Community driven Enhancements in SQL Server 2017
While SQL Server 2016 runs faster, SQL Server 2017 promises to run even faster and empower customers to run smarter with intelligent database features like the ability to run advanced analytics using Python in a parallelized and highly scalable way, the ability to store and analyze graph data, adaptive query processing and resumable online indexing allowing customers to deploy it on platform of their choice (Windows or Linux). SQL Server is one of the most popular DBMS in SQL Community and is a preferred choice of RDBMS among customers and ISVs owing to its strong community support. In SQL Server 2017 CTP 2.0, we have released several customer delighters and community driven enhancements based on the learnings and feedback from customers and community from in-market releases of SQL Server.
Smart Differential Backup – A new column modified_extent_page_count is introduced in sys.dm_db_file_space_usage to track differential changes in each database file of the database. The new column modified_extent_page_count will allow DBAs, SQL Community and backup ISVs to build smart backup solution which performs differential backup if percentage changed pages in the database is below a threshold (say 70-80%) else perform full database backup. With large number of changes in the database, cost and time to complete differential backup is similar to that of full database backup so there is no real benefit of taking differential backup in this case but it can rather increase the restore time of database. By adding this intelligence to the backup solutions, customers can now save on restore and recovery time while using differential backups.
Consider a scenario where you previously had a backup plan to take full database backup on weekends and differential backup daily. In this case, if the database is down on Friday, you will need to restore full db backup from Sunday, differential backups from Thursday and then T-log backups from Friday. By leveraging modified_extent_page_count in your backup solution, you can now take full database backup on Sunday and lets say by Wednesday, if 90% of pages have changed, the backup solution should take full database backup rather than differential backup. Now, if the database goes down on Friday, you can restore the full db backup from Wednesday, small differential backup from Thursday and T-log backups from Friday to restore and recover the database quickly compared to the previous scenario. This feature was requested by customers and community in connect item 511305.
USE <database-name>
GO
select CAST(ROUND((modified_extent_page_count*100.0)/allocated_extent_page_count,2)
as decimal(9,2))
from sys.dm_db_file_space_usage GO
select CAST(ROUND((SUM(modified_extent_page_count)*100.0)/SUM(allocated_extent_page_count),2)
as decimal(9,2))
as '% Differential Changes since last backup'
from sys.dm_db_file_space_usage
Smart Transaction Log Backup – In upcoming release of SQL Server 2017 CTP, a new DMF sys.dm_db_log_stats(database_id) will be released which exposes a new column log _since_last_log_backup_mb. The column log _since_last_log_backup_mb will empower DBAs, SQL Community and backup ISVs to build intelligent T-log backup solutions which takes backup based on the transactional activity on the database. This intelligence in the T-log backup solution will ensure the transaction log size doesn't grow due to high burst of transactional activity in short time if the T-log backup frequency is too low. It will also help avoid situation where scheduled transaction log backup creates too many T-log backup files even when there is no transactional activity on the server adding to the storage, file management and restore overheads. The monitoring solutions and ISVs can also setup alerts based on the transaction activity of the T-log to avoid and avert T-log growth issues caused due to high transactional activity on the database.
SELECT INTO … ON FileGroup - One of the highly voted connect items and highly requested feature ask from SQL community to support loading tables into specified filegroups while using SELECT INTO is now made available in SQL Server 2017 CTP 2.0. SELECT INTO is commonly used in DW scenario for creating intermediate staging tables and inability to specify filegroup was one of the major pain points to create and load tables in filegroups different from the default filegroup of the user loading the table. Starting SQL Server 2017 CTP 2.0, SELECT INTO T-SQL syntax supports loading a table into a filegroup other than a default filegroup of the user using the ON <Filegroup name> keyword in TSQL syntax shown below
ALTER DATABASE [AdventureWorksDW2016] ADD FILEGROUP FG2
select * from sys.database_files
ALTER DATABASE [AdventureWorksDW2016]
ADD FILE ( NAME='FG2_Data', FILENAME = '/var/opt/mssql/data/AdventureWorksDW2016_Data1.mdf' ) TO FILEGROUP FG2; GO
SELECT * INTO [dbo].[FactResellerSalesXL] ON FG2 from [dbo].[FactResellerSales];
Tempdb Setup improvements – One of the constant feedback from customers, SQL community and field after doing the SQL Server 2016 setup improvements is to uplift the maximum initial file size restriction of 1GB for tempdb in setup. For SQL Server 2017, the setup will allow initial tempdb file size up to 256 GB (262,144 MB) per file with a warning to customers if the file size is set to value greater than 1GB and if IFI is not enabled. It is important to understand the implication of not enabling instant file initialization (IFI) where setup time can increase exponentially depending on the initial size of tempdb data file specified. IFI is not applicable to transaction log size so specifying larger value of transaction log can invariably increase the setup time while starting up tempdb during setup irrespective of the IFI setting for SQL Server service account.
