Running SQL Server + ASP.Net Core in a container on Linux in Azure Container Service on Docker Swarm - Part 3
In previous post, I created an ASP.Net Core Container application interacting SQL Server Container. In this post, I'll port this application to Azure. I am going to use Azure Container Service (ACS) with Docker Swarm as orchestrator.
Let me start by creating a ACS cluster. I've followed instructions as described here . Point to remember while setting up this cluster to allow running SQL Server as Container is to choose VMs with at least 4GB ob RAM. This is a pre-requisite to run SQL Server Container using Docker.
With Docker Swarm as a container orchestrator, authoring microservice-style, multi-container application using docker-compose file is an easy process. Earlier, as described, in post 1, a SQL Server Container image was created and pushed to Docker Hub. Similarly, in post 2, an ASP.Net Core image was created and pushed to Docker Hub.
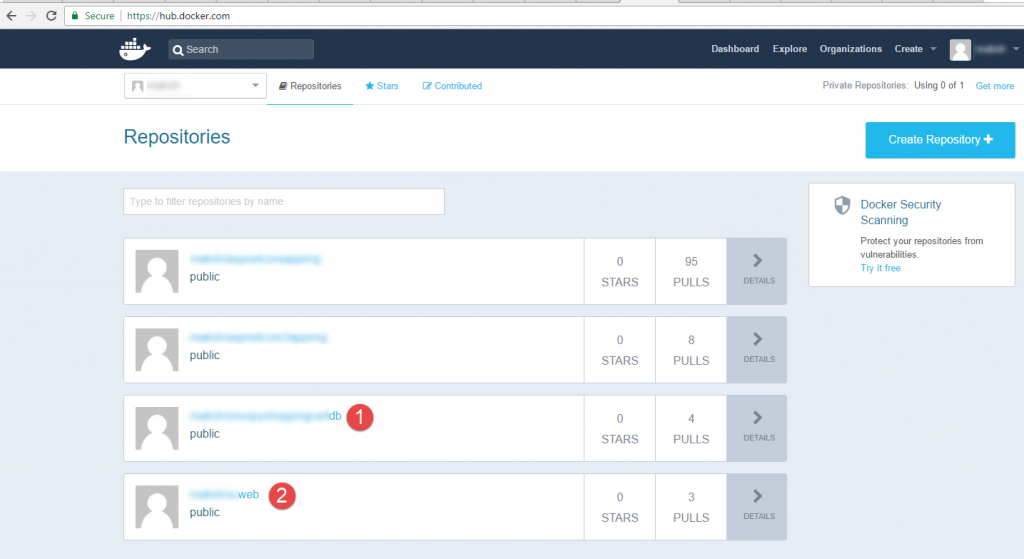
A docker-compose file will use these 2 images to deploy application in ACS. A network is also needed so that both these containers can run from within same network. docker-compose file looks something like below.
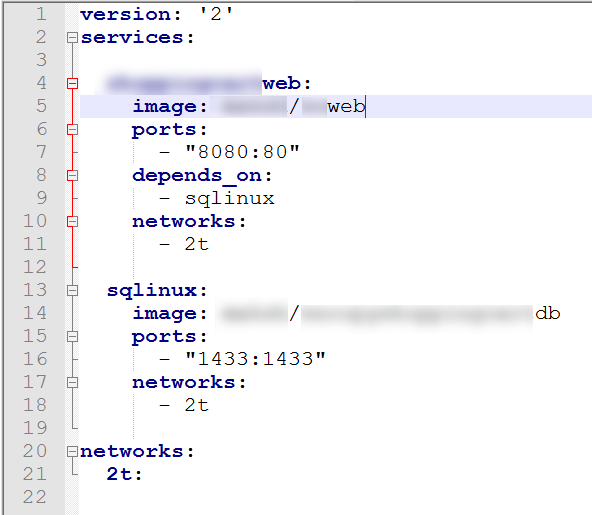
This file has got 2 services and 1 network defined. Each service is created from their respective image. XXXweb service uses ASP.Net Core image. It uses port 8080 on the container host and 80 on the container itself. It has dependency on other service, named sqlinux. This service resides in network 2t (short-form for 2 tier!).
Other service is sqlinux. This service uses the SQL Server Container image. It runs on port 1433 on both container host as well as container. It also resides in network 2t.
Connect to ACS cluster from Windows machine as instructed here.
set the Docker Host variable on local Docker CLI environment using following command.

With Docker Host set, It is easy to interact with ACS cluster in Azure from local machine. Any command executed after setting up DOCKER_HOST, gets executed on ACS cluster. Refer this to understand more on setting up this variable.
