Writing custom CloudScript
CloudScript is one of PlayFab's most versatile features. It allows client code to request execution of any kind of custom server-side functionality you can implement, and it can be used with virtually anything. In addition to explicit execution requests from client or server code, CloudScript can be executed in response to PlayStream events (by creating a rule) or as part of a scheduled task.
Note
CloudScript using Azure Functions improves on what made CloudScript great with more supported languages and better debugging workflows.
This tutorial covers writing your CloudScript code. See the CloudScript quickstart for help with uploading your CloudScript files to your title.
Note
This tutorial demonstrates Unity code samples, but CloudScript works similarly for all SDKs.
Prerequisites for this tutorial:
- Unity environment set up with the PlayFab Unity SDK
- The title ID is set in the
PlayFabSharedSettingsobject. - The project can successfully log in a user.
- The title ID is set in the
Getting started: helloWorld
Our helloWorld example works on a brand new title, with no modifications in Game Manager. The default CloudScript file for a new title includes a handler called helloWorld. It utilizes a few basic features, input parameters, logging, currentPlayerId, and return parameters.
The following sample shows the default helloWorld function code (minus comments).
// CloudScript (JavaScript)
handlers.helloWorld = function (args, context) {
var message = "Hello " + currentPlayerId + "!";
log.info(message);
var inputValue = null;
if (args && args.hasOwnProperty("inputValue"))
inputValue = args.inputValue;
log.debug("helloWorld:", { input: inputValue });
return { messageValue: message };
}
Deconstruct the code
The handler object is pre-defined in the PlayFab CloudScript environment. You should add any of your CloudScript functions to this object.
helloWorldis a function made available to your title and SDKs, because it's defined in the handler object.argsis an arbitrary object which comes from the caller. It's parsed from JSON, and can contain any data formatted in any way.
See FunctionParameter in the next section.
Warning
You should treat this object with zero trust. A hacked client or malicious user can provide any information here in any format.
Contextis an advanced parameter. In this example, it's null. This parameter is server-controlled and safe.currentPlayerIdis a global variable, which is set to the PlayFabId of the player requesting this call. This parameter is server-controlled and safe. Note: When using ExecuteEntityCloudScript API this parameter is null unless the entity has a MasterPlayerID in its entity chain.log.info:logis a global object. It's primarily used for debugging your CloudScript. Thelogobject exposes the following methods:info,debug, anderror. There are more details later in this tutorial.return: any object you return is serialized as JSON, and returned to the caller. You may return any JSON serialize-able object with any data you wish.
Warning
It is your responsibility if your CloudScript returns secret data to your clients. A hacked client or malicious user can examine the returned data, even if you don't display it to the user in regular game play.
Executing CloudScript functions from a Unity game client
Calling a CloudScript function from within a client is straightforward. You first have to create an ExecuteCloudScriptRequest, and set the ActionId property to the name of the CloudScript function you wish to execute (in this case it would be helloWorld), then send the object to PlayFab via our API.
Note
You can only call CloudScript methods attached to the handlers JavaScript object.
To execute CloudScript methods, you'll need the following lines of code in your client.
// Build the request object and access the API
private static void StartCloudHelloWorld()
{
PlayFabClientAPI.ExecuteCloudScript(new ExecuteCloudScriptRequest()
{
FunctionName = "helloWorld", // Arbitrary function name (must exist in your uploaded cloud.js file)
FunctionParameter = new { inputValue = "YOUR NAME" }, // The parameter provided to your function
GeneratePlayStreamEvent = true, // Optional - Shows this event in PlayStream
}, OnCloudHelloWorld, OnErrorShared);
}
// OnCloudHelloWorld defined in the next code block
Deconstruct the code
ExecuteCloudScriptRequest is the request type for any call to PlayFabClientAPI.ExecuteCloudScript.
ExecuteCloudScriptRequest.FunctionNameis a string. The value should match the name of the function defined in CloudScript. In this case,helloWorld.ExecuteCloudScriptRequest.FunctionParametercan be any object, able to be serialized to JSON. It becomes the first args parameter in thehelloWorldfunction (refer to the args in the previous section).ExecuteCloudScriptRequest.GeneratePlayStreamEventis optional. If true, an event is posted to PlayStream, which you can view in Game Manager, or utilize for other PlayStream triggers.
