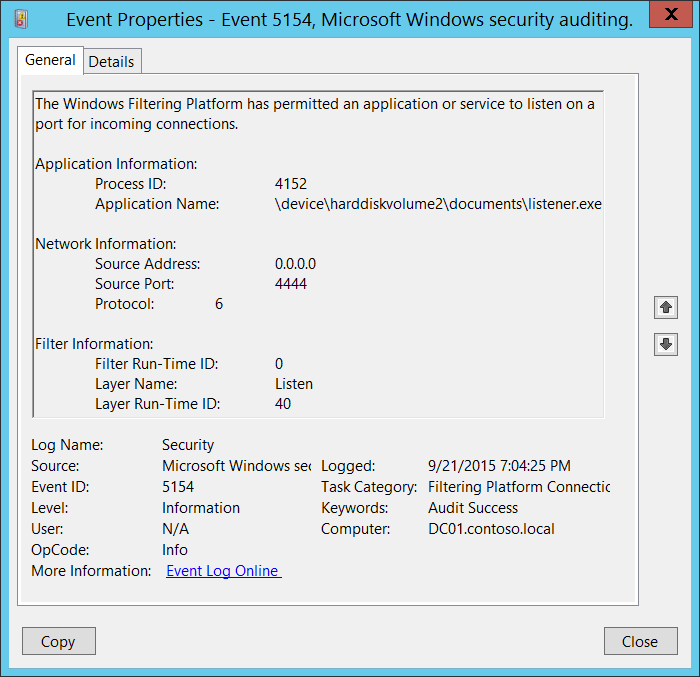
5154(S): The Windows Filtering Platform has permitted an application or service to listen on a port for incoming connections.
Subcategory: Audit Filtering Platform Connection
Event Description:
This event generates every time Windows Filtering Platform permits an application or service to listen on a port.
Note For recommendations, see Security Monitoring Recommendations for this event.
Event XML:
- <Event xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/win/2004/08/events/event">
- <System>
<Provider Name="Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing" Guid="{54849625-5478-4994-A5BA-3E3B0328C30D}" />
<EventID>5154</EventID>
<Version>0</Version>
<Level>0</Level>
<Task>12810</Task>
<Opcode>0</Opcode>
<Keywords>0x8020000000000000</Keywords>
<TimeCreated SystemTime="2015-09-22T02:04:25.757462900Z" />
<EventRecordID>287929</EventRecordID>
<Correlation />
<Execution ProcessID="4" ThreadID="3968" />
<Channel>Security</Channel>
<Computer>DC01.contoso.local</Computer>
<Security />
</System>
- <EventData>
<Data Name="ProcessId">4152</Data>
<Data Name="Application">\\device\\harddiskvolume2\\documents\\listener.exe</Data>
<Data Name="SourceAddress">0.0.0.0</Data>
<Data Name="SourcePort">4444</Data>
<Data Name="Protocol">6</Data>
<Data Name="FilterRTID">0</Data>
<Data Name="LayerName">%%14609</Data>
<Data Name="LayerRTID">40</Data>
</EventData>
</Event>
Required Server Roles: None.
Minimum OS Version: Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista.
Event Versions: 0.
Field Descriptions:
Application Information:
Process ID [Type = Pointer]: hexadecimal Process ID of the process that was permitted to listen on the port. Process ID (PID) is a number used by the operating system to uniquely identify an active process. To see the PID for a specific process you can, for example, use Task Manager (Details tab, PID column):
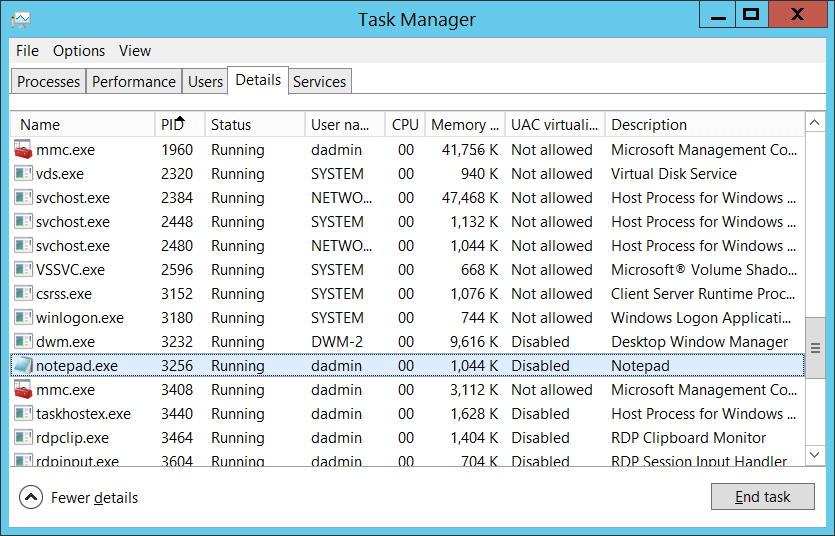
If you convert the hexadecimal value to decimal, you can compare it to the values in Task Manager.
