User-based authentication
There are plans to remove certificate-based authentication to Microsoft Dynamics 365 finance and operations apps. The admin center that replaces Microsoft Dynamics Lifecycle Services no longer includes the option to download certificates. Regression suite automation tool (RSAT) usage must transition to replace certificates with user-based authentication. Finance and operations apps don't support authentication by service principals such as app registrations, or by managed identities. Therefore, user-based authentication is the only option.
We recommend that you use user-based authentication whenever possible. However, under some conditions, this approach isn't possible. User-based authentication requires that a standard Microsoft online identity provider (https://login.microsoftonline.com) is used to validate user accounts. It also requires that user authentication is configured without multifactor authentication (MFA) for accounts that are used to connect to finance and operations apps test environments. User account authentication times out and fails if an attempt is made to sign in by using a user account where MFA is enabled.
We also recommend that access to a finance and operations apps environment requires MFA. MFA should be disabled only for test accounts that RSAT uses for the finance and operations apps test environments. You can configure this approach in Microsoft Entra ID by using Conditional Access policies. For more information about this configuration, see the online documentation. The use of Conditional Access policies is a premium feature that you must subscribe to.
Finance and operations apps on-premises hosted environments aren't supported with Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) user account identities. Therefore, environments of this type that are deployed as local business data (LBD) environments can't use user-based authentication.
Set up user-based authentication
The setup of user-based authentication requires some extra steps. However, after it's centrally configured, the setup of individual RSAT client environments becomes more seamless, and you don't have to worry about installing certificates that are granted access to the test environment.
After this setup is completed, access to finance and operations apps test environments occurs when a user who's identified by a user account name and password signs in, just as when normal users sign in.
When tests are run, RSAT requires passwords for test user accounts from parameter files. Test cases that don't have a test user account in parameter files are run by using the admin user from RSAT settings. RSAT then needs a password for that user too.
An Azure key vault must be used to safely maintain passwords. Each company must create and grant access for the key vault that's used with RSAT.
The key vault is created as a resource under a subscription in the Azure portal. A user who has technical experience in your organization and the required access must create the key vault. The key vault is centrally created once and then shared by RSAT client installations.
Use the key vault to add secrets that use the name of test accounts. However, remove any characters that aren't allowed. For example, to use an account that's named frontname_surname@mydomain.com as a secret name, you must remove illegal characters and change it to frontnamesurnamemydomaincom.
The secret value is where the password is provided. Make sure that you enter the password exactly as it must be entered during sign-in. No changes should be made to the password when it's saved as the secret value.
Follow best practices, and regularly renew the password for test accounts. When new passwords are set, remember to update the matching secret value in the key vault.
Important
Include only test accounts that are used for testing in sandbox, user acceptance testing (UAT), or DevBox environments. We strongly discourage you from using any real user accounts as test accounts, because of the risk that unintended access through these accounts might expose access to business data. In addition, grant test accounts only access to sign in to finance and operations apps that are hosted in sandbox, UAT, or DevBox environments. Avoid granting them access to production environments, because such access has potential risks.
RSAT automatically transforms test user accounts and removes illegal characters when it looks up passwords. Continue to use full account names to specify the test user accounts in parameter files and RSAT settings.
RSAT must be granted access to the key vault. To grant this access, create an app registration in Microsoft Entra ID under the same tenant where the key vault was created. This app registration is a shared identity that's used by the key vault and RSAT.
The app registration that's created has an application (client) ID and a secret. This secret is identified by a secret ID and has a secret value that acts as a password for the connection.
The app registration must be granted access to the key vault. In the Azure portal, look up the key vault resource, use access policies, and create a new policy that grants Get and List secret permissions to the app registration as the selected principal.
Information that you collect while you set up the key vault and app registration is required to complete the setup in RSAT. First select User-Based as the authentication method. New fields for the setup then become available, as shown in the following illustration. Provide the tenant ID, key vault URL, client ID, secret ID, and secret value that you previously collected.