Now navigate to the location where docker-compose file is available in command prompt. Execute following command to ensure that there are no services already running on ACS cluster.
To deploy application, run following command.
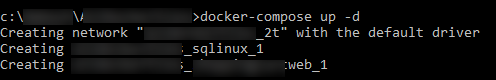
As can be see above, the instructions in docker-compose file are executed and 2 services and 1 network gets deployed to ACS. By running following command, verify if services are created as expected.
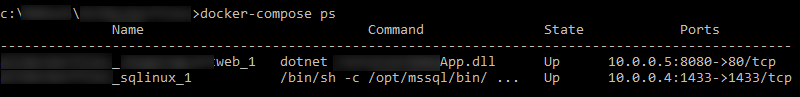
This command shows state of the container and nodes along-with IP address where each service (container) is running. With the containers running as expected, its time to verify if the application is running. Grab the agent FQDN from the ACS dashboard.
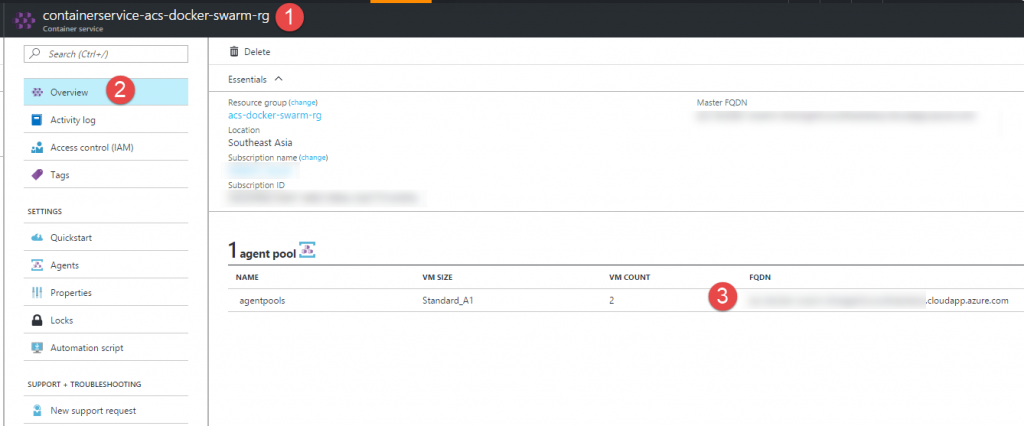
Append the port used for the ASP.Net Core app to it and hit enter.
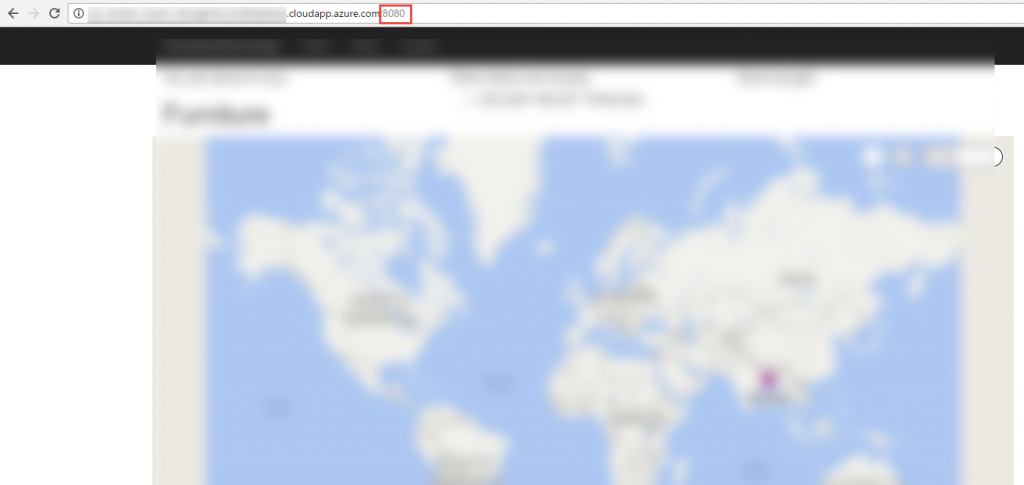
Application is now running in ACS using Docker Swarm as an orchestrator.
This concludes this blog series on getting SQL Server and ASP.Net Core run in a container on Linux in Azure Container Service on Docker Swarm. Combination of SQL Server and ASP.Net Core is a very common to create enterprise applications. Being able to take this combination into world of containers is very important milestone. It is now easy to move such applications to either Linux or Windows platform. ACS offers even more productivity gain by abstracting away the infrastructure/orchestration concerns to deploy these application in Azure.