Instruções passo a passo: conexão usando tarefas e solicitações HTTP XML
Este exemplo mostra como usar as interfaces IXMLHTTPRequest2 e IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback junto com tarefas para enviar solicitações HTTP GET e POST para um serviço Web em um aplicativo UWP (Plataforma Universal do Windows). Ao combinar IXMLHTTPRequest2 com tarefas, você pode escrever um código que compõe outras tarefas. Por exemplo, você pode usar a tarefa de download como parte de uma cadeia de tarefas. A tarefa de download também pode responder quando o trabalho é cancelado.
Dica
Você também pode usar o SDK REST do C++ para executar solicitações HTTP de um aplicativo UWP usando o aplicativo C++ ou de um aplicativo C++do desktop. Para obter mais informações, consulte SDK REST do C++ (nome de código "Casablanca").
Para obter mais informações sobre grupos de tarefas, confira Paralelismo de Tarefa. Para obter mais informações sobre como usar tarefas em um aplicativo UWP, consulte a Programação assíncrona no C++ e Criando operações assíncronas no C++ para aplicativos UWP.
Este documento mostra primeiro como criar HttpRequest e suas classes de suporte. Em seguida, mostra como usar essa classe de um aplicativo UWP que usa C++ e XAML.
Para obter um exemplo que usa IXMLHTTPRequest2 mas não usa tarefas, consulte Início rápido: Conectando-se usando solicitação HTTP XML (IXMLHTTPRequest2).
Dica
IXMLHTTPRequest2 e IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback são as interfaces que recomendamos para uso em um aplicativo UWP. Você também pode adaptar este exemplo para uso em um aplicativo de desktop.
Pré-requisitos
O suporte a UWP é opcional no Visual Studio 2017 e posterior. Para instalá-lo, abra o Instalador do Visual Studio no menu Iniciar do Windows e escolha a sua versão do Visual Studio. Clique no botão Modificar e verifique se o bloco Desenvolvimento UWP está marcado. Em Componentes opcionais, verifique se as Ferramentas UWP do C++ estão marcadas. Use v141 para Visual Studio 2017 ou v142 para Visual Studio 2019.
Definindo as Classes HttpRequest, HttpRequestBuffersCallback e HttpRequestStringCallback
Quando você usa a interface IXMLHTTPRequest2 para criar solicitações da Web via HTTP, implemente a interface IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback para receber a resposta do servidor e reagir a outros eventos. Este exemplo define a classeHttpRequest para criar solicitações da Web e as classes HttpRequestBuffersCallback e HttpRequestStringCallback para processar respostas. As classes HttpRequestBuffersCallback e HttpRequestStringCallback dão suporte à classe HttpRequest e você trabalha apenas com a classe HttpRequest do código do aplicativo.
Os métodos GetAsync, PostAsync da classe HttpRequest permitem que você inicie operações HTTP GET e POST, respectivamente. Esses métodos usam a classe HttpRequestStringCallback para ler a resposta do servidor como uma cadeia de caracteres. Os métodos SendAsync e ReadAsync permitem que você transmita por streaming grandes conteúdos em partes. Cada um desses métodos retorna concurrency::task para representar a operação. Os GetAsync métodos e PostAsync produzem task<std::wstring> valor, onde a parte representa a wstring resposta do servidor. Os métodosSendAsync e ReadAsync produzem valores task<void>; essas tarefas são concluídas quando as operações de envio e leitura são concluídas.
Como as interfaces IXMLHTTPRequest2 agem de forma assíncrona, este exemplo usa concurrency::task_completion_event para criar uma tarefa que é concluída depois que o objeto de retorno de chamada é concluído ou cancela a operação de download. A classe HttpRequest cria uma continuação com base na tarefa a partir dessa tarefa para definir o resultado final. A classe HttpRequest usa uma continuação com base em tarefa para garantir que a tarefa de continuação seja executada mesmo que a tarefa anterior produza um erro ou seja cancelada. Para obter mais informações sobre as continuações com base em tarefas em C++, consulte Paralelismo de tarefas.
