3.1.1 Abstract Data Model
Services are programs that execute on a machine whose life cycle and execution properties are governed by the rules defined by the SCM. The state diagram that models these rules follows.
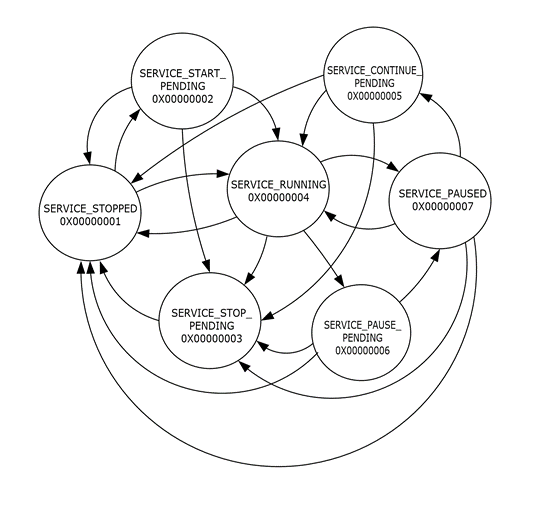
Figure 1: State Diagram in which life cycle and execution properties are governed by the rules defined in SCM
|
From state |
To state |
Cause |
|---|---|---|
|
SERVICE_STOPPED |
SERVICE_RUNNING |
|
|
SERVICE_STOPPED |
SERVICE_START_PENDING |
|
|
SERVICE_START_PENDING |
SERVICE_RUNNING |
|
|
SERVICE_START_PENDING |
SERVICE_STOP_PENDING |
|
|
SERVICE_START_PENDING |
SERVICE_STOPPED |
|
|
SERVICE_STOP_PENDING |
SERVICE_STOPPED |
|
|
SERVICE_RUNNING |
SERVICE_PAUSED |
|
|
SERVICE_RUNNING |
SERVICE_PAUSE_PENDING |
|
|
SERVICE_RUNNING |
SERVICE_STOPPED |
|
|
SERVICE_RUNNING |
SERVICE_STOP_PENDING |
|
|
SERVICE_PAUSE_PENDING |
SERVICE_PAUSED |
|
|
SERVICE_PAUSE_PENDING |
SERVICE_STOP_PENDING |
|
|
SERVICE_PAUSE_PENDING |
SERVICE_STOPPED |
|
|
SERVICE_PAUSED |
SERVICE_RUNNING |
|
|
SERVICE_PAUSED |
SERVICE_CONTINUE_PENDING |
|
|
SERVICE_PAUSED |
SERVICE_STOP_PENDING |
|
|
SERVICE_PAUSED |
SERVICE_STOPPED |
|
|
SERVICE_CONTINUE_PENDING |
SERVICE_RUNNING |
|
|
SERVICE_CONTINUE_PENDING |
SERVICE_STOP_PENDING |
|
|
SERVICE_CONTINUE_PENDING |
SERVICE_STOPPED |
|
The Service Control Manager Remote Protocol is used to manage these services on a remote machine by operating on the SCM on that machine.
The Service Control Manager maintains the following ADM elements.
|
Value |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
SCM database |
A collection of service records. |
|
SecurityDescriptor |
A security descriptor, as specified in [MS-AZOD] section 1.1.1.3, that is used to control an access to the SCM database. |
|
GroupList |
An ordered list of strings that services can specify as a ServiceGroup. |
|
BootAccepted |
A flag indicating whether a successful call to RNotifyBootConfigStatus has already been made to the server. This element is not accessible via any method and is internal to the protocol implementation. |
The SCM database is used by the Service Control Manager to add, modify, or configure services. Updates to the database are atomic. In the database there is a unique record, known as the service record, used to represent each installed service. A unique service name is used as the key for each service record.
The Service Record maintains the following ADM elements.
|
Value |
Meaning |
|---|---|
|
ServiceName |
A unique name for the service.
|
|
DisplayName |
Service display name.
The name is case-preserved in the Service Control Manager. Display name comparisons are always case-insensitive. Can specify a localized string using the following format:<29>
The DisplayName cannot match any other DisplayName or another ServiceName. The DisplayName can match the ServiceName if it they both refer to the same service. |
|
Description |
Description of the service.
|
|
DependOnService |
Service that starts before this service.
|
|
ErrorControl |
Severity of the error if this service fails to start during startup. For the supported values, see dwErrorControl in section 3.1.4.11. |
|
FailureActions |
Actions that the service controller takes on each failure of the service. These actions are queried and set using SERVICE_FAILURE_ACTIONSA (section 2.2.39) and SERVICE_FAILURE_ACTIONSW (section 2.2.40) via the RQueryServiceConfig2A (section 3.1.4.36), RQueryServiceConfig2W (section 3.1.4.37), RChangeServiceConfig2A (section 3.1.4.34), and RChangeServiceConfig2W (section 3.1.4.35) server methods. |
|
ServiceGroup |
Name of the service group the service belongs to for the purposes of load ordering. Each service can optionally specify only one group name. |
|
ImagePath |
Full qualified path to the service binary file. |
|
ObjectName |
If the service is a user-mode program, the name of the account under which the service executes. If the service is a driver, the name of the driver object that IO manager creates for the driver in the ObjectManager namespace. |
|
Password |
Password associated with the account specified in ObjectName. |
|
RequiredPrivileges |
Required privileges for the service. Privileges determine the type of system operations that can be performed. The privilege constants are detailed in [MS-LSAD] Privilege Data Model (section 3.1.1.2.1). |
|
ServiceSidType |
Type of service security identifier (SID). |
|
FailureActionsOnNonCrashFailures |
Failure action setting of a service that determines when FailureActions are to be executed. |
|
DependOnGroup |
Service groups that MUST be started before this service. |
|
Start |
Defines when to start the service. |
|
Type |
Type of service. |
|
TriggerInfo |
Trigger setting of the service.<30> |
|
PreferredNode |
Preferred node setting of the service.<31> |
|
Tag |
A number that is unique within the Group. Refer to the definition of Group as defined previously in this table. For driver services that have SERVICE_BOOT_START or SERVICE_SYSTEM_START start types [see dwStartType in RChangeServiceConfigW (section 3.1.4.11), RCreateServiceW (section 3.1.4.12), RChangeServiceConfigA (section 3.1.4.22), RCreateServiceA (section 3.1.4.23), and RCreateServiceWOW64A (section 3.1.4.41)], the server starts each service based on its Tag's position within the Group. |
|
SecurityDescriptor |
A security descriptor, as specified in [MS-AZOD] section 1.1.1.3, that describes the client access rights for changing service configuration. |
|
ServiceStatus |
The server maintains a SERVICE_STATUS (section 2.2.47) to keep track of the service runtime information. |
|
HandleCount |
Counter for the number of RPC context handles currently created for this service record. This element is not accessible via any method and is internal to the protocol implementation. |
|
Deleted |
The flag that is set when the service record has been marked for deletion. This element is not accessible via any method and is internal to the protocol implementation. |