Depending on the language, the final part of the ExecuteCloudScript line involves making the request to the PlayFab CloudScript server, and the Result and Error handling part, specific for the language.
For example, in Unity, JavaScript, or AS3, Error and Result handling is provided using callback functions.
The following is an example of error handling methods.
private static void OnCloudHelloWorld(ExecuteCloudScriptResult result) {
// CloudScript returns arbitrary results, so you have to evaluate them one step and one parameter at a time
Debug.Log(JsonWrapper.SerializeObject(result.FunctionResult));
JsonObject jsonResult = (JsonObject)result.FunctionResult;
object messageValue;
jsonResult.TryGetValue("messageValue", out messageValue); // note how "messageValue" directly corresponds to the JSON values set in CloudScript
Debug.Log((string)messageValue);
}
private static void OnErrorShared(PlayFabError error)
{
Debug.Log(error.GenerateErrorReport());
}
Intermediate Overview: Globals and advanced arguments
CloudScript is a set of JavaScript functions compiled with V8 and hosted on PlayFab's servers. It has access to any server API listed in the PlayFab API reference documentation, along with a logger, the PlayFab ID of the player making the CloudScript request, and any information included with the request, all in the form of preset objects.
CloudScript functions themselves are properties of a global handlers object. The following table shows a complete list of these predefined variables.
| Name | Use |
|---|---|
| server | Has access to all server-side API calls listed in the PlayFab API reference documentation. They can be called (synchronously) like so: var result = server.AuthenticateUserTicket(request); |
| http | Performs synchronous HTTP requests, like so: http.request(url, method, content, contentType, headers, logRequestAndResponse). The headers object contains properties corresponding to various headers and their values. logRequestAndResponse is a boolean that determines whether the title should log any errors in the request as part of the response. |
| log | Creates log statements and adds them to the response. Logs have three levels: log.info(), log.debug(), and log.error(). All three levels take a message string, along with an optional object containing extra data to include with the log. For example, log.info('hello!', { time: new Date() }); |
| currentPlayerId | PlayFab ID of the player who triggered the CloudScript call. |
| handlers | Global object that contains all CloudScript functions for your title. Functions can be added or called through this object. For example, handlers.pop = function() {};, handlers.pop();. |
| script | Global object that contains Revision and titleId. Revision represents the Revision Number for the currently executing CloudScript, and titleId represents the ID for the current title. |
In addition, all handler functions are passed two parameters, detailed below.
| Name | Use |
|---|---|
| args | First parameter to a handler function. An object representation of the FunctionParameter field of an ExecuteCloudscript request. |
| context | Second parameter to a handler function. Additional information about the request when it is triggered by a PlayStream event action, including the data from the event that triggered the action (context.playStreamEvent) and the profile data for the player associated with it. (context.playerProfile) |
CloudScript functions can be called through the ExecuteCloudScript API, or by a preset PlayStream event action.
Full details about the response to ExecuteCloudScript can be found in the ExecuteCloudScriptResult.
Intermediate: FunctionParameter and args
In the previous section, we described how to populate the request.FunctionParameter, and view that info in the args parameter. The CloudScript quickstart demonstrates how to upload new CloudScript.
Putting both together, we can provide another example of how to pass arguments from client to CloudScript. Take the previous example, and modify the CloudScript code and your client code as shown below.
