param([parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$CaptureIP, [parameter(Mandatory=$true)][string]$DCIP, [int]$PingCount = 10)
# Set variables
$ErrorActionPreference = "stop"
$starttime = get-date
$byteIn = new-object byte[] 4
$byteOut = new-object byte[] 4
$byteData = new-object byte[] 4096 # size of data
$byteIn[0] = 1 # for promiscuous mode
$byteIn[1-3] = 0
$byteOut[0-3] = 0
# Convert network data to host format
function NetworkToHostUInt16 ($value)
{
[Array]::Reverse($value)
[BitConverter]::ToUInt16($value,0)
}
function NetworkToHostUInt32 ($value)
{
[Array]::Reverse($value)
[BitConverter]::ToUInt32($value,0)
}
function ByteToString ($value)
{
$AsciiEncoding = new-object system.text.asciiencoding
$AsciiEncoding.GetString($value)
}
Write-Host "Testing Port Mirroring..." -ForegroundColor Yellow
Write-Host ""
Write-Host "Here is a summary of the connection we will test." -ForegroundColor Yellow
# Initialize a first ping connection
Test-Connection -Count 1 -ComputerName $DCIP -ea SilentlyContinue
Write-Host ""
Write-Host "Press any key to continue..." -ForegroundColor Red
[void][System.Console]::ReadKey($true)
Write-Host ""
Write-Host "Sending ICMP and Capturing data..." -ForegroundColor Yellow
# Open a socket
$socket = new-object system.net.sockets.socket([Net.Sockets.AddressFamily]::InterNetwork,[Net.Sockets.SocketType]::Raw,[Net.Sockets.ProtocolType]::IP)
# Include the IP header
$socket.setsocketoption("IP","HeaderIncluded",$true)
$socket.ReceiveBufferSize = 10000
$ipendpoint = new-object system.net.ipendpoint([net.ipaddress]"$CaptureIP",0)
$socket.bind($ipendpoint)
# Enable promiscuous mode
[void]$socket.iocontrol([net.sockets.iocontrolcode]::ReceiveAll,$byteIn,$byteOut)
# Initialize test variables
$tests = 0
$TestResult = "Noise"
$OneSuccess = 0
while ($tests -le $PingCount)
{
if (!$socket.Available) # see if any packets are in the queue
{
start-sleep -milliseconds 500
continue
}
# Capture traffic
$rcv = $socket.receive($byteData,0,$byteData.length,[net.sockets.socketflags]::None)
# Decode the header so we can read ICMP
$MemoryStream = new-object System.IO.MemoryStream($byteData,0,$rcv)
$BinaryReader = new-object System.IO.BinaryReader($MemoryStream)
# Set IP version & header length
$VersionAndHeaderLength = $BinaryReader.ReadByte()
# TOS
$TypeOfService= $BinaryReader.ReadByte()
# More values, and the Protocol Number for ICMP traffic
# Convert network format of big-endian to host format of little-endian
$TotalLength = NetworkToHostUInt16 $BinaryReader.ReadBytes(2)
$Identification = NetworkToHostUInt16 $BinaryReader.ReadBytes(2)
$FlagsAndOffset = NetworkToHostUInt16 $BinaryReader.ReadBytes(2)
$TTL = $BinaryReader.ReadByte()
$ProtocolNumber = $BinaryReader.ReadByte()
$Checksum = [Net.IPAddress]::NetworkToHostOrder($BinaryReader.ReadInt16())
# The source and destination IP addresses
$SourceIPAddress = $BinaryReader.ReadUInt32()
$DestinationIPAddress = $BinaryReader.ReadUInt32()
# The source and destimation ports
$sourcePort = [uint16]0
$destPort = [uint16]0
# Close the stream reader
$BinaryReader.Close()
$memorystream.Close()
# Cast DCIP into an IPaddress type
$DCIPP = [ipaddress] $DCIP
$DestinationIPAddressP = [ipaddress] $DestinationIPAddress
#Ping the DC at the end after starting the capture
Test-Connection -Count 1 -ComputerName $DCIP -ea SilentlyContinue | Out-Null
# This is the match logic - check to see if Destination IP from the Ping sent matches the DCIP entered by in the ATA Console
# The only way the ATA Gateway should see a destination of the DC is if Port Spanning is configured
if ($DestinationIPAddressP -eq $DCIPP) # is the destination IP eq to the DC IP?
{
$TestResult = "Port Spanning success!"
$OneSuccess = 1
} else {
$TestResult = "Noise"
}
# Put source, destination, test result in Powershell object
new-object psobject | add-member -pass noteproperty CaptureSource $([system.net.ipaddress]$SourceIPAddress) | add-member -pass noteproperty CaptureDestination $([system.net.ipaddress]$DestinationIPAddress) | Add-Member -pass NoteProperty Result $TestResult | Format-List | Out-Host
#Count tests
$tests ++
}
if ($OneSuccess -eq 1)
{
Write-Host "Port Spanning Success!" -ForegroundColor Green
Write-Host ""
Write-Host "At least one packet which was addressed to the DC, was picked up by the Gateway." -ForegroundColor Yellow
Write-Host "A little noise is OK, but if you don't see a majority of successes, you might want to re-run." -ForegroundColor Yellow
} else {
Write-Host "No joy, all noise. You may want to re-run, increase the number of Ping Counts, or check your config." -ForegroundColor Red
}
Write-Host ""
Write-Host "Press any key to continue..." -ForegroundColor Red
[void][System.Console]::ReadKey($true)
Verifiera portspegling med Net Mon
Installera Microsoft Network Monitor 3.4 på den ATA-gateway som du vill verifiera.
