Realçar pontos de dados nos Visuais do Power BI
Este artigo descreve como realçar dados em elementos visuais do Power BI.
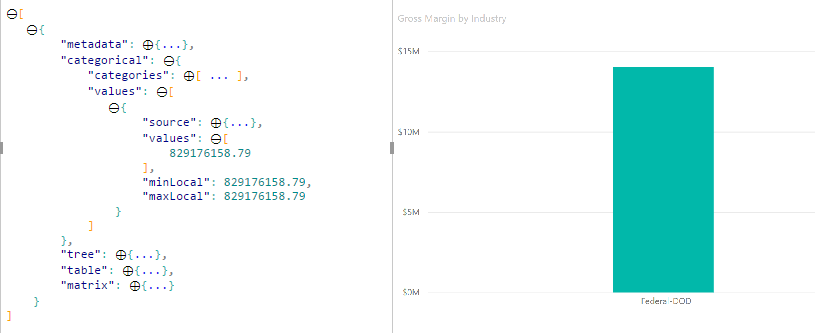
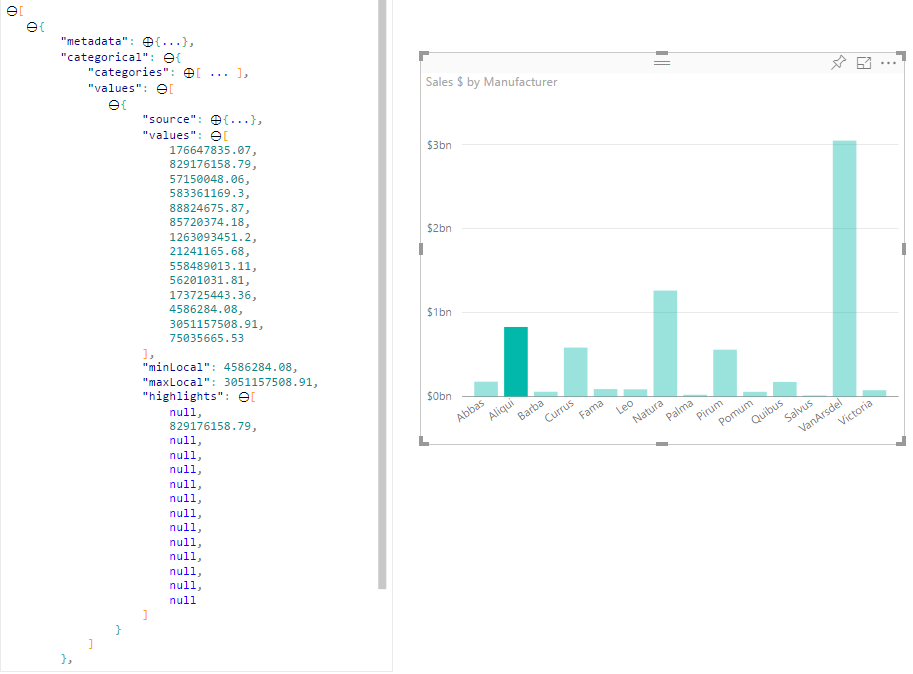
Por padrão, quando um elemento é selecionado, a matriz no dataView objeto é filtrada values para mostrar apenas os valores selecionados. Quando a values matriz é filtrada, todos os outros elementos visuais na página mostram apenas os dados selecionados.
Se você definir a supportsHighlight propriedade em seu capabilities.json arquivo como true, isso resultará na matriz não filtrada values completa junto com uma highlights matriz. A highlights matriz tem o mesmo comprimento que a matriz de valores e todos os valores não selecionados são definidos como null. Com essa propriedade habilitada, os dados apropriados no visual são realçados comparando a values matriz com a highlights matriz.
No exemplo, observe que:
- Sem suporte a realce, a seleção é o
valuesúnico valor na matriz e a única barra apresentada na visualização de dados. - Com suporte a
valuesrealce, todos os valores estão na matriz. Ahighlightsmatriz contém umnullvalor para elementos não realçados. Todas as barras aparecem na visualização de dados e a barra realçada tem uma cor diferente.
Também pode haver várias seleções e destaques parciais. Os valores realçados são apresentados na visualização de dados.
Nota
O mapeamento da exibição de dados de tabela não oferece suporte ao recurso de destaques.
Realce pontos de dados com mapeamento de exibição de dados categórico
Para elementos visuais com mapeamento de exibição de dados categóricos, adicione "supportsHighlight": true ao capabilities.json arquivo. Por exemplo:
{
"dataRoles": [
{
"displayName": "Category",
"name": "category",
"kind": "Grouping"
},
{
"displayName": "Value",
"name": "value",
"kind": "Measure"
}
],
"dataViewMappings": [
{
"categorical": {
"categories": {
"for": {
"in": "category"
}
},
"values": {
"for": {
"in": "value"
}
}
}
}
],
"supportsHighlight": true
}
Depois de remover o código desnecessário, o código-fonte visual padrão se parece com o exemplo a seguir:
"use strict";
// ... default imports list
import { FormattingSettingsService } from "powerbi-visuals-utils-formattingmodel";
import DataViewCategorical = powerbi.DataViewCategorical;
import DataViewCategoryColumn = powerbi.DataViewCategoryColumn;
import PrimitiveValue = powerbi.PrimitiveValue;
import DataViewValueColumn = powerbi.DataViewValueColumn;
import { VisualFormattingSettingsModel } from "./settings";
export class Visual implements IVisual {
private target: HTMLElement;
private formattingSettings: VisualFormattingSettingsModel;
private formattingSettingsService: FormattingSettingsService;
constructor(options: VisualConstructorOptions) {
console.log('Visual constructor', options);
this.formattingSettingsService = new FormattingSettingsService();
this.target = options.element;
this.host = options.host;
}
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
this.formattingSettings = this.formattingSettingsService.populateFormattingSettingsModel(VisualFormattingSettingsModel, options.dataViews);
console.log('Visual update', options);
}
// Returns properties pane formatting model content hierarchies, properties and latest formatting values, Then populate properties pane.