handlers.helloWorld = function (args) {
// ALWAYS validate args parameter passed in from clients (Better than we do here)
var message = "Hello " + args.name + "!"; // Utilize the name parameter sent from client
log.info(message);
return { messageValue: message };
}
// Build the request object and access the API
private static void StartCloudHelloWorld()
{
PlayFabClientAPI.ExecuteCloudScript(new ExecuteCloudScriptRequest()
{
FunctionName = "helloWorld", // Arbitrary function name (must exist in your uploaded cloud.js file)
FunctionParameter = new { name = "YOUR NAME" }, // The parameter provided to your function
GeneratePlayStreamEvent = true, // Optional - Shows this event in PlayStream
}, OnCloudHelloWorld, OnErrorShared);
}
private static void OnCloudHelloWorld(ExecuteCloudScriptResult result) {
// CloudScript returns arbitrary results, so you have to evaluate them one step and one parameter at a time
Debug.Log(JsonWrapper.SerializeObject(result.FunctionResult));
JsonObject jsonResult = (JsonObject)result.FunctionResult;
object messageValue;
jsonResult.TryGetValue("messageValue", out messageValue); // note how "messageValue" directly corresponds to the JSON values set in CloudScript
Debug.Log((string)messageValue);
}
private static void OnErrorShared(PlayFabError error)
{
Debug.Log(error.GenerateErrorReport());
}
After making these changes, you can now easily send and receive data between CloudScript and your clients.
Note
It is important to point out that any data coming from your clients is susceptible to hacking and exploitation.
You will always want to validate input parameters prior to updating your back end. The process for validating input parameters will vary from title to title, but the most basic validation will check to ensure inputs are within acceptable ranges and periods.
Intermediate: Calling the server APIs
As mentioned before, within CloudScript methods, you have access to the full set of Server API calls. This enables your cloud code to act as a dedicated server.
