Operations Manager 2007/2012: High I/O peaks when writing on disk
Hi all,
In large Operations Manager environments, I/O peaks when writing in disks can affect the management servers (including the RMS, if it's SCOM 2007) and/or the agents that are managing many workflows.
The reasons behind high I/O peaks include:
• Number of management packs installed (the number of management packs influence the number of workflows),
• Agent or MS acting as proxy for a considerable number of devices,
• ESE store version, depending on the Windows Version,
• Anti-Virus Exceptions not applied.
• Other
The case solved in which we based this post, was in a SCOM 2007 environment, but this can also be applied for 2012 versions.
The Operations Manager Health service stores records of transactions that are not finished in something called "version store." The version store enables the Extensible Storage Engine (ESE) to track and to manage current transactions. It has a list of operations that are performed by active transactions that are maintained by the HealthService service. This list is an in-memory list of modifications that are made to the HealthService store database. There is a default size optimized for a typical installation of each Operations Manager role. However, the default size may be insufficient for certain Operations Manager environments.
In order to get a solution for this, here are the changes on the registry that should be made:
1 - We recommend changing the following registry keys values so that agents\ Management Server can better manage the load:
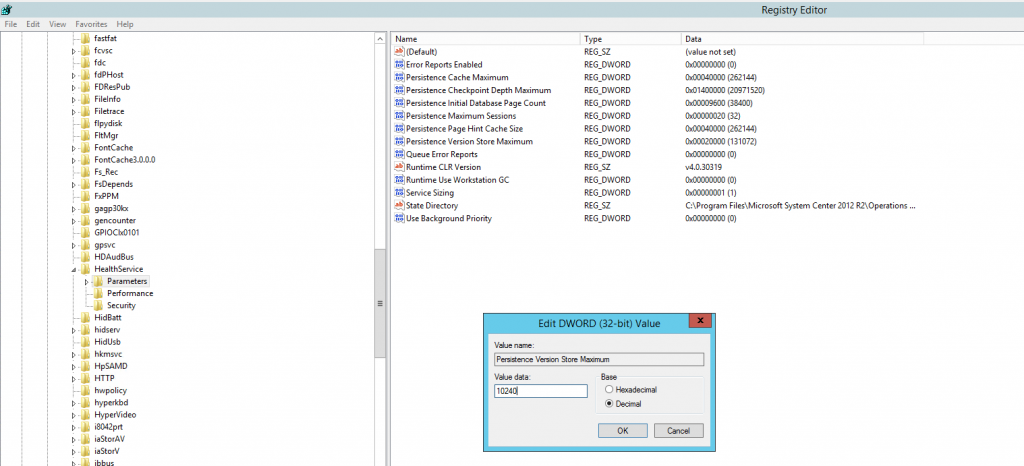
Subkey: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE \System\CurrentControlSet\Services\HealthService\Parameters Type: REG_DWORD Name: Persistence Version Store Maximum Base: Decimal
The default size of the version store depends on the Operations Manager role and is defined as the number of 16-kilobyte pages to allocate in memory. The default values are as follows:
Agent (workstation operating systems): 640 (10 megabytes) Agent (server operating systems): 1920 (30 megabytes)
Management Server: 5120 (80 megabytes)
It is recommended to set the version store size to double its default size for each machine. For example, if you set the version store size on a computer that hosts a Management Server role, set the registry value to 10240 (decimal) .