// This method is called once every time we open properties pane or when the user edit any format property.
public getFormattingModel(): powerbi.visuals.FormattingModel {
return this.formattingSettingsService.buildFormattingModel(this.formattingSettings);
}
}
Importe as interfaces necessárias para processar dados do Power BI:
import DataViewCategorical = powerbi.DataViewCategorical;
import DataViewCategoryColumn = powerbi.DataViewCategoryColumn;
import PrimitiveValue = powerbi.PrimitiveValue;
import DataViewValueColumn = powerbi.DataViewValueColumn;
Crie o elemento raiz div para valores de categoria:
export class Visual implements IVisual {
private target: HTMLElement;
private formattingSettings: VisualFormattingSettingsModel;
private formattingSettingsService: FormattingSettingsService;
private div: HTMLDivElement; // new property
constructor(options: VisualConstructorOptions) {
console.log('Visual constructor', options);
this.formattingSettingsService = new FormattingSettingsService();
this.target = options.element;
this.host = options.host;
// create div element
this.div = document.createElement("div");
this.div.classList.add("vertical");
this.target.appendChild(this.div);
}
// ...
}
Limpe o conteúdo dos elementos div antes de renderizar novos dados:
// ...
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
this.formattingSettings = this.formattingSettingsService.populateFormattingSettingsModel(VisualFormattingSettingsModel, options.dataViews);
console.log('Visual update', options);
while (this.div.firstChild) {
this.div.removeChild(this.div.firstChild);
}
// ...
}
Obtenha as categorias e os valores de medida do dataView objeto:
