Выбор API или технологии для разработки решений для Outlook
В этой статье описаны API и технологии, которые можно использовать для расширения Outlook 2013 и Outlook 2016. Кроме того, статья поможет вам решить, какие именно API или технологии больше подходят для выбранного вами сценария.
Майкрософт поддерживает различные API и технологии, расширяющие возможности Outlook:
Starting in Office 2013, the apps for Office platform opens up opportunities to extend Outlook functionality across Outlook clients on the desktop, tablet and smart phone. The platform includes a JavaScript API for Office and a schema for app manifests.
В решениях Outlook чаще всего использовались такие API, как объектная модель, соответствующая основная сборка взаимодействия Outlook (PIA), а также API обмена сообщениями (MAPI).
В некоторых сферах применения используются вспомогательные API, дополняющие MAPI.
Outlook Social Connector (OSC) provider extensibility and the Weather Bar extensibility serve specific scenarios of their niche markets.
This article explains the selection criteria for the Надстройки Office platform, the object model, PIA, and MAPI. Note that Надстройки Office use the JavaScript API for Office and do not call into the object model, and vice versa. Solutions that use the other APIs can use one or more APIs. For example, a COM add-in written in C++ can use the object model, MAPI, and auxiliary APIs in the same solution.
To get the most benefit from this article, you should be familiar with Outlook at the user level and have general software development knowledge. However, you do not need to have a comprehensive understanding of the features that these APIs or technologies support. The article helps answer the following questions:
Если у вас есть только общее представление о целях решения,предполагаемом рынке и доступных ресурсах, то какие другие критерии следует использовать для выбора API?
Зачем надо рассматривать надстройки Office и когда надо выбирать создание приложений вместо надстроек?
Если решение нужно запускать в более ранних версиях Outlook, включая Outlook 2003, как это влияет на выбор API?
Если решение должно обрабатывать папки Outlook, содержащие тысячи элементов, и предлагать возможность изменения этих элементов, какой API-интерфейс лучше всего использовать?
Если в решении интенсивно используется бизнес-логика Outlook и взаимодействие с другими приложениями Office, оптимальный выбор — объектная модель Outlook.
Что дают объектная модель и MAPI для расширения возможностей Outlook?
If you can use either the object model or MAPI to achieve your task, how should you decide which API to use?
Objective evaluation criteria
This section describes criteria that you can use to compare the Надстройки Office platform, object model, PIA, and MAPI to determine which better meets your needs. Different criteria can be more or less important, depending on your projects and available resources.
The tables in this section define evaluation criteria in the following categories:
Функциональные критерии — описание того, что можно и чего нельзя реализовать с помощью данной технологии.
Критерии разработки — описание средств разработки или сведений, необходимых для использования технологии.
Критерии безопасности — описание проблем безопасности и доступа, связанных с этой технологией.
Deployment criteriaDescribes the recommended deployment and distribution methods for the technology.
Objective evaluation criteria for the apps for Office platform
Starting in Office 2013, developers can use the Надстройки Office platform to extend web services and content into the context of Office rich and web clients. An Надстройка Office is a web page that is developed using common web technologies, hosted inside an Office client application (such as Outlook), and can run on-premises or in the cloud. Of the few types of Надстройки Office, the type that Outlook supports is called mail apps. While the object model, PIA, and MAPI are often used to automate Outlook at an application level, you can use the JavaScript API for Office to interact at an item level with the content and properties of an email message, meeting request, or appointment. You can publish mail apps to the Магазин Office or an internal Exchange catalog.
End users and administrators can install mail apps on an Exchange mailbox, and use mail apps in the Outlook rich client as well as Outlook Web App. As a developer, you can choose to make your mail app available on only the desktop, or also on the tablet or smart phone. Figure 1 shows an example of a YouTube mail app, which is described in detail in Пример: создание почтового приложения для просмотра видеороликов YouTube в Outlook. The YouTube mail app allows end users select a URL for a YouTube video and watch the video within Outlook or Outlook Web App, on the desktop or tablet.
Рис. 1. Почтовое приложение YouTube активно для выбранного сообщения, которое содержит URL-адрес видео на YouTube.com
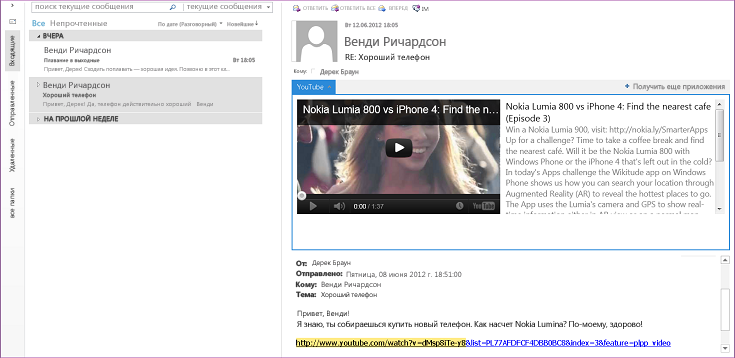
After a user installs a mail app, the app is available for use in the app bar when the current context matches the activation conditions that the app specifies. A mail apps allows you to specify rules about the currently selected item that activate a mail app only if certain conditions are met. For example, the YouTube mail app that lets you play a YouTube video within Outlook is relevant only when the selected Outlook item contains a URL to a video on YouTube.com. In this case, you would specify that the app should be active only when the selected message contains such a URL.
The following tables show the evaluation criteria for the Надстройки Office platform.