You can also correlate this process ID with a process ID in other events, for example, “4688: A new process has been created” Process Information\New Process ID.
Application Name [Type = UnicodeString]: full path and the name of the executable for the process.
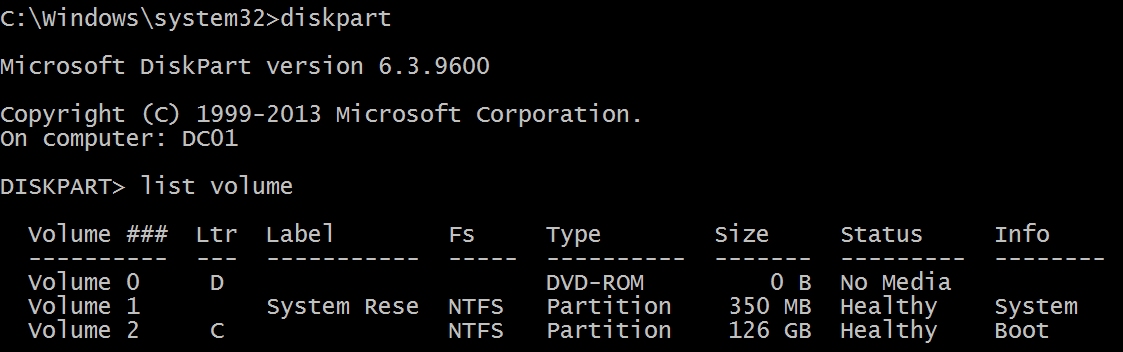
Logical disk is displayed in format \device\harddiskvolume#. You can get all local volume numbers by using diskpart utility. The command to get volume numbers using diskpart is “list volume”:
Network Information:
Source Address [Type = UnicodeString]: local IP address on which application requested to listen on the port.
IPv4 Address
IPv6 Address
:: - all IP addresses in IPv6 format s
0.0.0.0 - all IP addresses in IPv4 format
127.0.0.1, ::1 - localhost
Source Port [Type = UnicodeString]: source TCP\UDP port number that was requested for listening by application.
Protocol [Type = UInt32]: protocol number. For example:
6 – TCP.
17 – UDP.
More information about possible values for this field: https://technet.microsoft.com/library/cc959827.aspx.
Filter Information:
Filter Run-Time ID [Type = UInt64]: unique filter ID that allows application to listen on the specific port. By default Windows firewall won't prevent a port from being listened by an application and if this application doesn’t match any filters you'll get value 0 in this field.
To find a specific Windows Filtering Platform filter by ID, run the following command: netsh wfp show filters. As a result of this command, the filters.xml file will be generated. Open this file and find specific substring with required filter ID (<filterId>), for example:

Layer Name [Type = UnicodeString]: Application Layer Enforcement layer name.