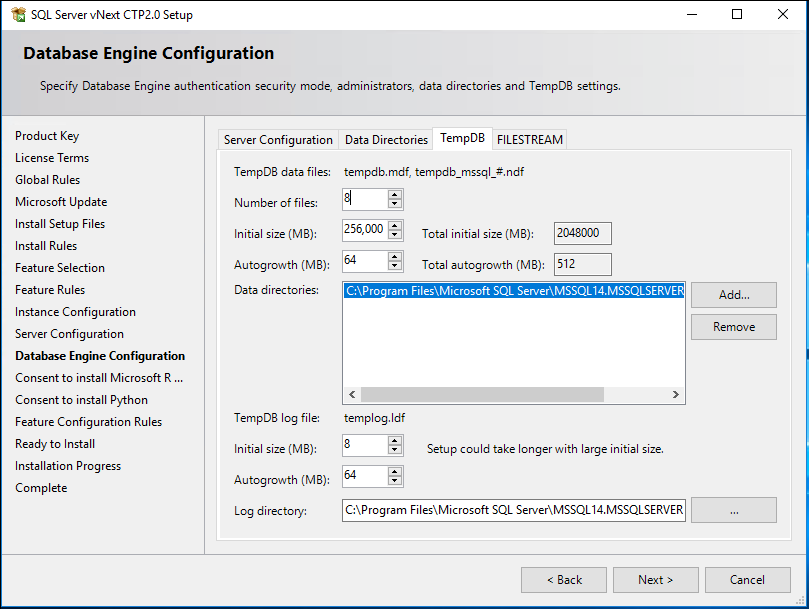
Tempdb Monitoring and Planning – Few months back, SQL Server Tiger team surveyed SQL Community to identify common challenges experienced by customer with tempdb. Tempdb space planning and monitoring were found to be top challenges experienced by customers with tempdb. As a first step to facilitate tempdb space planning and monitoring, a new performant DMV sys.dm_tran_version_store_space_usage is introduced in SQL Server 2017 to track version store usage per database. This new DMV will be useful in monitoring tempdb for version store usage for dbas who can proactively plan tempdb sizing based on the version store usage requirement per database without any performance toll or overheads of running it on production servers.
Transaction Log Monitoring and diagnostics – One of highly voted connect items and highly requested ask in the community is to expose transaction log VLF information in DMV. T-log space issues, high VLFs and log shrink issues are some of the common challenges experienced by DBAs. Some of our monitoring ISVs have asked for DMVs to expose VLF information and t-log space usage for monitoring and alerting. A new DMV sys.dm_db_log_info is introduced in SQL Server 2017 CTP 2.0 to expose the VLF information similar to DBCC LOGINFO to monitor, alert and avert potential Tlog issues experienced by customers.
In addition to sys.dm_db_log_info, a new DMF sys.dm_db_log_stats(database_id) will released in upcoming CTP release of SQL Server 2017 which will expose aggregated transaction log information per database. We will share more details on this DMF once it is released.
Improved Backup performance for small databases on high end servers – After migrating existing in market release of SQL Server to high end servers, customers may experience dip in backup performance when taking backups of small to medium databases. This happens as we need to iterate the buffer pool to drain the on-going I/Os. The backup time is not just the function of database size but also a function of active buffer pool size. In SQL Server 2017, we have optimized the way we drain the on-going I/Os during backup resulting in dramatic gains in backup performance for small to medium databases. We have seen more than 100x improvement when taking system database backups on a 2TB machine. More extensive performance testing results on various database sizes is shared below. The performance gain reduces as the database size increases as the pages to backup and backup IO takes more time compared to iterating buffer pool. This improvement will help improve the backup performance for customers hosting multiple small databases on a large high end servers with large memory.