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
this.formattingSettings = this.formattingSettingsService.populateFormattingSettingsModel(VisualFormattingSettingsModel, options.dataViews);
console.log('Visual update', options);
while (this.div.firstChild) {
this.div.removeChild(this.div.firstChild);
}
const dataView: DataView = options.dataViews[0];
const categoricalDataView: DataViewCategorical = dataView.categorical;
const categories: DataViewCategoryColumn = categoricalDataView.categories[0];
const categoryValues = categories.values;
const measures: DataViewValueColumn = categoricalDataView.values[0];
const measureValues = measures.values;
const measureHighlights = measures.highlights;
// ...
}
Onde categoryValues é uma matriz de valores de categoria, measureValues é uma matriz de medidas e measureHighlights é as partes destacadas de valores.
Nota
Se os measureHighlights valores da propriedade forem inferiores aos categoryValues valores da propriedade, então o valor foi parcialmente realçado.
Enumere a categoryValues matriz e obtenha os valores e destaques correspondentes:
// ...
const measureHighlights = measures.highlights;
categoryValues.forEach((category: PrimitiveValue, index: number) => {
const measureValue = measureValues[index];
const measureHighlight = measureHighlights && measureHighlights[index] ? measureHighlights[index] : null;
console.log(category, measureValue, measureHighlight);
});
Crie div elementos para p exibir e visualizar valores de exibição de dados no DOM visual:
categoryValues.forEach((category: PrimitiveValue, index: number) => {