Функциональные критерии
| Criteria | Поддержка почтовых приложений в приложениях для платформы Office |
|---|---|
| Application domain | The scope of activity of a mail app is virtually any supported message or appointment item in the user's Exchange mailbox that the user has selected and that satisfies the activation conditions. The permissions of a mail app determine its access to the properties and specific entities (such as an email address or telephone number) that exist for that item. For example, a mail app requesting the read/write mailbox permission can read and write all the properties of any item in the user's mailbox; create, read, and write to any folder or item; and send an item from that mailbox. |
| Major objects | The JavaScript API for Office provides a few objects at the top level that are shared by all the types of Надстройки Office: Office, Context, and AysncResult. The next level in the API that is applicable and specific to mail apps includes the Mailbox, Item, and UserProfile objects, which support accessing information about the user and the item currently selected in the user's mailbox. At the data level, the CustomProperties and RoamingSettings objects support persisting properties set up by the mail app for the selected item and for the user's mailbox, respectively. Item-level objects include the Appointment and Message objects that inherit from Item, and the MeetingRequest object that inherits from Message. These represent the types of Outlook items that support mail apps: calendar items of appointments and meetings, and message items such as email messages, meeting requests, responses, and cancellations. Beyond this level in the API are item-level properties (such as Appointment.subject) as well as objects and properties that support certain known Entities objects (for example Contact, MeetingSuggestion, PhoneNumber, and TaskSuggestion). See Обзор архитектуры и функций надстроек Outlook for a summary of the features supported for mail apps. |
| Модель доступа к данным | API JavaScript для Office представляет перечисленные ниже функции в виде иерархического набора объектов: среды выполнения приложения, почтового ящика пользователя и его профиля, а также данных об элементе. |
| Модели потоков | Каждое почтовое приложение выполняется в своем собственном процессе отдельно от процесса Outlook. |
| Архитектуры приложений | Почтовое приложение в Outlook — это набор веб-страниц HTML и JavaScript, размещенных как отдельный процесс внутри элемента управления браузера, который, в свою очередь, размещен внутри процесса среды выполнения приложения, обеспечивающего безопасность и изоляцию. |
| Remote usage | Mail apps use the JavaScript API for Office to access data about the current user, mailbox, and selected item stored on the corresponding Exchange Server. Provided that they have the appropriate permissions and use the appropriate technique for cross-domain access, mail apps can also call Exchange Web Services and other third-party web services to extend their functionality. |
| Транзакции | API JavaScript для Office не поддерживает транзакции. |
| Доступность | API-интерфейс JavaScript для Office доступен для почтовых ящиков на сервере Exchange Server 2013, начиная с Outlook 2013. |
Критерии разработки
| Criteria | Поддержка почтовых приложений в приложениях для платформы Office |
|---|---|
| Languages and tools | You can implement mail apps using any common web technology, including HTML5, JavaScript, CSS3, XML, and REST APIs. You can use your preferred web development tool. Alternatively, using Napa, Visual Studio 2012, or a later version of these tools provides conveniences that save you time in development. |
| Managed implementation | Можно использовать управляемые страницы ASPX для реализации серверного кода для почтовых приложений, если это допустимо в данной области применения. |
| Scriptable | API JavaScript для Office непосредственно используется в сценариях. |
| Test and debug tools | You can use any web development tools you prefer. Napa and Visual Studio provide an integrated development environment that facilitates app testing and debugging. Устранение неполадок активации надстроек Outlook and Пример. Свойства отладки элементов Outlook provide further help in troubleshooting and debugging mail apps. |
| Expert availability | Programmers who have the required level of web development expertise for Надстройки Office are relatively easy to find. The platform is intended for both professional and non-professional developers. |
| Доступные сведения | Information about developing and posting Надстройки Office is available at Build apps for Office and SharePoint. Specific documentation for mail apps is available at Надстройки Outlook. |
| Developer and deployment licensing | О платформе лицензирования приложений для Office можно прочитать в статье Лицензирование надстроек Office и SharePoint. |
Security criteria
| Criteria | Поддержка почтовых приложений в приложениях для платформы Office |
|---|---|
| Разрешения времени разработки | Для разработки почтовых приложений не требуются специальные разрешения. |
| Разрешения при установке | По умолчанию конечные пользователи и администраторы могут устанавливать почтовые приложения с низким уровнем доверия, для которых требуется ограниченный доступ или разрешение на чтение элемента, и администраторы могут устанавливать приложения с высоким уровнем доверия, для которых требуется разрешение на чтение и запись в почтовом ящике. |
| Разрешения времени выполнения | Почтовые приложения запрашивают разрешения определенного уровня, основанные на трехуровневой модели разрешений: ограниченный доступ, чтение элемента и чтение и запись почтового ящика. |
| Встроенные функции безопасности | Среда выполнения надстроек Office предоставляет следующие преимущества, чтобы предотвратить повреждение среды пользователя приложением: изолирует процесс, в котором выполняется приложение. Не предусматривает замены DLL- или EXE-файлов, а также компонентов ActiveX. Упрощает установку или удаление приложений пользователем. Администраторы и пользователи могут управлять доступными почтовыми приложениями, а также указывать, надо ли перед установкой почтового приложения предоставлять требуемое разрешение. При использовании полнофункциональных клиентов управляет использованием памяти и ЦП, чтобы предотвратить атаки типа "отказ в обслуживании". |
| Функции мониторинга безопасности | Для почтовых приложений отслеживаются следующие ресурсы: использование ядра ЦП. Использование памяти. Число сбоев. Длительность блокировки приложения. Время ответа регулярного выражения. Число повторных оценок регулярных выражений. Администраторы могут переопределять параметры по умолчанию, управляющие использованием ресурсов. |
Условия развертывания
| Criteria | Поддержка почтовых приложений в приложениях для платформы Office |
|---|---|
| Требования к платформе сервера | Почтовый ящик пользователя, для которого устанавливается почтовое приложение, должен размещаться в Exchange Server 2013 или более поздней версии. |
| Требования к платформе клиента | Для работы почтового приложения в полнофункциональном клиенте Outlook на компьютере необходимо установить Outlook 2013 и Internet Explorer 9 или более поздней версии этих приложений. |
| Методы развертывания | You can publish mail apps to the Магазин Office or to an Exchange catalog that makes the app available to users on that Exchange Server. Administrators or users can then choose to install a mail app from the Магазин Office or Exchange catalog, by using either the Exchange Admin Center (EAC) or by running remote Windows PowerShell cmdlets. You can access the EAC from the Outlook Backstage view or Outlook Web App, or by directly signing into the EAC for your mailbox. Дополнительные сведения см. в статье Развертывание и установка надстроек Outlook для тестирования. |
| Deployment notes | Once you install a mail app on Outlook or Outlook Web App, the mail app is available for that mailbox on both Outlook clients. |
Objective evaluation criteria for the object model and PIA
Solutions that run on the client computer can use the Outlook object model or PIA to programmatically access Outlook items, such as contacts, messages, calendar items, meeting requests, and tasks. Unlike MAPI, the Outlook object model and PIA can provide event notifications for Outlook user-interface changes, such as changing the current folder or displaying an Outlook inspector.
