Windows 7 new features:
Accessibility improvements. Microsoft has revamped the accessibility features in Windows 7 with improved speech recognition and a new Magnifier utility with full-screen and lens-mode views.
Action Center. While previous versions of Windows included a feature called Windows Security Center that monitored the various security features of the system, Windows 7 takes this functionality to the next level with Action Center. In addition to monitoring security, Action Center also monitors the OS's maintenance features and consolidates alerts from numerous Windows features into a single interface.
Backup and Restore. Windows Vista's stellar backup and restore features have been streamlined and simplified in Windows 7. Like its predecessor, Windows 7 supports both data backup and image-based system backup, but now the UIs are more segregated.
Bitlocker To Go. The full-drive encryption feature that first debuted in Windows Vista has been updated in Windows 7 to support removable USB storage devices like flash memory drives and portable hard drives.
Blu-Ray support. Windows 7 natively supports Blu-Ray optical discs and enables you to write to Blu-Ray recordable media.
Credential Manager. The new and improved Windows 7 Credential Manager lets you save credentials, like user names and passwords, so that you can more easily logon on to Web sites, networked computers, and other resources automatically. Credentials are saved in the Windows Vault and can be backed up and restored to encrypted Managed Information Card (MIC) files. (Credential Manager uses Windows CardSpace technology.)
Device Stage. This Longhorn-style user experience will be made available for multi-function devices such as smart phones, multifunction printers, portable media players, and the like. Through this UI, you'll be able to access the features that are unique to each device. Each Device Stage page can be extensively customized by the device maker.
Devices and Printers. This activity center provides a central location for interacting with any hardware devices--digital cameras, mice, displays, keyboards, and the like--that may be attached to your PC.
DirectAccess. This feature is aimed at business users who need to securely access corporate network resources while away from the office. Essentially a simple replacement for VPN connections, DirectAccess requires Windows Server 2008 R2 on the server-side.
DirectX 11. Windows 7 includes the latest version of the DirectX multimedia libraries.
Display improvements. Windows 7 includes numerous improvements related to computer displays, including integrated display color calibration, improved high DPI support, ClearType, and improved support for external displays. A new Windows Key + P keyboard shortcut helps you easily switch between connected displays.
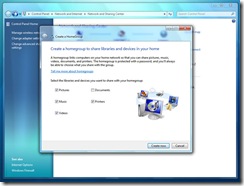
HomeGroup. Microsoft has consolidated the most common network-based sharing tasks into a single simple interface called HomeGroup. Computers in a HomeGroup can easily share documents, digital media files, and printers over a home network.
Internet Explorer. Windows 7 ships with the latest version of Microsoft's Web browser, Internet Explorer 8.
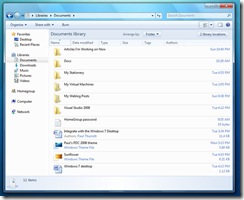
Libraries. In Windows 7, Microsoft has realized a long-term goal to replace the static special shell folders from previous Windows versions and replace them with virtualized shell locations that aggregate content from a variety of physical locations. Libraries are implemented as virtual folders and the views they present are the results of search queries. Libraries are also the basis for HomeGroup file and digital media content sharing.
Location-Aware Printing . Windows 7 utilizes different default printers for each of the network locations you've configured on the system so you won't mistakenly print a child's school project to the work printer. When you're at work, you'll print to the work printer, and when you're at home, you'll print to the home printer.
MinWin. The componentized core of Windows 7, which includes both the traditional operating system kernel as well as the minimum necessary surrounding support technologies to create a bootable (and, for Microsoft, testable) system. Note that, in Windows 7, MinWin isn't a feature per se but is rather the foundation upon which the rest of the OS is built.
Parental Controls. The parental control functionality that debuted in Windows Vista is updated in Windows 7 to support multiple games rating systems and parental control providers.
Power Config. Windows 7 includes a new Power Config utility that provides reports identifying problems, settings, applications, and other things that may be reducing the power efficiency of your PC.
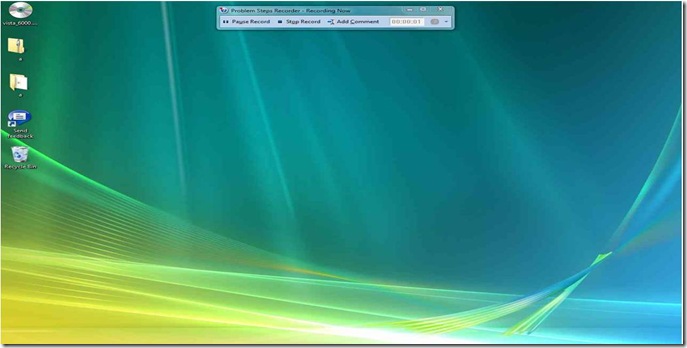
Problem Steps Recorder. Windows 7 includes a new utility called the Problem Steps Recorder that captures screen shots of the steps a user is taking so that help desk personnel can provide a fix without physically having to visit the desktop.