Common server tasks:
- Update player statistics and data.
- Grant items and currency.
- Randomly generate game data.
- Securely calculate battle results and more...
See the Server APIs listed in our PlayFab API Reference documentation for required parameters and object structures.
The following example is from within a potential CloudScript handler.
// CloudScript (JavaScript)
//See: JSON.parse, JSON.stringify, parseInt and other built-in javascript helper functions for manipulating data
var currentState; // here we are calculating the current player's game state
// here we are fetching the "SaveState" key from PlayFab,
var playerData = server.GetUserReadOnlyData({"PlayFabId" : currentPlayerId, "Keys" : ["SaveState"]});
var previousState = {}; //if we return a matching key-value pair, then we can proceed otherwise we will need to create a new record.
if(playerData.Data.hasOwnProperty("SaveState"))
{
previousState = playerData.Data["SaveState"];
}
var writeToServer = {};
writeToServer["SaveState"] = previousState + currentState; // pseudo Code showing that the previous state is updated to the current state
var result = server.UpdateUserReadOnlyData({"PlayFabId" : currentPlayerId, "Data" : writeToServer, "Permission":"Public" });
if(result)
{
log.info(result);
}
else
{
log.error(result);
}
Advanced: PlayStream event action
A CloudScript function can be configured to run in response to a PlayStream event.
- In any browser:
- Visit the PlayFab Game Manager.
- Find your Title.
- Under Build in the sidebar, go to the Automation tab.
- Go to the Rules tab.
The page will look like the example provided below.
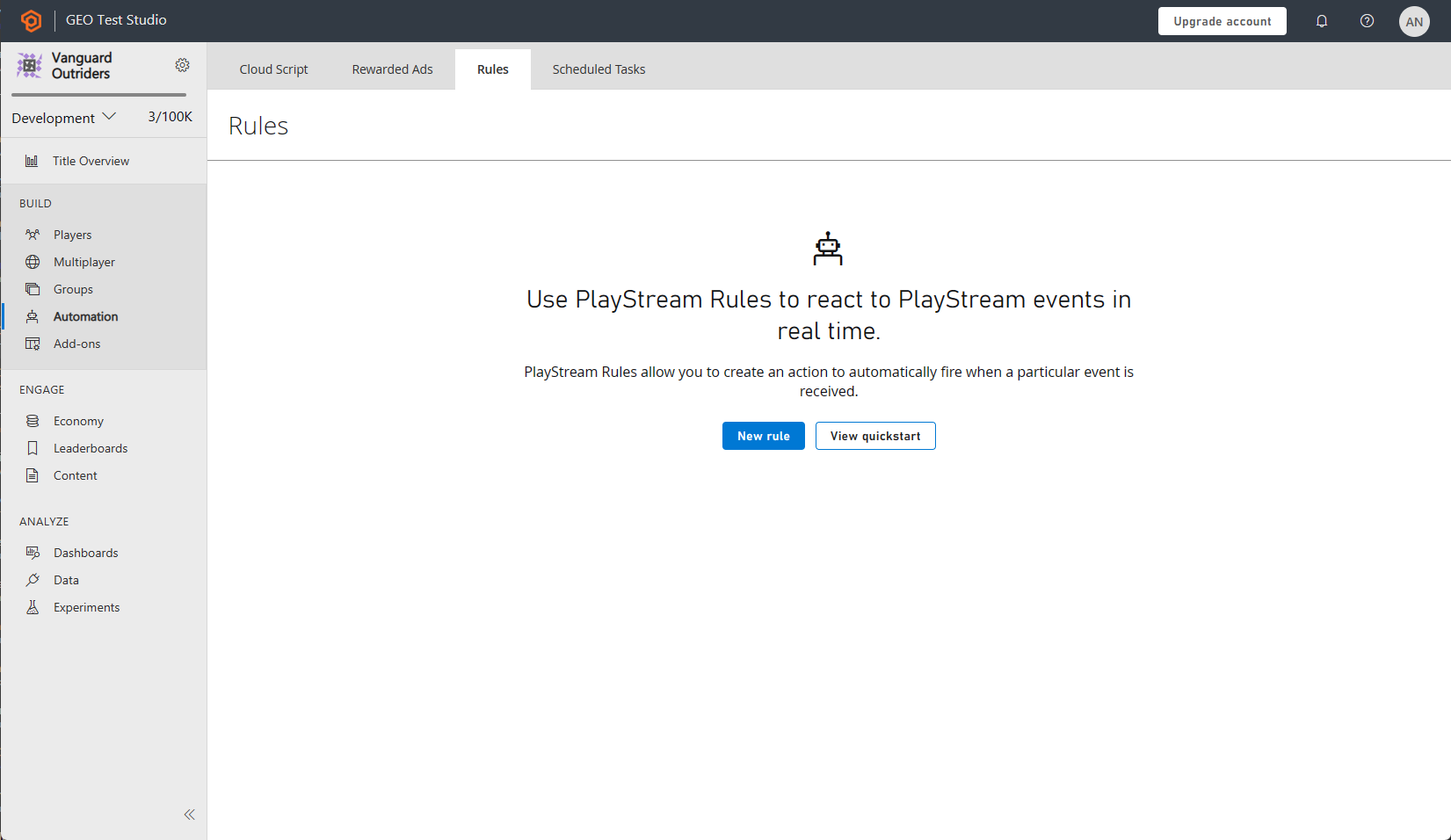
Use the New Rule button to create a new rule.
- Give the new Rule a name.
- Select an Event type that will be used as a trigger for a condition or an action.
- To make the Rule trigger a CloudScript function, add an Action with the button in that section.
- Then select the option in the Type drop-down menu.