Примечание.
Чтобы решение могло обращаться к данным, хранящимся в почтовом ящике Microsoft Exchange или в PST-файле личных папок, на клиентском компьютере, на котором запущено приложение, необходимо установить и настроить Outlook. > Объектная модель Outlook и PIA поддерживают одинаковые функции для расширения Outlook. PIA определяет управляемые интерфейсы, которые сопоставляются с объектной моделью COM и с которым может взаимодействовать управляемое решение. В остальной части данного раздела большая часть критериев применения, защиты и развертывания применима как к объектной модели, так и к PIA. Дополнительную информацию о том, как PIA обеспечивает взаимодействие между COM и .NET Framework см. в статьях Введение во взаимодействие между COM и .NET и Архитектура PIA Outlook.
В приведенных ниже таблицах перечислены условия оценки для объектной модели Outlook и PIA.
Функциональные критерии
| Criteria | Объектная модель Outlook или PIA |
|---|---|
| Application domain | Add-ins or standalone applications that use the Outlook object model or PIA typically handle user-specific messages, customize the Outlook user interface, or create custom item types for specialized solutions such as customer relationship management (CRM) solutions that integrate with Outlook. The Outlook object model or PIA is sometimes used for message processing in an informal workflow process, especially where application development on the Microsoft Exchange Server is not permitted. Unlike browser-based clients, cached-mode operation allows Outlook solutions to work when the user is offline or disconnected from the corporate network. |
| Major objects | The top-level object in the Outlook object model and PIA is the Outlook Application object. Explorers, Conversation, Inspectors, Views, NavigationPane, SolutionsModule, FormRegion, and related objects represent elements of the Outlook user interface. The NameSpace, Stores, Folders, Accounts, AccountSelector, AddressEntries, ExchangeUser, and related objects support extending Outlook sessions, profiles, user accounts, message stores, and folders. At the data level, a number of item-level objects, such as MailItem, AppointmentItem, ContactItem, and TaskItem, represent the built-in Outlook item types. The PropertyAccessor, Table, Search, ItemProperties, UserDefinedProperties, Attachments, Categories, Recipients, RecurrencePattern, Reminders, Rules, and related objects support customizing and manipulating item-level objects. |
| Data-access model | Объектная модель Outlook и PIA представляют все данные в виде иерархического набора объектов и коллекций. |
| Threading models | All calls to the Outlook object model and PIA execute on Outlook's main foreground thread. The only threading model that the Outlook object model supports is single-threaded apartment (STA). Calling the Outlook object model or PIA from a background thread is not supported and can lead to errors and unexpected results in your solution. |
| Application architectures | Typically, COM add-ins and other Office applications use the Outlook object model to extend Outlook. Managed solutions can use the Outlook PIA and the COM interoperability layer of Visual Studio and the .NET Framework to access the Outlook object model. Visual Studio provides templates and additional class libraries and manifests to facilitate Office document and application customizations. For more information about using Visual Studio to develop managed add-ins for Outlook, see Architecture of Application-Level Add-Ins and Outlook Solutions. The Outlook object model also supports Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) macros and Windows Scripting Host (WSH), but does not support Windows Service applications. |
| Remote usage | The Outlook object model and PIA can be used only on a computer on which Outlook is installed. The Outlook object model can be used to access information stored in Exchange that is available in the Outlook application. |
| Транзакции | Объектная модель Outlook и PIA не поддерживают транзакции. |
| Доступность | The Outlook object model is currently available in all versions of Outlook. The PIA is available in versions of Outlook since Outlook 2003. There have been extensions and improvements with each new version of Outlook. |
Development criteria
| Criteria | Объектная модель Outlook или PIA |
|---|---|
| Languages and tools | You can implement Outlook object model applications by using any COM or automation-compatible language, such as Visual Basic or C#, as well as non-COM languages, such as native C or C++. Инструменты разработчика Microsoft Office в Microsoft Visual Studio 2010 are the preferred tools for development of managed add-ins for Outlook 2010 and Outlook 2007. Microsoft Visual Studio 2005 Tools for the Microsoft Office System are the preferred tools for Outlook 2003. You can also use Инструменты разработчика Office в Visual Studio 2010 to create solutions for 32-bit and 64-bit versions of Outlook. When you build a solution in Инструменты разработчика Office в Visual Studio 2010 or Microsoft Visual Studio Tools for the Microsoft Office System, specifying the Any CPU option for the target platform results in managed solutions that work for both 32-bit and 64-bit versions of Outlook 2010. |
| Managed implementation | PIA Outlook позволяет использовать объектную модель Outlook в среде с управляемым кодом, которая поддерживается широким набором библиотек классов и технологий, которые устраняют многие ограничения надстроек VBA и COM. PIA — это com-оболочка, которая выступает в качестве моста между управляемыми и COM-средами. Дополнительные сведения см. в статье Why Use the Outlook PIA. |
| Scriptable | Объектную модель Outlook можно использовать в сценариях. |
| Test and debug tools | No special debugging tools are needed to use the Outlook object model or PIA. On the other hand, you can use Visual Studio to provide an integrated development environment that facilitates application testing and debugging. |
| Expert availability | Developers who can successfully develop applications by using the Outlook object model or PIA are relatively easy to find. The Outlook object model and PIA are intended for add-ins created by using widely available development tools, such as Visual Studio. These tools provide design-time environments that simplify the development process. |
| Доступные сведения | Information about programming by using the Outlook object model is available in both Microsoft and third-party resources. For more information about the Outlook object model, see the Outlook 2010 Developer Reference. For more information about the Outlook PIA, see the Outlook 2010 Primary Interop Assembly Reference. For examples of managed Outlook solutions developed by using Office development tools in Visual Studio, see Outlook Solutions with Visual Studio. |
| Developer and deployment licensing | Чтобы узнать, требуются ли дополнительные лицензии для использования Outlook и объектной модели Outlook в приложениях, обратитесь к лицензионным соглашениям для Microsoft Exchange и подписки на Microsoft Developer Network (MSDN). |
Security criteria
| Criteria | Объектная модель Outlook или PIA |
|---|---|
| Разрешения времени разработки | Для разработки приложений с помощью объектной модели Outlook или PIA не требуются специальные разрешения. |
| Setup permissions | No special permissions are required to install applications that use the Outlook object model or PIA. However, local administrator rights are required to install Office and Outlook. |
| Run-time permissions | Для запуска приложений, использующих объектную модель Outlook или PIA, не требуются специальные разрешения. |