Para dar suporte ao cancelamento, as classes HttpRequest, HttpRequestBuffersCallbacke HttpRequestStringCallback usam tokens de cancelamento. As HttpRequestBuffersCallback e HttpRequestStringCallback usam o método concurrency::cancellation_token::register_callback para permitir que o evento de conclusão da tarefa responda ao cancelamento. Esse retorno de chamada de cancelamento anula o download. Para saber mais informações sobre cancelamento, confira Cancelamento.
Para Definir a Classe HttpRequest
No menu principal, escolha Arquivo>Novo>Projeto.
Use o modelo Aplicativo em Branco (Windows Universal) do C++ para criar um projeto de aplicativo XAML em branco. Este exemplo nomeia o projeto
UsingIXMLHTTPRequest2.Adicione ao projeto um arquivo de cabeçalho chamado HttpRequest.h e um arquivo de origem chamado HttpRequest.cpp.
Em pch.h, adicione este código:
#include <ppltasks.h> #include <string> #include <sstream> #include <wrl.h> #include <msxml6.h>Em HttpRequest.h, adicione este código:
#pragma once #include "pch.h" inline void CheckHResult(HRESULT hResult) { if (hResult == E_ABORT) { concurrency::cancel_current_task(); } else if (FAILED(hResult)) { throw Platform::Exception::CreateException(hResult); } } namespace Web { namespace Details { // Implementation of IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback used when partial buffers are needed from the response. // When only the complete response is needed, use HttpRequestStringCallback instead. class HttpRequestBuffersCallback : public Microsoft::WRL::RuntimeClass< Microsoft::WRL::RuntimeClassFlags<Microsoft::WRL::ClassicCom>, IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback, Microsoft::WRL::FtmBase> { public: HttpRequestBuffersCallback(IXMLHTTPRequest2* httpRequest, concurrency::cancellation_token ct = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()) : request(httpRequest), cancellationToken(ct), responseReceived(false), dataHResult(S_OK), statusCode(200) { // Register a callback function that aborts the HTTP operation when // the cancellation token is canceled. if (cancellationToken != concurrency::cancellation_token::none()) { registrationToken = cancellationToken.register_callback([this]() { if (request != nullptr) { request->Abort(); } }); } dataEvent = concurrency::task_completion_event<void>(); } // Called when the HTTP request is being redirected to a new URL. IFACEMETHODIMP OnRedirect(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, PCWSTR) { return S_OK; } // Called when HTTP headers have been received and processed. IFACEMETHODIMP OnHeadersAvailable(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, DWORD statusCode, PCWSTR reasonPhrase) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { this->statusCode = statusCode; this->reasonPhrase = reasonPhrase; concurrency::critical_section::scoped_lock lock(dataEventLock); dataEvent.set(); } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Called when a portion of the entity body has been received. IFACEMETHODIMP OnDataAvailable(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, ISequentialStream* stream) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { // Store a reference on the stream so it can be accessed by the task. dataStream = stream; // The work must be done as fast as possible, and must not block this thread, // for example, waiting on another event object. Here we simply set an event // that can be processed by another thread. concurrency::critical_section::scoped_lock lock(dataEventLock); dataEvent.set(); } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Called when the entire entity response has been received. IFACEMETHODIMP OnResponseReceived(IXMLHTTPRequest2* xhr, ISequentialStream* responseStream) { responseReceived = true; return OnDataAvailable(xhr, responseStream); } // Called when an error occurs during the HTTP request. IFACEMETHODIMP OnError(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, HRESULT