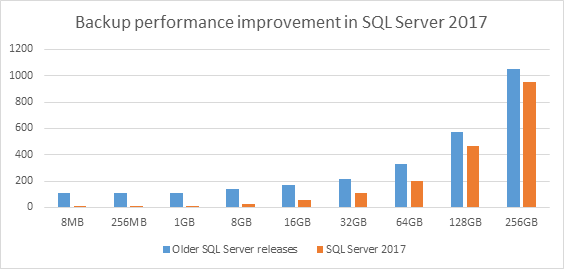
| DB Size | Older SQL Server releases |
SQL Server 2017 | Improvement |
| 8MB | 107 |
0.4 |
642x |
| 256MB | 108 |
1 |
108x |
| 1GB | 110 |
4 |
27.5 |
| 8GB | 139 |
24 |
5.79x |
| 16GB | 168 |
59 |
2.85x |
| 32GB | 216 |
108 |
2.12x |
| 64GB | 332 |
200 |
66% |
| 128GB | 569 |
469 |
21.32% |
| 256GB | 1055 |
953 |
10.70% |
Processor Information in sys.dm_os_sys_info – Another highly requested feature among customers, ISVs and SQL community to expose processor information in sys.dm_os_sys_info is released in SQL Server 2017 CTP 2.0. The new columns will allow you to programmatically query processor information for the servers hosting SQL Server instance useful in managing large deployments of SQL Server. New columns exposed in sys.dm_os_sys_info DMV are socket_count, core_count, cores_per_socket.
Capturing Query Store runtime statistics in DBCC CLONEDATABASE – DBCC CLONEDATABASE has proved to be extremely useful in exporting the query store metadata for regression testing and tuning. DBCC CLONEDATABASE didn't capture the runtime statistics which is flushed every 15 mins which required customers to manually execute sp_query_store_flush_db before running DBCC CLONEDATABASE to flush and capture query store runtime statistics in database clone. Starting SQL 2016 SP1 CU2 and SQL Server 2017 CTP 2.0, DBCC CLONEDATABASE will flush runtime statistics while cloning to avoid missing query store runtime statistics in database clone. In addition to this, DBCC CLONEDATABASE is further enhanced to support and clone fulltext indexes. We also fixed several bugs caused when cloning database using some of latest features (AlwaysEncrypted, RLS, Dynamic data masking, Temporal) and released the fixes in SQL Server 2016 SP1 CU2 and SQL Server 2017 CTP 2.0.
Thank you to all the SQL Community members in sharing your valuable feedback and making SQL Server 2017 smarter and a preferred choice of RDBMS for customers.
Parikshit Savjani
Senior PM, SQL Server Tiger Team Twitter | LinkedIn
Follow us on Twitter: @mssqltiger | Team Blog: Aka.ms/sqlserverteam
Comments
- Anonymous
April 26, 2017
The comment has been removed - Anonymous
April 26, 2017
The comment has been removed - Anonymous
April 27, 2017
Hello Parikshit,"This happens as we need to iterate the buffer pool to drain the on-going I/Os. The backup time is not just the function of database size but also a function of active buffer pool size. In SQL Server 2017..." - Could you please elaborate why draining the I/Os needed in the presence of CHECKPOINT and Write-ahead log (WAL) as well as backing up part of T log file to capture changes made during backup operation ? Appreciate your response. Thank you.- Anonymous
June 16, 2017
Hi Anil,Sorry for the delay in reply as I missed it completely. The draining of the I/Os will be done by Lazywriter as part of checkpoint process when the backup is in process. Also we are talking about full database backup here and not tlog backup. backup itself will not trigger IOs but while the database is being backed up, the Lazywriter process may be flushing the dirty pages to disk which is the on-going IOs we are talking about here.
- Anonymous
- Anonymous
May 01, 2017
WOW !!! Thanks