| Built-in security features | The Outlook object model and PIA communicate with Exchange by using MAPI and with Active Directory by using Active Directory Service Interfaces (ADSI). The current security context of the user who is running the application is used to determine what resources that code can access. By default, add-ins are trusted for full access to all objects, properties, and methods in the Outlook object model or PIA. IT administrators can exercise control over which add-ins and objects can access the Outlook object model or PIA. The Outlook object model and PIA prevent code that is run outside the Outlook process from accessing secure objects and methods. |
| Функции мониторинга безопасности | Outlook отслеживает следующие метрики надстройки, чтобы определить, должна ли она отключать надстройку: Параметр папки завершения запуска Элемент открытый частота вызова Администраторы могут использовать групповую политику для переопределения параметров пользователей и управления надстройками, которые выполняются на компьютерах пользователя. Дополнительные сведения см. в разделе Условия производительности для поддержания работы надстроек. |
Условия развертывания
| Criteria | Объектная модель Outlook или PIA |
|---|---|
| Требования к платформе сервера | Объектная модель Outlook и PIA представляют собой клиентские технологии. |
| Требования к платформе клиента | Приложения, которые используют объектную модель Outlook или PIA для доступа к данным Exchange, требуют, чтобы на локальном компьютере было установлено приложение Outlook. |
| Методы развертывания | Приложения, использующие объектную модель Outlook или PIA, распространяются с использованием стандартного программного обеспечения для установки приложений. |
| Deployment notes | Because Outlook should not be installed on the Exchange Server, applications that use the Outlook object model or PIA cannot be run on the Exchange Server. |
Objective evaluation criteria for MAPI
You can use MAPI to access items and folders in public and private stores, as well as to access the properties stored with each item. All versions of Outlook use MAPI. You can create clients that use MAPI, and can create MAPI servers and MAPI forms handlers, as well. The information in this section applies only to MAPI client applications.
Примечание.
[!Примечание] MAPI is a mature mechanism used to access information in Exchange or in a personal folders (.pst) file, and MAPI provides some capabilities that are not available in any other API. However, MAPI does not work well outside an intranet, maintains an open connection for the duration of the MAPI session, and can be difficult to learn. MAPI does not enforce Outlook business logic, so you must take special care to ensure that Outlook business logic is maintained.
The following tables show evaluation criteria for MAPI.
Функциональные критерии
| Criteria | MAPI |
|---|---|
| Application domain | Client applications that use MAPI access a user mailbox or public folder information stored in Exchange, and user directory information stored in Active Directory. Client applications that use MAPI are typically email clients, such as Outlook, and applications that require complex email processing. |
| Major objects | MAPI objects are all obtained through the IMAPISession: IUnknown interface. The session object provides the client access to objects for working with MAPI profiles, status, message service provider administration, message store tables, and address books. The message store table contains objects for the message store, folders, messages, attachments, and recipients. The address book tables contain objects for messaging users and distribution lists. |
| Data-access model | MAPI представляет сообщения и пользователей в виде иерархического набора объектов. |
| Threading models | There are no specific threading prohibitions. However, applications that use free-threading should avoid sharing MAPI objects among threads due to the high costs of marshaling the object. MAPI and MAPI service providers use free-threading. |
| Application architectures | MAPI client applications are typically Windows Forms-based client applications. However, you can use MAPI to write N-tier applications. |
| Remote usage | MAPI uses remote procedure calls (RPCs) to communicate with the Exchange Server. Typically RPCs are intentionally blocked from passing through Internet firewalls. |
| Транзакции | MAPI не поддерживает транзакции. |
| Доступность | A MAPI stub currently ships with all versions of Windows. Office installs its own MAPI subsystem when it installs Outlook. No changes to MAPI are anticipated at this time. |
Development criteria
| Criteria | MAPI |
|---|---|
| Languages and tools | You can directly access MAPI by using C or C++. Other languages that can access the C/C++ calling convention may be able to access MAPI. The use of managed languages, such as Visual Basic or C#, is not supported. You must compile separate MAPI solutions for 32-bit and 64-bit versions of Outlook. |
| Managed implementation | MAPI is an unmanaged component. Use of MAPI is not supported under the COM interoperability layer of Visual Studio and the .NET Framework. |
| Scriptable | MAPI нельзя использовать в сценариях напрямую. |
| Test and debug Tools | No special debugging tools are needed to debug applications that use MAPI. On the other hand, you can use MFCMAPI. MFCMAPI uses MAPI to provide access to MAPI stores through a graphical user interface, and facilitates investigation of issues when you extend Outlook by using MAPI. |
| Expert availability | Expert MAPI programmers can be difficult to find, and learning the technology can take a significant amount of time. In addition to the Microsoft communities, there are only a small number of high-quality third-party websites that provide helpful MAPI development information. |
| Доступные сведения | Имеются как источники Microsoft, так и книги других издателей, в которых описывается программирование MAPI. |
| Лицензирование для разработчиков и развертывания | Для разработки приложений, использующих MAPI, не требуется специальное лицензирование. |
Security criteria
| Criteria | MAPI |
|---|---|
| Design-time permissions | The developer must have permissions to access the data in the Exchange store. Exchange stores user and distribution list information in Active Directory, so developers who create MAPI client applications that access that information must have the ability to retrieve and set that information. |
| Setup permissions | Для настройки приложений на основе MAPI обычно требуются права локального администратора или права на установку программного обеспечения. |
| Разрешения времени выполнения | Для запуска приложения на основе MAPI, как правило, достаточно, чтобы у пользователя были необходимые разрешения на доступ к данным в хранилище Exchange или в файле личных папок (PST). |
| Встроенные функции безопасности | Профили MAPI на большинстве платформ можно защищать паролями. |
Условия развертывания
| Criteria | MAPI |
|---|---|
| Требования к платформе сервера | Сервер Exchange, на котором хранятся пользовательские данные для пользователей клиентского приложения MAPI, должен быть правильно настроен, чтобы разрешить доступ клиентам MAPI. |
| Требования к платформе клиента | Установщик клиентского приложения должен убедиться в том, что на компьютере имеется требуемая версия MAPI и что она правильно настроена с помощью файла Mapisvc.inf. |
| Методы развертывания | Приложения, использующие MAPI, можно развертывать на клиентских компьютерах с помощью стандартных технологий распространения программного обеспечения. |
| Deployment notes | The installer should verify that the correct version of MAPI is available. |
Decision factors for the apps for Office platform
Because Надстройки Office use web technologies, they are best for connecting to services in the cloud or on-premises, and bringing the services into the context of the rich client and web client. By requesting appropriate permissions, mail apps also allow reading, writing, or sending items in a mailbox.
