HTTPS and Keep-Alive Connections
As we explore network performance on the “real-world web”, one bad pattern in particular keeps recurring, and it’s not something that our many IE9 Networking Performance Improvements alone will resolve.
The bad pattern is the use of Connection: close semantics for HTTPS connections. In this bad pattern, a website allows only a single request and response on every HTTPS connection before closing the connection.
Defeating HTTP/1.1’s default Keep-Alive behavior is a bad practice for regular HTTP connections but it’s far worse for HTTPS connections because the initial setup costs of a HTTPS connection are far higher than a regular HTTP connection. Not only does the browser pay the performance penalty of setting up a new TCP/IP connection, including the handshake and initial congestion window sizing, but the request’s progress is also penalized by the time required to complete the HTTPS handshake used to secure the connection.
To do all of that work and then only use it for one HTTP request and response is a terrible waste of resources-- it's like paving a highway, allowing a single car to drive down it, and then dynamiting the road after it passes. You then need to pave a new highway for the next car, only to subsequently blow it up, and so on. This bad pattern can dramatically slow down the loading of the page and increase the load on your server.
Browsers have no choice but to close the connection when directed by the server; it would be a violation of the standard (and almost certainly wouldn’t work) to try to ignore the server’s directive to close the connection.
A while ago, I saw one site that was particularly bad in this regard—it was a shopping site that showed many product thumbnails on every page; the page included 200 thumbnail images, each delivered over HTTPS, and each from a server in Asia that closed the connection after every single response. While browsers work their hardest to load this page, performing multiple connections in parallel, each page on the site took several minutes to load. Using Fiddler to simulate exactly the same site, but allowing connection reuse, the site’s pages would load in about 15 seconds. I haven’t been back to that site since (they may not be in business any longer) but the problem can even be seen on “big” sites used by millions of people every day.
You can observe Connection Reuse with Fiddler’s Timeline tab. Right-click on the tab and change the view to Server PortMap and then look to see how many connections are reused.
On a site that makes good use of Keep-Alive, you’ll see that many connections are reused for multiple requests.
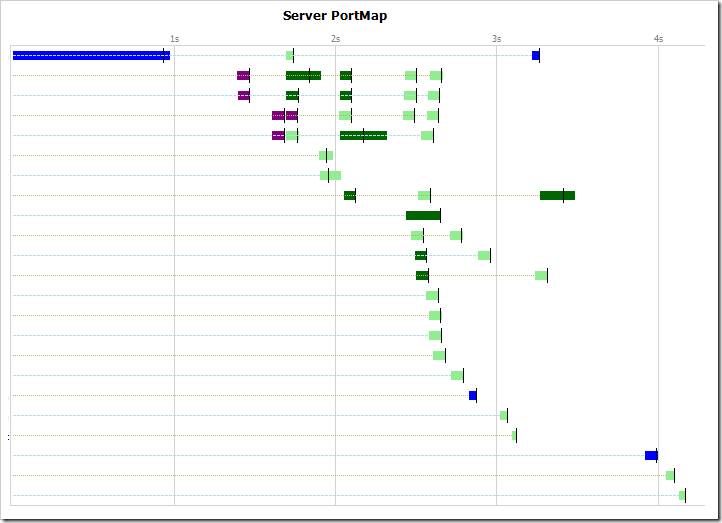
This site only has more than 6 lines (the connections-per-host limit) because it “shards” its requests across a number of related domains.
