Connecting clients to game servers
PlayFab game servers are containerized applications. When game servers are deployed to Azure, their networking environment is virtualized, and the game server will not have direct access to its Internet accessible IP addresses.
Instead, game servers using GetAdaptersInfo (Windows) or GetIfAddrs (Linux) will observe a single network adapter with non-unique IP addresses that have been configured through Network Address Translation (NAT44).
This usage of network virtualization and NAT allows game servers to maintain connections even as underlying Azure infrastructure may be changing. All game servers have IPv4 connectivity, but IPv6 connectivity will be added in the future.
Note
All Game Servers have IPv4 connectivity - IPv6 connectivity will be added in the future.
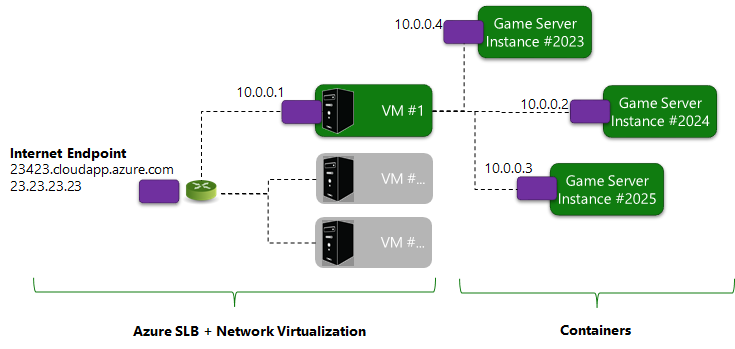
You may configure a Server deployment to pack multiple Game Server instances on a single virtual machine. For the most part, this does not modify the network environment, as each containerization allows each Game Server instance to have independent IP addresses and TCP/UDP port spaces.
However, all instances on a single virtual machine share the physical network infrastructure, and can create network contention.
While testing high-density configurations, it is important to test that typical contention does not cause unacceptable game play issues.
Different virtual machine sizes and operating systems are provisioned with differing levels of bandwidth. To see the bandwidth provisioned for a specific SKU, please see Azure’s throughput documentation.
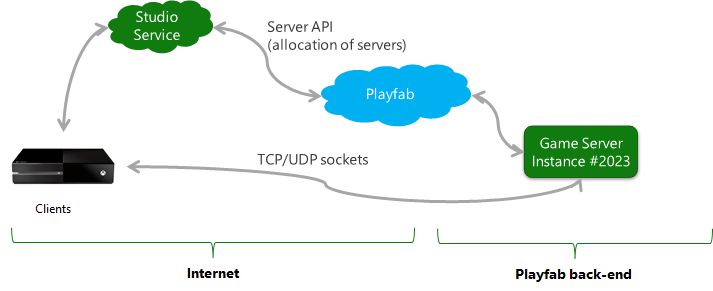
Game servers are allocated through service-to-service calls through the PlayFab server API. The connection information required for client connectivity is passed through these services and clients, which typically use TCP or UDP sockets to drive a direct connection to the game server. Typically, game servers will listen on well-known UDP and TCP ports selected by the game developer.
Game clients need the Internet-facing IP address of your game servers to connect to them. Clients also need port-forwarding information to allow well-known ports to which the server is listening, to be addressable through the Azure network virtualization apparatus.
- Public IPv4 Address
- A mapping of developer-provided ports (by name) to the Internet-facing port.
| Game Server Protocol Name | Protocol | Internet-facing Port |
|---|---|---|
| Multiplayer | UDP | 3098 |
| Debugger | TCP | 23222 |
Enabling TCP/UDP ports for game servers
The port requirements provided through Game Manager or the Entity API CreateBuild enables game clients to contact the virtual machine. It also configures the firewall on the resident operating system to enable network traffic on the ports you specify.
Public Internet-facing ports and IP addresses used by multiplayer servers
The IP addresses used by the multiplayer VMs are drawn from the general pool of IP addresses used by Azure VMs. These IPs are specified as the AzureCloud service tag. For more information, see service tags on-premises. All VMs use a port range of 30000-31000 for game traffic and 50000-55000 for remote access (SSH/RDP) traffic.