How to Use the BizTalk WCF Service Publishing Wizard to Publish Service Metadata for a WCF Receive Location for Content-Based Routing
You use the BizTalk WCF Service Publishing Wizard to create a WCF service to publish service metadata for existing WCF receive locations for content-based routing.
Note
You must build your BizTalk projects before running the BizTalk WCF Service Publishing Wizard. The BizTalk projects must include schemas to publish as WCF services. Before you publish service metadata for the WCF adapters, you must also create the WCF receive locations by using the BizTalk Server Administration console or the BTSTask command-line tool included with BizTalk Server. For more information about how to create a WCF receive location, see the appropriate topic for each WCF adapter in WCF Adapters.
To publish service metadata for an existing WCF receive location for content-based routing
Click Start, point to All Programs, point to BizTalk Server, and then click BizTalk WCF Service Publishing Wizard.
Note
To create and publish WCF service metadata for BizTalk orchestrations and schemas, you use the BizTalk WCF Service Publishing Wizard. To publish orchestrations and schemas as Web services with the SOAP adapter, you use the BizTalk Web Services Publishing Wizard.
On the Welcome to the BizTalk WCF Service Publishing Wizard page, click Next.
On the WCF Service Type page, select the Metdata only endpoint (MEX) option to publish the WCF services to provide service metadata for the WCF receive location that you will select in the next step.
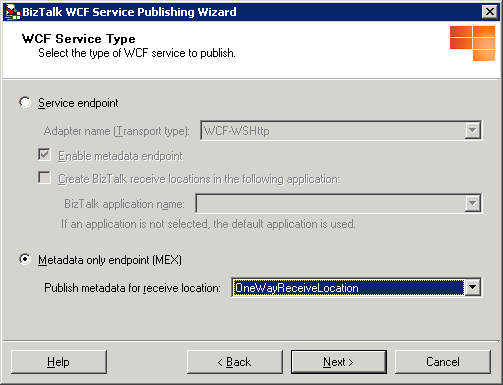
On the WCF Service Type page, in the Publish metadata for receive location drop-down list, select a WCF receive location to publish service metadata for, and then click Next.
On the Create WCF Service page, select Publish schemas as WCF service, and then click Next.
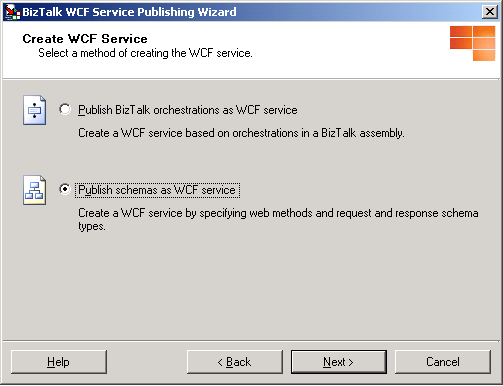
On the WCF Service page, define the WCF service contract(s) to publish service metadata for. You use the tree in the Web service description dialog box to add, remove, rename, and edit the Web service description nodes for the WCF services to publish. The Information dialog box provides information about the selected node and displays any errors in the current node or any subnodes:
The root node to the tree (Web service description) describes the WCF service contracts to publish. The virtual directory name uses the root node as the default name. You can modify the Web service description name for the WCF services to publish by selecting Rename web service description.
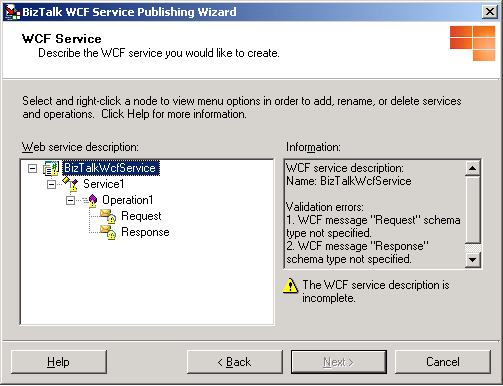
The Web method node, Operation1, of the default service node, Service1, shown by default in the Web service description dialog box can be used for a request-response receive location. If you selected a one-way WCF receive location for this service contract, right-click the default Web method node, click Delete web method, and then create a one-way Web method as follows: Right-click the default service node, point to Add web method, and then click One-Way.
To add a new WCF service, right-click the Web service description name, and then click Add web service. This creates a new WCF service without any WCF operations. To modify the name of the WCF service, right-click the WCF service node, click Rename web service, and then press ENTER to accept the new name.
To add a new WCF operation, right-click the WCF service node, point to Add Web Method, and then click One-way (for a request WCF operation) or Request-response (for a request-response WCF operation).
To set the request and response schema types, right-click the Request or Response node, and then click Select schema type. In the Request Message Type dialog box, type the name of the assembly containing the document schema in the BizTalk assembly file text box or click Browse to search for the assembly. The Available schema types list view displays each root element of the schema. Select a root node to add as the request or response schema type.
Note
If you installed the BizTalk assembly file into the global assembly cache (GAC), make sure that the assembly in the GAC has been updated with the assembly that you will select in the Request Message Type dialog box. If the GAC has the same fully qualified name, the BizTalk WCF Service Publishing Wizard uses the assembly file in the GAC instead of the one you selected.