const measureValue = measureValues[index];
const measureHighlight = measureHighlights && measureHighlights[index] ? measureHighlights[index] : null;
console.log(category, measureValue, measureHighlight);
// div element. it contains elements to display values and visualize value as progress bar
let div = document.createElement("div");
div.classList.add("horizontal");
this.div.appendChild(div);
// div element to visualize value of measure
let barValue = document.createElement("div");
barValue.style.width = +measureValue * 10 + "px";
barValue.style.display = "flex";
barValue.classList.add("value");
// element to display category value
let bp = document.createElement("p");
bp.innerText = category.toString();
// div element to visualize highlight of measure
let barHighlight = document.createElement("div");
barHighlight.classList.add("highlight")
barHighlight.style.backgroundColor = "blue";
barHighlight.style.width = +measureHighlight * 10 + "px";
// element to display highlighted value of measure
let p = document.createElement("p");
p.innerText = `${measureHighlight}/${measureValue}`;
barHighlight.appendChild(bp);
div.appendChild(barValue);
barValue.appendChild(barHighlight);
div.appendChild(p);
});
Aplique os estilos necessários para os elementos usarem flexboxe defina cores para os elementos div:
div.vertical {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
div.horizontal {
display: flex;
flex-direction: row;
}
div.highlight {
background-color: blue
}
div.value {
background-color: red;
display: flex;
}
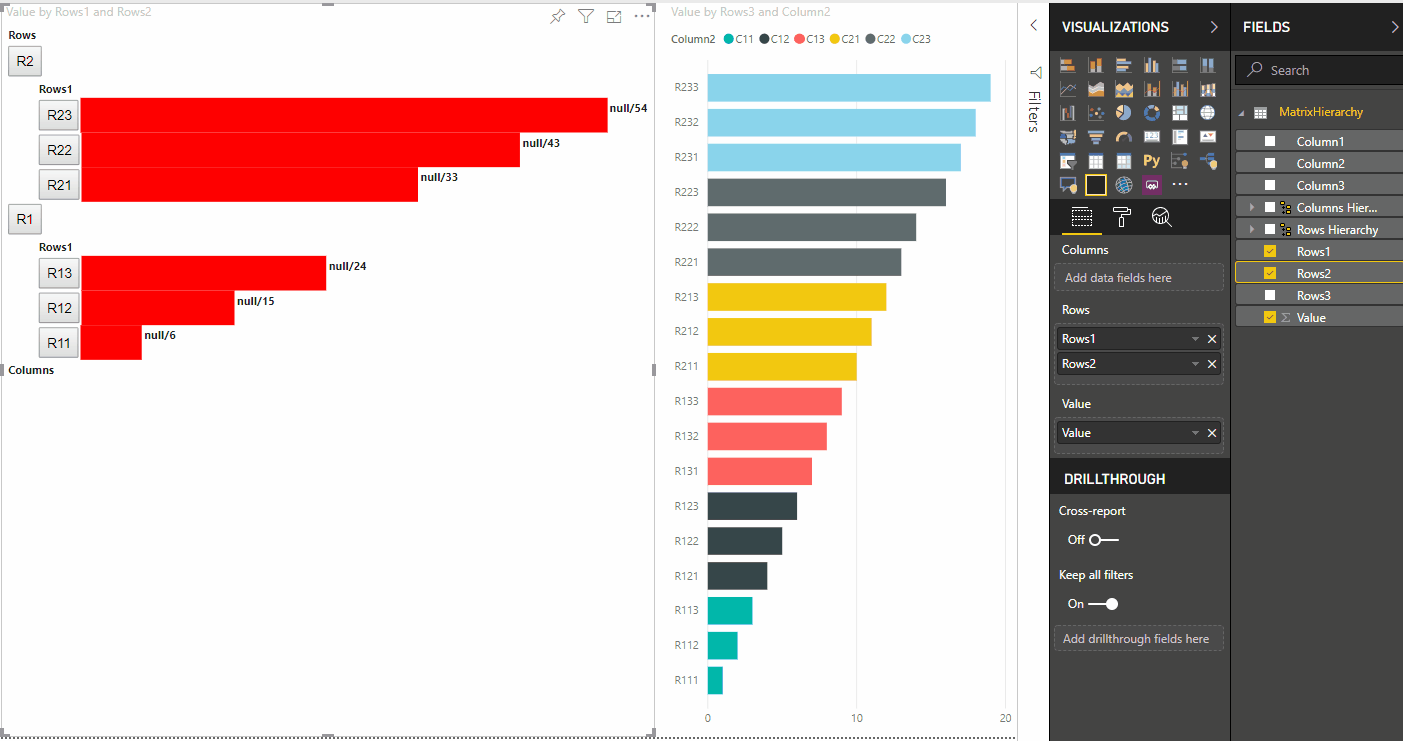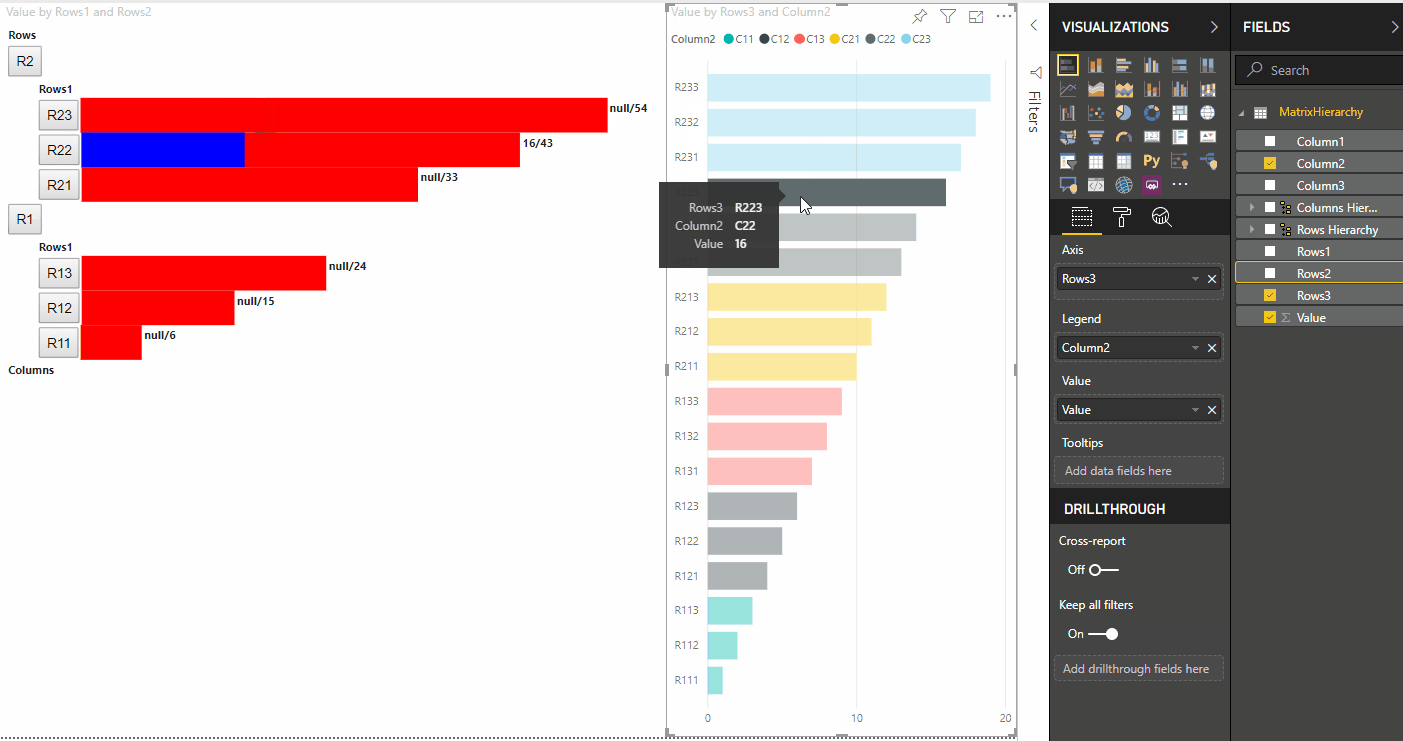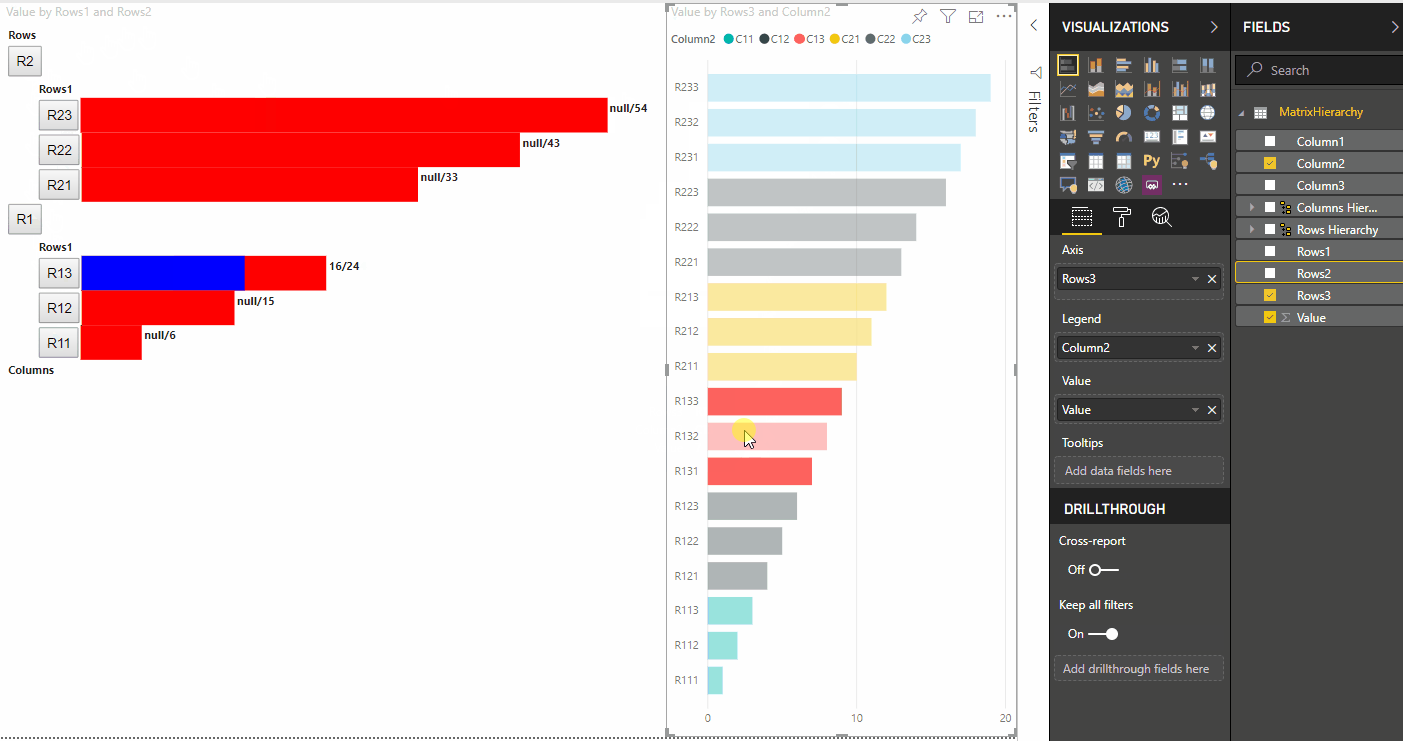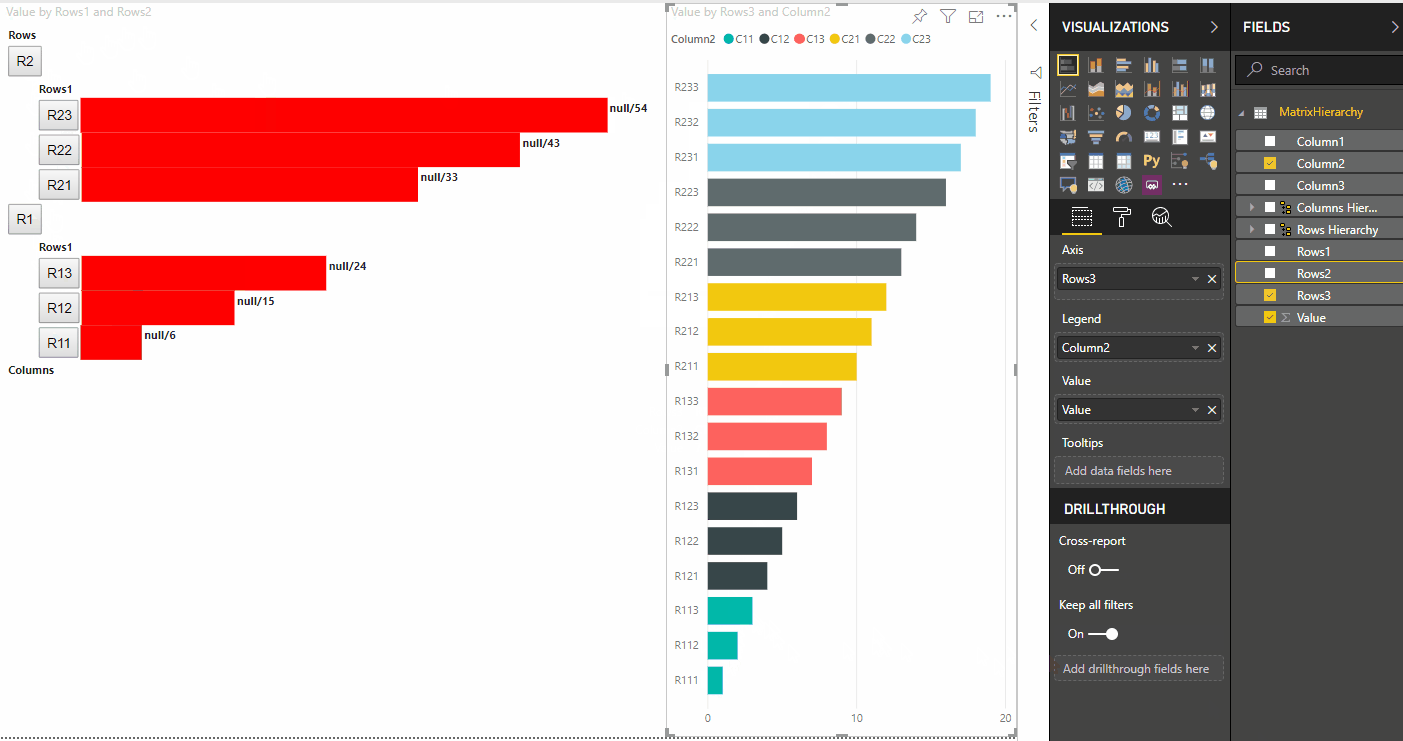