- Select the helloWorld function in the Cloud Script Function drop-down menu.
- Select the Save action button.
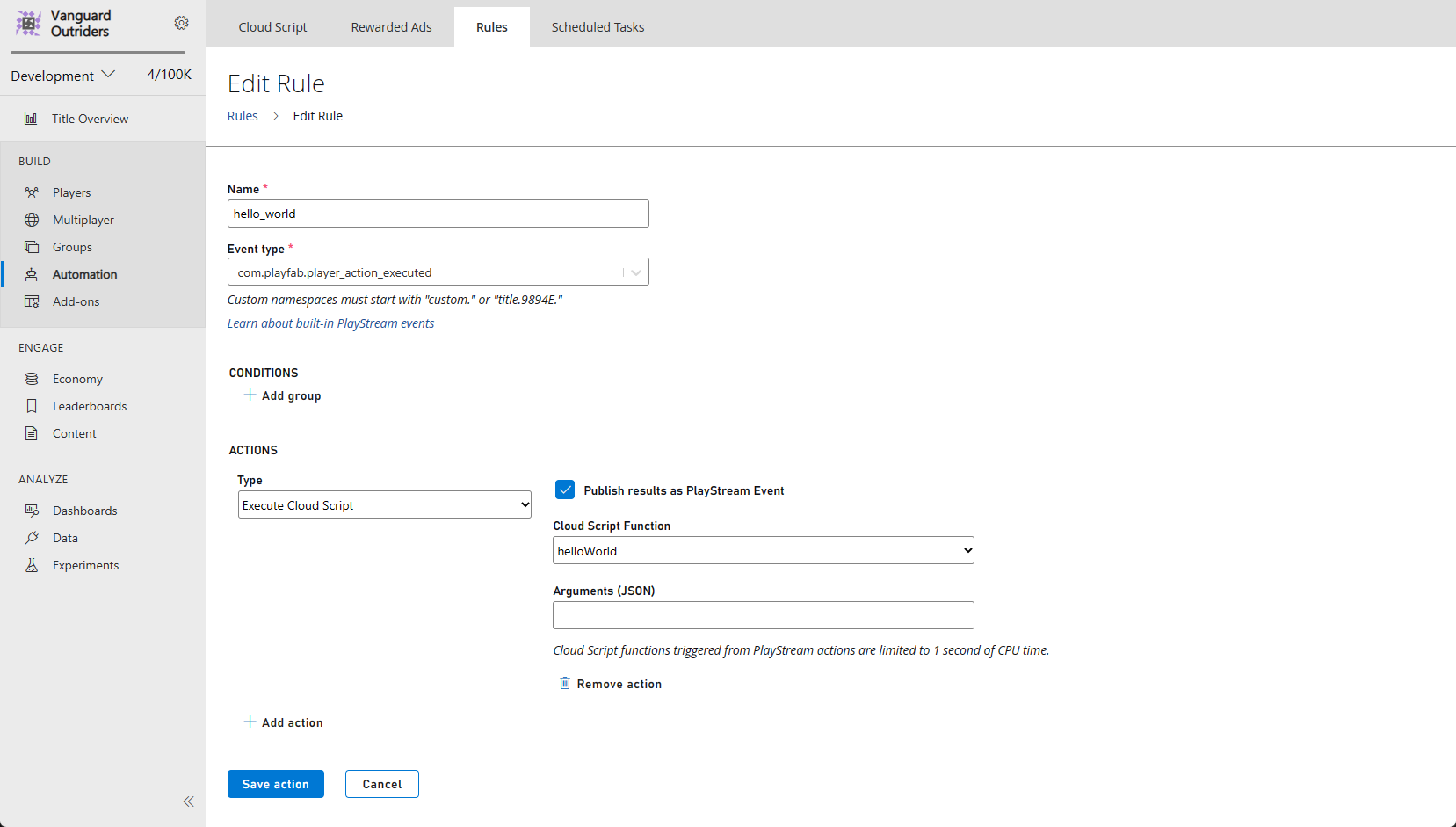
This Rule is now set to trigger on any event of your selected type. To test it:
- Check the Publish results as PlayStream Event box.
- Save the Action.
- Then trigger an event.
- In the PlayStream Monitor, a new event that corresponds to the CloudScript execution should be present which contains the appropriate information.
- For more information on checking a PlayStream event in the debugger, see the following section Advanced: Debugging CloudScript.
Note
Event actions can only use the live revision when calling CloudScript functions. If you cannot find the helloWorld function in the drop-down, this is the most likely reason.
Advanced: Debugging CloudScript
Note
Debugging is much easier with CloudScript using Azure Functions. Learn more on how to use local debugging for CloudScript using Azure Functions.
Logging
One of the most important tools for debugging code is logging. Our CloudScript provides a utility for performing the function.
This takes the form of the log object, which can log any message desired using the Info, Debug, and Error methods.
Additionally, the HTTP object will log any errors it comes across while making requests by setting the logRequestAndResponse parameter. While setting these logs up is simple, accessing them takes a bit of finesse.
Here is an example of a CloudScript function that uses all 4 types of logs.
handlers.logTest = function(args, context) {
log.info("This is a log statement!");
log.debug("This is a debug statement.");
log.error("This is... an error statement?");
// the last parameter indicates we want logging on errors
http.request('https://httpbin.org/status/404', 'post', '', 'text/plain', null, true);
};
To run this example, add this function to your live revision before proceeding.
The logTest function can be called using ExecuteCloudScript as shown below.
