Install and configure the Operational Data Service in BizTalk Server
Starting with BizTalk Server 2016 Feature Pack 1, send tracking to Power BI using the Power BI template provided, or create your own.
What is operational data
Operational data is information on the instances and messages flowing through your BizTalk Server environment. To learn more, see Operational Data Service.
Prerequisites
Download and install Power BI Desktop on any computer that has network access to your BizTalk Server.
Install Feature Pack 2 or newer feature pack on your BizTalk Server.
Install IIS on the BizTalk Server. In most BizTalk Server environments, IIS is already installed. See Hardware and Software Requirements for BizTalk Server 2016. Confirm IIS is installed by opening Internet Information Services Manager.
Optional. Install and configure a Power BI Gateway to connect PowerBI.com with your on-premises BizTalk Server. If you're not using an on-premises BizTalk Server, then you don't need the gateway.
Steps
Run Windows PowerShell as Administrator (Start menu, type PowerShell, right click, and select Run as administrator).
Go to the BizTalk installation folder (for example, type:
cd 'C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft BizTalk Server 2016\').In the following text, replace
Default Web Site,operationalDataServiceAppPool,domain\user,password, anddomain\groupwith your values:FeaturePack.ConfigureServices.ps1 -Service operationaldata -WebSiteName '<Default Web Site>' -ApplicationPool <operationalDataServiceAppPool> -ApplicationPoolUser <domain>\<user\> -ApplicationPoolUserPassword <password> -AuthorizationRoles '<domain>\<group1\>, <domain>\<group2\>, <domain>\<user\>, <domain>\<user2\>'- Service: The service to be configured (OperationalData for Power BI)
- WebSiteName: The existing IIS web site that hosts the service. The default value is Default Web Site.
- ApplicationPool: The Application Pool used by the service. If it exists, a new one is not created. The default value is DefaultAppPool.
- ApplicationPoolUser: Configures the application pool to run as this user identity. Must have BizTalk Server Operator, or higher privileges.
- ApplicationPoolUserPassword: Password for the ApplicationPoolUser
- AuthorizationAccount: List of authorized Groups or Users that can use this service
In the following example, we use the
Default Web Site, create an application pool namedPowerBIAppPool, run the appPool as thebootcampbts2016\btsserviceaccount, useBIZTALK-serviceacctas the user account password, and give theBizTalk Server Administratorsgroup permissions. Be sure to enter the following, including the single quotes surrounding values with spaces:FeaturePack.ConfigureServices.ps1 -Service operationaldata -WebSiteName 'Default Web Site' -ApplicationPool PowerBIAppPool -ApplicationPoolUser bootcampbts2016\btsservice -ApplicationPoolUserPassword BIZTALK-serviceacct -AuthorizationRoles 'BOOTCAMPBTS2016\BizTalk Server Administrators'When complete, the BizTalkOperationalDataService application is created within IIS:
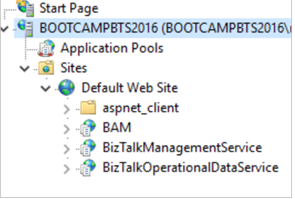
To confirm it’s working, browse to
http://localhost/BizTalkOperationalDataService.If you are prompted to sign-in, sign in with an account that is member of the domain\group you entered in the previous step (
-AuthorizationRoles 'BOOTCAMPBTS2016\BizTalk Server Administrators').If you are prompted to open or save BizTalkOperationalDataService.json, then your install completed. You can save it locally, and then open it in notepad or Visual Studio to see the contents.
Warning
The BizTalkOperationalDataService application in IIS uses a web.config file. Elements within web.config are case sensitive. So when you execute the Windows PowerShell script, be sure to enter the correct case for -AuthorizationRoles value. If you’re not sure of the case, here’s an easy way to find out:
- Open Computer Management, and expand Local Users and Groups.
- Select Groups, and scroll down to the SQLServer… groups.
- In the following example, notice BOOTCAMPBTS2016 is in all caps. If you see all caps, then enter the computer name in all caps.