A seguinte visão do visual é o resultado:
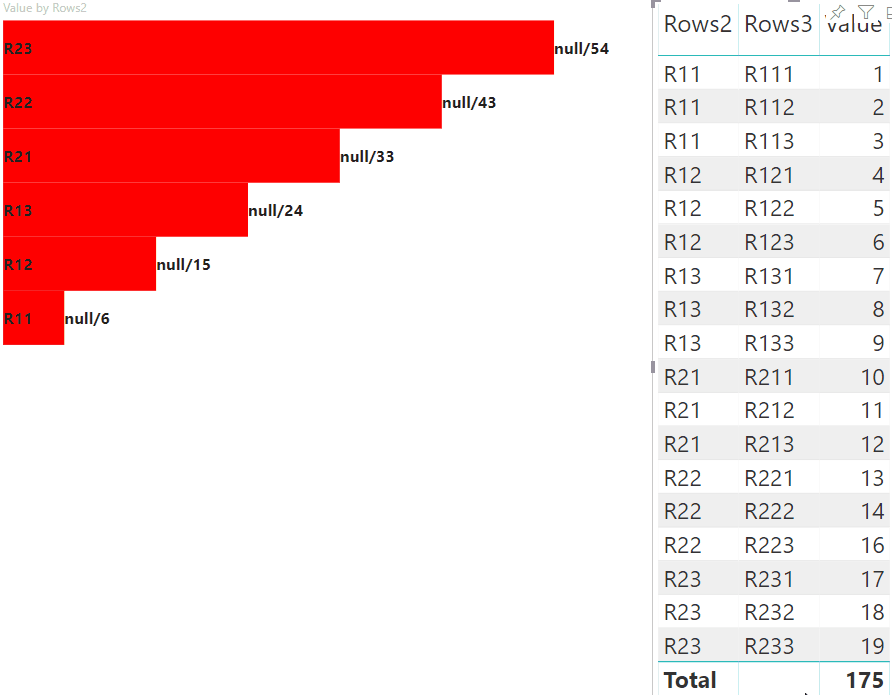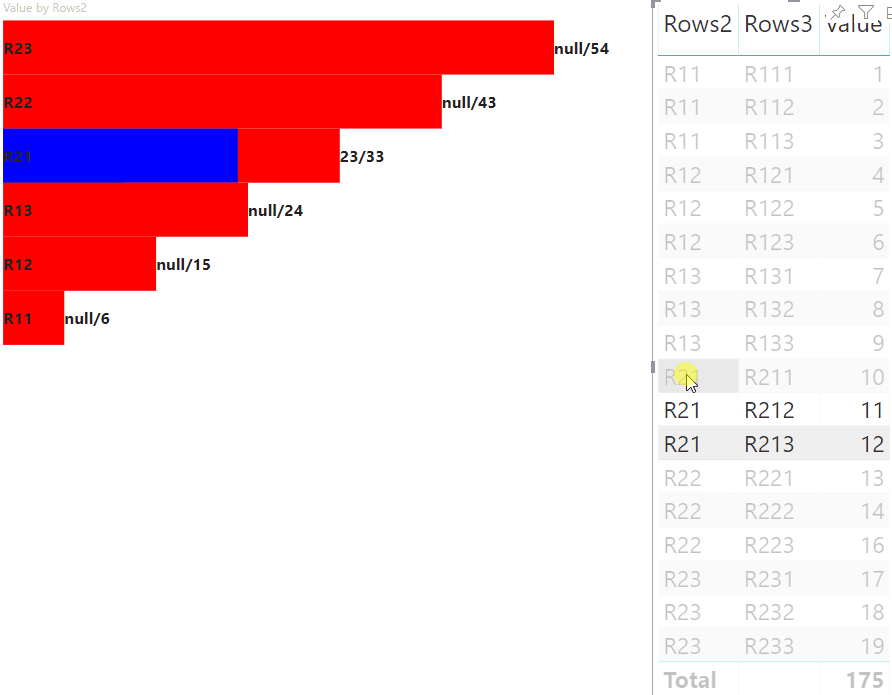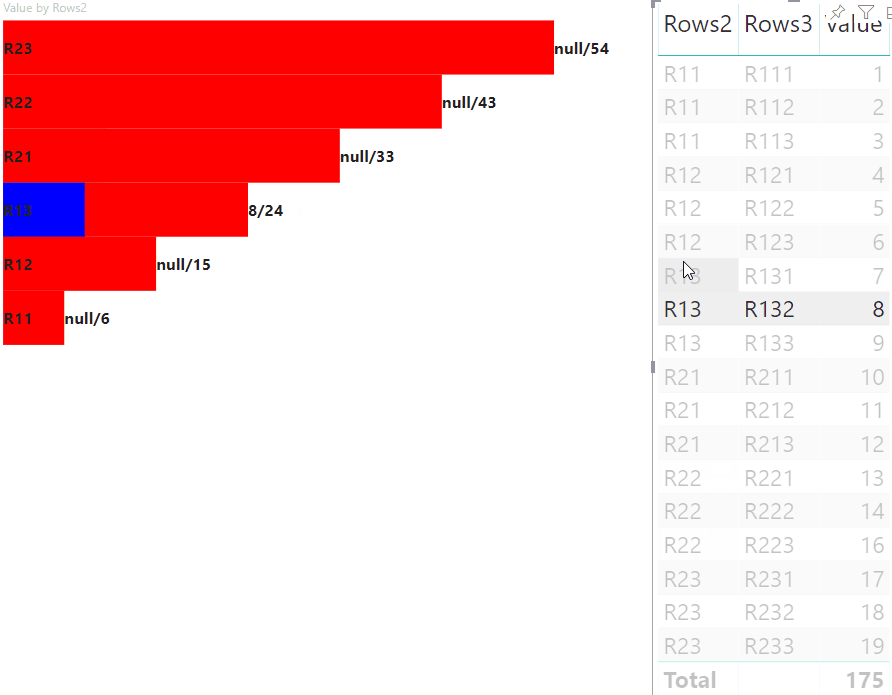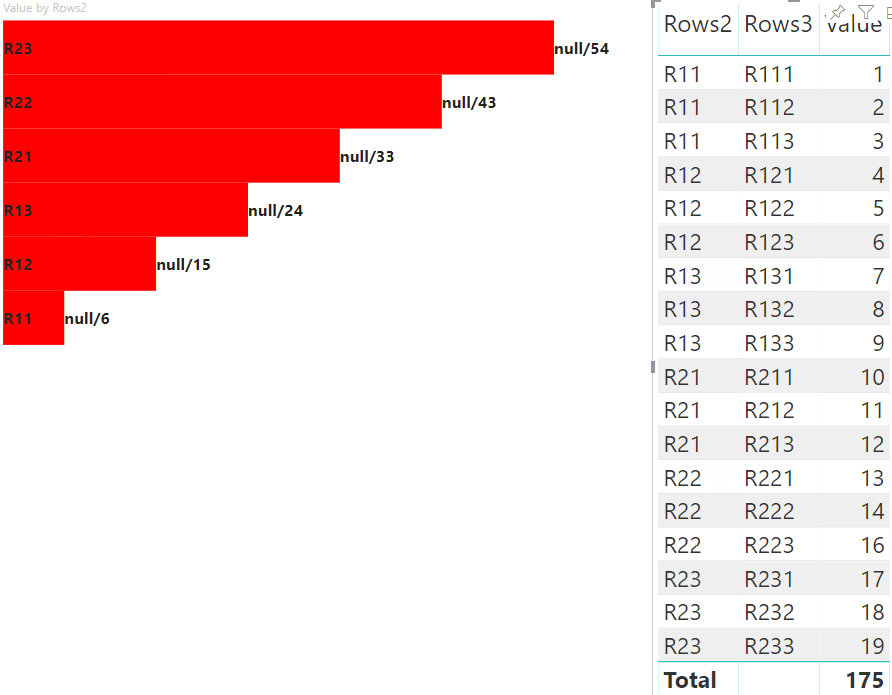
Realçar pontos de dados com mapeamento de exibição de dados de matriz
Para elementos visuais com mapeamento de exibição de dados de matriz, adicione "supportsHighlight": true ao capabilities.json arquivo. Por exemplo:
{
"dataRoles": [
{
"displayName": "Columns",
"name": "columns",
"kind": "Grouping"
},
{
"displayName": "Rows",
"name": "rows",
"kind": "Grouping"
},
{
"displayName": "Value",
"name": "value",
"kind": "Measure"
}
],
"dataViewMappings": [
{
"matrix": {
"columns": {
"for": {
"in": "columns"
}
},
"rows": {
"for": {
"in": "rows"
}
},
"values": {
"for": {
"in": "value"
}
}
}
}
],
"supportsHighlight": true
}
Os dados de exemplo para criar uma hierarquia para mapeamento de exibição de dados de matriz:
| Linha1 | Linha2 | Linha3 | Coluna1 | Column2 | Column3 | Valores |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R11 | R111 | C1 | C11 | C111 | 1 |
| R1 | R11 | R112 | C1 | C11 | C112 | 2 |
| R1 | R11 | R113 | C1 | C11 | C113 | 3 |
| R1 | R12 | R121 | C1 | C12 | C121 | 4 |
| R1 | R12 | R122 | C1 | C12 | C122 | 5 |
| R1 | R12 | R123 | C1 | C12 | C123 | 6 |
| R1 | R13 | R131 | C1 | C13 | C131 | 7 |
| R1 | R13 | R132 | C1 | C13 | C132 | 8 |
| R1 | R13 | R133 | C1 | C13 | C133 | 9 |
| R2 | R21 | R211 | C2 | C21 | C211 | 10 |
| R2 | R21 | R212 | C2 | C21 | C212 | 11 |
| R2 | R21 | R213 | C2 | C21 | C213 | 12 |
| R2 | R22 | R221 | C2 | C22 | C221 | 13 |
