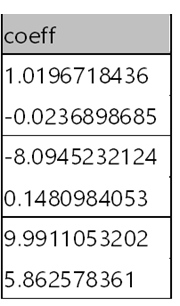
series_fit_poly_fl()
Область применения: ✅Microsoft Fabric✅Azure Data Explorer
Функция series_fit_poly_fl() — это определяемая пользователем функция (UDF), которая применяет многономиальную регрессию к серии. Эта функция принимает таблицу, содержащую несколько рядов (динамические числовые массивы) и создает наиболее подходящий полиномический многоном для каждой серии с помощью полиномиальной регрессии. Эта функция возвращает как многономиальные коэффициенты, так и интерполированный многономиальный по диапазону ряда.
Примечание.
- Используйте собственную функцию series_fit_poly() вместо функции, описанной в этом документе. Встроенная функция предоставляет те же функции и лучше подходит для производительности и масштабируемости. Этот документ предоставляется только для справочных целей.
- Для линейной регрессии равномерно распределенной серии, созданной оператором make-series, используйте собственную функцию series_fit_line().
Необходимые компоненты
- Подключаемый модуль Python должен быть включен в кластере. Это необходимо для встроенного Python, используемого в функции.
- Подключаемый модуль Python должен быть включен в базе данных. Это необходимо для встроенного Python, используемого в функции.
Синтаксис
T | invoke series_fit_poly_fl(,,, y_series y_fit_series степень fit_coeff [, x_series ], [ x_istime ])
Дополнительные сведения о соглашениях синтаксиса.
Параметры
| Имя (название) | Type | Обязательно | Описание |
|---|---|---|---|
| y_series | string |
✔️ | Имя столбца входной таблицы, содержащего зависимые переменные. То есть, серия подходит. |
| y_fit_series | string |
✔️ | Имя столбца для хранения оптимальной серии. |
| fit_coeff | string |
✔️ | Имя столбца для хранения наиболее подходящих многономиальных коэффициентов. |
| градус | int |
✔️ | Обязательный порядок полиномиального соответствия. Например, 1 для линейной регрессии, 2 для квадратной регрессии и т. д. |
| x_series | string |
Имя столбца, содержащего независимую переменную, то есть ось x или времени. Этот параметр является необязательным и необходим только для неравномерного пространства рядов. Значение по умолчанию — пустая строка, так как x является избыточной для регрессии равномерно разделенного ряда. | |
| x_istime | bool |
Этот параметр необходим только в том случае, если указан x_series , и это вектор даты и времени. |
Определение функции
Вы можете определить функцию, внедрив код как определяемую запросом функцию или создав ее в качестве хранимой функции в базе данных следующим образом:
Определите функцию с помощью следующей инструкции let. Разрешения не требуются.
Внимание
Инструкция let не может выполняться самостоятельно. За ним следует оператор табличного выражения. Чтобы запустить рабочий пример, см. примерыseries_fit_poly_fl().
let series_fit_poly_fl=(tbl:(*), y_series:string, y_fit_series:string, fit_coeff:string, degree:int, x_series:string='', x_istime:bool=False)
{
let kwargs = bag_pack('y_series', y_series, 'y_fit_series', y_fit_series, 'fit_coeff', fit_coeff, 'degree', degree, 'x_series', x_series, 'x_istime', x_istime);
let code = ```if 1:
y_series = kargs["y_series"]
y_fit_series = kargs["y_fit_series"]
fit_coeff = kargs["fit_coeff"]
degree = kargs["degree"]
x_series = kargs["x_series"]
x_istime = kargs["x_istime"]
def fit(ts_row, x_col, y_col, deg):
y = ts_row[y_col]
if x_col == "": # If there is no x column creates sequential range [1, len(y)]
x = np.arange(len(y)) + 1
else: # if x column exists check whether its a time column. If so, normalize it to the [1, len(y)] range, else take it as is.
if x_istime:
x = pd.to_numeric(pd.to_datetime(ts_row[x_col]))
x = x - x.min()
x = x / x.max()
x = x * (len(x) - 1) + 1
else:
x = ts_row[x_col]
coeff = np.polyfit(x, y, deg)
p = np.poly1d(coeff)
z = p(x)
return z, coeff
result = df
if len(df):
result[[y_fit_series, fit_coeff]] = df.apply(fit, axis=1, args=(x_series, y_series, degree,), result_type="expand")
```;
tbl
| evaluate python(typeof(*), code, kwargs)
};
// Write your query to use the function here.
