Enable Virtual Tables to support Dataverse events
You can allow Virtual entities to participate in asynchronous Dataverse Event Framework pipeline events and in the PowerAutomate Dataverse connector When a row is added, modified or deleted trigger. This capability is enabled as part of Dataverse business events. More information: Microsoft Dataverse business events
Without the configuration described in this article, most virtual entities don't participate in the Event Framework pipeline like other entities. Because virtual entities don't participate in the event pipeline, you can't register plug-in steps against Create, Update, and Delete (CUD) events that occur, and although CUD events appear for these entities in the Power Automate Dataverse connector, an error is thrown when people try to save a flow that uses them.
This is because virtual entities represent data stored in an external source. Dataverse has access to that data source as a client, but other systems can update that data at any time without passing through the Dataverse event framework.
There are two steps to enable this:
Configuring data in a table called Virtual Entity Metadata. When data in this table is configured to enable them, a set of new APIs provide the means for the external system to notify Dataverse when CUD events occur.
When there's a Virtual Entity Metadata row associated with the EntityMetadata.Metadataid for a Virtual table, the following three settings can control whether an external source can notify your virtual table.
When individually enabled using the Virtual Entity Metadata
IsOnExternalCreatedEnabled,IsOnExternalDeletedEnabled, andIsOnExternalUpdatedEnabledboolean properties, the following bound Actions become available to be called by external services.Action/Message Description OnExternalCreatedContains data about a record that was created in an external system exposed as a virtual table in Dataverse. OnExternalUpdatedContains data about a record that was updated in an external system exposed as a virtual table in Dataverse. OnExternalDeletedContains data about a record that was deleted in an external system exposed as a virtual table in Dataverse. The external system which controls the data must send an authenticated HTTP request to Dataverse using the APIs that have data in Virtual Entity Metadata. An authenticated service principal account typically performs this call. More information: Build web applications using server-to-server (S2S) authentication
But any application or user that can perform a call to Dataverse can send the http request needed to notify Dataverse that the event occurred.
Note
Virtual entities using the OData Provider and non relational date sources may allow certain plug-in step registrations, for example only on events outside the transaction. But these events are not available for use with the Power Automate Dataverse connector. There is no change to this behavior. But for more reliable event notification, the approach described in this topic is recommended.
How to enable notification APIs for virtual tables
You can enable notification APIs by manually configuring them in the maker portal (make.powerapps.com/) or using code.
Enable manually using the maker portal
Let's say we have a Person Virtual Table with these properties, the Name property is new_People.
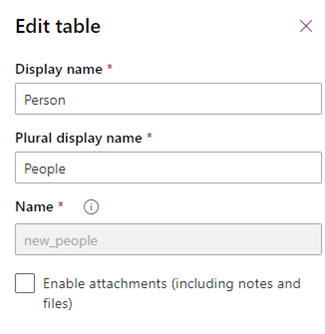
In Power Apps (make.powerapps.com), within your solution, select +New and then select Virtual Entity Metadata.