| R2 | R22 | R222 | C2 | C22 | C222 | 14 |
| R2 | R22 | R223 | C2 | C22 | C223 | 16 |
| R2 | R23 | R231 | C2 | C23 | C231 | 17 |
| R2 | R23 | R232 | C2 | C23 | C232 | 18 |
| R2 | R23 | R233 | C2 | C23 | C233 | 19 |
Crie o projeto visual padrão e aplique o exemplo do capabilities.json arquivo.
Depois de remover o código desnecessário, o código-fonte visual padrão se parece com o exemplo a seguir:
"use strict";
// ... default imports
import { FormattingSettingsService } from "powerbi-visuals-utils-formattingmodel";
import { VisualFormattingSettingsModel } from "./settings";
export class Visual implements IVisual {
private target: HTMLElement;
private formattingSettings: VisualFormattingSettingsModel;
private formattingSettingsService: FormattingSettingsService;
constructor(options: VisualConstructorOptions) {
console.log('Visual constructor', options);
this.formattingSettingsService = new FormattingSettingsService();
this.target = options.element;
this.host = options.host;
}
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
this.formattingSettings = this.formattingSettingsService.populateFormattingSettingsModel(VisualFormattingSettingsModel, options.dataViews);
console.log('Visual update', options);
}
/**
* Returns properties pane formatting model content hierarchies, properties and latest formatting values, Then populate properties pane.
* This method is called once every time we open properties pane or when the user edit any format property.
*/
public getFormattingModel(): powerbi.visuals.FormattingModel {
return this.formattingSettingsService.buildFormattingModel(this.formattingSettings);
}
}