hrError) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { concurrency::critical_section::scoped_lock lock(dataEventLock); dataHResult = hrError; dataEvent.set(); } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Create a task that completes when data is available, in an exception-safe way. concurrency::task<void> CreateDataTask(); HRESULT GetError() const { return dataHResult; } int GetStatusCode() const { return statusCode; } std::wstring const& GetReasonPhrase() const { return reasonPhrase; } bool IsResponseReceived() const { return responseReceived; } // Copy bytes from the sequential stream into the buffer provided until // we reach the end of one or the other. unsigned int ReadData( _Out_writes_(outputBufferSize) byte* outputBuffer, unsigned int outputBufferSize); private: ~HttpRequestBuffersCallback() { // Unregister the callback. if (cancellationToken != concurrency::cancellation_token::none()) { cancellationToken.deregister_callback(registrationToken); } } // Signals that the download operation was canceled. concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken; // Used to unregister the cancellation token callback. concurrency::cancellation_token_registration registrationToken; // The IXMLHTTPRequest2 that processes the HTTP request. Microsoft::WRL::ComPtr<IXMLHTTPRequest2> request; // Task completion event that is set when data is available or error is triggered. concurrency::task_completion_event<void> dataEvent; concurrency::critical_section dataEventLock; // We cannot store the error obtained from IXHR2 in the dataEvent since any value there is first-writer-wins, // whereas we want a subsequent error to override an initial success. HRESULT dataHResult; // Referenced pointer to the data stream. Microsoft::WRL::ComPtr<ISequentialStream> dataStream; // HTTP status code and reason returned by the server. int statusCode; std::wstring reasonPhrase; // Whether the response has been completely received. bool responseReceived; }; }; // Utility class for performing asynchronous HTTP requests. // This class only supports one outstanding request at a time. class HttpRequest { public: HttpRequest(); int GetStatusCode() const { return statusCode; } std::wstring const& GetReasonPhrase() const { return reasonPhrase; } // Whether the response has been completely received, if using ReadAsync(). bool IsResponseComplete() const { return responseComplete; } // Start an HTTP GET on the specified URI. The returned task completes once the entire response // has been received, and the task produces the HTTP response text. The status code and reason // can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). concurrency::task<std::wstring> GetAsync( Windows::Foundation::Uri^ uri, concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()); // Start an HTTP POST on the specified URI, using a string body. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). concurrency::task<std::wstring> PostAsync( Windows::Foundation::Uri^ uri, PCWSTR contentType, IStream* postStream, uint64 postStreamSizeToSend, concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()); // Start an HTTP POST on the specified URI, using a stream body. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). concurrency::task<std::wstring> PostAsync( Windows::Foundation::Uri^ uri, const std::wstring& str, concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()); // Send a request but don't return the response. Instead, let the caller read it with ReadAsync(). concurrency::task<void> SendAsync( const std::wstring& httpMethod, Windows::Foundation::Uri^ uri, concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()); // Read a chunk of data from the HTTP response, up to a specified length or until we reach the end // of the response, and store the value in the provided buffer. This is useful for large content, // enabling the streaming of the result. concurrency::task<void> ReadAsync( Windows::Storage::Streams::IBuffer^ readBuffer, unsigned int offsetInBuffer, unsigned int requestedBytesToRead); static void CreateMemoryStream(IStream **stream); private: // Start a download of the specified URI using the specified method. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). concurrency::task<std::wstring> DownloadAsync( PCWSTR httpMethod, PCWSTR uri, concurrency::cancellation_token cancellationToken, PCWSTR contentType, IStream* postStream, uint64 postStreamBytesToSend); // Referenced pointer to the callback, if using SendAsync/ReadAsync. Microsoft::WRL::ComPtr<Details::HttpRequestBuffersCallback> buffersCallback; int statusCode; std::wstring reasonPhrase; // Whether the response has been completely received, if using ReadAsync(). bool responseComplete; }; };Em HttpRequest.cpp, adicione este código:
#include "pch.h" #include "HttpRequest.h" #include <robuffer.h> #include <shcore.h> using namespace concurrency; using namespace Microsoft::WRL; using namespace Platform; using namespace std; using namespace Web; using namespace Windows::Foundation; using namespace Windows::Storage::Streams; // Implementation of IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback used when only the complete response is needed. // When processing chunks of response data as they are received, use HttpRequestBuffersCallback instead. class HttpRequestStringCallback : public RuntimeClass<RuntimeClassFlags<ClassicCom>, IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback, FtmBase> { public: HttpRequestStringCallback(IXMLHTTPRequest2* httpRequest, cancellation_token ct = concurrency::cancellation_token::none()) : request(httpRequest), cancellationToken(ct) { // Register a callback function that aborts the HTTP operation when // the cancellation token is canceled. if (cancellationToken != cancellation_token::none()) { registrationToken = cancellationToken.register_callback([this]() { if (request != nullptr) { request->Abort(); } }); } } // Called when the HTTP request is being redirected to a new URL. IFACEMETHODIMP OnRedirect(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, PCWSTR) { return S_OK; } // Called when HTTP headers have been received and processed. IFACEMETHODIMP OnHeadersAvailable(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, DWORD statusCode, PCWSTR reasonPhrase) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { this->statusCode = statusCode; this->reasonPhrase = reasonPhrase; } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Called when a portion of the entity body has been received. IFACEMETHODIMP OnDataAvailable(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, ISequentialStream*) { return S_OK; } // Called when the entire entity response has been received. IFACEMETHODIMP OnResponseReceived(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, ISequentialStream* responseStream) { wstring wstr; HRESULT hr = ReadUtf8StringFromSequentialStream(responseStream, wstr); // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { completionEvent.set(make_tuple<HRESULT, wstring>(move(hr), move(wstr))); } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Simulate the functionality of DataReader.ReadString(). // This is needed because DataReader requires IRandomAccessStream and this // code has an ISequentialStream that does not have a conversion to IRandomAccessStream like IStream does. HRESULT ReadUtf8StringFromSequentialStream(ISequentialStream* readStream, wstring& str) { // Convert the response to Unicode wstring. HRESULT hr; // Holds the response as a Unicode string. wstringstream ss; while (true) { ULONG cb; char buffer[4096]; // Read the response as a UTF-8 string. Since UTF-8 characters are 1-4 bytes long, // we need to make sure we only read an integral number of characters. So we'll // start with 4093 bytes. hr = readStream->Read(buffer, sizeof(buffer) - 3, &cb); if (FAILED(hr) || (cb == 0)) { break; // Error or no more data to process, exit loop. } if (cb == sizeof(buffer) - 3) { ULONG subsequentBytesRead; unsigned int i, cl; // Find the first