In contrast, here’s a site which does not allow connection reuse:
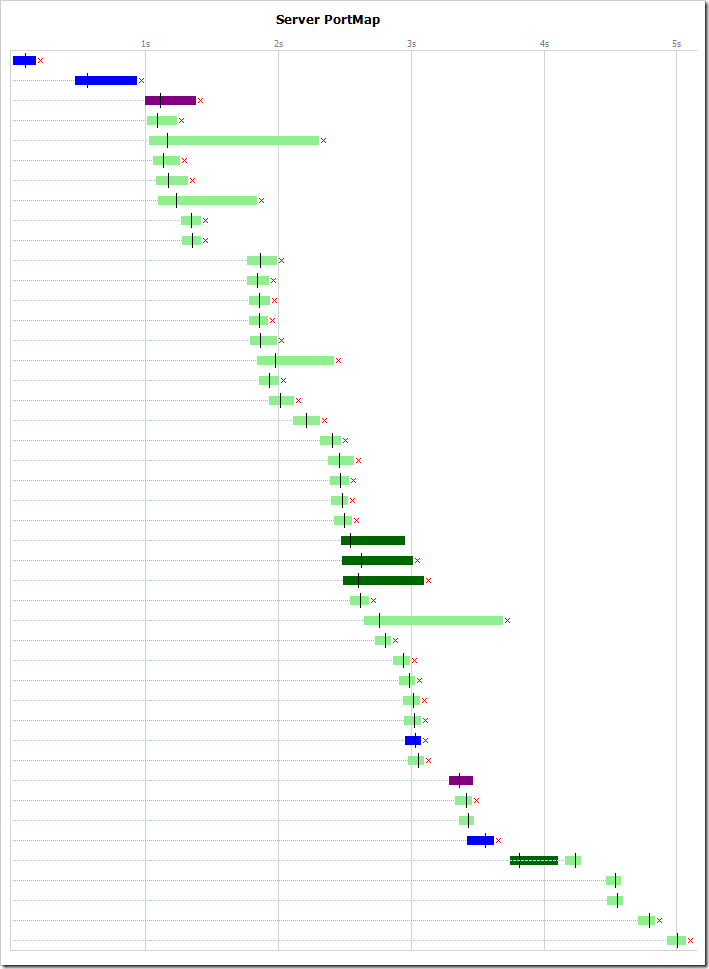
The chart shows that each request is made on a new connection, and a small red-x after each transfer indicates that the server is using the Connection: close pattern. Only a few connections are reused (near the bottom of the trace) as these are cross-domain requests to a server that is configured for better performance.
Overall, loading of the site is delayed due to the overhead in establishing HTTPS connections. The performance penalty will be even larger for clients that have longer round-trip times (e.g. on 3G connections, or more geographically distant users).
Our team did a bit of research into this bad pattern, and we found two common origins of the bad pattern.
In the first, a thoughtful web developer or operations team reasons: “Hey, HTTPS connections are expensive to maintain on the server. Let’s be sure to tear those down as soon as possible to free up the server to accept new connections.” That, of course, completely misses the point that if the server wasn’t tearing down the connections, the server would be under significantly lighter load to begin with!Sites that were deliberately written with this bad pattern load slowly in all browsers.
We also found another root cause—ancient advice for the configuration of Apache+OpenSSL. Prior to IE6, ancient and unpatched versions of IE sometimes encountered connection failures when interacting with HTTPS servers when Keep-Alive is used. That problem was fixed nearly a decade ago, but outdated 1999-era configuration advice continues to harm performance for unaware server administrators:
https://www.modssl.org/docs/2.8/ssl_faq.html#ToC49
https://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.0/ssl/ssl_faq.html
SetEnvIf User-Agent ".*MSIE.*" \
nokeepalive ssl-unclean-shutdown \
downgrade-1.0 force-response-1.0https://www.faqs.org/docs/securing/chap29sec245.html
SSLOptions +ExportCertData +StrictRequire
SetEnvIf User-Agent ".*MSIE.*" nokeepalive ssl-unclean-shutdown
SetEnvIf Request_URI \.gif$ gif-image
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/ssl_request_log \
"%t %h %{SSL_PROTOCOL}x %{SSL_CIPHER}x \"%r\" %b" env=!gif-image
</VirtualHost>
Four years ago, there was a public call to update the guidance to reflect the fact that users of more modern browsers were paying an unneeded performance penalty. Finally, in June 2010, the default guidance was changed in recognition of the fact that the problem never affected IE6 and later:
BrowserMatch ".*MSIE [1-5].*" \
nokeepalive ssl-unclean-shutdown \
downgrade-1.0 force-response-1.0
Unfortunately, many major Apache installations still haven’t been updated with even this guidance. Also, alert readers will spot a very obvious problem with the “new” regular expression.
In the expression above, any IE version that starts with “1” will be treated as outdated and served connection slowly without Keep-Alive. Internet Explorer 1.0 didn’t even support SSL at all (SSL was added in 2.0), but worse, this loosely-written regular expression will also match future MSIE 10.0, MSIE 11.0, MSIE 12.0 (etc)user-agent strings. Hence, Apache hosts will one day find that the newest browsers are forced into the “slow” lane!
At the very least, Apache hosts should update their regular expression to this:
BrowserMatch ".*MSIE [2-5]\..*" \
nokeepalive ssl-unclean-shutdown \
downgrade-1.0 force-response-1.0
…but ultimately, they should probably remove this hack altogether. The ancient Internet Explorer 6’s marketshare is in decline, and there’s almost never any business reason to try to accommodate even older browsers.
Thanks for your help in building a faster web!