Importe as interfaces necessárias para processar dados do Power BI:
import DataViewMatrix = powerbi.DataViewMatrix;
import DataViewMatrixNode = powerbi.DataViewMatrixNode;
import DataViewHierarchyLevel = powerbi.DataViewHierarchyLevel;
Crie dois div elementos para o layout visual:
constructor(options: VisualConstructorOptions) {
// ...
this.rowsDiv = document.createElement("div");
this.target.appendChild(this.rowsDiv);
this.colsDiv = document.createElement("div");
this.target.appendChild(this.colsDiv);
this.target.style.overflowY = "auto";
}
Verifique os update dados no método para garantir que o visual obtenha dados:
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
this.formattingSettings = this.formattingSettingsService.populateFormattingSettingsModel(VisualFormattingSettingsModel, options.dataViews);
console.log('Visual update', options);
const dataView: DataView = options.dataViews[0];
const matrixDataView: DataViewMatrix = dataView.matrix;
if (!matrixDataView ||
!matrixDataView.columns ||
!matrixDataView.rows ) {
return
}
// ...
}
Limpe o div conteúdo dos elementos antes de renderizar novos dados:
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
// ...
// remove old elements
// to better performance use D3js pattern:
// https://d3js.org/#enter-exit
while (this.rowsDiv.firstChild) {
this.rowsDiv.removeChild(this.rowsDiv.firstChild);
}
const prow = document.createElement("p");
prow.innerText = "Rows";
this.rowsDiv.appendChild(prow);
while (this.colsDiv.firstChild) {
this.colsDiv.removeChild(this.colsDiv.firstChild);
}
const pcol = document.createElement("p");
pcol.innerText = "Columns";
this.colsDiv.appendChild(pcol);
// ...