byte of the last UTF-8 character in the buffer. for (i = cb - 1; (i >= 0) && ((buffer[i] & 0xC0) == 0x80); i--); // Calculate the number of subsequent bytes in the UTF-8 character. if (((unsigned char)buffer[i]) < 0x80) { cl = 1; } else if (((unsigned char)buffer[i]) < 0xE0) { cl = 2; } else if (((unsigned char)buffer[i]) < 0xF0) { cl = 3; } else { cl = 4; } // Read any remaining bytes. if (cb < i + cl) { hr = readStream->Read(buffer + cb, i + cl - cb, &subsequentBytesRead); if (FAILED(hr)) { break; // Error, exit loop. } cb += subsequentBytesRead; } } // First determine the size required to store the Unicode string. int const sizeRequired = MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0, buffer, cb, nullptr, 0); if (sizeRequired == 0) { // Invalid UTF-8. hr = HRESULT_FROM_WIN32(GetLastError()); break; } unique_ptr<char16[]> wstr(new(std::nothrow) char16[sizeRequired + 1]); if (wstr.get() == nullptr) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; break; } // Convert the string from UTF-8 to UTF-16LE. This can never fail, since // the previous call above succeeded. MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0, buffer, cb, wstr.get(), sizeRequired); wstr[sizeRequired] = L'\0'; // Terminate the string. ss << wstr.get(); // Write the string to the stream. } str = SUCCEEDED(hr) ? ss.str() : wstring(); return (SUCCEEDED(hr)) ? S_OK : hr; // Don't return S_FALSE. } // Called when an error occurs during the HTTP request. IFACEMETHODIMP OnError(IXMLHTTPRequest2*, HRESULT hrError) { HRESULT hr = S_OK; // We must not propagate exceptions back to IXHR2. try { completionEvent.set(make_tuple<HRESULT, wstring>(move(hrError), wstring())); } catch (std::bad_alloc&) { hr = E_OUTOFMEMORY; } return hr; } // Retrieves the completion event for the HTTP operation. task_completion_event<tuple<HRESULT, wstring>> const& GetCompletionEvent() const { return completionEvent; } int GetStatusCode() const { return statusCode; } wstring GetReasonPhrase() const { return reasonPhrase; } private: ~HttpRequestStringCallback() { // Unregister the callback. if (cancellationToken != cancellation_token::none()) { cancellationToken.deregister_callback(registrationToken); } } // Signals that the download operation was canceled. cancellation_token cancellationToken; // Used to unregister the cancellation token callback. cancellation_token_registration registrationToken; // The IXMLHTTPRequest2 that processes the HTTP request. ComPtr<IXMLHTTPRequest2> request; // Task completion event that is set when the // download operation completes. task_completion_event<tuple<HRESULT, wstring>> completionEvent; int statusCode; wstring reasonPhrase; }; // Copy bytes from the sequential stream into the buffer provided until // we reach the end of one or the other. unsigned int Web::Details::HttpRequestBuffersCallback::ReadData( _Out_writes_(outputBufferSize) byte* outputBuffer, unsigned int outputBufferSize) { // Lock the data event while doing the read, to ensure that any bytes we don't read will // result in the correct event getting triggered. concurrency::critical_section::scoped_lock lock(dataEventLock); ULONG bytesRead; CheckHResult(dataStream.Get()->Read(outputBuffer, outputBufferSize, &bytesRead)); if (bytesRead < outputBufferSize) { // We need to reset the data event, which we can only do by creating a new one. dataEvent = task_completion_event<void>(); } return bytesRead; } // Create a task that completes when data is available, in an exception-safe way. task<void> Web::Details::HttpRequestBuffersCallback::CreateDataTask() { concurrency::critical_section::scoped_lock lock(dataEventLock); return create_task(dataEvent, cancellationToken); } HttpRequest::HttpRequest() : responseComplete(true), statusCode(200) { } // Start a download of the specified URI using the specified method. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). task<wstring> HttpRequest::DownloadAsync(PCWSTR httpMethod, PCWSTR uri, cancellation_token cancellationToken, PCWSTR contentType, IStream* postStream, uint64 postStreamSizeToSend) { // Create an IXMLHTTPRequest2 object. ComPtr<IXMLHTTPRequest2> xhr; CheckHResult(CoCreateInstance(CLSID_XmlHttpRequest, nullptr, CLSCTX_INPROC, IID_PPV_ARGS(&xhr))); // Create callback. auto stringCallback = Make<HttpRequestStringCallback>(xhr.Get(), cancellationToken); CheckHResult(stringCallback ? S_OK : E_OUTOFMEMORY); auto completionTask = create_task(stringCallback->GetCompletionEvent()); // Create a request. CheckHResult(xhr->Open(httpMethod, uri, stringCallback.Get(), nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr)); if (postStream != nullptr && contentType != nullptr) { CheckHResult(xhr->SetRequestHeader(L"Content-Type", contentType)); } // Send the request. CheckHResult(xhr->Send(postStream, postStreamSizeToSend)); // Return a task that completes when the HTTP operation completes. // We pass the callback to the continuation because the lifetime of the // callback must exceed the operation to ensure that cancellation // works correctly. return completionTask.then([this, stringCallback](tuple<HRESULT, wstring> resultTuple) { // If the GET operation failed, throw an Exception. CheckHResult(std::get<0>(resultTuple)); statusCode = stringCallback->GetStatusCode(); reasonPhrase = stringCallback->GetReasonPhrase(); return std::get<1>(resultTuple); }); } // Start an HTTP GET on the specified URI. The returned task completes once the entire response // has been received, and the task produces the HTTP response text. The status code and reason // can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). task<wstring> HttpRequest::GetAsync(Uri^ uri, cancellation_token cancellationToken) { return DownloadAsync(L"GET", uri->AbsoluteUri->Data(), cancellationToken, nullptr, nullptr, 0); } void HttpRequest::CreateMemoryStream(IStream **stream) { auto randomAccessStream = ref new Windows::Storage::Streams::InMemoryRandomAccessStream(); CheckHResult(CreateStreamOverRandomAccessStream(randomAccessStream, IID_PPV_ARGS(stream))); } // Start an HTTP POST on the specified URI, using a string body. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). task<wstring> HttpRequest::PostAsync(Uri^ uri, const wstring& body, cancellation_token cancellationToken) { int length = 0; ComPtr<IStream> postStream; CreateMemoryStream(&postStream); if (body.length() > 0) { // Get the required buffer size. int size = WideCharToMultiByte(CP_UTF8, // UTF-8 0, // Conversion type body.c_str(), // Unicode string to convert static_cast<int>(body.length()), // Size nullptr, // Output buffer 0, // Output buffer size nullptr, nullptr); CheckHResult((size != 0) ? S_OK : HRESULT_FROM_WIN32(GetLastError())); std::unique_ptr<char[]> tempData(new char[size]); length = WideCharToMultiByte(CP_UTF8, // UTF-8 0, // Conversion type body.c_str(), // Unicode string to convert static_cast<int>(body.length()), // Size tempData.get(), // Output buffer size, // Output buffer size nullptr, nullptr); CheckHResult((length != 0) ? S_OK : HRESULT_FROM_WIN32(GetLastError())); CheckHResult(postStream->Write(tempData.get(), length, nullptr)); } return DownloadAsync(L"POST", uri->AbsoluteUri->Data(), cancellationToken, L"text/plain;charset=utf-8", postStream.Get(), length); } // Start an HTTP POST on the specified URI, using a stream body. The returned task produces the // HTTP response text. The status code and reason can be read with GetStatusCode() and GetReasonPhrase(). task<wstring> HttpRequest::PostAsync(Uri^ uri, PCWSTR contentType, IStream* postStream, uint64 postStreamSizeToSend, cancellation_token cancellationToken) { return DownloadAsync(L"POST", uri->AbsoluteUri->Data(), cancellationToken, contentType, postStream, postStreamSizeToSend); } // Send a request but don't return the response. Instead, let the caller read it with ReadAsync(). task<void> HttpRequest::SendAsync(const wstring& httpMethod, Uri^ uri, cancellation_token cancellationToken) { // Create an IXMLHTTPRequest2 