The following are common reasons why mail apps are a better choice for developers than add-ins:
You can use existing knowledge of and the benefits of web technologies such as HTML, JavaScript, and CSS. For power users and new developers, XML, HTML, and JavaScript require less significant ramp-up time than COM-based APIs, including the object model and MAPI.
You can use a simple web deployment model to update your mail app (including the web services that the app uses) on your web server without any complex installation on the Outlook client. In fact, any updates to the mail app, with the exception of the app manifest, do not require any updating on the Office client. You can update the code or user interface of the mail app conveniently just on the web server. This presents a significant advantage over the administrative overhead involved in updating add-ins.
You can use a common web development platform for mail apps that can roam across the Outlook rich client and Outlook Web App on the desktop, tablet, and smartphone. On the other hand, add-ins use the object model for the Outlook rich client and, hence, can run on only that rich client on a desktop form factor.
You can enjoy rapid turnaround of building and releasing apps via the Магазин Office.
Because of the three-tier permissions model, users and administrators perceive better security and privacy in mail apps than add-ins, which have full access to the content of each account in the user's profile. This, in turn, encourages user consumption of apps.
В зависимости от ситуации применения могут существовать функции, доступные только в почтовых приложениях и не поддерживаемые надстройками:
Можно указать, чтобы почтовое приложение активировалось только в определенных контекстах (например, приложение отображается на панели приложения в Outlook, только если выбранная пользователем встреча имеет класс IPM.Appointment.Contoso или если текст сообщения электронной почты содержит номер отслеживания пакета или идентификатор клиента).
Можно активировать почтовое приложение, если выбранное сообщение содержит определенные известные объекты, такие как адрес, контакт, адрес электронной почты, предложение встречи или предложение задачи.
Можно использовать проверку подлинности по маркерам удостоверения, а также веб-службы Exchange.
However, the following features are unique to add-ins and may make them a more appropriate choice than mail apps in some circumstances:
You can use add-ins to extend or automate Outlook at an application-level, because the object model and PIA have extensive integration with Outlook features (such as all Outlook item types, user interface, sessions, and rules). At the item-level, add-ins can interact with an item in read or compose mode. With mail apps, you cannot automate Outlook at the application level, and you can extend Outlook's functionality in the context of only the read-mode of the supported items (messages and appointments) in the user's mailbox.
You can specify custom business logic for a new item type.
Можно изменять и добавлять собственные команды на ленте и в представлении Backstage.
Можно создать настраиваемую страницу формы или область формы.
Можно обнаруживать события, такие как отправка элемента или изменение его свойств.
Вы можете использовать надстройки в Outlook 2013 и Exchange Server 2013, так же, как в более ранних версиях Outlook и Exchange. С другой стороны, почтовые приложения работают с Outlook и Exchange, начиная с Outlook 2013 и Exchange Server 2013 (более ранние версии не поддерживаются).
For more information about scenarios that the object model and PIA support, see the next section, Decision factors for the object model or PIA. For a comparison of the Надстройки Office platform with other extensibility technologies for Office, see The background on apps for Office and SharePoint.
Решающие факторы для объектной модели или PIA
Сценарии базового плана, которые поддерживает объектная модель Outlook или PIA
Как правило, объектная модель или PIA используется для решений, которые видоизменяют пользовательский интерфейс Outlook или используют бизнес-логику Outlook. Ниже перечислены основные сценарии, в которых решения Outlook используют объектная модель или PIA.
- Настройка пользовательского интерфейса Outlook
- Добавление, удаление, чтение, запись, фильтрация, поиск и сортировка элементов Outlook
- Настройка полей, форм и свойств элемента
- Обработка таких событий Outlook, как переключение между папками или открытие элемента
- Автоматизация Outlook и интеграция с другими приложениями Office
Сценарии, которые поддерживает объектная модель или PIA, начиная с Outlook 2007
В дополнение к основным сценариям, если решение Outlook поддерживает какие-либо из приведенных в следующем списке сценариев, а ваше решение предназначено для работы в Outlook 2007 или более поздней версии, но не в более ранних версиях, можно использовать как объектную модель, так и PIA. На рисунке 3 показаны основные объекты или члены, которые можно использовать в объектной модели Outlook для расширения каждого сценария (за исключением интерфейса IDTExtensibility2 в модели объектов автоматизации Visual Studio и интерфейса IRibbonExtensibility в объектной модели Office, которые можно интегрировать с объектной моделью Outlook).
