Segurança de transporte com autenticação básica
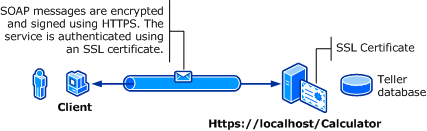
A ilustração a seguir mostra um serviço e um cliente do WCF (Windows Communication Foundation). O servidor precisa de um certificado X.509 válido que possa ser usado para o protocolo SSL e os clientes precisam confiar no certificado do servidor. Além disso, o serviço Web já tem uma implementação de SSL que pode ser usada. Para obter mais informações sobre como habilitar a autenticação básica no IIS (Serviços de Informações da Internet), consulte Autenticação Básica.
| Característica | Descrição |
|---|---|
| Modo de segurança | Transport |
| Interoperabilidade | Com serviços e clientes de serviços Web existentes |
| Autenticação (servidor) Autenticação (cliente) |
Sim (usando HTTPS) Sim (por meio de nome de usuário/senha) |
| Integridade | Sim |
| Confidencialidade | Yes |
| Transport | HTTPS |
| Associação | WSHttpBinding |
Serviço
O código e a configuração a seguir devem ser executados independentemente. Realize um dos seguintes procedimentos:
Crie um serviço autônomo usando o código sem configuração.
Crie um serviço usando a configuração fornecida, mas não defina nenhum ponto de extremidade.
Código
O código a seguir mostra como criar um ponto de extremidade de serviço que usa um nome de usuário do domínio do Windows e uma senha para a segurança de transferência. Observe que o serviço requer um certificado X.509 para autenticação no cliente. Para obter mais informações, consulte Trabalhando com certificados e Como configurar uma porta com um certificado SSL.
// Create the binding.
WSHttpBinding binding = new WSHttpBinding();
binding.Security.Mode = SecurityMode.Transport;
binding.Security.Transport.ClientCredentialType =
HttpClientCredentialType.Basic;
// Create the URI for the endpoint.
Uri httpUri = new Uri("https://localhost/Calculator");
// Create the service host and add an endpoint.
ServiceHost myServiceHost = new ServiceHost(
typeof(ServiceModel.Calculator), httpUri);
myServiceHost.AddServiceEndpoint(
typeof(ServiceModel.ICalculator), binding, "");
// Open the service.
myServiceHost.Open();
Console.WriteLine("Listening...");
Console.WriteLine("Press Enter to exit.");
Console.ReadLine();
// Close the service.
myServiceHost.Close();
' Create the binding.
Dim binding As New WSHttpBinding()
binding.Security.Mode = SecurityMode.Transport
binding.Security.Transport.ClientCredentialType = HttpClientCredentialType.Basic
' Create the URI for the endpoint.
Dim httpUri As New Uri("https://localhost/Calculator")
' Create the service host and add an endpoint.
Dim myServiceHost As New ServiceHost(GetType(ServiceModel.Calculator), httpUri)
myServiceHost.AddServiceEndpoint(GetType(ServiceModel.ICalculator), binding, "")
' Open the service.
myServiceHost.Open()
Console.WriteLine("Listening...")
Console.WriteLine("Press Enter to exit.")
Console.ReadLine()
' Close the service.
myServiceHost.Close()
Configuração
O seguinte configura um serviço para usar a autenticação básica com segurança no nível do transporte:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<configuration>
<system.serviceModel>
<bindings>
<wsHttpBinding>
<binding name="UsernameWithTransport">
<security mode="Transport">
<transport clientCredentialType="Basic" />
</security>
</binding>
</wsHttpBinding>
</bindings>
<services>
<service name="BasicAuthentication.Calculator">
<endpoint address="https://localhost/Calculator"
binding="wsHttpBinding"
bindingConfiguration="UsernameWithTransport"
name="BasicEndpoint"
contract="BasicAuthentication.ICalculator" />
</service>
</services>
</system.serviceModel>
</configuration>
Cliente
Código
O código a seguir mostra o código do cliente que inclui o nome de usuário e a senha. Observe que o usuário deve fornecer um nome de usuário e senha válidos do Windows. O código para retornar o nome de usuário e a senha não é mostrado aqui. Use uma caixa de diálogo ou outra interface para consultar o usuário para obter as informações.
Observação
O nome de usuário e a senha só podem ser definidos usando código.
// Create the binding.
WSHttpBinding myBinding = new WSHttpBinding();
myBinding.Security.Mode = SecurityMode.Transport;
myBinding.Security.Transport.ClientCredentialType =
HttpClientCredentialType.Basic;
// Create the endpoint address. Note that the machine name
// must match the subject or DNS field of the X.509 certificate
// used to authenticate the service.
EndpointAddress ea = new
EndpointAddress("https://machineName/Calculator");
// Create the client. The code for the calculator
// client is not shown here. See the sample applications
// for examples of the calculator code.
CalculatorClient cc =
new CalculatorClient(myBinding, ea);
// The client must provide a user name and password. The code
// to return the user name and password is not shown here. Use
// a database to store the user name and passwords, or use the
// ASP.NET Membership provider database.
cc.ClientCredentials.UserName.UserName = ReturnUsername();
cc.ClientCredentials.UserName.Password = ReturnPassword();
try
{
// Begin using the client.
cc.Open();
Console.WriteLine(cc.Add(100, 11));
Console.ReadLine();
// Close the client.
cc.Close();
}
' Create the binding.
Dim myBinding As New WSHttpBinding()
myBinding.Security.Mode = SecurityMode.Transport
myBinding.Security.Transport.ClientCredentialType = HttpClientCredentialType.Basic
' Create the endpoint address. Note that the machine name
' must match the subject or DNS field of the X.509 certificate
' used to authenticate the service.
Dim ea As New EndpointAddress("https://machineName/Calculator")
' Create the client. The code for the calculator
' client is not shown here. See the sample applications
' for examples of the calculator code.
Dim cc As New CalculatorClient(myBinding, ea)
' The client must provide a user name and password. The code
' to return the user name and password is not shown here. Use
' a database to store the user name and passwords, or use the
' ASP.NET Membership provider database.
cc.ClientCredentials.UserName.UserName = ReturnUsername()
cc.ClientCredentials.UserName.Password = ReturnPassword()
' Begin using the client.
Try
cc.Open()
Console.WriteLine(cc.Add(100, 11))
Console.ReadLine()
' Close the client.
cc.Close()
Catch tex As TimeoutException
Console.WriteLine(tex.Message)
cc.Abort()
Catch cex As CommunicationException
Console.WriteLine(cex.Message)
cc.Abort()
Finally
Console.WriteLine("Closed the client")
Console.ReadLine()
End Try
Configuração
O código a seguir mostra a configuração do cliente.
Observação
Não é possível usar a configuração para definir o nome de usuário e a senha. A configuração mostrada aqui deve ser aumentada usando código para definir o nome de usuário e a senha.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<configuration>
<system.serviceModel>
<bindings>
<wsHttpBinding>
<binding name="WSHttpBinding_ICalculator" >
<security mode="Transport">
<transport clientCredentialType="Basic" />
</security>
</binding>
</wsHttpBinding>
</bindings>
<client>
<endpoint address="https://machineName/Calculator"
binding="wsHttpBinding"
bindingConfiguration="WSHttpBinding_ICalculator"
contract="ICalculator"
name="WSHttpBinding_ICalculator" />
</client>
</system.serviceModel>
</configuration>