Define conversation steps with waterfalls in the v3 JavaScript SDK
APPLIES TO: SDK v3
A conversation is a series of messages exchanged between user and bot. When the bot's objective is to lead the user through a series of steps, you can use a waterfall to define the steps of the conversation.
A waterfall is a specific implementation of a dialog that is most commonly used to collect information from the user or guide the user through a series of tasks. The tasks are implemented as an array of functions where the results of the first function are passed as input into the next function, and so on. Each function typically represents one step in the overall process. At each step, the bot prompts the user for input, waits for a response, and then passes the result to the next step.
This article will help you understand how a waterfall works and how you can use it to manage conversation flow.
Conversation steps
A conversation typically involves several prompt/response exchanges between the user and the bot. Each prompt/response exchange is a step forward in the conversation. You can create a conversation using a waterfall with as few as two steps.
For example, consider the following greetings dialog. The first step of the waterfall prompts for the user's name and the second step uses the response to greet the user by name.
bot.dialog('greetings', [
// Step 1
function (session) {
builder.Prompts.text(session, 'Hi! What is your name?');
},
// Step 2
function (session, results) {
session.endDialog(`Hello ${results.response}!`);
}
]);
What makes this possible is the use of prompts. The Bot Framework SDK for Node.js provides several different types of built-in prompts that you can use to ask the user for various types of information.
The following sample code shows a dialog that uses prompts to collect various pieces of information from the user throughout a 4-step waterfall.
var inMemoryStorage = new builder.MemoryBotStorage();
// This is a dinner reservation bot that uses a waterfall technique to prompt users for input.
var bot = new builder.UniversalBot(connector, [
function (session) {
session.send("Welcome to the dinner reservation.");
builder.Prompts.time(session, "Please provide a reservation date and time (e.g.: June 6th at 5pm)");
},
function (session, results) {
session.dialogData.reservationDate = builder.EntityRecognizer.resolveTime([results.response]);
builder.Prompts.text(session, "How many people are in your party?");
},
function (session, results) {
session.dialogData.partySize = results.response;
builder.Prompts.text(session, "Whose name will this reservation be under?");
},
function (session, results) {
session.dialogData.reservationName = results.response;
// Process request and display reservation details
session.send(`Reservation confirmed. Reservation details: <br/>Date/Time: ${session.dialogData.reservationDate} <br/>Party size: ${session.dialogData.partySize} <br/>Reservation name: ${session.dialogData.reservationName}`);
session.endDialog();
}
]).set('storage', inMemoryStorage); // Register in-memory storage
In this example, the default dialog has four functions, each one representing a step in the waterfall. Each step prompts the user for input and sends the results to the next step to be processed. This process continues until the last step executes, thereby confirming the reservation and ending the dialog.
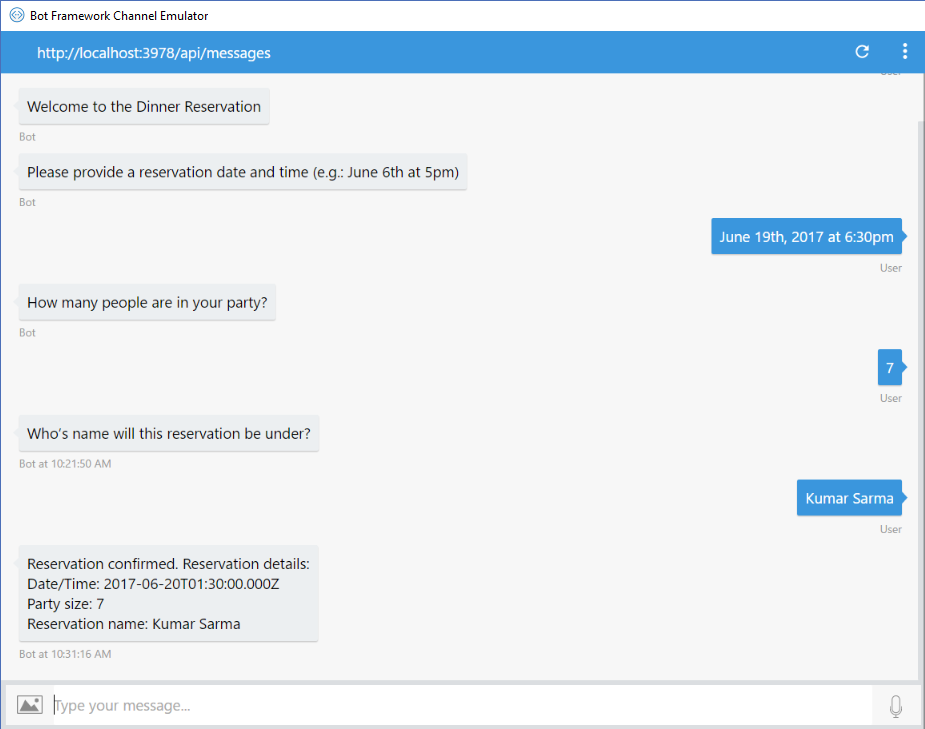
The following screenshot shows the results of this bot running in the Bot Framework Emulator.
