Data and privacy for custom text classification
This article provides high-level details about how data is processed by custom text classification. Remember that you're responsible for your use and the implementation of this technology, which includes complying with all laws and regulations that apply to you. For example, it's your responsibility to:
- Understand where your data is processed and stored by the custom text classification service to meet regulatory obligations for your application.
- Ensure you have all necessary licenses, proprietary rights, or other permissions required for the content in your dataset that's used as the basis for building your custom text classification models.
It's your responsibility to comply with all applicable laws and regulations in your jurisdiction.
What data does custom text classification process?
Custom text classification processes the following data:
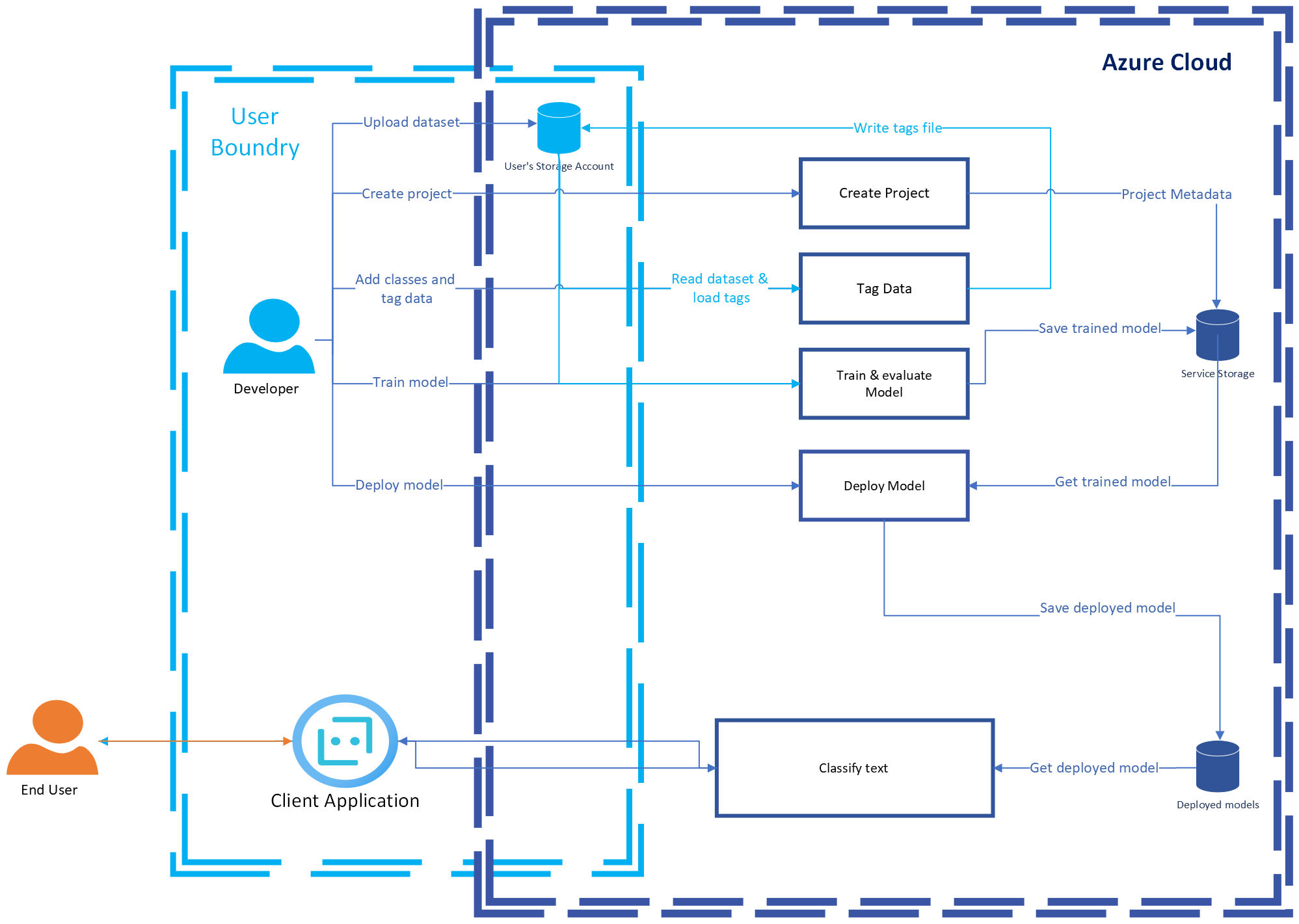
User's dataset and tags file: As a prerequisite to creating a custom text classification project, users need to upload their dataset to their Azure Blob Storage container. A tags file is a JSON-formatted file that contains references to a user's tagged data and classes. The user can either bring their own tags or they can tag their data through the UI experience in the Language Studio. Either way, a tags file that contains tagged data and classes is essential for the training.
A user's dataset is split into train and test sets, where the split can either be predefined by developers in a tags file or chosen at random during training. The train set and the tags file are processed during training to create the custom text classification model. The test set is later processed by the trained model to evaluate its performance.
Custom text classification models: Based on the user's request to train the model, custom text classification processes the provided tagged data to output a trained model. The user can choose to train a new model or overwrite an existing one. The trained model is then stored on the service's side and used for processing the model evaluation. After the developer is content with the model's performance, they request to deploy the model for consumption use. The deployed model is also stored on the service's side, which is used to process the user's requests for prediction through the Analyze API.
Data sent for classification: This data is the user's text sent from a customer's client application through the Analyze API to be processed for text classification by the custom machine learning model. Output of the processed data contains the predicted classes along with their confidence scores. This output is returned to the client's application to perform an action to fulfill the user's request.
Custom text classification doesn't collect or store any customer data to improve its machine-learned models or for product improvement purposes. We use aggregate telemetry, such as which APIs are used and the number of calls from each subscription and resource, for service monitoring purposes.
How does custom text classification process data?
The following diagram illustrates how your data is processed.
How is data retained, and what customer controls are available?
Custom text classification is a data processor for General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) purposes. In compliance with GDPR policies, custom text classification users have full control to view, export, or delete any user content either through the Language Studio or programmatically by using Language APIs.
Your data is only stored in your Azure Storage account. custom text classification only has access to read from it during training.
Customer controls include:
- Tagged data provided by the user as a prerequisite to train the model is saved in the customer's Azure Storage account that's connected to the project during creation. Customers can edit or remove tags whenever they want through the Language Studio.
- Custom text classification projects metadata is stored in the service's side until the customer deletes the project. The project's metadata are the fields that you fill in when you create your project, such as project name, description, language, name of connected blob container, and tags file location.
- Trained custom text classification models are stored in the service's Azure Storage accounts until the customer deletes them. The model is overwritten each time the user retrains it.
- Deployed custom text classification models persist in the service's Azure Storage accounts until the customer deletes the deployment or deletes the model itself. The model is overwritten each time the user deploys to the same deployment name.
Optional: Security for customers' data
Azure services are implemented while maintaining appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect customer data in the cloud.
To learn more about Microsoft's privacy and security commitments, see the Microsoft Trust Center.