-Eric Lawrence
Comments
Anonymous
March 26, 2011
Opera 10.0+ has "Opera/9.80" in its user agent string. This would be acceptable solution for Internet Explorer, too.Anonymous
March 26, 2011
Yes, lying to accommodate buggy software has a long history, and its own set of tradeoffs. However, the number of servers which make this mistake for all versions far outnumbers those using the new-but-still-bad guidance published last year.Anonymous
March 26, 2011
How is this behaviour by websites and webservers going to change?Anonymous
March 27, 2011
@Hal: Websites can update their buggy Apache configuration files and will immediately start loading more quickly.Anonymous
March 27, 2011
We have a load balancer from f5 which, when using compression and chunked transfers (ie when we flush the response before it ends) it automatically adds a connection-close header. Also, asp.net sometimes adds this header as described here: www.epocalipse.com/.../avoiding-connection-close-when-returning-a-304-not-modified-status-code-in-aspnet-part-2Anonymous
March 28, 2011
Eric this is a great article on the impact of Connection:Close ! We observed a similar issue on a major website and posted an article on the same topic at: blog.catchpoint.com/.../relying_on_web_performance_monitoring_to_discover_release_problemsAnonymous
March 30, 2011
Various resources (see end) also include the following directives for later versions of Internet Explorer: BrowserMatch "MSIE [6-9]" ssl-unclean-shutdown Do you any more details on this? Is it still required for Internet Explorer 10? newestindustry.org/.../dear-apache-software-foundation-fix-the-msie-ssl-keepalive-settings stackoverflow.com/.../what-must-i-do-to-make-content-such-as-images-served-over-https-be-cached-client confluence.atlassian.com/.../General+Apache+Configuration+NotesAnonymous
March 30, 2011
Sorry, that was a brain explosion on the previous comment. Internet Explorer 10 doesn't exist yet. Nonetheless do you know why people are specifying ssl-unclean-shutdown for later versions of Internet Explorer? My concern, like what you pointed out with the regex people have been using in your post, is that a similar problem could exist when Internet Explorer 10 is released if ssl-unclean-shutdown is still required for that browser version - the regex won't match and ssl-unclean-shutdown won't be applied. Of course if Internet Explorer 10 doesn't need ssl-unclean-shutdown then it will all be conveniently moot ;)Anonymous
March 30, 2011
Hi Eric! I saw some really weird IE behaviour in case you shard CSS files and CSS images across different domains when using SSL. Any chance you have an insight on this? I wrote some more analysis about this here: webforscher.wordpress.com/.../domain-sharding-and-ssl Kind regards, MarkusAnonymous
April 03, 2011
@Markus: Thanks for the note and writeup. Yes, we actually saw this a few months ago and we know what causes it; basically, you have to have #cross-origin HTTPS references > max-connections-per-server and you can hit an unnecessary client closure issue. We're looking at addressing this for a future release of IE. Thx.Anonymous
April 15, 2011
I'm with Simon, seeing "ssl-unclean-shutdown" applied to IE. Anyone have more insight on which versions of IE that should apply to?Anonymous
April 15, 2011
The comment has been removedAnonymous
April 15, 2011
@Adam: you can safely remove the complete SetEnvIF. I have it in none of my virtual hosts and the https ones work just fine with all versions of IE (versions before 6 do not count).Anonymous
November 10, 2011
The comment has been removedAnonymous
January 08, 2012
The comment has been removedAnonymous
January 08, 2012
The comment has been removedAnonymous
October 07, 2013
are there any similar settings which can be done in IIS 7, we have similar problem in our sharepoint site, all css/js/images are loading grudally in subsequent page refresh... ?Anonymous
October 08, 2013
@Siddharth: Unless you've done something very strange, IIS will never close connections like this. You might consider capturing a SAZ File with Fiddler and asking your question in the Fiddler Discussion group: fiddler2.com/rAnonymous
December 13, 2013
HTTP/1.1 servers default to the keep-alive setting of the Connection header. Why then do most browsers include Connection: keep-alive in their requests even when they know that the target server supports HTTP/1.1? [EricLaw] You're correct that this is unnecessary and it's probably done only for historical reasons. My understanding is that the .NET HTTP objects only send the header on the first request, a behavior that some developers found confusing.Anonymous
February 09, 2014
Eric, thanks for the explanation - one thing I don't understand is that the CONNECT Request from IE9 (in my case) is HTTP 1.0 rather than HTTP 1.1. Is this because Apache told IE it would not accept 1.1 or does IE always use CONNECT HTTP 1.0? [EricLaw] For historical reasons, IE always uses HTTP/1.0 for its CONNECT tunnels. We pondered changing this a few times but couldn't think of any benefit to doing so. (Inside the tunnel, the secure traffic is HTTP/1.1 by default)