Create a conversation with multiple waterfalls
You can use multiple waterfalls within a conversation to define whatever conversation structure your bot requires. For example, you might use one waterfall to manage the conversation flow and use additional waterfalls to collect information from the user. Each waterfall is encapsulated in a dialog and can be invoked by calling the session.beginDialog function.
The following code sample shows how to use multiple waterfalls in a conversation. The waterfall within the greetings dialog manages the flow of the conversation, while the waterfall within the askName dialog collects information from the user.
bot.dialog('greetings', [
function (session) {
session.beginDialog('askName');
},
function (session, results) {
session.endDialog('Hello %s!', results.response);
}
]);
bot.dialog('askName', [
function (session) {
builder.Prompts.text(session, 'Hi! What is your name?');
},
function (session, results) {
session.endDialogWithResult(results);
}
]);
Advance the waterfall
A waterfall progresses from step to step in the sequence that the functions are defined in the array. The first function within a waterfall can receive the arguments that are passed to the dialog. Any function within a waterfall can use the next function to proceed to the next step without prompting user for input.
The following code sample shows how to use the next function within a dialog that walks the user through the process of providing information for their user profile. In each step of the waterfall, the bot prompts the user for a piece of information (if necessary), and the user's response (if any) is processed by the subsequent step of the waterfall. The final step of the waterfall in the ensureProfile dialog ends that dialog and returns the completed profile information to the calling dialog, which then sends a personalized greeting to the user.
var inMemoryStorage = new builder.MemoryBotStorage();
// This bot ensures user's profile is up to date.
var bot = new builder.UniversalBot(connector, [
function (session) {
session.beginDialog('ensureProfile', session.userData.profile);
},
function (session, results) {
session.userData.profile = results.response; // Save user profile.
session.send(`Hello ${session.userData.profile.name}! I love ${session.userData.profile.company}!`);
}
]).set('storage', inMemoryStorage); // Register in-memory storage
bot.dialog('ensureProfile', [
function (session, args, next) {
session.dialogData.profile = args || {}; // Set the profile or create the object.
if (!session.dialogData.profile.name) {
builder.Prompts.text(session, "What's your name?");
} else {
next(); // Skip if we already have this info.
}
},
function (session, results, next) {
if (results.response) {
// Save user's name if we asked for it.
session.dialogData.profile.name = results.response;
}
if (!session.dialogData.profile.company) {
builder.Prompts.text(session, "What company do you work for?");
} else {
next(); // Skip if we already have this info.
}
},
function (session, results) {
if (results.response) {
// Save company name if we asked for it.
session.dialogData.profile.company = results.response;
}
session.endDialogWithResult({ response: session.dialogData.profile });
}
]);
Note
This example uses two different data bags to store data: dialogData and userData. If the bot is distributed across multiple compute nodes, each step of the waterfall could be processed by a different node. For more information about storing bot data, see Manage state data.
End a waterfall
A dialog that is created using a waterfall must be explicitly ended, otherwise the bot will repeat the waterfall indefinitely. You can end a waterfall by using one of the following methods:
session.endDialog: Use this method to end the waterfall if there is no data to return to the calling dialog.session.endDialogWithResult: Use this method to end the waterfall if there is data to return to the calling dialog. Theresponseargument that is returned can be a JSON object or any JavaScript primitive data type. For example:session.endDialogWithResult({ response: { name: session.dialogData.name, company: session.dialogData.company } });session.endConversation: Use this method to end the waterfall if the end of the waterfall represents the end of the conversation.
As an alternative to using one of these three methods to end a waterfall, you can attach the endConversationAction trigger to the dialog. For example:
bot.dialog('dinnerOrder', [
//...waterfall steps...,
// Last step
function(session, results){
if(results.response){
session.dialogData.room = results.response;
var msg = `Thank you. Your order will be delivered to room #${session.dialogData.room}`;
session.endConversation(msg);
}
}
])
.endConversationAction(
"endOrderDinner", "Ok. Goodbye.",
{
matches: /^cancel$|^goodbye$/i,
confirmPrompt: "This will cancel your order. Are you sure?"
}
);
Next steps
Using waterfall, you can collect information from the user with prompts. Let's dive into how you can prompt user for input.