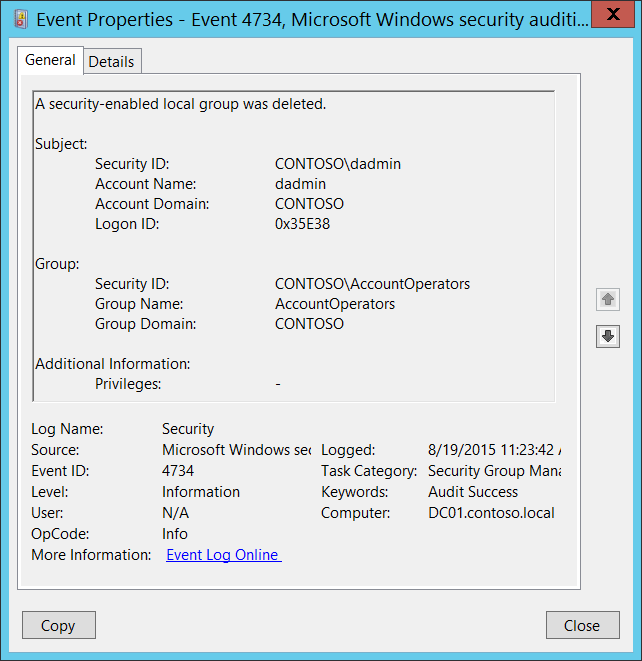
4734(S): A security-enabled local group was deleted.
Subcategory: Audit Security Group Management
Event Description:
This event generates every time security-enabled (security) local group is deleted.
This event generates on domain controllers, member servers, and workstations.
Note For recommendations, see Security Monitoring Recommendations for this event.
Event XML:
- <Event xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/win/2004/08/events/event">
- <System>
<Provider Name="Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing" Guid="{54849625-5478-4994-A5BA-3E3B0328C30D}" />
<EventID>4734</EventID>
<Version>0</Version>
<Level>0</Level>
<Task>13826</Task>
<Opcode>0</Opcode>
<Keywords>0x8020000000000000</Keywords>
<TimeCreated SystemTime="2015-08-19T18:23:42.426245700Z" />
<EventRecordID>175039</EventRecordID>
<Correlation />
<Execution ProcessID="520" ThreadID="1072" />
<Channel>Security</Channel>
<Computer>DC01.contoso.local</Computer>
<Security />
</System>
- <EventData>
<Data Name="TargetUserName">AccountOperators</Data>
<Data Name="TargetDomainName">CONTOSO</Data>
<Data Name="TargetSid">S-1-5-21-3457937927-2839227994-823803824-6605</Data>
<Data Name="SubjectUserSid">S-1-5-21-3457937927-2839227994-823803824-1104</Data>
<Data Name="SubjectUserName">dadmin</Data>
<Data Name="SubjectDomainName">CONTOSO</Data>
<Data Name="SubjectLogonId">0x35e38</Data>
<Data Name="PrivilegeList">-</Data>
</EventData>
</Event>
Required Server Roles: None.
Minimum OS Version: Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista.
Event Versions: 0.
Field Descriptions:
Subject:
- Security ID [Type = SID]: SID of account that requested the “delete group” operation. Event Viewer automatically tries to resolve SIDs and show the account name. If the SID cannot be resolved, you will see the source data in the event.
Note A security identifier (SID) is a unique value of variable length used to identify a trustee (security principal). Each account has a unique SID that is issued by an authority, such as an Active Directory domain controller, and stored in a security database. Each time a user logs on, the system retrieves the SID for that user from the database and places it in the access token for that user. The system uses the SID in the access token to identify the user in all subsequent interactions with Windows security. When a SID has been used as the unique identifier for a user or group, it cannot ever be used again to identify another user or group. For more information about SIDs, see Security identifiers.
Account Name [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of the account that requested the “delete group” operation.
Account Domain [Type = UnicodeString]: subject’s domain or computer name. Formats vary, and include the following:
Domain NETBIOS name example: CONTOSO
Lowercase full domain name: contoso.local
Uppercase full domain name: CONTOSO.LOCAL
For some well-known security principals, such as LOCAL SERVICE or ANONYMOUS LOGON, the value of this field is “NT AUTHORITY”.
For local user accounts, this field will contain the name of the computer or device that this account belongs to, for example: “Win81”.
Logon ID [Type = HexInt64]: hexadecimal value that can help you correlate this event with recent events that might contain the same Logon ID, for example, “4624: An account was successfully logged on.”
Group:
Security ID [Type = SID]: SID of deleted group. Event Viewer automatically tries to resolve SIDs and show the group name. If the SID cannot be resolved, you will see the source data in the event.
Group Name [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of the group that was deleted. For example: ServiceDesk
Group Domain [Type = UnicodeString]: domain or computer name of the deleted group. Formats vary, and include the following:
Domain NETBIOS name example: CONTOSO
Lowercase full domain name: contoso.local
Uppercase full domain name: CONTOSO.LOCAL
For a local group, this field will contain the name of the computer to which this new group belongs, for example: “Win81”.
Built-in groups: Builtin
Additional Information:
- Privileges [Type = UnicodeString]: the list of user privileges which were used during the operation, for example, SeBackupPrivilege. This parameter might not be captured in the event, and in that case appears as “-”. See full list of user privileges in “Table 8. User Privileges.”.
Security Monitoring Recommendations
For 4734(S): A security-enabled local group was deleted.
Important For this event, also see Appendix A: Security monitoring recommendations for many audit events.
If you have a list of critical local or domain security groups in the organization, and need to specifically monitor these groups for any change, especially group deletion, monitor events with the “Group\Group Name” values that correspond to the critical local or domain security groups. Examples of critical local or domain groups are built-in local administrators group, domain admins, enterprise admins, and so on.
If you need to monitor each time a local or domain security group is deleted, to see who deleted it and when, monitor this event. Typically, this event is used as an informational event, to be reviewed if needed.