Примеры
В следующих примерах для запуска функции используется оператор вызова.
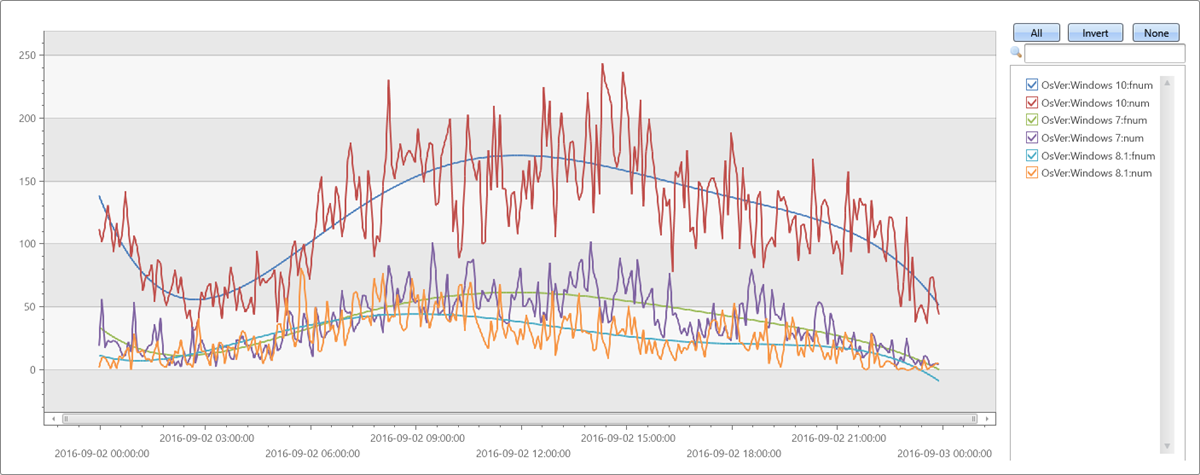
Соответствует пятому порядку полиномиал для регулярного временных рядов
Чтобы использовать определяемую запросом функцию, вызовите ее после внедренного определения функции.
let series_fit_poly_fl=(tbl:(*), y_series:string, y_fit_series:string, fit_coeff:string, degree:int, x_series:string='', x_istime:bool=False)
{
let kwargs = bag_pack('y_series', y_series, 'y_fit_series', y_fit_series, 'fit_coeff', fit_coeff, 'degree', degree, 'x_series', x_series, 'x_istime', x_istime);
let code = ```if 1:
y_series = kargs["y_series"]
y_fit_series = kargs["y_fit_series"]
fit_coeff = kargs["fit_coeff"]
degree = kargs["degree"]
x_series = kargs["x_series"]
x_istime = kargs["x_istime"]
def fit(ts_row, x_col, y_col, deg):
y = ts_row[y_col]
if x_col == "": # If there is no x column creates sequential range [1, len(y)]
x = np.arange(len(y)) + 1
else: # if x column exists check whether its a time column. If so, normalize it to the [1, len(y)] range, else take it as is.