object. ComPtr<IXMLHTTPRequest2> xhr; CheckHResult(CoCreateInstance(CLSID_XmlHttpRequest, nullptr, CLSCTX_INPROC, IID_PPV_ARGS(&xhr))); // Create callback. buffersCallback = Make<Web::Details::HttpRequestBuffersCallback>(xhr.Get(), cancellationToken); CheckHResult(buffersCallback ? S_OK : E_OUTOFMEMORY); ComPtr<IXMLHTTPRequest2Callback> xhrCallback; CheckHResult(buffersCallback.As(&xhrCallback)); // Open and send the request. CheckHResult(xhr->Open(httpMethod.c_str(), uri->AbsoluteUri->Data(), xhrCallback.Get(), nullptr, nullptr, nullptr, nullptr)); responseComplete = false; CheckHResult(xhr->Send(nullptr, 0)); // Return a task that completes when the HTTP operation completes. // Since buffersCallback holds a reference on the callback, the lifetime of the callback will exceed // the operation and ensure that cancellation works correctly. return buffersCallback->CreateDataTask().then([this]() { CheckHResult(buffersCallback->GetError()); statusCode = buffersCallback->GetStatusCode(); reasonPhrase = buffersCallback->GetReasonPhrase(); }); } // Read a chunk of data from the HTTP response, up to a specified length or until we reach the end // of the response, and store the value in the provided buffer. This is useful for large content, // enabling the streaming of the result. task<void> HttpRequest::ReadAsync(Windows::Storage::Streams::IBuffer^ readBuffer, unsigned int offsetInBuffer, unsigned int requestedBytesToRead) { if (offsetInBuffer + requestedBytesToRead > readBuffer->Capacity) { throw ref new InvalidArgumentException(); } // Return a task that completes when a read completes. // We pass the callback to the continuation because the lifetime of the // callback must exceed the operation to ensure that cancellation // works correctly. return buffersCallback->CreateDataTask().then([this, readBuffer, offsetInBuffer, requestedBytesToRead]() { CheckHResult(buffersCallback->GetError()); // Get a pointer to the location to copy data into. ComPtr<IBufferByteAccess> bufferByteAccess; CheckHResult(reinterpret_cast<IUnknown*>(readBuffer)->QueryInterface(IID_PPV_ARGS(&bufferByteAccess))); byte* outputBuffer; // Returned internal pointer, do not free this value. CheckHResult(bufferByteAccess->Buffer(&outputBuffer)); // Copy bytes from the sequential stream into the buffer provided until // we reach the end of one or the other. readBuffer->Length = buffersCallback->ReadData(outputBuffer + offsetInBuffer, requestedBytesToRead); if (buffersCallback->IsResponseReceived() && (readBuffer->Length < requestedBytesToRead)) { responseComplete = true; } }); }
Usando a Classe HttpRequest em um Aplicativo UWP
Esta seção demonstra como usar a classe HttpRequest em um aplicativo UWP. O aplicativo fornece uma caixa de entrada que define um recurso de URL e comandos de botão que executam operações GET e POST e um comando de botão que cancela a operação atual.
Para Usar a Classe HttpRequest
Em MainPage.xaml, defina o elemento StackPanel da seguinte maneira.
<StackPanel HorizontalAlignment="Left" Width="440" Background="{StaticResource ApplicationPageBackgroundThemeBrush}"> <TextBox x:Name="InputTextBox" TextWrapping="Wrap" Text="http://www.fourthcoffee.com/"/> <StackPanel Orientation="Horizontal"> <Button x:Name="GetButton" Content="Get" Background="Green" Click="GetButton_Click"/> <Button x:Name="PostButton" Content="Post" Background="Blue" Click="PostButton_Click"/> <Button x:Name="CancelButton" Content="Cancel" Background="Red" IsEnabled="False" Click="CancelButton_Click"/> <ProgressRing x:Name="ResponseProgressRing" /> </StackPanel> <TextBlock x:Name="ResponseTextBlock" TextWrapping="Wrap"/> </StackPanel>Em MainPage.xaml.h, adicione esta diretiva
#include:#include "HttpRequest.h"Em MainPage.xaml.h, adicione estas variáveis de membro
privateà classeMainPage:// Produces HTTP requets. Web::HttpRequest m_httpRequest; // Enables us to cancel the active HTTP request. concurrency::cancellation_token_source m_cancelHttpRequestSource;Em MainPage.xaml.h, declare o