- Настройка пользовательского интерфейса — лента Office Fluent, область навигации, область задач
- Настройка форм в качестве регионов форм и их развертывание надстройками
- Установка и получение встроенных свойств на уровне элемента, которые не предоставляются в объектной модели
- Перечисление и просмотр множества элементов в папке
- Пометка элементов как задач
- Общий доступ к календарям, RSS-каналам и папкам
- Добавление, удаление, сохранение и получение уровня блокировки, пути, размера и типа вложения
- Управление правилами, часовыми поясами и представлениями
- Добавление или удаление категории в основном списке категорий для текущего профиля
- Получение подробных сведений для учетной записи в текущем профиле
- Получение подробных сведений о списке рассылки Exchange или пользователе Exchange в качестве записи адреса
- Хранение частных данных для решений
Сценарии, которые поддерживает объектная модель или PIA, начиная с Outlook 2010
Если решение Outlook предназначено для работы в Outlook 2010, а не в более ранних версиях, можно использовать объектную модель или PIA для поддержки сценариев, приведенных в следующем разделе. На рисунке 3 показаны основные объекты или члены, которые можно использовать в объектной модели Outlook для расширения каждого сценария (за исключением интерфейсов IRibbonControl, IRibbonExtensibility и IRibbonUI в объектной модели Office, которые можно интегрировать с объектной моделью Outlook).
- Настройка пользовательского интерфейса Outlook 2010, например представления Office Backstage и контекстных меню
- Управление разнородными элементами беседы и доступ к ним
- Управление выбором элементов в проводнике или поиск выделенного фрагмента
- Управление выбором вложений в инспекторе
- Поддержка нескольких учетных записей Exchange в одном профиле
- Создание карточки контакта для адресной записи
- Упорядочение папок конкретных решений в модуле "Решения"
Сценарии, которые поддерживает объектная модель или PIA, начиная с Outlook 2013
Если решение предназначено для работы в Outlook 2013, а не в более ранних версиях, можно использовать объектную модель или PIA для поддержки сценариев, описанных в перечисленных ниже ресурсах.
- Представление просмотра для всех контактов в текущей папке
- Выбор встроенного ответа в области чтения
- Отображение диалогового окна проверки адреса или полного имени для контакта
- Определение того, что свойства элемента прочитаны
Решающие факторы для MAPI
В общем случае MAPI используется для доступа к данным на MAPI-сервере, например Microsoft Exchange Server, и выполнения таких задач, как:
Создание настраиваемого поставщика услуг, например поставщика адресных книг, поставщика транспорта или поставщика хранилища.
Создание процесса-приемника.
Создание профиля и операции с ним.
Run an application as a Windows NT service.
Run tasks on a background thread. For example, enumerating numerous items in a folder and modifying the items' properties in a background thread can optimize performance.
For more information and code samples, see the Справочник по MAPI для Outlook and MFCMAPI.
Кроме того, если ваше решение работает в более ранней версии Outlook, чем Outlook 2007, а в решении применяются перечисленные ниже сценарии, используйте MAPI для расширения этих сценариев.
- Установка и получение встроенных свойств на уровне элемента, которые не предоставляются в объектной модели.
- Управление учетными записями, вложениями, списками рассылки Exchange, пользователями Exchange и хранилищами.
- Хранение частных данных для решений.
- Manage a message store for an account.
Since Outlook 2007, the object model has supported a range of features that, prior to Outlook 2007, developers had to resort to MAPI or other APIs such as Microsoft Collaboration Data Objects (CDO) 1.2.1 and Microsoft Exchange Client Extensions. So if any of the scenarios in the previous list applies to your solution, but your solution runs on Outlook 2007 or Outlook 2010, you can and should use the Outlook object model or PIA to support these scenarios. For more information about Outlook 2007 enhancements that unify Outlook development technologies, see What's New for Developers in Outlook 2007 (Part 1 of 2).
Решающие факторы для вспомогательных API
The Outlook auxiliary APIs can integrate with Outlook business logic or MAPI in some scenarios where the object model or MAPI does not provide a solution. Use the Outlook auxiliary APIs in the following scenarios:
- Account management: Manage account information, manipulate accounts, provide notification on account changes, and protect accounts from spam.
- Замедление данных: обтекание объекта в предпочтительном символьном формате, а не предоставление объекта в его исходном формате.
- Перевод времени календарей и поддержка часовых поясов: перевод календарей Outlook на летнее время.
- Состояние доступности: предоставление сведений о доступности в календарях.
- Изображения контактов: определение вида изображения контакта в Outlook.
- Действительность элемента: определение наличия несохраненных изменений в элементе Outlook.
- Классификация элемента: выбор категории для элемента Outlook после его отправки.
For more information about the auxiliary APIs, see the Additional resourcesAuxiliary APIs section.
Automating Outlook by in-process vs. out-of-process Solutions
Примечание.
Описание автоматизации Outlook в этом и следующем разделах выходит за рамки надстроек Office, которые предназначены для расширения функциональности клиента или веб-приложения Office, но не для их автоматизации.
Outlook supports automation by using add-ins that run in the same foreground process as the Outlook process, and by standalone solutions that run in their own separate process outside of the Outlook process. Generally, to automate Outlook, use an add-in to interact with Outlook through the object model, PIA, or MAPI, and in less common scenarios, through an auxiliary API (such as HrProcessConvActionForSentItem). Use an out-of-process solution only when it's necessary (for example, when you're writing a MAPI client application that uses the Tzmovelib.dll file to rebase Outlook calendars for customers, or enumerating numerous items in a folder and modifying the items' properties in a background thread to optimize performance).