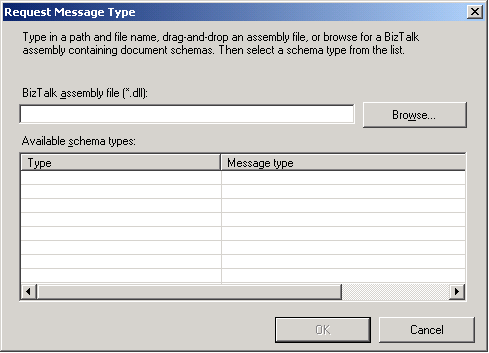
You can rename the Request and Response nodes without affecting the generated code. After defining your schemas, you can rename the part elements, which modifies the WCF operation parameter name. You can see the changes by viewing the service metadata for the WCF services to publish.
Note
You cannot use spaces when renaming any of the Web service description nodes.
Click Next to continue the wizard.
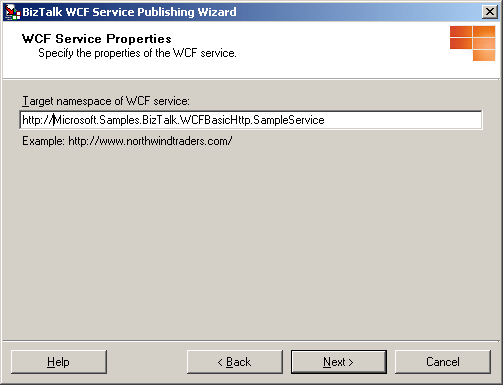
On the WCF Service Properties page, in the Targetnamespace of the WCF service text box, type a target namespace for the WCF services, and then click Next.
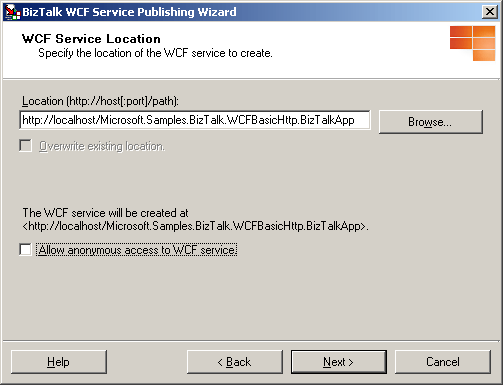
On the WCF Service Location page, in the Location text box, type the Web directory name where the WCF services are generated. You can accept the default location (
http://localhost/<Web service description name>), type a location for the WCF services in the Location text box, or click Browse and select a Web directory. Select any of the following options:Overwrite existing project. This option is available only if the Web directory already exists. You will be able to publish to the same location only if you select this option. Otherwise, you must enter a different project location.
Allow anonymous access to WCF service. This option adds anonymous access to the created virtual directory. By default, the virtual directory inherits the access privileges from its parent virtual directory or the Web site (if it is a top-level virtual directory).
When you finish this page, click Next.
Note
The project location can exist on a different server. To publish the WCF services to a different server, type the project name as
http://<servername>/<WCF service location>.Note
The project location can exist on a non-default Web site. When publishing to a non-default Web site, include the port number of the Web site in the URL. For example,
http://<servername>:8080/<WCF service location>.Note
The BindingInfo.xml file that the wizard creates in the \App_Data\Temp folder of the Web application uses the default values for the pipelines. The default value for the receive pipeline is the Microsoft.BizTalk.DefaultPipelines.XMLReceive pipeline, and the default value for the send pipeline is the Microsoft.BizTalk.DefaultPipelines.PassThruTransmit pipeline.
On the WCF Service Summary page, review your settings for the WCF services.
Click Create to create the WCF services.
Click Finish to complete the BizTalk WCF Service Publishing Wizard.
To configure the Web application for publishing service metadata
Enable ASP.NET for the Web application that the BizTalk WCF Service Publishing Wizard created. For more information, see Enabling Web Services.
Note
If you are using another version of the Windows operating system, you must add the Identity Account of the Application Pool to the BizTalk Server Administrators group. After you add the appropriate account to the BizTalk Server Administrators group, you need to restart the IIS service for the setting to take effect.
Open a command prompt, go to the folder where the BizTalk WCF Service Publishing Wizard created the WCF services in %SystemDrive%\InetPub\, and then open the Web.config file using Notepad.
In Notepad, add the following line inside the <system.web> element:
<trust level="Full" originUrl="" />Note
This setting is optional and it grants the ASP.NET application hosting the published WCF service access to any resource that is subject to operating system security. This is the trust level that WCF requires when you have Windows SharePoint Services installed and running on the same machine with the published WCF services.
In Internet Explorer, in the Address box, type the URL for the WCF service using the format http://host[:port]/apppath/wcfservicename.svc to test the published WCF service. The parameters are described in the following table.
Parameter Value host[:port] The name of the computer where you have deployed your WCF service. A colon and the port number can follow this server name. apppath The name of your virtual directory and the Web application path. wcfservicename.svc The name of the WCF service .svc file. To prevent unintentional disclosure of potentially sensitive service metadata, we recommend that you disable this behavior in the production environment by performing the following tasks:
In Notepad, open Web.config in the folder where the BizTalk WCF Service Publishing Wizard created the WCF service in %SystemDrive%\InetPub\.
In Notepad, set the httpGetEnabled attribute in the <serviceMetadata> element to false as following line:
<serviceMetadata httpGetEnabled="false" httpsGetEnabled="false" />
See Also
How to Use the BizTalk WCF Service Publishing Wizard to Publish Schemas as WCF Services
Walkthrough: Publishing WCF Services with the WCF-NetMsmq Adapter