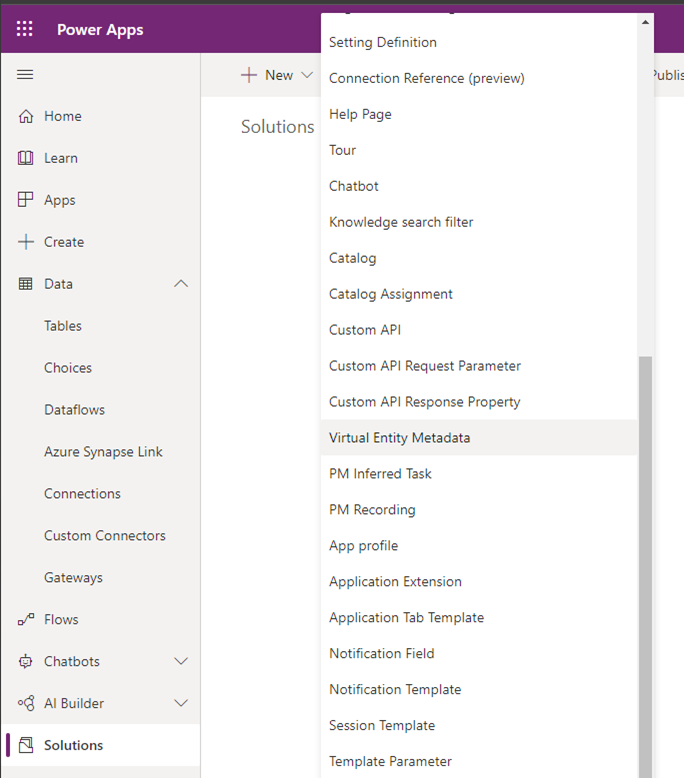
This opens the following form:
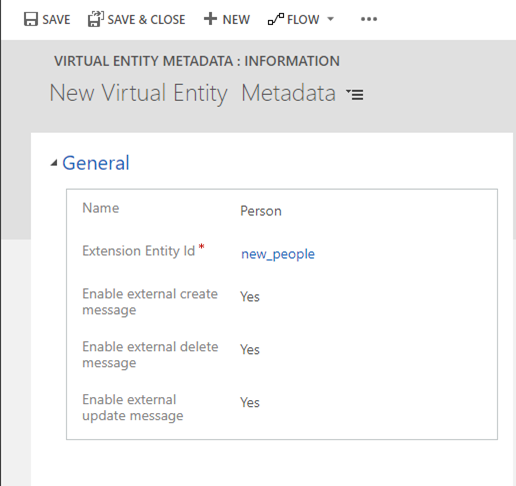
Complete the form, setting the Extension Entity Id value to the name of your virtual table. You aren't required to enable all three messages. You can set one or more of them and come back to enable the rest later.
When you have enabled these messages, you can observe and confirm what was added using the steps in View the messages created to support your virtual table.
Set managed properties using the maker portal
If you don't want people who install your managed solution to change the Virtual Entity Metadata behaviors, you should set the managed property to prevent it using the following steps.
In your solution, select the Virtual Entity Metadata and select the ellipsis (...) and then select Managed Properties.
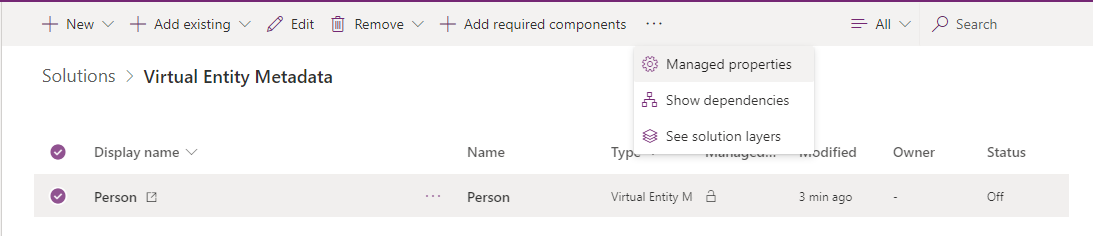
In the Managed Properties pane, deselect Allow Customizations and press Done.
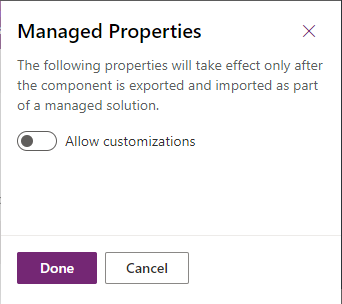
This setting won't do anything until the Virtual Entity Metadata record is included in a managed solution.
Enable with code
You may want to automate the creation of Virtual Entity Metadata for your virtual entities.