if x_istime:
x = pd.to_numeric(pd.to_datetime(ts_row[x_col]))
x = x - x.min()
x = x / x.max()
x = x * (len(x) - 1) + 1
else:
x = ts_row[x_col]
coeff = np.polyfit(x, y, deg)
p = np.poly1d(coeff)
z = p(x)
return z, coeff
result = df
if len(df):
result[[y_fit_series, fit_coeff]] = df.apply(fit, axis=1, args=(x_series, y_series, degree,), result_type="expand")
```;
tbl
| evaluate python(typeof(*), code, kwargs)
};
//
// Fit fifth order polynomial to a regular (evenly spaced) time series, created with make-series
//
let max_t = datetime(2016-09-03);
demo_make_series1
| make-series num=count() on TimeStamp from max_t-1d to max_t step 5m by OsVer
| extend fnum = dynamic(null), coeff=dynamic(null), fnum1 = dynamic(null), coeff1=dynamic(null)
| invoke series_fit_poly_fl('num', 'fnum', 'coeff', 5)
| render timechart with(ycolumns=num, fnum)
Выходные данные
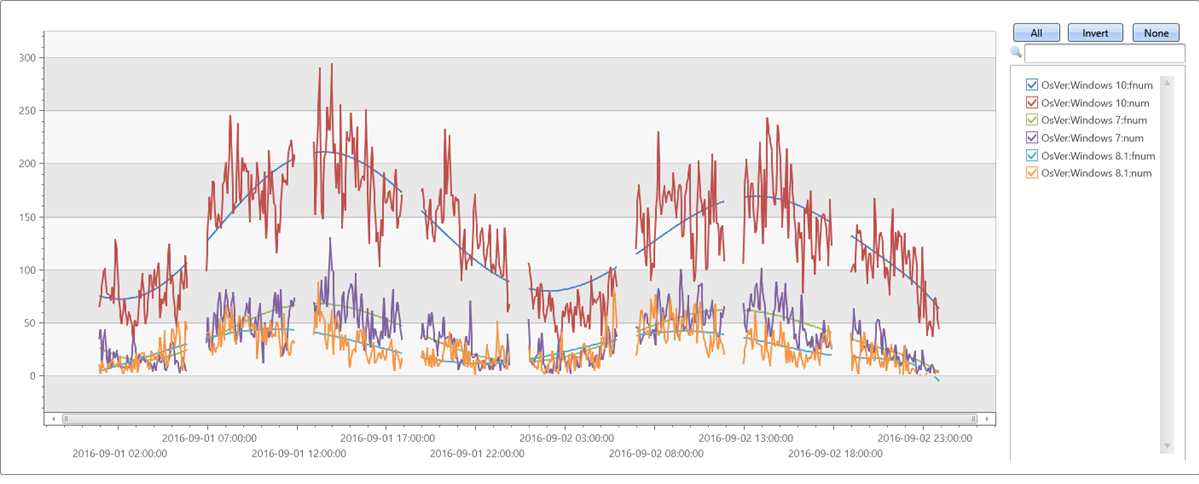
Тестирование нерегулярных временных рядов
Чтобы использовать определяемую запросом функцию, вызовите ее после внедренного определения функции.
let series_fit_poly_fl=(tbl:(*), y_series:string, y_fit_series:string, fit_coeff:string, degree:int, x_series:string='', x_istime:bool=False)
{
let kwargs = bag_pack('y_series', y_series, 'y_fit_series', y_fit_series, 'fit_coeff', fit_coeff, 'degree', degree, 'x_series', x_series, 'x_istime', x_istime);
let code = ```if 1:
y_series = kargs["y_series"]
y_fit_series = kargs["y_fit_series"]
fit_coeff = kargs["fit_coeff"]
degree = kargs["degree"]
x_series = kargs["x_series"]
x_istime = kargs["x_istime"]
def fit(ts_row, x_col, y_col, deg):
y = ts_row[y_col]
if x_col == "": # If there is no x column creates sequential range [1, len(y)]
x = np.arange(len(y)) + 1
else: # if x column exists check whether its a time column. If so, normalize it to the [1, len(y)] range, else take it as is.