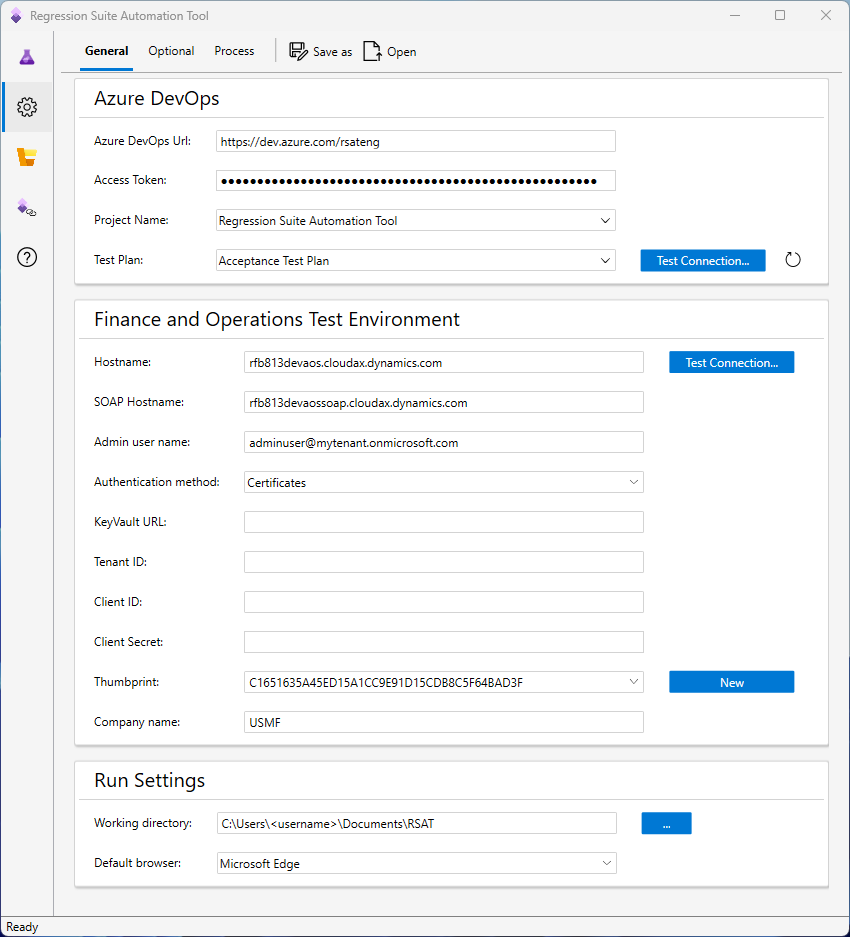
Notice that a thumbprint must still be selected for a certificate. However, this certificate is used only locally. It isn't used to gain access. You can select New next to the field to create a new certificate that's locally installed. You don't have to install the certificate in the hostname environment.
The secrets for the app registration or client ID have an expiry and must be periodically renewed in Microsoft Entra ID. Therefore, the secret ID and the secret value must be periodically updated. Obtain updated values from the individual in your company who maintains this information.
Settings files that are saved and loaded from RSAT settings don't include the client secret. This secret is excluded as a security precaution. The client secret must be manually entered and is saved only in the save storage that you use as the Windows vault with Credential Manager. Keep this fact in mind when you configure an environment to run RSAT by using the command-line interface (CLI) (for example, by using pipelines). You must sign in to the environment by using the user account that RSAT is started under. Then manually provide the client secret value in RSAT settings to save it in the vault, so that it's used during playback.
Disable MFA for test accounts
As was previously mentioned, user-based authentication doesn't work for accounts where MFA is enabled.
Although you can configure tenants in Microsoft Entra ID and disable the security defaults to disable MFA, we don't recommend this approach, because it disables MFA for all accounts.
The secure approach is to disable MFA only for the test accounts that RSAT uses to run test cases, and only for environments that are used during testing. You can configure this approach by using Conditional Access policies. For more information, see Building a Conditional Access policy.