The VirtualEntityMetadata table has the following columns that you can set:
| Schema Name Logical Name |
Display Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
ExtensionOfRecordIdextensionofrecordid |
Virtual Entity | Lookup | The name of the virtual entity that these settings are for. |
IsCustomizableiscustomiable |
Is Customizable | ManagedProperty | Controls whether the virtual entity metadata can be changed or deleted when included in a managed solution. |
IsOnExternalCreatedEnabledisonexternalcreatedenabled |
Enable external create message | Boolean | Enables a message to send information about new records created in the external data source. |
IsOnExternalDeletedEnabledisonexternaldeletedenabled |
Enable external delete message | Boolean | Enables a message to send information about deleted records in the external data source. |
IsOnExternalUpdatedEnabledisonexternalupdatedenabled |
Enable external update message | Boolean | Enables a message to send information about updated records in the external data source. |
Namename |
Name | String | The name of the settings. |
VirtualEntityMetadataIdvirtualentitymetadataid |
VirtualEntityMetadata | Uniqueidentifier | Unique identifier for entity instances |
When creating these types of solution components, we recommend that you set the IsCustomizable managed property to be false unless you want to allow people who install your managed solution to be able to change these settings.
We also recommend that you add the Virtual Entity Metadata** record to a specific solution when you create it. In both examples below, you'll see how the Solution.UniqueName is passed with the request that creates the record.
Using Web API
When you use the Web API, the first task is to get the MetadataId of the virtual table. The following example returns the MetadataId for a virtual entity named new_people.
Request:
GET [Organization Uri]/api/data/v9.1/EntityDefinitions(LogicalName='new_people')?$select=MetadataId HTTP/1.1
OData-MaxVersion: 4.0
OData-Version: 4.0
Accept: application/json
Authorization: Bearer [REDACTED]
Response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
{
"@odata.context": "[Organization Uri]/api/data/v9.1/$metadata#EntityDefinitions(MetadataId)/$entity",
"MetadataId": "b198e6f3-3dd6-4c0b-9570-702f0c10d577"
}
Then, create the virtual entity metadata record while associating it to the Entity entitytype using the MetadataId retrieved in the first step.
Note the use of the MSCRM.SolutionUniqueName header set to the Solution.UniqueName value. This adds the virtual entity metadata record to the solution as it is created. More information: HTTP headers
Request:
POST [Organization Uri]/api/data/v9.1/virtualentitymetadatas HTTP/1.1
MSCRM.SolutionUniqueName: YourSolutionUniqueName
OData-MaxVersion: 4.0
OData-Version: 4.0
Accept: application/json
Authorization: Bearer [REDACTED]
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
{
"@odata.type": "Microsoft.Dynamics.CRM.virtualentitymetadata",
"name": "Person Virtual Metadata",
"iscustomizable": {
"@odata.type": "Microsoft.Dynamics.CRM.BooleanManagedProperty",
"Value": false,
"CanBeChanged": false
},
"isonexternalcreatedenabled": true,
"isonexternaldeletedenabled": true,
"isonexternalupdatedenabled": true,
"extensionofrecordid@odata.bind": "entities(b198e6f3-3dd6-4c0b-9570-702f0c10d577)"
}
Response:
HTTP/1.1 204 No Content
Using SDK for .NET
Regardless of whether you use early or late bound types, the first task is to retrieve the MetadataId of the table, which is retrieved in the same way for both cases. In this case for a virtual table named new_people using CrmServiceClient. Alternately, the ServiceClient class can be used.