if x_istime:
x = pd.to_numeric(pd.to_datetime(ts_row[x_col]))
x = x - x.min()
x = x / x.max()
x = x * (len(x) - 1) + 1
else:
x = ts_row[x_col]
coeff = np.polyfit(x, y, deg)
p = np.poly1d(coeff)
z = p(x)
return z, coeff
result = df
if len(df):
result[[y_fit_series, fit_coeff]] = df.apply(fit, axis=1, args=(x_series, y_series, degree,), result_type="expand")
```;
tbl
| evaluate python(typeof(*), code, kwargs)
};
let max_t = datetime(2016-09-03);
demo_make_series1
| where TimeStamp between ((max_t-2d)..max_t)
| summarize num=count() by bin(TimeStamp, 5m), OsVer
| order by TimeStamp asc
| where hourofday(TimeStamp) % 6 != 0 // delete every 6th hour to create unevenly spaced time series
| summarize TimeStamp=make_list(TimeStamp), num=make_list(num) by OsVer
| extend fnum = dynamic(null), coeff=dynamic(null)
| invoke series_fit_poly_fl('num', 'fnum', 'coeff', 8, 'TimeStamp', True)
| render timechart with(ycolumns=num, fnum)
Выходные данные
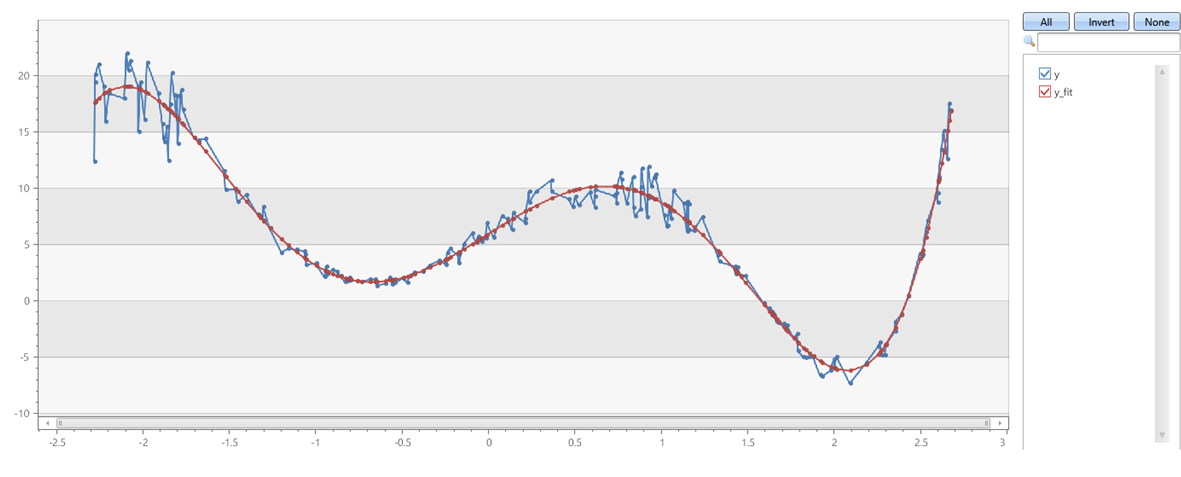
Пятый порядок полиномиальных с шумом на осях x и y
Чтобы использовать определяемую запросом функцию, вызовите ее после внедренного определения функции.
let series_fit_poly_fl=(tbl:(*), y_series:string, y_fit_series:string, fit_coeff:string, degree:int, x_series:string='', x_istime:bool=False)
{
let kwargs = bag_pack('y_series', y_series, 'y_fit_series', y_fit_series, 'fit_coeff', fit_coeff, 'degree', degree, 'x_series', x_series, 'x_istime', x_istime);
let code = ```if 1:
y_series = kargs["y_series"]
y_fit_series = kargs["y_fit_series"]
fit_coeff = kargs["fit_coeff"]
degree = kargs["degree"]
x_series = kargs["x_series"]
x_istime = kargs["x_istime"]
def fit(ts_row, x_col, y_col, deg):
y = ts_row[y_col]
if x_col == "": # If there is no x column creates sequential range [1, len(y)]
x = np.arange(len(y)) + 1
else: # if x column exists check whether its a time column. If so, normalize it to the [1, len(y)] range, else take it as is.
if x_istime:
x = pd.to_numeric(pd.to_datetime(ts_row[x_col]))
x = x - x.min()
x = x / x.max()
x = x * (len(x) - 1) + 1
else:
x = ts_row[x_col]
coeff = np.polyfit(x, y, deg)
p = np.poly1d(coeff)
z = p(x)
return z, coeff
result = df
if len(df):
result[[y_fit_series, fit_coeff]] = df.apply(fit, axis=1, args=(x_series, y_series, degree,), result_type="expand")
```;
tbl
| evaluate python(typeof(*), code, kwargs)
};
range x from 1 to 200 step 1
| project x = rand()*5 - 2.3
| extend y = pow(x, 5)-8*pow(x, 3)+10*x+6
| extend y = y + (rand() - 0.5)*0.5*y
| summarize x=make_list(x), y=make_list(y)
| extend y_fit = dynamic(null), coeff=dynamic(null)
| invoke series_fit_poly_fl('y', 'y_fit', 'coeff', 5, 'x')
|fork (project-away coeff) (project coeff | mv-expand coeff)
| render linechart
Выходные данные