Windows 8 / Windows Server 2012: The New Task Manager
It’s day 6 of our Launch Series. Today we are going to talk about Task Manager and the new benefits it provides. For our Developers, there were 3 main goals that they focused on for the new Task Manager. These included the following:
- Optimize Task Manager for the most common scenarios. Focus on the scenarios that the data points to: (1) use the applications tab to find and close a specific application, or (2) go to the processes tab, sort on resource usage, and kill some processes to reclaim resources.
- Use modern information design to achieve functional goals. Build a tool that is thoughtful and modern by focusing on information design and data visualization.
- Don’t remove functionality. We explicitly set a goal to not remove functionality, but rather to augment, enhance, and improve.
As part of these new changes, it has been given a simpler basic interface design, as well as a much more capable detailed view. Its expanded capabilities better match the way it is used for troubleshooting. Specific changes include the following:
- Simple initial interface with list of running apps and End task option.
- Detailed interface with these new capabilities:
- Clearer relationship between apps and processes.
- Easy to read performance metrics per process.
- Expanded PC performance information – similar to Resource Monitor default view.
- App performance history.
- List of Startup programs, with option to disable.
Windows 8: Processes tab
Windows Server 2012: Processes tab
There are obvious differences between each OS. Notably, the App history and Startup tabs missing from Server 2012, as well as the Disk and Network columns. With that, let’s take a look at each tab.
Processes
This tab shows running apps and background processes. Where a process has multiple windows open, this is shown to the user as a number following the process name, and a control to expand the view to see these window names. Processes are listed in alphabetical order in groups, by default. The order can be changed by clicking on any of the column names. The status of Modern apps is not shown by default, but can be enabled by selecting View, Status values, Show suspended status. Some background and system processes also provide an option to expand and view child objects. This is the case for processes that are hosting a service. Expand the process to see which service(s) are running in the process. This should help make service performance issues much easier to diagnose, compared with previous versions of Task Manager, which showed processes and services separately.
Performance
The Performance tab shows graphs and details of the 4 key PC performance metrics. Also note the Open Resource Monitor link at the bottom, providing a path to this other interface when you need to do additional troubleshooting.
Windows 8: Performance tab
Windows Server 2012: Performance tab
This tab gives clear information about the key performance metrics that are relevant to Windows, and presents the information in a clearer, more direct way. CPU, Memory, Disk, and Network resources have their own subpages on this tab, and new information has been added to the display. Previously, the Networking display was a separate tab, and there was no graphical display of memory or disk resource usage.
NOTE The Disk counter has been removed from the Performance tab in Windows Server 2012. This is because there is significant performance impact to collect Disk metrics on a Server due to the overhead Task Manager may cause in querying each Disk IO for each process/thread on individual disk. Disk metrics are very useful while troubleshooting performance related issues on the server. An easier way to check Disk metrics is to use Resource Monitor. This is a simple tool to use which can show you Disk Activity filtered by each process and storage details as shown below:
App history
The App History tab shows the total resources used by individual apps since Windows was installed, or since the last time the usage history was deleted. Clearing that usage history is an option just above the list of apps. This tab can be useful to understand which apps may be using a large amount of network bandwidth, or finding which may be reducing battery life by consuming a lot of CPU time.
Windows 8: App history tab
Startup
The Startup tab is another useful troubleshooting feature in the new Task Manager. In addition to showing all of the non-system startup items in your configuration, there is a startup performance impact assessment. This will show as “Not measured” for some time when new items are added to the startup configuration. When sufficient data has been collected, this will show an impact level – High, Medium or Low. To disable an item, simply right-click and select Disable. This can help make Task Manager a useful tool not only for cleaning up the running configuration, but also to help in ad-hoc startup troubleshooting.
NOTE this tab is not present on Windows Server 2012
Windows 8: Startup tab
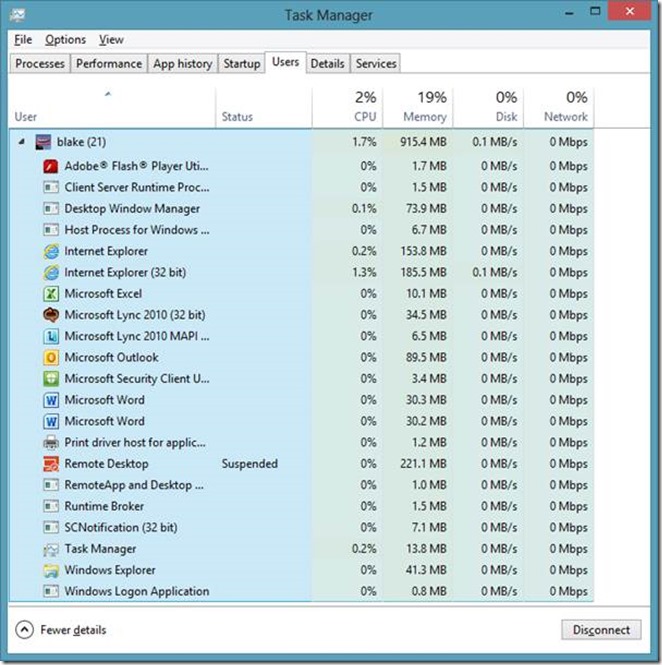
Users
The Users tab is where you can go to view the processes running in each user’s session. This differs from the old Task Manager interface where all users’ processes were shown on the Process tab.
Windows 8: Users tab
Windows Server 2012: Users tab
Details
The Details tab is where the new Task Manager interface provides the same column selection choices and process list as in the old Task Manager. This is useful for viewing all processes together, or if sorting by a cumulative performance metric is needed.
Windows 8: Details tab
Windows Server 2012: Details tab
Services
The Services tab is the last tab in the details interface. As shown below, this gives a view very similar to the old Task Manager.
Windows 8: Services tab
Windows Server 2012: Services tab
This concludes our first look at the new Task Manager. Tomorrow we will be going over the New Swap File. In the meantime, check out the original Windows 8 Task Manager blog here: The Windows 8 Task Manager
-AskPerf blog Team