var service = new CrmServiceClient(conn);
// var service = new ServiceClient(conn);
var retrieveEntityRequest = new RetrieveEntityRequest
{
LogicalName = "new_people",
EntityFilters = EntityFilters.Entity
};
var retrieveEntityResponse = (RetrieveEntityResponse)service.Execute(retrieveEntityRequest);
var entityId = retrieveEntityResponse.EntityMetadata.MetadataId;
Using early-bound types
With early-bound types, you can use the VirtualEntityMetadata class generated using Power Platform CLI pac modelbuilder build command. More information: Late-bound and Early-bound programming using the SDK for .NET
var virtualEntityMetadata = new VirtualEntityMetadata
{
Name = "Person Virtual Metadata",
ExtensionOfRecordId = new EntityReference("entity", entityId.Value),
IsCustomizable = new BooleanManagedProperty(false),
IsOnExternalCreatedEnabled = true,
IsOnExternalDeletedEnabled = true,
IsOnExternalUpdatedEnabled = true,
};
Using late-bound types
There are two ways to instantiate the virtual entity metadata instance using late-bound types, either is equivalent:
var virtualEntityMetadata = new Entity("virtualentitymetadata");
virtualEntityMetadata["name"] = "Person Virtual Metadata";
virtualEntityMetadata["extensionofrecordid"] = new EntityReference("entity", entityId.Value);
virtualEntityMetadata["iscustomizable"] = new BooleanManagedProperty(false);
virtualEntityMetadata["isonexternalcreatedenabled"] = true;
virtualEntityMetadata["isonexternaldeletedenabled"] = true;
virtualEntityMetadata["isonexternalupdatedenabled"] = true;
Or:
var virtualEntityMetadata = new Entity("virtualentitymetadata") {
Attributes = new AttributeCollection {
{ "name","Person Virtual Metadata" },
{ "extensionofrecordid", new EntityReference("entity", entityId.Value)},
{ "iscustomizable",new BooleanManagedProperty(false)},
{ "isonexternalcreatedenabled",true },
{ "isonexternaldeletedenabled",true },
{ "isonexternalupdatedenabled",true}
}
};
Creating the record
When creating the record, use the CreateRequest Class rather than the IOrganizationService.Create method so you can include the SolutionUniqueName optional parameter which adds the record to your solution when you create it. More information: Passing optional parameters with a request
var createRequest = new CreateRequest
{
Target = virtualEntityMetadata
};
createRequest["SolutionUniqueName"] = "YourSolutionUniqueName";
service.Execute(createRequest);
View the messages created to support your virtual table
An easy way to verify that the messages you enabled exist is to examine the Web API $metadata service document.
You can do this in your browser. Using the Url for your organization, type the following into your browser:
[Organization Uri]/api/data/v9.2/$metadata
This is a large XML document, but you can search for 'OnExternalCreated' and find the definition of the action, in this case for the new_people virtual table.
<Action Name="OnExternalCreated" IsBound="true">
<Parameter Name="entityset" Type="Collection(mscrm.new_people)" Nullable="false"/>
<Parameter Name="Target" Type="mscrm.crmbaseentity" Nullable="false"/>
</Action>
You can see that this is an OData Action bound to the new_people entityset.
You'll find similar actions for OnExternalDeleted, and OnExternalUpdated:
<Action Name="OnExternalDeleted" IsBound="true">
<Parameter Name="entityset" Type="Collection(mscrm.new_people)" Nullable="false"/>
<Parameter Name="Target" Type="mscrm.crmbaseentity" Nullable="false"/>
</Action>
<Action Name="OnExternalUpdated" IsBound="true">
<Parameter Name="entityset" Type="Collection(mscrm.new_people)" Nullable="false"/>
<Parameter Name="Target" Type="mscrm.crmbaseentity" Nullable="false"/>
</Action>
View the messages using the plug-in registration tool
When you register a plug-in step using the plug-in registration tool, you'll find these messages.
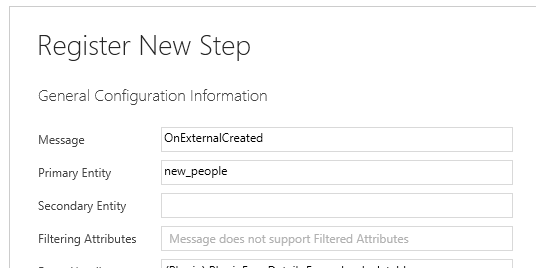
Use the messages to notify Dataverse of changes
To notify Dataverse of changes, you must call the appropriate API. You can use either the Dataverse Web API or the SDK for .NET.
Before using these messages, you may want to use the procedure describe in View the messages created to support your virtual table to confirm that they exist.
Using the Web API
Because these APIs are OData actions bound to an table collection, you can follow the pattern documented here: Use Web API actions> Bound actions> Actions bound to a table collection. The following are some examples showing the use of the new_people virtual table.
If the ID value is known by the calling system, it should always be included.
The entity instance passed using the Target Parameter must have the appropriate @odata.type annotation property set to define the type of entity. If this isn't included, an error is returned.
These calls should always return 204: No Content.
OnExternalCreated
For this action, the values should include all the properties set when the record was created.