Надстройки являются предпочтительным решением для автоматизации Outlook, так как Outlook доверяет только объекту Application , переданного надстройке во время события OnConnection(Object, ext_ConnectMode, Object, Array) надстройки. Чтобы избежать появления предупреждений системы безопасности объектной модели, можно наследовать все объекты, свойства и методы от этого объекта Application. Если надстройка создает новый экземпляр объекта Application , Outlook не доверяет этому объекту, даже если надстройка находится в списке доверенных надстроек. Любые объекты, свойства и методы, производные от такого объекта Application , не будут доверенными, а заблокированные свойства и методы будут вызывать предупреждения системы безопасности. Дополнительные сведения о защите объектной модели в Outlook см. в статье Security Behavior of the Outlook Object Model.
Автоматизация Outlook с помощью управляемых и неуправляемых решений
Outlook supports automation by add-ins and standalone applications, written in managed or unmanaged languages. The more commonly used managed languages are C# and Visual Basic. C++ and Delphi tools are more common in unmanaged development. Available expertise is one consideration when choosing between managed and unmanaged development.
If your solution uses only the object model, you can consider developing a managed solution by using the PIA, or Office development tools in Visual Studio. The Office development tools in Visual Studio provide project templates and visual designers that simplify creating custom user interfaces and developing Office solutions.
On the other hand, because MAPI was developed years before the .NET Framework, and Microsoft does not provide managed wrappers for MAPI, Microsoft does not support using MAPI in managed code. If you are using MAPI, you must develop an unmanaged solution. For more information, see The support guidelines for client-side messaging development.
Нишевые API и технологии
Outlook Social Connector (OSC) и панель прогноза погоды поддерживают очень специфичные сценарии использования Outlook.
Outlook Social Connector (OSC) provider extensibility
The Outlook Social Connector (OSC) provider extensibility supports developing a provider for a social network to allow users to view, in Outlook and other Office client applications, friends and activities updates on that social network. Figure 6 shows the OSC displaying in the People Pane the activities of a person in social network sites.
Рисунок 6. OSC, отображающий данные социальной сети в области Люди
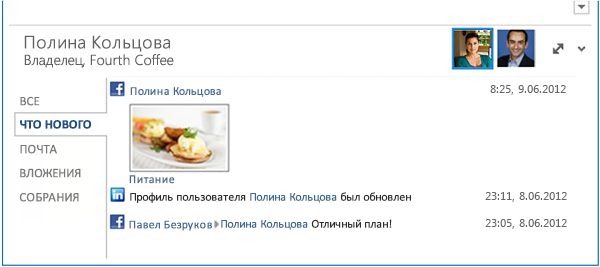
The OSC in Outlook allows users to view, in the People Pane, an aggregation of emails, attachments, and meeting requests from a person in Outlook. In an organizational environment, users who collaborate on a SharePoint site can see document updates and other site activities of this person on the SharePoint site. Outlook Social Connector provider extensibility supports developing a provider for the OSC to synchronize and surface social network updates in Outlook. Common OSC providers (such as Facebook and LinkedIn) are installed by default with Outlook. Depending on the social network sites that an Outlook user has signed into, the user can see, in the People Pane, updates such as photos, status, and activities on the corresponding social networks.
Weather Bar extensibility
Starting in Outlook 2013, the Weather Bar allows developers to plug in a third-party weather web service for the Weather Bar, to provide weather conditions data for a user-chosen location. The Weather Bar in Outlook displays weather conditions and forecast for a geographic location. A user can choose one or multiple locations, and conveniently see weather data in the Weather Bar in the calendar module. Figure 7 shows the Weather Bar displaying a three-day forecast for New York, NY.
Рис. 7. Панель прогноза погоды в Outlook
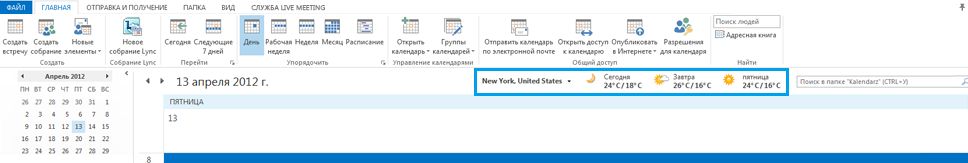
By default, Outlook uses weather data provided by MSN Weather. The Weather Bar supports third-party weather data web services which follow a defined protocol to communicate with Outlook. As long as a third-party weather data service supports this protocol, users can choose that weather data service to provide weather data in the Weather Bar.
See the Additional resourcesprimary references, resources, and code samples section for more information about using OSC provider extensibility and the Weather Bar extensibility.
Заключение
Чтобы определить оптимальные API или технологии для решения, нужно сначала установить цели вашего решения.
The versions of Outlook you intend your solution to support.
The high-priority scenarios of your solution. Does your solution mainly interact with the content and properties of a message or appointment item? Or does your solution automate Outlook at an application level? If so, do these scenarios involve enumerating, filtering, or modifying folders that contain many Outlook items?
First, verify whether the mail app support in the Надстройки Office platform meets your needs. See the Functional Criteria section of Objective evaluation criteria for the apps for Office platform to determine whether the major objects and features support your scenarios. See the section Decision factors for the apps for Office platform to verify whether mail apps are a better choice than add-ins for your scenarios. In general, develop your solution as an app, if possible, to take advantage of the platform's support across Outlook clients over different form factors.
If your scenarios require you to extend beyond message and appointment items, or require you to automate Outlook at an application level, try to match your scenarios with those outlined in the section Decision factors for the object model or PIA. If the object model (or PIA) of your target Outlook versions supports your scenarios, and your solution does not manipulate folders with many items, you should implement your solution as an add-in, in either a managed or unmanaged language.
If the object model (or PIA) of a target Outlook version does not support some of your scenarios, verify whether the scenarios in the Decision factors for MAPI or Decision factors for the Auxiliary APIs section meet your needs. If MAPI meets your needs, you should implement your solution in unmanaged code. If an auxiliary API solves one of your scenarios, you can use managed or unmanaged code.
If your solution uses MAPI, you must implement it in unmanaged code, such as C++. Otherwise, the decision to use managed or unmanaged code to create the solution generally depends on your available resources and their expertise. As for deciding whether to implement the solution as an add-in or standalone application, choose an add-in to avoid the user constantly invoking the Outlook Object Model Guard, unless your scenario requires manipulation of folders that contain numerous items. In the latter scenario, implementing the solution to run as a background thread can optimize Outlook performance.