}
Crie a treeWalker função para percorrer a estrutura de dados da matriz:
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
// ...
const treeWalker = (matrixNode: DataViewMatrixNode, index: number, levels: DataViewHierarchyLevel[], div: HTMLDivElement) => {
}
// ...
}
Onde matrixNode é o nó atual, levels são colunas de metadados desse nível hierárquico, div - elemento pai para elementos HTML filho.
O treeWalker é a função recursiva, precisa criar div elemento e p para texto como cabeçalho, e chamar a função para elementos filho do nó:
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
// ...
const treeWalker = (matrixNode: DataViewMatrixNode, index: number, levels: DataViewHierarchyLevel[], div: HTMLDivElement) => {
// ...
if (matrixNode.children) {
const childDiv = document.createElement("div");
childDiv.classList.add("vertical");
div.appendChild(childDiv);
const p = document.createElement("p");
const level = levels[matrixNode.level]; // get current level column metadata from current node
p.innerText = level.sources[level.sources.length - 1].displayName; // get column name from metadata
childDiv.appendChild(p); // add paragraph element to div element
matrixNode.children.forEach((node, index) => treeWalker(node, levels, childDiv, ++levelIndex));
}
}
// ...
}
Chame a função para elementos raiz da coluna e linha da estrutura de exibição de dados da matriz:
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
// ...
const treeWalker = (matrixNode: DataViewMatrixNode, index: number, levels: DataViewHierarchyLevel[], div: HTMLDivElement) => {
// ...
}
// ...
// remove old elements
// ...
// ...
const rowRoot: DataViewMatrixNode = matrixDataView.rows.root;
rowRoot.children.forEach((node) => treeWalker(node, matrixDataView.rows.levels, this.rowsDiv));
const colRoot = matrixDataView.columns.root;
colRoot.children.forEach((node) => treeWalker(node, matrixDataView.columns.levels, this.colsDiv));
}
Gere selectionID para nós e crie botões para exibir nós:
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
// ...
const treeWalker = (matrixNode: DataViewMatrixNode, index: number, levels: DataViewHierarchyLevel[], div: HTMLDivElement) => {
const selectionID: ISelectionID = this.host.createSelectionIdBuilder()
.withMatrixNode(matrixNode, levels)
.createSelectionId();
let nodeBlock = document.createElement("button");
nodeBlock.innerText = matrixNode.value.toString();
nodeBlock.addEventListener("click", (event) => {
// call select method in the selection manager
this.selectionManager.select(selectionID);
});
nodeBlock.addEventListener("contextmenu", (event) => {
// call showContextMenu method to display context menu on the visual
this.selectionManager.showContextMenu(selectionID, {
x: event.clientX,
y: event.clientY
});
event.preventDefault();
});
// ...
}
// ...
}
A etapa principal do realce é criar outra matriz de valores.
O objeto do nó terminal tem duas propriedades para a matriz de valores, valor e realce:
JSON.stringify(options.dataViews[0].matrix.rows.root.children[0].children[0].children[0], null, " ");
{
"level": 2,
"levelValues": [
{
"value": "R233",
"levelSourceIndex": 0
}
],
"value": "R233",
"identity": {
"identityIndex": 2
},
"values": {
"0": {
"value": null,
"highlight": null
},
"1": {
"value": 19,
"highlight": 19
}
}
}
Onde value representa o valor do nó sem aplicar uma seleção do outro visual, highlight indica qual parte dos dados foi realçada.
Nota
Se o valor de highlight é menor do que o valor de value, então value foi parcialmente realçado.
Adicione código para processar a values matriz do nó se ela for apresentada:
public update(options: VisualUpdateOptions) {
// ...
const treeWalker = (matrixNode: DataViewMatrixNode, index: number, levels: DataViewHierarchyLevel[], div: HTMLDivElement) => {
// ...
if (matrixNode.values) {
const sumOfValues = Object.keys(matrixNode.values) // get key property of object (value are 0 to N)
.map(key => +matrixNode.values[key].value) // convert key property to number
.reduce((prev, curr) => prev + curr) // sum of values
let sumOfHighlights = sumOfValues;
sumOfHighlights = Object.keys(matrixNode.values) // get key property of object (value are 0 to N)
.map(key => matrixNode.values[key].highlight ? +matrixNode.values[key].highlight : null ) // convert key property to number if it exists
.reduce((prev, curr) => curr ? prev + curr : null) // convert key property to number
// create div container for value and highlighted value
const vals = document.createElement("div");
vals.classList.add("vertical")
vals.classList.replace("vertical", "horizontal");
// create paragraph element for label
const highlighted = document.createElement("p");
// Display complete value and highlighted value
highlighted.innerText = `${sumOfHighlights}/${sumOfValues}`;
// create div container for value
const valueDiv = document.createElement("div");
valueDiv.style.width = sumOfValues * 10 + "px";
valueDiv.classList.add("value");
// create div container for highlighted values
const highlightsDiv = document.createElement("div");
highlightsDiv.style.width = sumOfHighlights * 10 + "px";
highlightsDiv.classList.add("highlight");
valueDiv.appendChild(highlightsDiv);
// append button and paragraph to div containers to parent div
vals.appendChild(nodeBlock);
vals.appendChild(valueDiv);
vals.appendChild(highlighted);
div.appendChild(vals);
} else {
div.appendChild(nodeBlock);
}
if (matrixNode.children) {
// ...
}
}
// ...
}
O resultado é um visual com botões e valores, como highlighted value/default value.