privatemétodoProcessHttpRequest:// Displays the result of the provided HTTP request on the UI. void ProcessHttpRequest(concurrency::task<std::wstring> httpRequest);Em MainPage.xaml.cpp, adicione estas instruções
using:using namespace concurrency; using namespace std; using namespace Web;Em MainPage.xaml.cpp, implemente os métodos
GetButton_Click,PostButton_ClickeCancelButton_Clickda classeMainPage.void MainPage::GetButton_Click(Object^ sender, RoutedEventArgs^ e) { // Create a new cancellation token source for the web request. m_cancelHttpRequestSource = cancellation_token_source(); // Set up the GET request parameters. auto uri = ref new Uri(InputTextBox->Text); auto token = m_cancelHttpRequestSource.get_token(); // Send the request and then update the UI. ProcessHttpRequest(m_httpRequest.GetAsync(uri, token)); } void MainPage::PostButton_Click(Object^ sender, RoutedEventArgs^ e) { // Create a new cancellation token source for the web request. m_cancelHttpRequestSource = cancellation_token_source(); // Set up the POST request parameters. auto uri = ref new Uri(InputTextBox->Text); wstring postData(L"This is sample POST data."); auto token = m_cancelHttpRequestSource.get_token(); // Send the request and then update the UI. ProcessHttpRequest(m_httpRequest.PostAsync(uri, postData, token)); } void MainPage::CancelButton_Click(Object^ sender, RoutedEventArgs^ e) { // Disable the Cancel button. // It will be re-enabled during the next web request. CancelButton->IsEnabled = false; // Initiate cancellation. m_cancelHttpRequestSource.cancel(); }Dica
Se o aplicativo não exigir suporte para cancelamento, passe concurrency::cancellation_token::none para os métodos
HttpRequest::GetAsynceHttpRequest::PostAsync.Em MainPage.xaml.cpp, implemente o método
MainPage::ProcessHttpRequest.// Displays the result of the provided HTTP request on the UI. void MainPage::ProcessHttpRequest(task<wstring> httpRequest) { // Enable only the Cancel button. GetButton->IsEnabled = false; PostButton->IsEnabled = false; CancelButton->IsEnabled = true; // Clear the previous response and start the progress ring. ResponseTextBlock->Text = ""; ResponseProgressRing->IsActive = true; // Create a continuation that shows the results on the UI. // The UI must be updated on the ASTA thread. // Therefore, schedule the continuation to run on the current context. httpRequest.then([this](task<wstring> previousTask) { try { // // Show the result on the UI. wstring response = previousTask.get(); if (m_httpRequest.GetStatusCode() == 200) { // The request succeeded. Show the response. ResponseTextBlock->Text = ref new String(response.c_str()); } else { // The request failed. Show the status code and reason. wstringstream ss; ss << L"The server returned " << m_httpRequest.GetStatusCode() << L" (" << m_httpRequest.GetReasonPhrase() << L')'; ResponseTextBlock->Text = ref new String(ss.str().c_str()); } } catch (const task_canceled&) { // Indicate that the operation was canceled. ResponseTextBlock->Text = "The operation was canceled"; } catch (Exception^ e) { // Indicate that the operation failed. ResponseTextBlock->Text = "The operation failed"; // TODO: Handle the error further. (void)e; } // Enable the Get and Post buttons. GetButton->IsEnabled = true; PostButton->IsEnabled = true; CancelButton->IsEnabled = false; // Stop the progress ring. ResponseProgressRing->IsActive = false; }, task_continuation_context::use_current()); }Nas propriedades do projeto, em Vinculador, Entrada, especifique
shcore.libemsxml6.lib.
Veja aqui o aplicativo em execução:
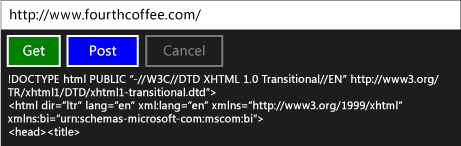
Próximas etapas
Instruções passo a passo do runtime de simultaneidade
Confira também
Paralelismo de tarefas
Cancelamento no PPL
Programação assíncrona em C++
Criando operações assíncronas em C++ para aplicativos UWP
Início Rápido: Conectando usando a Classe de tarefa de solicitação HTTP XML (IXMLHTTPREQUEST2)(Runtime de Simultaneidade)
Classe task_completion_event