Segurança de transporte com autenticação de certificado
Este artigo discute o uso de certificados X.509 para autenticação de servidor e cliente ao usar a segurança de transporte. Para obter mais informações sobre os certificados X.509, confira Certificados de chave pública X.509. Os certificados devem ser emitidos por uma autoridade de certificação, que geralmente é um emissor de certificados terceirizado. Em um domínio do Windows Server, os Serviços de Certificados do Active Directory podem ser usados para emitir certificados para computadores cliente no domínio. Nesse cenário, o serviço é hospedado no IIS (Serviços de Informações da Internet), que é configurado com o protocolo SSL. O serviço é configurado com um certificado SSL (X.509) para permitir que os clientes verifiquem a identidade do servidor. O cliente também é configurado com um certificado X.509 que permite que o serviço verifique a identidade do cliente. O certificado do servidor deve ser confiável para o cliente e o certificado do cliente deve ser confiável para o servidor. O mecanismo de como o serviço e o cliente verificam a identidade uns dos outros está além do escopo deste artigo. Para obter mais informações, consulte Assinatura Digital na Wikipédia.
Esse cenário implementa um padrão de mensagens de solicitação/resposta, conforme ilustrado pelo diagrama a seguir.
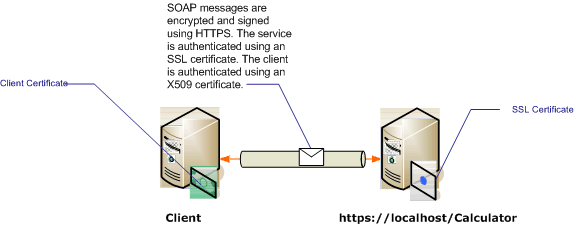
Para obter mais informações sobre como usar um certificado com um serviço, consulte Trabalhando com certificados e Como configurar uma porta com um certificado SSL. A tabela a seguir descreve as diversas características do cenário.
| Característica | Descrição |
|---|---|
| Modo de segurança | Transport |
| Interoperabilidade | Com serviços e clientes de serviços Web existentes. |
| Autenticação (servidor) Autenticação (cliente) |
Sim (usando um certificado SSL) Sim (usando um certificado X.509) |
| Integridade dos Dados | Sim |
| Confidencialidade dos dados | Yes |
| Transport | HTTPS |
| Associação | WSHttpBinding |
Configurar o serviço
Como o serviço nesse cenário é hospedado no IIS, ele é configurado com um arquivo web.config. O web.config a seguir mostra como configurar o WSHttpBinding para usar a segurança de transporte e as credenciais do cliente X.509.
<configuration>
<system.serviceModel>
<protocolMapping>
<add scheme="https" binding="wsHttpBinding" />
</protocolMapping>
<bindings>
<wsHttpBinding>
<!-- configure wsHttp binding with Transport security mode and clientCredentialType as Certificate -->
<binding>
<security mode="Transport">
<transport clientCredentialType="Certificate"/>
</security>
</binding>
</wsHttpBinding>
</bindings>
<!--For debugging purposes set the includeExceptionDetailInFaults attribute to true-->
<behaviors>
<serviceBehaviors>
<behavior>
<serviceDebug includeExceptionDetailInFaults="True" />
</behavior>
</serviceBehaviors>
</behaviors>
</system.serviceModel>
</configuration>
Configurar o cliente
O cliente pode ser configurado no código ou em um arquivo app.config. O exemplo a seguir mostra como configurar o cliente no código.
// Create the binding.
var myBinding = new WSHttpBinding();
myBinding.Security.Mode = SecurityMode.Transport;
myBinding.Security.Transport.ClientCredentialType =
HttpClientCredentialType.Certificate;
// Create the endpoint address. Note that the machine name
// must match the subject or DNS field of the X.509 certificate
// used to authenticate the service.
var ea = new
EndpointAddress("https://localhost/CalculatorService/service.svc");
// Create the client. The code for the calculator
// client is not shown here. See the sample applications
// for examples of the calculator code.
var cc =
new CalculatorClient(myBinding, ea);
// The client must specify a certificate trusted by the server.
cc.ClientCredentials.ClientCertificate.SetCertificate(
StoreLocation.CurrentUser,
StoreName.My,
X509FindType.FindBySubjectName,
"contoso.com");
// Begin using the client.
Console.WriteLine(cc.Add(100, 1111));
//...
cc.Close();
Como alternativa, você pode configurar o cliente em um arquivo App.config conforme mostrado no seguinte exemplo:
<configuration>
<system.serviceModel>
<client>
<!-- this endpoint has an https: address -->
<endpoint address=" https://localhost/CalculatorService/service.svc "
behaviorConfiguration="endpointCredentialBehavior"
binding="wsHttpBinding"
bindingConfiguration="Binding1"
contract="Microsoft.Samples.TransportSecurity.ICalculator"/>
</client>
<behaviors>
<endpointBehaviors>
<behavior name="endpointCredentialBehavior">
<clientCredentials>
<clientCertificate findValue="contoso.com"
storeLocation="CurrentUser"
storeName="My"
x509FindType="FindBySubjectName" />
</clientCredentials>
</behavior>
</endpointBehaviors>
</behaviors>
<bindings>
<wsHttpBinding>
<!-- configure wsHttpbinding with Transport security mode
and clientCredentialType as Certificate -->
<binding name="Binding1">
<security mode="Transport">
<transport clientCredentialType="Certificate"/>
</security>
</binding>
</wsHttpBinding>
</bindings>
</system.serviceModel>
<startup><supportedRuntime version="v4.0" sku=".NETFramework,Version=v4.0"/></startup></configuration>