If your scenarios include showing social network information or updates in Outlook, you should use the OSC provider extensibility to create a COM-visible DLL. You can do this in either a managed or unmanaged language.
If you are interested in plugging in a third-party weather data service to the Weather Bar, you can follow the protocol defined by Weather Bar extensibility and provide the appropriate web services. You can create these web services in a managed language.
Выбрав API или технологии для использования в решении, вы можете обратиться к дополнительной документации и примерам кода в разделе Дополнительные ресурсы: основные ссылки, ресурсы и примеры кода.
Обзор платформы надстроек Office дает хорошую общую информацию о настройках Office, включая архитектуру и жизненный цикл разработки.
Подробный план ресурсов, посвященных разработке почтовых приложений, см. в статье Надстройки Outlook.
См. также: "Объектная модель и PIA"
В приведенных ниже ресурсах можно найти дополнительные сведения об использовании объектной модели и PIA.
Объект Account
NameSpace.Accounts property
Учетные записи: несколько учетных записей в профиле
Объект Account
Использование нескольких учетных записей для одного профиля в Outlook
Управление несколькими учетными записями Exchange в Outlook 2010
Адресная книга и пользователи Exchange
Доступ к информации о пользователе или списке рассылки Exchange из адресной книги
Отображение имени и расположения офиса каждого руководителя из списка рассылки Exchange
Объект AddressEntries
Объект AddressLists
Объект ExchangeDistributionList
Объект ExchangeUser
SelectNamesDialog object
Вложения
Объект Attachment
Объект AttachmentSelection
Событие AttachmentAdd для объекта элемента
Событие AttachmentRead для объекта элемента
Событие AttachmentRemove для объекта элемента
Событие BeforeAttachmentAdd для объекта элемента
Событие BeforeAttachmentPreview для объекта элемента
Событие BeforeAttachmentRead для объекта элемента
Событие BeforeAttachmentSave для объекта элемента
BeforeAttachmentWrite event per item object
Вложения: выбор в инспекторе
Свойство Inspector.AttachmentSelection
Автоматизация Outlook
Категории
Объект Category
NameSpace.Categories property
Контакты: проверка адреса и полного имени
Беседы
Объект Conversation
Объект ConversationHeader
Объект SimpleItems
ConversationID property per item object
События
Проводник: ответ в тексте
Свойство Explorer.ActiveInlineResponse
Explorer.InlineResponse event
Элементы: основные свойства, поля и формы
Объект ItemProperties
Объект UserProperties
Элементы: настройка свойств
PropertyAccessor object
Элементы: перечисление, фильтрация и сортировка
Эффективность фильтрации элементы типа контакт в папке Контакты в Outlook 2010 (машинный перевод)
Table object
Элементы: пометка как задач
См. следующие свойства, связанные с задачами, в некоторых объектах элементов, таких как объект MailItem:
Свойство TaskCompleteDate
Свойство TaskDueDate
Свойство TaskStartDate
Свойство TaskSubject
ToDoTaskOrdinal property
Элементы: выбор в проводнике
Метод Selection.GetSelection
Selection.Location property
Разное: визитные карточки, правила и представления
Создание правила для перемещения определенных электронных сообщений в папку
Объект Rules
Объект RuleActions
Объект RuleConditions
Объект TimeZones
Views object
Безопасность
Доступ
SharingItem object
Решения: папки для определенных решений
Решения: хранение данных
Пользовательский интерфейс: настройка областей формы
Walkthrough: Add a Form Region to an Existing Page on a Form
Объект FormRegion
FormRegionStartup object
Пользовательский интерфейс: настройка в Outlook 2007
Ориентация решений пользовательского интерфейса на выпуски 2007 и 2010 системы Microsoft Office
Справочник по объектной модели элемента управления представления Outlook
IDTExtensibility2 interface
Объект IRibbonExtensibility
NavigationPane object
Пользовательский интерфейс: настройка в Outlook 2010
Расширение пользовательского интерфейса Office Fluent для Outlook
Настройка контекстного меню карточки контакта в Outlook 2010 (машинный перевод)
Объект IRibbonControl
Объект IRibbonExtensibility
IRibbonUI object
Пользовательский интерфейс: папки с определенными решениями
Добавление папки для решения конкретных решениях модулю в Outlook 2010 (машинный перевод)
Объект SolutionsModule
См. также: Вспомогательные API
В приведенных ниже ресурсах можно найти дополнительные сведения об использовании вспомогательных API Outlook.
Управление учетными записями
Категоризация элементов
Изображения контактов
Замедление данных
сведения о занятости
Элемент валюты
Перемещение календарей
Сведения о сохранении TZDEFINITION в потоке для помещения в двоичное свойство
Анализ потока из двоичного свойства для считывания структуры TZDEFINITION
Анализ потока из двоичного свойства для считывания структуры TZREG
См. также: "Основные ссылки, ресурсы и примеры кода"
В приведенных ниже ресурсах можно найти дополнительные сведения о основных ресурсах и примерах кода для Outlook.
Основные справочники и ресурсы
- Надстройки Office
- Справочник разработчика Outlook 2013
- Справочное руководство по основной сборке взаимодействия Outlook 2010
- Справочник по MAPI для Outlook
- Outlook 2013 Auxiliary Reference
- Справочник по поставщикам Outlook Social Connector
- Расширение панели прогноза погоды в Outlook
- Схема XML для отображения сведений о погоде в Outlook
- Схема XML для отображения расположения касательно прогноза погоды в Outlook
- Новые возможности схем XML для Outlook 2010
- Outlook 2010: справочник по схеме XML
- Разработка решений Outlook 2010 для 32- и 64-разрядных систем
Примеры кода
- Mail apps samples
- Примеры кода объектной модели: Как это сделать в Outlook
- PIA code samples: Инструкции (справочник по основной сборке взаимодействия для Outlook 2013)
- Примеры MAPI
- Примеры кода вспомогательного API: примеры задач