Viktigt
Installera inte Microsoft Message Analyzer eller någon annan programvara för trafikinsamling på ATA Gateway.
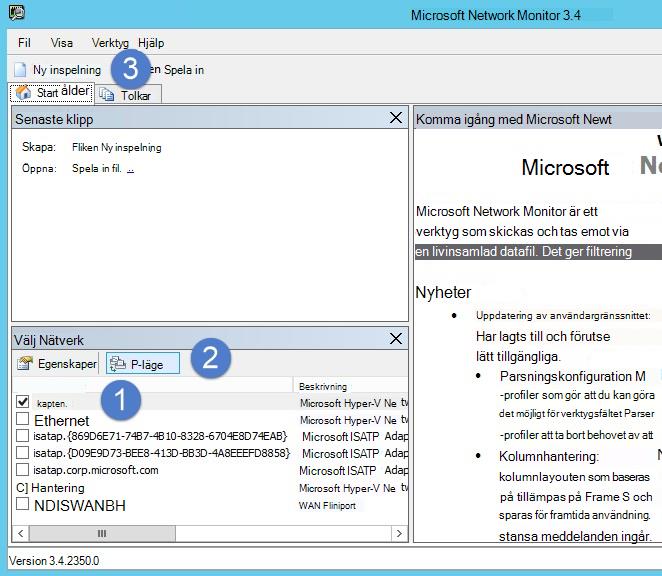
Öppna Nätverksövervakaren och skapa en ny avbildningsflik.
Välj endast avbildningsnätverkskortet eller det nätverkskort som är anslutet till växelporten som är konfigurerad som portspeglingsmål.
Kontrollera att P-läge är aktiverat.
Klicka på Ny avbildning.
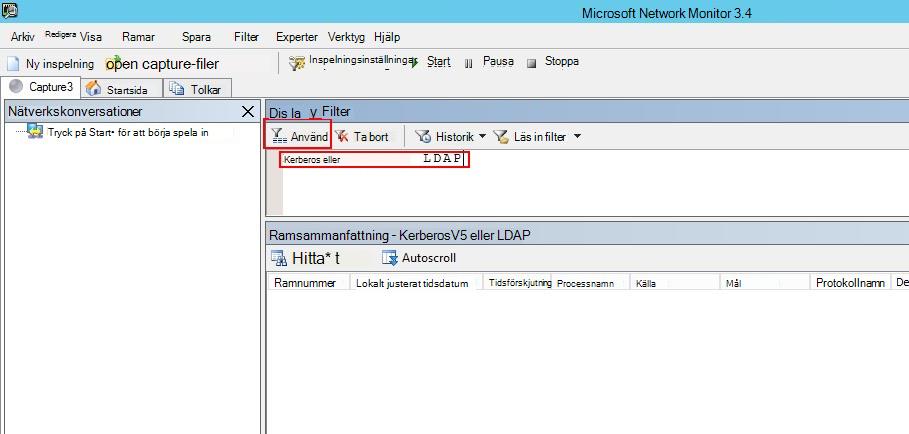
I fönstret Visningsfilter anger du följande filter: KerberosV5 ELLER LDAP och klickar sedan på Använd.
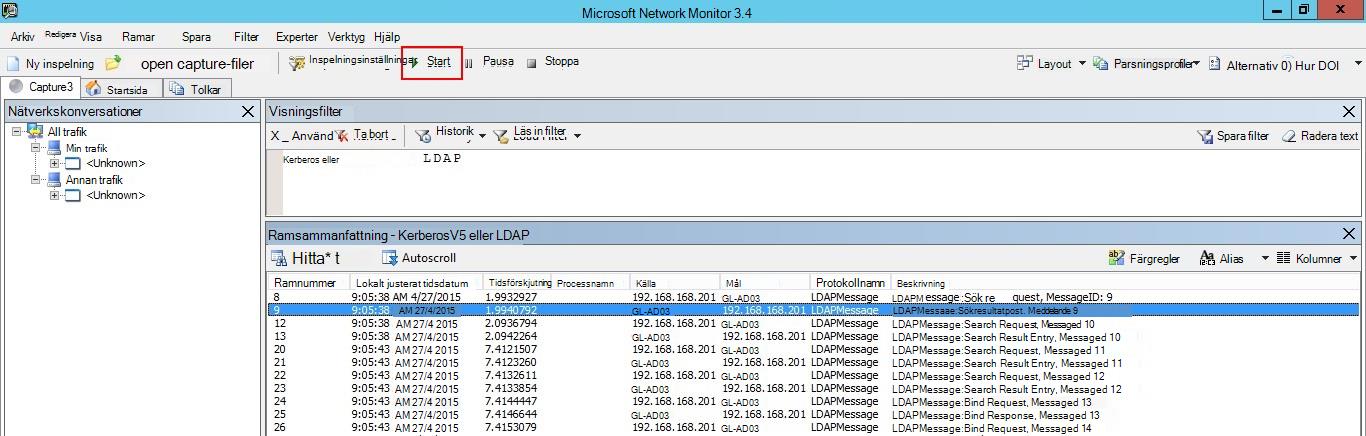
Klicka på Start för att starta avbildningssessionen. Om du inte ser trafik till och från domänkontrollanten granskar du konfigurationen för portspegling.
Obs!
Det är viktigt att se till att du ser trafik till och från domänkontrollanterna.
Om du bara ser trafik i en riktning bör du arbeta med dina nätverks- eller virtualiseringsteam för att felsöka konfigurationen av portspegling.