// Invoke this on start of your application
void Login() {
PlayFabClientAPI.LoginWithCustomID(new LoginWithCustomIDRequest {
CreateAccount = true,
CustomId = "Starter"
}, result => RunLogTest(), null);
}
void RunLogTest() {
PlayFabClientAPI.ExecuteCloudScript(new ExecuteCloudScriptRequest {
FunctionName = "logTest",
// duplicates the response of the request to PlayStream
GeneratePlayStreamEvent = true
}, null, null);
}
// Logs evaluated in next code block
Setting GeneratePlayStreamEvent makes the CloudScript function call generate a PlayStream event, which includes the contents of the response. To find the contents of a PlayStream event:
Go to either the Game Manager home page for your Title or its PlayStream tab.
The PlayStream Debugger will display events as they come in.
When they arrive, select the small blue Info icon in the top right corner of the event, as shown below.
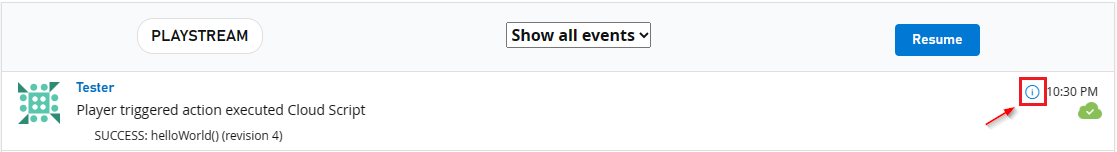
Selecting this will display the raw JSON of the event, which is detailed for each event here. An example of this JSON can be seen in the following example.
If we add the
LogScriptMonoBehavior to the scene, running the game will yield this in PlayStream.
The result of an ExecuteCloudScript call includes a field called Logs, which is a list of log objects generated by the CloudScript function.
You can see the three log calls, as well as the log from the invalid HTTP request. The HTTP request log also makes use of the Data field, unlike the log calls.
This field is a JavaScript object that can be populated by any information relevant to the log statement. Calls to log can make use of this field as well, using the second parameter, as indicated below.
handlers.logTest = function(args, context) {
log.info("This is a log statement!", { what: "Here on business." });
log.debug("This is a debug statement.", { who: "I am a doctor, sir" });
log.error("This is... an error statement?", { why: "I'm here to fix the plumbing. Probably.", errCode: 123 });
};
These calls will all populate the Data field in the result with their second parameter.
Since the logs are included in the result, the client-side code can respond to log statements. The error in the logTest function is forced, but the client code can be adapted to respond to it.
void RunLogTest()
{
PlayFabClientAPI.ExecuteCloudScript(
new ExecuteCloudScriptRequest
{
FunctionName = "logTest",
// handy for logs because the response will be duplicated on PlayStream
GeneratePlayStreamEvent = true
},
result =>
{
var error123Present = false;
foreach (var log in result.Logs)
{
if (log.Level != "Error") continue;
var errData = (JsonObject) log.Data;
object errCode;
var errCodePresent = errData.TryGetValue("errCode", out errCode);
if (errCodePresent && (ulong) errCode == 123) error123Present = true;
}
if (error123Present)
Debug.Log("There was a bad, bad error!");
else
Debug.Log("Nice weather we're having.");
}, null);
}
If this code is run, the output should indicate the presence of the error. Realistic error responses might be to display the error in the UI, or save a value in a log file.
Advanced: Errors
In development, CloudScript errors will often not be manually triggered - as in the case of log.error.
Fortunately, the response to ExecuteCloudScript contains an ExecuteCloudScriptResult which includes a ScriptExecutionError field. Adapting the last example from the logging section, we might use it as shown below.
void RunLogTest() {
PlayFabClientAPI.ExecuteCloudScript(new ExecuteCloudScriptRequest {
FunctionName = "logTest",
// handy for logs because the response will be duplicated on PlayStream
GeneratePlayStreamEvent = true
}, result => {
if(result.Error != null) {
Debug.Log(string.Format("There was error in the CloudScript function {0}:\n Error Code: {1}\n Message: {2}"
, result.FunctionName, result.Error.Error, result.Error.Message));
}
},
null);
}
In the event that some error occurred, this code would display it in the log.