2 - All management servers, that host a large amount of agentless objects may result in the MS running a large number of workflows: (network/URL/Linux/3rd party/VEEAM). This is an ESE DB setting which controls how often ESE writes to disk. A larger value will decrease disk IO caused by the SCOM healthservice but increase ESE recovery time in the case of a healthservice crash:
Subkey: HKLM \System\CurrentControlSet\Services\HealthService\Parameters Type: REG_DWORD
Name: Persistence Checkpoint Depth Maximum
Base: Decimal
SCOM 2007 and 2012 default existing registry value: 20971520New Value: 104857600 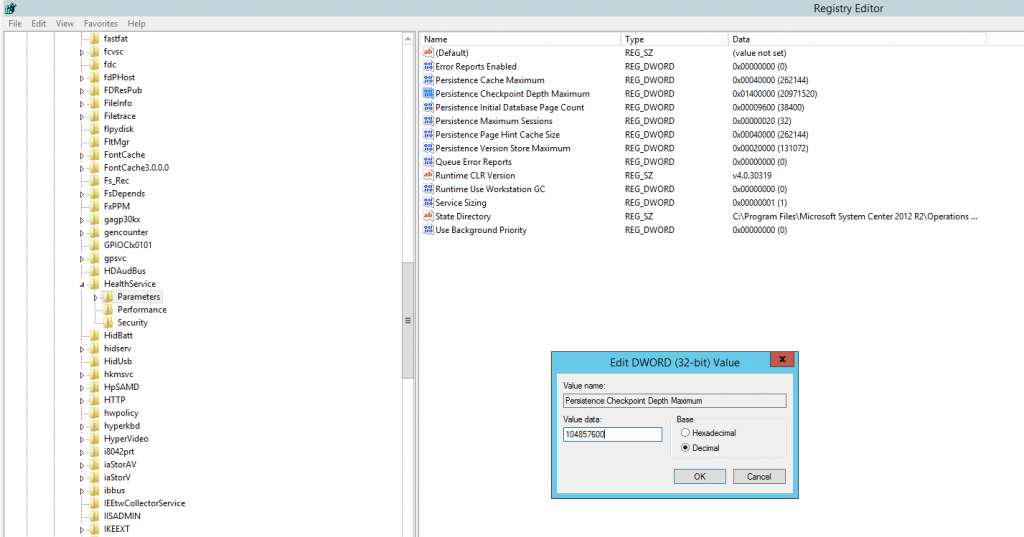
3 – All management servers in a large management group: This sets the maximum size of healthservice internal state queue. It should be equal or larger than the number of monitor based workflows running in a healthservice. Too small of a value, or too many workflows will cause state change loss. The following key should be created:
Subkey: HKLM \System\CurrentControlSet\Services\HealthService\Parameters Type: REG_DWORD
Name: State Queue Items
Base: Decimal
Value: 20480 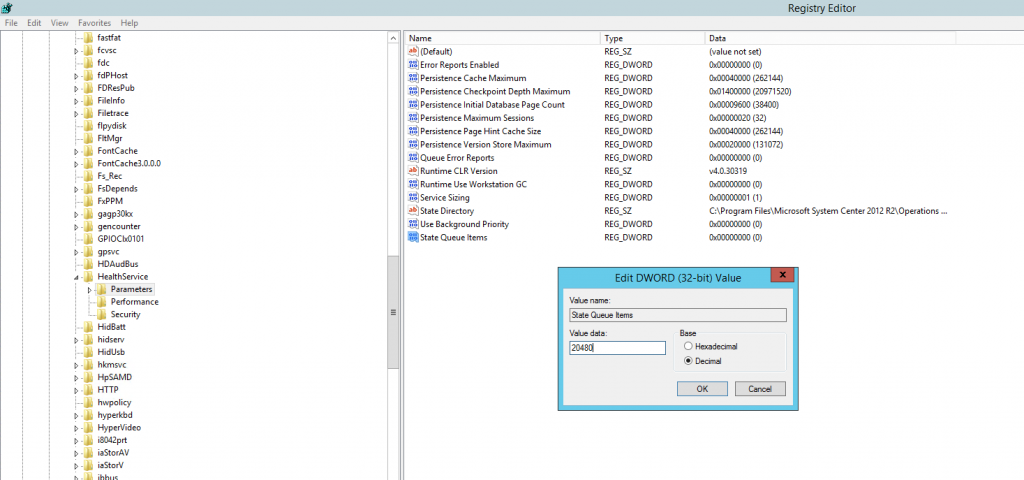
For further information regarding improving the performance of SCOM 2007 and 2012, please check the following blog post from our colleague Matt Goedtel: https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/mgoedtel/2010/08/24/performance-optimizations-for-operations-manager-2007-r2-and-2012/
Hope this is helpful!
Best regards
Bruno Afonso
Support Engineer
EMEA Customer Service & Support