DNS e seus mundos de Troubleshooting - Windows Server 2008/2012/2016 - Parte4 (Teoria e Prática)

Hello everyone, everything good!
Following is important configuration information and at the end a video with VIVO practice.
The Power of Aging: Important Moment of Setting Up Environment, Configuration, and Architecture. The Windows Server DNS server and DNS zones can be configured to automatically delete outdated records. During the scavenge process, obsolete records dynamically registered are searched in the DNS database and deleted. The replication process between servers ensures that the DNS zone keeps the most up-to-date information about the services.
In this way, it is a good practice to keep DNS servers in perfect working order to configure DNS to clean old or wrong DNS records automatically.
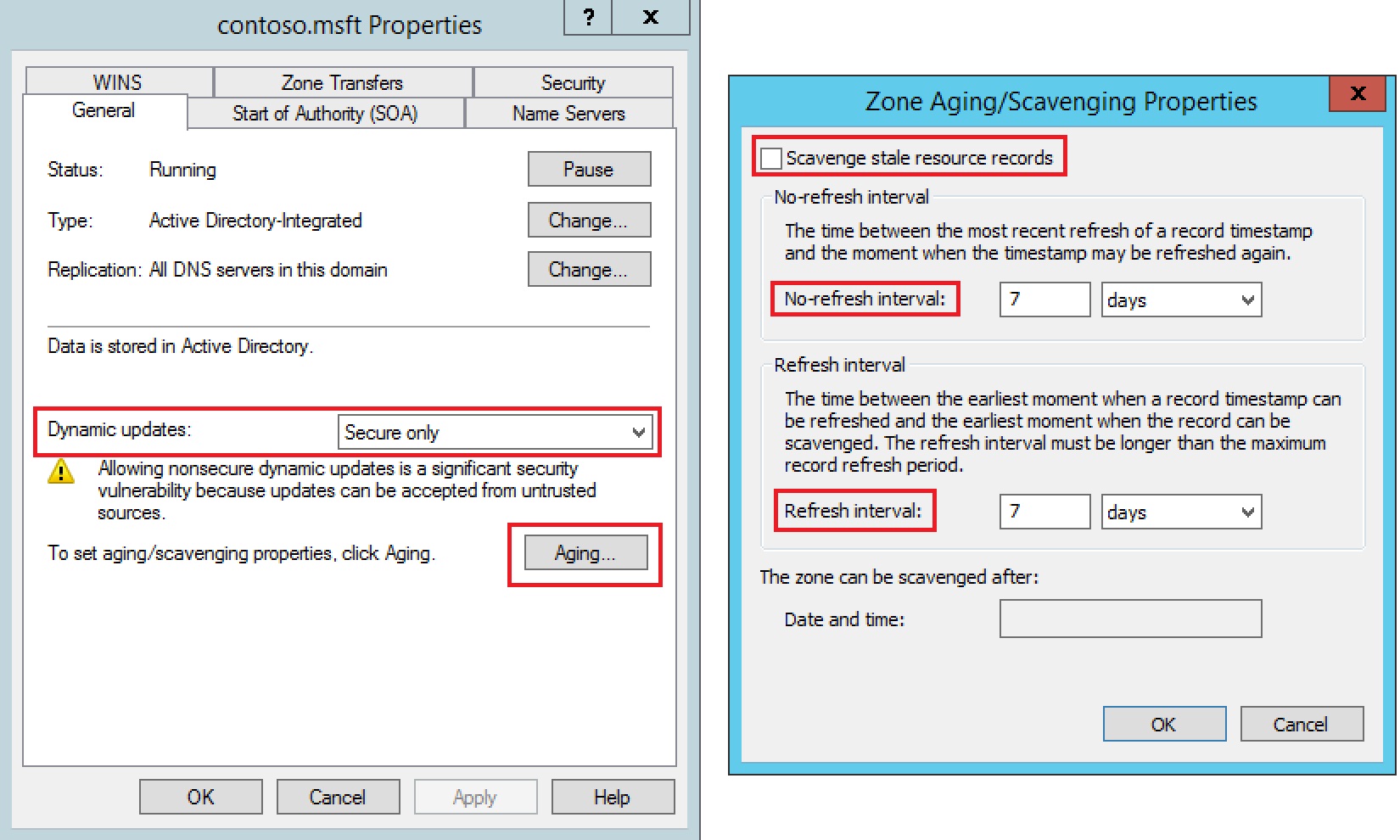
For a DNS zone to be updated by the scavenge process you must configure the zone with the "scavenge stale resource records" option.
[Important]
Part I - DNS Zone Configuration - Aging and Scavenge
This setting is not marked by default, and has to be done by hand.
The DNS Zone configuration parameters are:
No-refresh interval: default value - 7 days
Period of time when the dynamic record remains in the base without renewing the record's timestamp. It aims at reducing replication traffic by renewing the timestamp of the records. Any other update is allowed, for example, updating one IP address and is replicated to the other servers that host the DNS zone.
Refresh interval: default value - 7 days
Time period in which the timestamp of the records can be updated. As soon as the client updates the timestamp, the no-refresh period starts again and the log is replicated to the other servers that host the DNS zone. If the client does not update the registry during the refresh interval, the registry is considered obsolete and eligible to be deleted by the scavenge process.
The DNS stores name records for a specific period of time. Each record has a lifetime, TTL.
Whenever this value expires this record must be removed to avoid erroneous results when there is a DNS query.
Part II - DNS Server Configuration The scavenge process in a DNS zone for deletion of records can be performed by the DNS server either manually or automatically. Important: If the zone is not configured with the "scavenge stale resource records" option, no registry will be deleted by the scavenge process. To configure automatic scavenge check the "Enable automatic scavenging of stale records" option in the advanced DNS server properties.  Part III - Updating DNS Records
Part III - Updating DNS Records
Dynamic DNS records created in D1 during the non-refesh interval (default 7 days) do not update the timestamp.
After this interval, the refresh interval period starts (default 7 days), in which the registry can automatically update the timestamp.
If the timestamp is not updated at the end of the refresh interval, the record is considered obsolete, and is a candidate to be deleted when the scavenge process is run within the scavenging period. What I actually set: - Direct and Reverse Zones; -Protocols of the Network Card; -Among others; -We did a complete review and LIVE; See the link below: View FOL Hugs!