ReadyBoost. ReadyBoost first appeared in Windows Vista, providing users with a way to cheaply and easily improve the performance of their PCs by utilizing a USB memory key as a memory cache. In Windows 7, ReadyBoost is improved in numerous way: It supports multiple memory devices, can work with USB memory keys, Secure Digital (SD) memory cards, and other internal flash devices, and supports over 4 GB of storage.
Scenic Ribbon. Microsoft has evolved the Ribbon toolbar from Office 2007 and made it part of the operating system in Windows 7. This new version of the Ribbon, called the scenic Ribbon, is used by two Windows 7 applications, Paint and WordPad, and can be used by third party applications going forward as well.
Sensor support. Windows 7 includes support for hardware-based sensors, including GPS-based location sensors.
Start Menu (Enhanced). The Windows 7 Start Menu is an enhanced version of the Start Menu that debuted in Windows Vista.
Startup Repair. While this useful tool did debut with Windows Vista, it wasn't installed on PCs by default. In Windows 7, it is installed into the OS partition automatically and appears automatically when the system can't boot properly, fixing any problems and returning the system to its normal booting state.
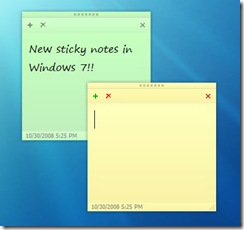
Sticky Notes. The Sticky Notes utility loses the bizarre Windows XP-style interface from previous Windows versions and supports ink and text input.
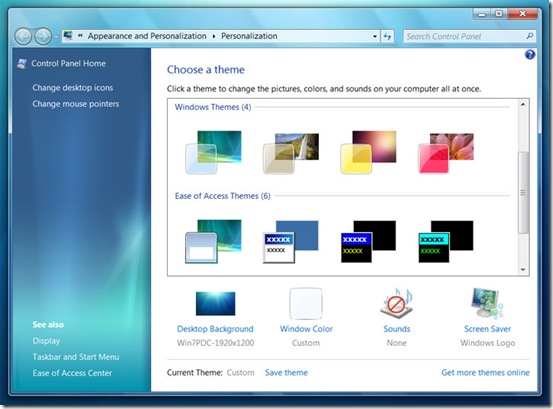
Styles. In Windows 7, Microsoft combines various system preferences--including the desktop background, the Aero glass window color, the system sounds, and the screen saver--into styles you can customize, save, and share with others.
System Restore. The Windows 7 version of System Restore works as before, providing a way to non-destructively return a PC to a previous point in time, but is more reliable, predictable, and effective than its predecessors.
Tablet PC. After making Tablet PC functionality available more broadly in Windows Vista, Microsoft is improving this technology in Windows 7 with better handwriting recognition that has improved accuracy, speed, and support for math expressions, personalized custom dictionaries, and 13 new languages.
User Account Control. While much reviled by certain users, the User Account Control (UAC) feature that debuted in Windows Vista played a huge role in making that system the most secure Windows version yet. In Windows 7, UAC is extensively updated to be less annoying, and the overall system has been fine-tuned to minimize the number of UAC prompts that interrupt users.
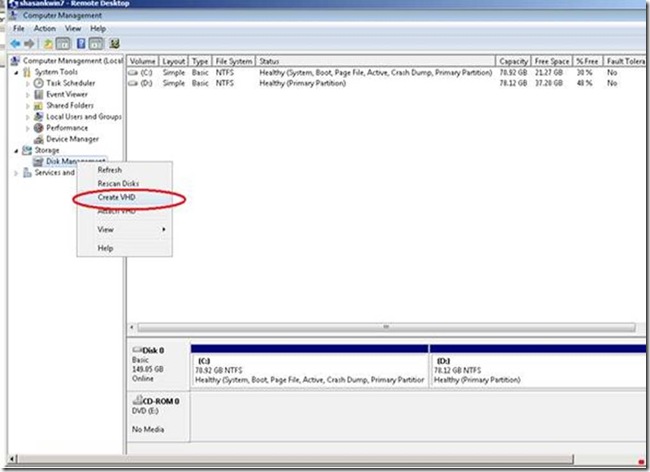
Virtual Hard Disk support. Windows 7 allows you to mount a Virtual Hard Disk (VHD) as a drive in Explorer so that you can navigate its contents like a physical hard disk. It also supports the ability to boot from VHD images.
VPN Reconnect. Windows 7 users who still need to make traditional VPN connections will benefit from a new VPN Reconnect feature that automatically reestablishes a VPN connection when you temporarily lose Internet connectivity.