POST [Organization Uri]/api/data/v9.1/new_peoples/Microsoft.Dynamics.CRM.OnExternalCreated HTTP/1.1
Authorization: Bearer [REDACTED]
Content-Type: application/json
{
"Target": {
"@odata.type": "Microsoft.Dynamics.CRM.new_people",
"new_name": "John",
"new_age": 23,
"new_lastname": "Doe",
"new_peopleid": "f6f5896b-bf08-455c-9bd3-526760cb3685"
}
}
OnExternalUpdated
For this action, only those properties that have changed should be included.
POST [Organization Uri]/api/data/v9.1/new_peoples/Microsoft.Dynamics.CRM.OnExternalUpdated HTTP/1.1
Authorization: Bearer [REDACTED]
Content-Type: application/json
{
"Target": {
"@odata.type": "Microsoft.Dynamics.CRM.new_people",
"new_age": 24,
"new_peopleid": "f6f5896b-bf08-455c-9bd3-526760cb3685"
}
}
OnExternalDeleted
For this action, only the unique identifier for the record is necessary.
POST [Organization Uri]/api/data/v9.1/new_peoples/Microsoft.Dynamics.CRM.OnExternalDeleted HTTP/1.1
Authorization: Bearer [REDACTED]
Content-Type: application/json
{
"Target": {
"@odata.type": "Microsoft.Dynamics.CRM.new_people",
"new_peopleid": "f6f5896b-bf08-455c-9bd3-526760cb3685"
}
}
Using the SDK for .NET
When using the SDK for .NET, you can use either early or late binding types. More information: Late-bound and Early-bound programming using the SDK for .NET
Early-bound types
This example uses the CrmServiceClient with early-bound types, though ServiceClient could also be used.
var service = new CrmServiceClient(conn);
// var service = new ServiceClient(conn);
//OnExternalCreated
var createPerson = new new_people
{
new_peopleId = new Guid("f6f5896b-bf08-455c-9bd3-526760cb3685"),
new_name = "John",
new_Age = 23,
new_LastName = "Doe"
};
var createRequest = new OnExternalCreatedRequest
{
Target = createPerson
};
service.Execute(createRequest);
//OnExternalUpdated
var updatePerson = new new_people
{
new_peopleId = new Guid("f6f5896b-bf08-455c-9bd3-526760cb3685"),
new_Age = 24
};
var updateRequest = new OnExternalUpdatedRequest
{
Target = updatePerson
};
service.Execute(updateRequest);
//OnExternalDeleted
var deletePerson = new new_people
{
new_peopleId = new Guid("f6f5896b-bf08-455c-9bd3-526760cb3685")
};
var deleteRequest = new OnExternalDeletedRequest
{
Target = deletePerson
};
Late-bound types
This example uses the CrmServiceClient with late-bound types, though ServiceClient could also be used.
var service = new CrmServiceClient(conn);
// var service = new ServiceClient(conn);
//OnExternalCreated
Entity createPerson = new Entity("new_people");
createPerson["new_peopleid"] = new Guid("f6f5896b-bf08-455c-9bd3-526760cb3685");
createPerson["new_name"] = "John";
createPerson["new_age"] = 23;
createPerson["new_lastname"] = "Doe";
var orgCreateRequest = new OrganizationRequest("OnExternalCreated");
orgCreateRequest["Target"] = createPerson;
service.Execute(orgCreateRequest);
//OnExternalUpdated
Entity updatePerson = new Entity("new_people");
updatePerson["new_peopleid"] = new Guid("f6f5896b-bf08-455c-9bd3-526760cb3685");
updatePerson["new_age"] = 24;
var orgUpdateRequest = new OrganizationRequest("OnExternalUpdated");
orgUpdateRequest["Target"] = updatePerson;
service.Execute(orgUpdateRequest);
//OnExternalDeleted
Entity deletePerson = new Entity("new_people");
deletePerson["new_peopleid"] = new Guid("f6f5896b-bf08-455c-9bd3-526760cb3685");
var orgDeleteRequest = new OrganizationRequest("OnExternalDeleted");
orgDeleteRequest["Target"] = deletePerson;
service.Execute(orgDeleteRequest);
See Also
Event framework
Microsoft Dataverse business events
Get started with virtual tables (entities)