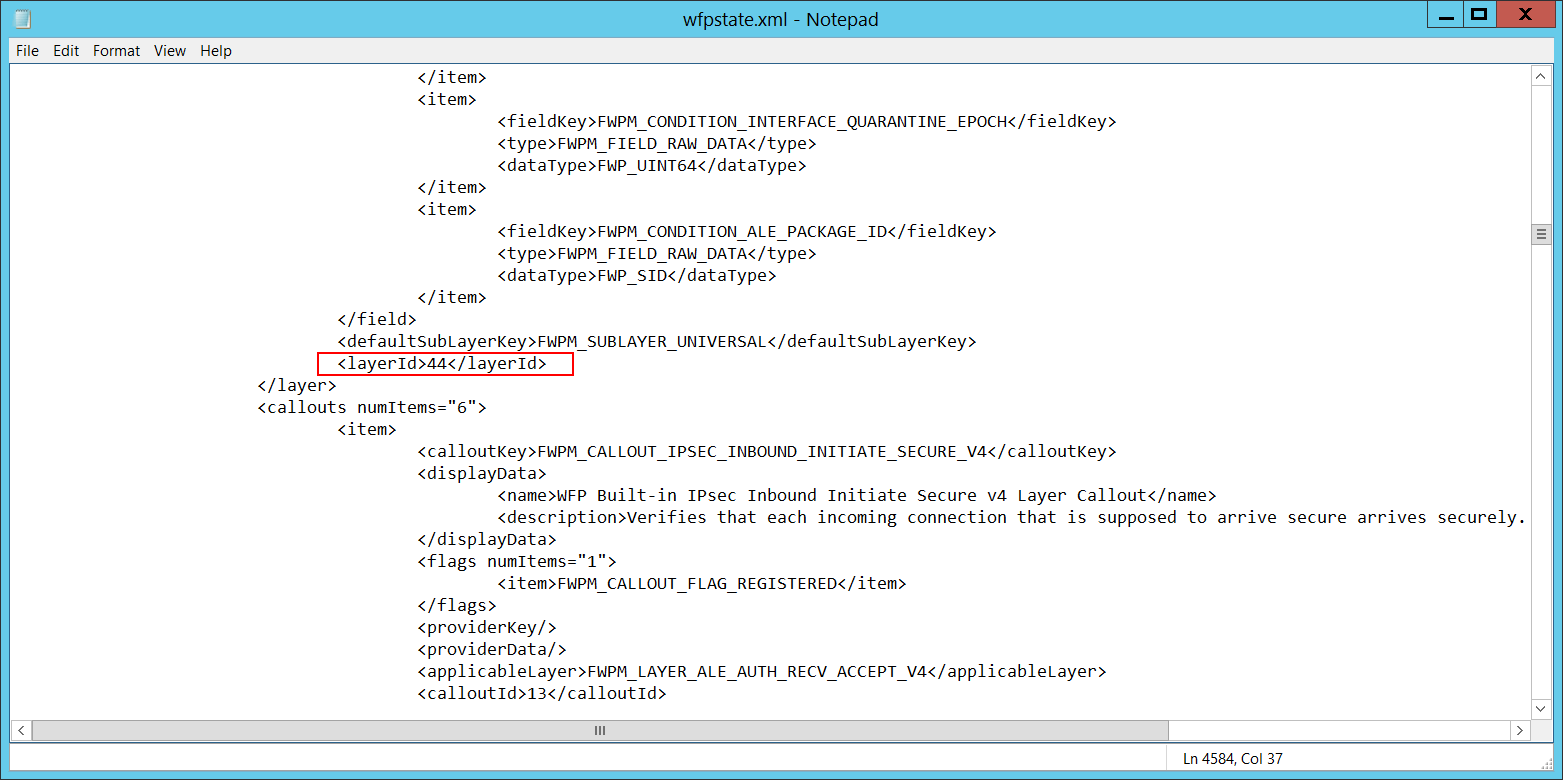
Layer Run-Time ID [Type = UInt64]: Windows Filtering Platform layer identifier. To find a specific Windows Filtering Platform layer ID, run the following command: netsh wfp show state. As a result of this command, the wfpstate.xml file will be generated. Open this file and find specific substring with required layer ID (<layerId>), for example:
Security Monitoring Recommendations
For 5154(S): The Windows Filtering Platform has permitted an application or service to listen on a port for incoming connections.
If you've an “allowlist” of applications that are associated with certain operating systems or server roles, and that are expected to listen on specific ports, monitor this event for “Application Name” and other relevant information.
If a certain application is allowed to listen only on specific port numbers, monitor this event for “Application Name” and “Network Information\Source Port.”
If a certain application is allowed to listen only on a specific IP address, monitor this event for “Application Name” and “Network Information\Source Address.”
If a certain application is allowed to use only TCP or UDP protocols, monitor this event for “Application Name” and the protocol number in “Network Information\Protocol.”
If you have a predefined application that should be used to perform the operation that was reported by this event, monitor events with “Application” not equal to your defined application.
You can monitor to see if “Application” isn't in a standard folder (for example, not in System32 or Program Files) or is in a restricted folder (for example, Temporary Internet Files).
If you have a pre-defined list of restricted substrings or words in application names (for example, “mimikatz” or “cain.exe”), check for these substrings in “Application.”
Typically this event has an informational purpose.