Windows Anytime Upgrade. This utility debuted in Windows Vista but was found to be too confusing for most users, so the electronic upgrade capability was removed. In Windows 7, Windows Anytime Upgrade returns to electronic upgrading and Microsoft promises you'll be able to upgrade from one version of Windows 7 to another in about 10 minutes now.
Windows Defender. The malware and spyware protection utility from Windows Vista continues in Windows 7 with a few changes: It's been integrated into the new Action Center and its centralized notification system. But Defender also drops the useful Software Explorer feature, so users will have to look elsewhere for a way to prevent unwanted applications from running a startup.
Windows Easy Transfer. The Windows Easy Transfer utility that debuted in Windows Vista has been substantially updated with a new user interface and new capabilities. As before, Easy Transfer helps you transfer files, folders, and program and system settings from your previous Windows install to your new one. This time around, however, the process is simpler and more streamlined.
Windows Explorer. Microsoft has significantly updated Windows Explorer yet again in Windows 7, this time with a new toolbar, a resizable search box, and a new navigational pane.
Windows Gadgets. The Windows Sidebar disappears in Windows 7, but the Gadgets continue on and are integrated with the desktop.
Windows Live. Windows 7 integrates with a growing collection of Windows Live services, including Windows Live Photos, Windows Live Profile, Windows Live People, Windows Live Spaces, Windows Live Home, Windows Live SkyDrive, Windows Live Groups, Windows Live Calendar, Windows Live Events, Windows Live Hotmail, and more.
Windows Live Essentials. Available as an optional download, Windows Live Essentials is an application suite that includes a number of new versions of classic Windows applications, including Windows Live Mail (email and calendar), Windows Live Photo Gallery (photos), Windows Live Messenger (instant messaging), Windows Live Movie Maker (video editing), Windows Live Family Safety (enhanced parental controls), and more.
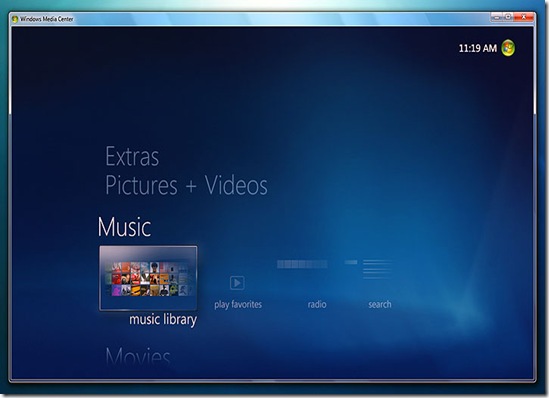
Windows Media Center. Microsoft's ten-foot UI for digital media content is improved with a slightly enhanced user interface, multi-touch support, HomeGroup integration, and various global broadcast TV standards.
Windows Media Player. Microsoft's media player received a major makeover in Windows 7 with several new features, including enhanced DVD playback, a new lightweight playback mode, dramatically improved format compatibility (including AAC and H.264), Windows Taskbar Jump List customization, PC-to-PC and media streaming, and a new Play To feature.
Windows PowerShell. Windows 7 ships with the Windows PowerShell 2.0 scripting environment and the Windows PowerShell Integrated Scripting Environment (ISE).
Windows Search. Windows 7 comes with the latest version of Windows Search, and unlike the version that first shipped with Windows Vista, you can now obtain instant search results from network-based file shares as well as local hard drives. Microsoft has also improved the performance of local searches, sorting, and grouping.
Windows Taskbar (Enhanced). The Windows Taskbar has been dramatically enhanced in Windows 7 to minimize clutter. New Taskbar features like Jump Lists, fly-over and full-screen icon previews, and more.
Windows Touch. Windows 7 builds on the Tablet PC and touch capabilities from previous Windows versions and adds pervasive support for multi-touch. All of the major UI components, including the Start Menu, Windows Taskbar, and Explorer, are touch-friendly in Windows 7.
Windows Troubleshooting. This new Windows 7 feature diagnoses and resolves common operating system and hardware issues. It works automatically, or you can visit the Troubleshooting control panel to find problems to troubleshoot. Windows Troubleshooting integrates with Action Center so you'll be notified when relevant new troubleshooters from Microsoft and third parties are made available.
Windows Update. Microsoft's utility for downloading and installing system updates has been enhanced in Windows 7 to take advantage of changes in the security model and to better expose optional and featured updates.
Wireless Device Network. Finally, Windows gains a way to use your wireless-equipped laptop as a wireless access point for other PCs when you're connected to a wired network.
XPS Viewer. While Windows Vista users are forced to use Internet Explorer to view XML Paper Specification (XPS) documents--essentially Microsoft's PDF knock-off--Windows 7 gains a dedicated XPS Viewer application.